Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Workshop on Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilers
Uploaded by
kcp1986Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Workshop on Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilers
Uploaded by
kcp1986Copyright:
Available Formats
Workshop on Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilers
BOILER SYSTEM COMPONENTS
A boiler operates using the feed water system, the steam system, the fuel system
and the draft system. The feed water system supplies water to the boiler. The
steam system controls and directs the steam produced in the boiler. The fuel
system supplies fuel and controls combustion to produce heat. The draft system
regulates the movement of air for combustion and evacuates gases of combustion.
Water, steam fittings and accessories are required to supply and control water and
steam in the boiler. Boiler fittings are components such as valves directly attached
to the boiler. Accessories are pieces of equipment not necessarily attached to the
boiler, but required for the operation of the boiler.
Safety Valves are the most important fittings on the boiler. They should open to
release pressure when pressure inside the boiler exceeds the maximum allowable
working pressure. Safety valves are installed at the highest part of the steam side of
the boiler. No other valve shall be installed between the boiler and the safety valve.
Safety valve capacity is measured in the amount of the steam that can be
discharged per hour. The safety valve will remain open until sufficient steam is
released and there is a specific amount of drop in pressure. This drop in pressure is
the blowdown of the safety valve. Safety valve capacity and blowdown is listed on
the data plate on the safety valve. Spring loaded safety valves are the most
common safety valves. A spring exerts pressure on the valve against the valve seat
to keep the valve closed. When pressure inside the boiler exceeds the set popping
pressure, the pressure forces the valve open to release. The BIS/IBR Code
specifies the design, materials and construction of safety valves. The number of
safety valves required and the frequency and procedures for testing safety valves is
also specified by the BIS/IBR Code. Adjustment or repairs to safety valves must be
performed by the manufacturer or an assembler authorized by the manufacturer.
Water fittings and accessories control the amount, pressure and temperature of
water supplied to and from the boiler. Water in the boiler must be maintained at the
normal operating water level . Low water conditions can damage the boiler and
could cause a boiler explosion. High water conditions can cause carryover.
Carryover occurs when small water droplets are carried in steam lines. Carryover
can result in water hammer. Water hammer is a banging condition caused by
hydraulic pressure that can damage equipment.
Feed water Valves control the flow of feed water from the feed water pump to the
boiler. Feed water stop valves are globe valves located on the feed water line. They
isolate the boiler from feed water accessories. The feed water stop valve is
positioned close to the boiler to stop the flow of water out of the boiler for
maintenance, or if the check valve malfunctions. The feed water check valve is
located next to the feed water stop valve and prevents feed water from flowing from
the boiler back to the feed water pump. The feed water check valve opens and
closes automatically with a swinging disc. When water is fed to the boiler it opens. If
water flows back from the boiler the valve closes.
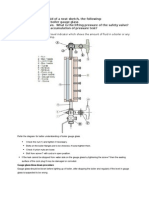
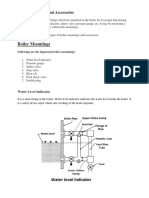
Water Column minimizes the water turbulence in the gage glass to provide accurate
water level reading. Water columns are located at the Normal Operating Water
Level or NOWL, with the lowest part of the water column positioned at least 3" above
National Productivity Council, Gandhinagar
Workshop on Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilers
the heating system. Water columns for high pressure boilers consist of the main
column and three tricocks. High and low water alarms or whistles may be attached
to the top and bottom tricocks.
The Gage Glass is used to visually monitor the water level in the boiler. Isolation
valves located at the top and bottom permit the changing of gage glasses.
A Blowdown Valve at the bottom of the gage glass is used to remove sludge and
sediment. Tubular gage glasses are used for pressure up to 28 kg/cm 2. All boilers
must have two methods of determining the boiler water level. The gage glass serves
as the primary method of determining boiler water level. If the water cannot be seen
in the gage glass, the tricocks are used as a secondary method of determining boiler
water level. The middle tricock is located at the NOWL. If water comes out of the
middle tricock, the gage glass is not functioning properly. If water comes out of the
top tricock, there is a high water condition in the boiler. If water comes out of the
bottom tricock, water may be safely added to the boiler. If steam comes out of the
bottom tricock, water must not be added to the boiler. Secure the fuel immediately.
Adding water could cause a boiler explosion.
Makeup Water replaces boiler water lost from leaks or from the lack of condensate
returned in the boiler. Makeup water is fed manually or automatically. Boilers can
have both manual and automatic systems. If the boiler has both, the manual always
bypasses the automatic system. Boiler operators must know how to supply makeup
water quickly to the boiler in the event of a low water condition. Manual systems
feed raw water with a hand operated valve. Automatic systems feed city water with
a float control valve mounted slightly below the NOWL. If the float drops from a low
water level, the valve in the city water line is open. As the water level rises, the float
rises to close the valve.
The Low Water Fuel Cut Off shuts off fuel to the burner in the event of a low water
condition in the boiler. The low water fuel cut off is located 25 mm to 150 mm below
the NOWL. Low water fuel cut offs are available with or without an integral water
column. Low water fuel cut offs must be tested monthly or more often depending on
plant procedures and requirements. Low water fuel cut offs operate using an electric
probe or a float sensor. The float senses a drop in water level. Switches in the low
water fuel cut off are wired to the burner control to shut off fuel to the burner when
the water level drops in the chamber.
The Feed water Regulator maintains the NOWL in the boiler by controlling the
amount of condensate return pumped to the boiler from the condensate return tank.
The correct water level is maintained with a feed water regulator, but boiler water
level must still be checked periodically by the boiler operator.
Feed water Pumps are used with feed water regulators to pump feed water to the
boiler. Pressure must be sufficient to overcome boiler water pressure to maintain the
NOWL in the boiler. For maximum safety, plants having one steam driven feed
water pump must have a back up feed water pump driven by electricity. Feed water
pumps may be reciprocating, centrifugal or turbine. Reciprocating feed water
pumps are steam driven and use a piston to discharge water to the feed water line.
They are limited in capacity and are used on small boilers. Centrifugal feed water
National Productivity Council, Gandhinagar
Workshop on Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilers
pumps are electric motor or steam driven. They are the most common feed water
pump. Centrifugal force moves water to the outside edge of the rotating impeller.
The casing directs water from the impeller to the discharge piping. Discharge
pressure is dependent on impeller speed. Turbine feed water pumps are steam
driven and operate similarly to centrifugal feed water pumps.
Feed water Heaters heat water before it enters the boiler drum to remove oxygen
and other gases which may cause corrosion. Feed water heaters are either open or
closed. Open feed water heaters allow steam and water to mix as they enter an
enclosed steel chamber. They are located above the feed water pump to produce a
positive pressure on the suction side of the pump. Closed feed water heaters have a
large number of tubes inside an enclosed steel vessel. Steam and water do not
come in contact, but feedwater goes through the tubes and steam is allowed in the
vessel to preheat the feed water. They are located on the discharge side of the feed
water pump.
Bottom Blowdown Valves release water from the boiler to reduce water level,
remove sludge and sediment, reduce chemical concentrations or drain the boiler.
Two valves are commonly used, a quick opening and screw valve. During blowdown
the quick opening valve is opened first, the screw valve is opened next and takes the
wear and tear from blowdown. Water is discharged to the blowdown tank. A
blowdown tank collects water to protect the sewer from the hot boiler water. After
blowdown, the screw valve is closed first and the quick opening valve is closed last.
Steam Fittings & Accessories remove air, control steam flow, and maintain the
required steam pressure in the boiler. Steam fittings are also used to direct steam to
various locations for heating and process.
Steam Pressure Gages and vacuum gages monitor pressure inside the boiler. The
range of these gages should be 1-1/2 to 2 times the Maximum Working Pressure
(MAWP) of the boiler.
Steam Valves commonly used include a gate valve used for the main steam stop
valve and the globe valve. The main steam stop valve cuts the boiler in online
allowing steam to flow from the boiler or takes it off line. This is an outside stem and
yoke or OS&Y valve. The position of the stem indicates whether the valve is open
or closed. The valve is opened with the stem out and closed with the stem in. This
provides quick information to the boiler operator.
The globe valve controls the flow of steam passing under the valve seat through the
valve. This change in direction causes a decrease in steam pressure. A globe valve
decreases steam flow and can be used to vary the amount of steam flow. Globe
valve should never be used as a main steam stop valve.
Steam Traps remove condensate from steam in lines from the boiler. Steam traps
work automatically and increase boiler plant efficiency. They also prevent water
hammer by expelling air and condensate from the steam lines without loss of steam.
Steam traps are located after the main steam header throughout the system. Steam
traps commonly used include the inverted bucket, the thermostatic and the float
thermostatic. In the inverted bucket steam trap steam enters the bottom flowing into
National Productivity Council, Gandhinagar
Workshop on Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilers
the inverted bucket. The steam holds the bucket up. As condensate fills the steam
trap the bucket loses buoyancy and sinks to open the discharge valve. The
thermostatic steam trap has a bellows filled with a fluid that boils at steam
temperature. As the fluid boils vapors expand the bellows to push the valve closed.
When the temperature drops below steam temperature, the bellows contract to open
the valve and discharge condensate.
A variation of the thermostatic steam trap is the float thermostatic steam trap. A float
opens and closes depending on the amount of condensate in the trap bowl.
Condensate is drawn out by return vacuum.
Steam Strainers remove scale or dirt from the steam and are located in the piping
prior to steam trap inlet. Scale or dirt can clog discharge orifices in the steam trap.
Steam strainers must be cleaned regularly.
The safety valve is the most important fitting on the boiler. The gage glass is used to
visually monitor the water level in the boiler. Tricocks are used as a secondary
device for determining water level in the boiler. Makeup water replaces water lost
from leaks or lack of condensate return to the boiler. The low water fuel cut off shuts
off fuel to the burner in the event of a low water condition. Steam pressure gages
and vacuum gages are used to indicate the pressure inside the boiler.
National Productivity Council, Gandhinagar
You might also like
- Boiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewFrom EverandBoiler Operation Engineer Exam, Interview Q&A, Terminology, and Boiler OverviewNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation and ControlDocument99 pagesBoiler Operation and Controlwassli100% (1)
- Boiler OperationDocument97 pagesBoiler Operationdeeli1100% (2)
- Ipc Cep-0038-EaDocument11 pagesIpc Cep-0038-EaCh FazalNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument5 pagesPower Plant EngineeringMonglafru MogNo ratings yet
- Automatic Operation of BoilerDocument23 pagesAutomatic Operation of BoilerSuhas KassaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument14 pagesBoiler Mountings and AccessoriesAnil DamaheNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation and Safety PrecautionDocument66 pagesBoiler Operation and Safety PrecautionSahil Mishra100% (1)
- Boiler Mounting & AccessoriesDocument14 pagesBoiler Mounting & Accessoriesshiraj36100% (1)
- Yeni Metin BelgesiDocument2 pagesYeni Metin BelgesiApolLLloNNo ratings yet
- Basic Boiler Mountings and Their FunctionDocument5 pagesBasic Boiler Mountings and Their FunctionChristian Cuevas100% (4)
- Boiler MountingsDocument21 pagesBoiler MountingsRoche Gallardo TampilNo ratings yet
- Different Feat.Document11 pagesDifferent Feat.TITU NATHNo ratings yet
- Steam Generators Lecture No.-3Document21 pagesSteam Generators Lecture No.-3rathoraryan2003No ratings yet
- Training Material of Boiler Operation: Drum and Internal DevicesDocument8 pagesTraining Material of Boiler Operation: Drum and Internal DevicesandreNo ratings yet
- Boiler Expt 2Document15 pagesBoiler Expt 2aashiquear100% (2)
- Boilers & SteamDocument25 pagesBoilers & SteamNarendra niranjan MathiyarasuNo ratings yet
- BOILER MOUNTINGS ADocument17 pagesBOILER MOUNTINGS Ahafiz aiman100% (1)
- BoilerDocument7 pagesBoilerAlexander LakraNo ratings yet
- Marine Boiler Water Level ControlDocument2 pagesMarine Boiler Water Level ControlPravin KumarNo ratings yet
- Marine Boiler Components and Safety SystemDocument9 pagesMarine Boiler Components and Safety SystemStef Turiano PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument9 pagesBoiler Mountings and AccessoriesArpit KapoorNo ratings yet
- Boiler Level ControlDocument20 pagesBoiler Level Controltinuvalsapaul100% (1)
- CH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsDocument13 pagesCH - Mates PH II - Boiler QuestionsArun GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Boiler Safety and Maintenance ProceduresDocument12 pagesBoiler Safety and Maintenance ProceduresNithin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument13 pagesBoiler Mountings and AccessoriesRoyalmechNo ratings yet
- Boiler - Mountings & AccesssesoriesDocument17 pagesBoiler - Mountings & AccesssesoriesNitric AcidNo ratings yet
- Boiler Maintenance: Boiler Fittings and AccessoriesDocument3 pagesBoiler Maintenance: Boiler Fittings and AccessoriesCam CamNo ratings yet
- Plug Valves: Pumps and Water Distribution 183Document2 pagesPlug Valves: Pumps and Water Distribution 183Rohit ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Building Services and Workshop TechnologyDocument21 pagesBuilding Services and Workshop Technologytiffa BosiboriNo ratings yet
- Construction Parts of BoilerDocument5 pagesConstruction Parts of BoilerMdParbhezNo ratings yet
- Phase II Boiler QuestionsDocument12 pagesPhase II Boiler Questionsabbutalibb5407No ratings yet
- GAPS Guidelines: Boiler FundamentalsDocument4 pagesGAPS Guidelines: Boiler FundamentalstilayeyidegNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument17 pagesBoiler Mountings and AccessoriesYogesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- ABA 2207 BUILDING SERVICES AND WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY Batch 01Document25 pagesABA 2207 BUILDING SERVICES AND WORKSHOP TECHNOLOGY Batch 01Sheryl CaneteNo ratings yet
- Turbine AuxillariesDocument139 pagesTurbine AuxillariesAwez RanaNo ratings yet
- Cascade, Feed Forward and Boiler Level ControlDocument4 pagesCascade, Feed Forward and Boiler Level ControlNïkĦïl ДkДvØØr100% (1)
- Boiler MountingsDocument12 pagesBoiler MountingsvikramnikhilanshiNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and Accessories Details With Video LectureDocument15 pagesBoiler Mountings and Accessories Details With Video LectureMahamudul Haque ShawonNo ratings yet
- Navien CleaningDocument3 pagesNavien CleaningKyle HarasymNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings SafetyDocument7 pagesBoiler Mountings SafetyPoloju Srinath100% (1)
- BG4Document26 pagesBG4Mandeep MalikNo ratings yet
- Feed WaterDocument2 pagesFeed WaterKapil_1983100% (1)
- Hydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsDocument2 pagesHydropneumatic Tank Control Systems: Drinking Water Tech TipsBlancaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings: School of Maritime Studies Vels University ThalamburDocument3 pagesBoiler Mountings: School of Maritime Studies Vels University ThalamburAayush AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Boiler Cont.Document9 pagesBoiler Cont.adnan mukhtarNo ratings yet
- CH2. Hot Water SupplyDocument13 pagesCH2. Hot Water SupplyPubudu KalpageNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Zerihun Kassa: UM at EABSC, Dec 2018Document32 pagesPrepared By: Zerihun Kassa: UM at EABSC, Dec 2018zerihun kassaNo ratings yet
- Boilers ClassificationDocument4 pagesBoilers ClassificationTech GuruNo ratings yet
- Boiler safety valves and controlsDocument2 pagesBoiler safety valves and controlsripalNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - 4 - Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument34 pagesLecture 3 - 4 - Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesFEALABREPORTSNo ratings yet
- Boiler Mountings and AccessoriesDocument3 pagesBoiler Mountings and AccessoriesSonjan FloresNo ratings yet
- Controlling Boiler Drum LevelDocument6 pagesControlling Boiler Drum LevelMourougapragash Subramanian100% (2)
- Cascade, Feed Forward and Boiler Level Control - Practical Process Control by Control GuruDocument3 pagesCascade, Feed Forward and Boiler Level Control - Practical Process Control by Control Guruuttam81d100% (1)
- Working Principle of BoilerDocument4 pagesWorking Principle of BoilerMark SaramillasNo ratings yet
- Boiler Fittings and AccessoriesDocument30 pagesBoiler Fittings and Accessorieskowsar0221No ratings yet
- Boiler Drum Level Controller PDFDocument14 pagesBoiler Drum Level Controller PDFmunna777100% (1)
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingFrom EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- BEARING (Recovered)Document40 pagesBEARING (Recovered)Rushikesh DandagwhalNo ratings yet
- Angular Contact Ball BearingsDocument3 pagesAngular Contact Ball BearingsDannyschNo ratings yet
- SKF BearingDocument28 pagesSKF Bearingvasuraj002No ratings yet
- Bearing TypesDocument7 pagesBearing TypesMaintenance Circle100% (1)
- Application of Bearings: Buyers GuideDocument46 pagesApplication of Bearings: Buyers Guidekcp1986No ratings yet
- Api 54Document2 pagesApi 54almandhari33100% (1)
- Kirloskar Brothers Limited Cross Section Assembly of Pump KPD 25/16QFDocument2 pagesKirloskar Brothers Limited Cross Section Assembly of Pump KPD 25/16QFkcp1986No ratings yet
- Type KPD-KPDQF: Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar PumpDocument49 pagesType KPD-KPDQF: Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar Pumpkcp1986100% (1)
- Centrifugal Pump Design - Rev 2Document11 pagesCentrifugal Pump Design - Rev 2jehadyam100% (1)
- 1.3 Energy Management & AuditDocument25 pages1.3 Energy Management & AuditEdd GithaeNo ratings yet
- Api 52Document3 pagesApi 52Sofiane HalimiNo ratings yet
- Api 62Document2 pagesApi 62saroaeroNo ratings yet
- 19 Introduction To Design of Helical SpringsDocument12 pages19 Introduction To Design of Helical SpringsPRASAD326100% (3)
- OutlineDrawing KPD25-16QFDocument1 pageOutlineDrawing KPD25-16QFkcp1986No ratings yet
- Kirloskar Brothers Limited Cross Section Assembly of Pump KPD 25/16QFDocument2 pagesKirloskar Brothers Limited Cross Section Assembly of Pump KPD 25/16QFkcp1986No ratings yet
- OutlineDrawing KPD25-16QFDocument1 pageOutlineDrawing KPD25-16QFkcp1986No ratings yet
- Type KPD-KPDQF: Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar PumpDocument49 pagesType KPD-KPDQF: Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar Pumpkcp1986100% (1)
- Plate Clucht Lesson 5 NewDocument15 pagesPlate Clucht Lesson 5 Newkcp1986No ratings yet
- Training Reliance Industries Ltd. Jamnagar Refinery ComplexDocument93 pagesTraining Reliance Industries Ltd. Jamnagar Refinery Complexसंजय घिल्डियालNo ratings yet
- 20 Design of Helical Springs For Variable LoadDocument16 pages20 Design of Helical Springs For Variable LoadPRASAD326No ratings yet
- 4.10 Brayton Cycle (Simple Gas Turbine Cycle) :: Fig.4.10. Brayton Cycle On P-V and T-S DiagramDocument3 pages4.10 Brayton Cycle (Simple Gas Turbine Cycle) :: Fig.4.10. Brayton Cycle On P-V and T-S DiagrammominjeelaniNo ratings yet
- Neptel - Design of Brakes-1Document9 pagesNeptel - Design of Brakes-1srideviNo ratings yet
- Pinch TechDocument32 pagesPinch TechDaniel Puello Rodelo100% (1)
- Brakes BasicsDocument7 pagesBrakes BasicsPushkin SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Flywheel: Flywheels-Function Need and OperationDocument11 pagesFlywheel: Flywheels-Function Need and OperationKristian John B Rabino100% (2)
- Energy Consideration: Heat Generated in BrakingDocument13 pagesEnergy Consideration: Heat Generated in BrakingabcmetumNo ratings yet
- MEng Presentation-M VD HovenDocument35 pagesMEng Presentation-M VD Hovenashoku2No ratings yet
- Energy considerations: II 1 2 1 2 t 1 TI I 1 2 ω − ω = +Document5 pagesEnergy considerations: II 1 2 1 2 t 1 TI I 1 2 ω − ω = +Sunny VermaNo ratings yet
- BrakesDocument11 pagesBrakesSiddartth M KumaarNo ratings yet
- Shell& Tube HT DesignDocument8 pagesShell& Tube HT Designvsraochemical1979100% (1)
- 6 SS Direct Fired Air HeaterDocument1 page6 SS Direct Fired Air HeaterYhony Gamarra VargasNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Gas Charging Kits Brochure WEBDocument12 pagesNitrogen Gas Charging Kits Brochure WEBmnvijaybabuNo ratings yet
- FW PumpDocument15 pagesFW PumpAJAY1381100% (1)
- AWWA M11 Steel Water Pipe - Design y Insatalation PDFDocument259 pagesAWWA M11 Steel Water Pipe - Design y Insatalation PDFJoaniNo ratings yet
- Aspe Databook Vol 2 PDFPDF 4 PDF FreeDocument471 pagesAspe Databook Vol 2 PDFPDF 4 PDF Freeadel cheriyanNo ratings yet
- Typical Turndown Ratio of Various Meter TypesDocument4 pagesTypical Turndown Ratio of Various Meter TypessbraofacebookNo ratings yet
- Piping Vs Piping SystemDocument4 pagesPiping Vs Piping SystemViệt Đặng XuânNo ratings yet
- Method of Statement Hanging BracketDocument9 pagesMethod of Statement Hanging Bracketmuhammad syauqi shaidan100% (2)
- 18R11A04P6 INTERNSHIP REPORT - (1) (2) WDocument70 pages18R11A04P6 INTERNSHIP REPORT - (1) (2) WSharath Chandra100% (4)
- CLASS 31451: DEP 31.38.01.15-Gen Class 31451, Rev. G Page 1 of 13Document13 pagesCLASS 31451: DEP 31.38.01.15-Gen Class 31451, Rev. G Page 1 of 13SaguesoNo ratings yet
- StandpipeDocument17 pagesStandpipedipuNo ratings yet
- B5M ElDocument3 pagesB5M ElBALAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Pmi ReportDocument5 pagesPmi ReportMANIMARAN QCNo ratings yet
- DJJ40153Document6 pagesDJJ40153SanNo ratings yet
- Registered Plumbing ContractorsDocument9 pagesRegistered Plumbing ContractorsviveknayeeNo ratings yet
- 3-Way Ball Valve (Spears)Document4 pages3-Way Ball Valve (Spears)Chan Chi Wong PenNo ratings yet
- WBB Wat Set 20 08 2019Document59 pagesWBB Wat Set 20 08 2019David FrederickNo ratings yet
- Mechanical & Electrical System Pre-Delivery Inspection ReportDocument94 pagesMechanical & Electrical System Pre-Delivery Inspection Reportsilhouette GhostNo ratings yet
- Nalanda Non Residential Specifications Part II ServicesDocument325 pagesNalanda Non Residential Specifications Part II ServicesJothimanikkam SomasundaramNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Protection RatesDocument1 pageCorrosion Protection RatesB Girish82% (57)
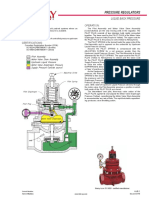
- Pressure Regulators: Operation: ApplicationDocument7 pagesPressure Regulators: Operation: Applicationedwin cuellarNo ratings yet
- Autodesk Revit 2018 MEP Fundamentals (Metric) PDFDocument5 pagesAutodesk Revit 2018 MEP Fundamentals (Metric) PDFГильермо РивасNo ratings yet
- HCi Product Listing 2022Document38 pagesHCi Product Listing 2022Karl MarxitoNo ratings yet
- G. Dry and Wet StandpipeDocument10 pagesG. Dry and Wet Standpipehermano balbonNo ratings yet
- RTR Question and Answer For OWS and Utility LinesDocument18 pagesRTR Question and Answer For OWS and Utility Linesjana.alqimmaNo ratings yet
- VdsDocument549 pagesVdsProject MarsysNo ratings yet
- Sateesh ResumeDocument4 pagesSateesh Resumerajput.sateesh2011No ratings yet
- Pump Head Calculations Using Darcy-Weisbach FormulaDocument6 pagesPump Head Calculations Using Darcy-Weisbach FormulaHind ZarifNo ratings yet
- CS Pipe + Flange + Forged + SpectacalDocument121 pagesCS Pipe + Flange + Forged + SpectacalTim Rahul ferrometNo ratings yet
- SP-RZF-04404-14-P-001-3 Piping Classes (14479)Document12 pagesSP-RZF-04404-14-P-001-3 Piping Classes (14479)Silvio DiazNo ratings yet