Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lime Usage in Construction
Lime Usage in Construction
Uploaded by
vijayrengarajuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lime Usage in Construction
Lime Usage in Construction
Uploaded by
vijayrengarajuCopyright:
Available Formats
Lime usage in construction
Civil engineering:
The addition of lime to clay containing soil improves soil properties (i.e. better densification). Its reaction
with water enables it to dry out damp soils. Lime is increasingly used to recycle excavated material from
sites in urban areas. Hydrated lime improves the performance of asphalt mixes used for road surfacing.
It increases their resistance against stripping, and also against rutting and age-hardening. In tunnel
construction, hydrated lime is used to improve the quality of mortars. Quicklime dries out the mud from
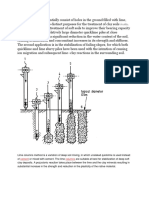
the excavation and therefore improves its handling. It is also used in the deep soil stabilisation process
(lime treated columns) to improve soft soils, reduce settlements and increase stability. Hydrated lime is
one of the components used to produce injection binders.
Construction materials:
Builders have made use of the binding properties of lime. For example, lime-based mortars are often
used in masonry and in plaster mixes for building facades. In addition, lime is being used increasingly in
modern building materials, such as for aerated concrete blocks, for hemp-lime blocks and for sand-lime
bricks. These materials are highly valued because they have excellent thermal and acoustic insulating
properties and they are easy to use
Lime Standards:
EN 459, Parts 1, 2, 3 for building lime
http://www.ima-europe.eu/sites/ima-europe.eu/files/minerals/Lime_Angl-WEB-2011.pdf
You might also like
- Building Materials - SIMRAN SAINIDocument33 pagesBuilding Materials - SIMRAN SAINISimranNo ratings yet
- Building Materials Construction Specification MaterialsDocument39 pagesBuilding Materials Construction Specification Materialswenceslao seeNo ratings yet
- Book Chapter 1Document7 pagesBook Chapter 1Bala VishnuNo ratings yet
- C2 MAJOR FINAL DOCmentDocument72 pagesC2 MAJOR FINAL DOCmentVamshi ChinthalaNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialsDocument13 pagesBuilding MaterialsPriyanka BasuNo ratings yet
- TBD 3206 Construction and Engineering Materials II - NotesDocument39 pagesTBD 3206 Construction and Engineering Materials II - NotesIsaac OgolaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregates ConcreteDocument32 pagesMechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregates ConcreteComet AstroNo ratings yet
- Me425 Group1 Cementprocesses Bulatao Monis OliverosDocument21 pagesMe425 Group1 Cementprocesses Bulatao Monis OliverosPETER PENNo ratings yet
- Detailed SpecificationDocument13 pagesDetailed SpecificationNazim MahamudNo ratings yet
- Plastic in ConcreteDocument35 pagesPlastic in ConcretesujithNo ratings yet
- ConstructionDocument6 pagesConstructionDela LutfianiNo ratings yet
- Construction Technology and Construction ManagementDocument31 pagesConstruction Technology and Construction Managementreddy maheshNo ratings yet
- Ecology NotesDocument6 pagesEcology Noteskerry luvaiNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Waste Crushed Tile Materials As Coarseaggregate in ConcreteDocument11 pagesUtilization of Waste Crushed Tile Materials As Coarseaggregate in ConcreteAndrea DeleonNo ratings yet
- Types of Cement and Their Common Uses in ConstructionDocument11 pagesTypes of Cement and Their Common Uses in Constructionprasadkolli949No ratings yet
- Advanced Construction Materials: Ar. Pallavi SharmaDocument7 pagesAdvanced Construction Materials: Ar. Pallavi SharmamariyaNo ratings yet
- TRAINING REPORT - Rate AnalysisDocument28 pagesTRAINING REPORT - Rate AnalysisvarshaNo ratings yet
- Narrative ProjectDocument17 pagesNarrative ProjectMyka Rovee LaderaNo ratings yet
- Earthwork: Earthworks Are Engineering Works Created Through The Moving or Processing of Parts of TheDocument11 pagesEarthwork: Earthworks Are Engineering Works Created Through The Moving or Processing of Parts of TheUsman ManiNo ratings yet
- Helath Monitoring of Earthen Building - 1Document32 pagesHelath Monitoring of Earthen Building - 1MITESH PATELNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General: Components and Grade of ConcreteDocument35 pages1.1 General: Components and Grade of ConcreteHari KaranNo ratings yet
- Matthew IssaDocument9 pagesMatthew Issarh.rassan.connectNo ratings yet
- Individual Work About ConcretingDocument13 pagesIndividual Work About ConcretingkristinaNo ratings yet
- Sand Brick Vs Clay BrickDocument2 pagesSand Brick Vs Clay BrickjohnNo ratings yet
- Highway MaterialDocument10 pagesHighway MaterialErish Ken DomingoNo ratings yet
- Group3 CE4101 SummaryDocument10 pagesGroup3 CE4101 SummaryJin KookNo ratings yet
- Craving ConcreteDocument50 pagesCraving ConcreteBharath Civil116No ratings yet
- LO ES1.03 Earth Materials 2017Document15 pagesLO ES1.03 Earth Materials 2017mohamedgouda52008No ratings yet
- Project Proposal Enhancing The Engineering Properties of Soft Clay by Using Carpet WastesDocument7 pagesProject Proposal Enhancing The Engineering Properties of Soft Clay by Using Carpet WastesAbdullah 17-BNCIV-0931No ratings yet
- Unit - Iii: Types of Concrete Aggregates and Concrete:: Lightweight AggregateDocument9 pagesUnit - Iii: Types of Concrete Aggregates and Concrete:: Lightweight AggregatedaraNo ratings yet
- Reactive Powder ConcreteDocument28 pagesReactive Powder ConcreteMolly JoseNo ratings yet
- Bricks.: Institue of Architecture, PatanDocument16 pagesBricks.: Institue of Architecture, PatanTEJAS TANK100% (1)
- Materials For Repair of BuildingsDocument50 pagesMaterials For Repair of Buildingsrohit kumar100% (1)
- Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Marble Waste Powder in Cement Concrete.Document36 pagesPartial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Marble Waste Powder in Cement Concrete.Harihara Priyadharshan100% (2)
- Types of ConcreteDocument6 pagesTypes of ConcreteHaris RiazNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument17 pagesChapter 1 - IntroductionVincent Nava100% (1)
- Project BookDocument57 pagesProject BookGLOBAL INFO-TECH KUMBAKONAMNo ratings yet
- Project BookDocument57 pagesProject BookGLOBAL INFO-TECH KUMBAKONAMNo ratings yet
- My SlidesDocument41 pagesMy SlidesBuddhisagar BastolaNo ratings yet
- Properties and Use of Construction MaterialsDocument13 pagesProperties and Use of Construction Materialsjake masonNo ratings yet
- Git NotesDocument19 pagesGit NotesZahid0% (1)
- Concrete MaterialsDocument2 pagesConcrete MaterialsVirgilio BiagtanNo ratings yet
- Hybrid BricksDocument24 pagesHybrid Bricksrajmohanroy50% (2)
- A) Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) - Also Known Simply As Portland Cement orDocument7 pagesA) Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) - Also Known Simply As Portland Cement orRoberto AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Types of ConcreteDocument5 pagesTypes of ConcretePaul Ivan Asencio CasumpangNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1 GeneralDocument57 pagesChapter-1: 1.1 Generalkundanam venkateshNo ratings yet
- BCM ReportDocument24 pagesBCM ReportPiyush ThakurNo ratings yet
- RPDocument24 pagesRPईशान्त शर्माNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Concrete: Partial Replacement of Coarse Aggregate With Ceramic Tile 2019-2020Document25 pages1.1 Concrete: Partial Replacement of Coarse Aggregate With Ceramic Tile 2019-2020Naveen S100% (2)
- BtechhDocument7 pagesBtechhcorbitecoNo ratings yet
- BMC Lecture - 1Document39 pagesBMC Lecture - 1Agerie BerihunNo ratings yet
- Ces 412 Unit 1 Les 1-2Document31 pagesCes 412 Unit 1 Les 1-2JessaNo ratings yet
- Cement and HydrationDocument9 pagesCement and HydrationTimothy HughesNo ratings yet
- Basic Building MaterialsDocument73 pagesBasic Building MaterialsSantosh Kumar MNo ratings yet
- Final Year ProjectDocument16 pagesFinal Year Projectkennedy100% (3)
- Introduction of Cement: When Was Cement Begin?Document11 pagesIntroduction of Cement: When Was Cement Begin?مايف سعدونNo ratings yet
- Cast in Place SystemsDocument4 pagesCast in Place SystemsMariel Paz MartinoNo ratings yet
- Composition of CementDocument5 pagesComposition of CementGian Aizel JavierNo ratings yet
- Water Abserbation Concrete RoadDocument11 pagesWater Abserbation Concrete RoadsethyankitaraniNo ratings yet