Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motherboard and Its Components
Uploaded by
Owais Afzal JanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Motherboard and Its Components
Uploaded by
Owais Afzal JanCopyright:
Available Formats
Motherboard and Its Components
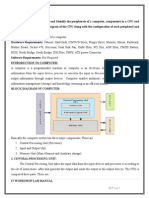
The most important component in any PC is the motherboard, also called as system board. It houses a
microprocessor, memory and slots for expansion, of the system. Some motherboards also contain the
drive interface logic, printer interface logic and serial interface logic integrated on it. Motherboard
comes in different sizes, shapes and models. The height and width of the motherboard is known as
motherboard form factor.
The main functional blocks of a motherboard are as follows:
i. CPU
ii. BIOS
iii. RAM
iv. Cache memory
v. Bus expansion slots
vi. On-board IO connectors
vii. On-board IDE connectors.
i. CPU: The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer in which majority of the
computing tasks are performed. The CPU may have a heat sink installed on it, to dissipate heat
generated by the CPU.
ii. BIOS (Basic Input Output System): BIOS is a ROM chip. It contains programs that are necessary for the
PC to boot and to access the various system components. BIOS also contains the programs for POST
(Power On Self Test).
iii. RAM (Random Access Memory): RAM is used for storing programs temporarily. Generally RAM is
located on SIMM (Single Inline Memory Module) or DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module).
iv. Cache Memory: The cache is the fastest memory which lies between CPU and RAM. The CPU can
access the frequently required data from cache more rapidly than from RAM.
v. Bus Expansion Slots/I/O Slots: System expansion is possible using the bus expansion slots in which
the adapters are installed. The different types of slots such as ISA, VESA, PCI are available on
motherboard.
vi. On-board I/O Connectors: In recent systems one or two serial ports (com1, com2) and parallel ports
(LPT1, LPT2) are present on motherboard.
vii. On-board IDE Connectors: Similar to serial and parallel parts the motherboard may have IDE
connectors for connecting. Floppy Disk Drives (FDD), Hard Disk Drives (HDD) and CD Drives.
You might also like
- The Motherboard and It'S ComponentsDocument12 pagesThe Motherboard and It'S ComponentsVanessaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Computer HardwareDocument12 pagesComputer HardwareAce BorresNo ratings yet
- The System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterDocument10 pagesThe System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterbogusbaikawNo ratings yet
- PC Hardware NotesDocument7 pagesPC Hardware NotesyelhankaNo ratings yet
- To Study MOTHERBOARD.: HistoryDocument6 pagesTo Study MOTHERBOARD.: Historyshyam ranaNo ratings yet
- Practical No 3 - Motherboard Components and TypesDocument10 pagesPractical No 3 - Motherboard Components and TypesAshish SethiNo ratings yet
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware and MaintenanceDocument10 pagesComputer Hardware and MaintenanceadityakmcsNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Its Component (11813705)Document10 pagesMotherboard and Its Component (11813705)DeePäk YädävNo ratings yet
- Lab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryDocument11 pagesLab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryasavariNo ratings yet
- External Hard Drive Mac External Hard Drive Network & Tablet Hard Drive Internal Drive Solid State Drive (SSD)Document5 pagesExternal Hard Drive Mac External Hard Drive Network & Tablet Hard Drive Internal Drive Solid State Drive (SSD)Hasibul AlamNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Mother BoardDocument28 pagesParts of A Mother BoardReilina KylaNo ratings yet
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDocument40 pagesA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourNo ratings yet
- Motherboard (Mainboard, System Board)Document34 pagesMotherboard (Mainboard, System Board)Akhila Dakshina100% (2)
- Computer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsDocument29 pagesComputer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsRajendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Motherboard EnglishDocument9 pagesMotherboard EnglishallamNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware ServicingJhayden BlueNo ratings yet
- Components of A MotherboardDocument114 pagesComponents of A Motherboarddeejhay14100% (1)
- MotherboardDocument41 pagesMotherboardjoseph rey ybiosaNo ratings yet
- A++ Note For SECE by TamiratDocument60 pagesA++ Note For SECE by TamiratHenock TadesseNo ratings yet
- Computer MotherboardDocument5 pagesComputer Motherboard44361brianmainaitl6j024No ratings yet
- From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Navigation Search BiosDocument5 pagesFrom Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia: Navigation Search Biosanon_635989584No ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462No ratings yet
- Motherboard: Prepared byDocument43 pagesMotherboard: Prepared bytapas_bayen9388No ratings yet
- Unit-1 PCDocument10 pagesUnit-1 PCnanobala15No ratings yet
- Glossary - ComputersDocument6 pagesGlossary - ComputersensarjusufovicNo ratings yet
- BIOS InstallationDocument5 pagesBIOS InstallationArif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 10 Parts of A Motherboard and Their Function - TuDocument3 pages10 Parts of A Motherboard and Their Function - TuNabbaNo ratings yet
- 1.assemble Computer HardwareDocument18 pages1.assemble Computer HardwareallyzamoiraNo ratings yet
- It 01Document22 pagesIt 01Anas Ismail AlmalayuNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardraze techNo ratings yet
- CHT Practical 1 KUKDocument3 pagesCHT Practical 1 KUKDhruv SharmaNo ratings yet
- IT Workshop Lab ManualDocument51 pagesIT Workshop Lab ManualMahesh BodaNo ratings yet
- IT Essential - Tutorial 2 - Answer - FinalDocument2 pagesIT Essential - Tutorial 2 - Answer - Finalahmed alloliNo ratings yet
- PCHardware PDFDocument4 pagesPCHardware PDFVuyolwethu NoroboloNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Prepared byDocument22 pagesProject Report: Prepared byumeshNo ratings yet
- CHM All NotesDocument28 pagesCHM All Notesabhishek.kunduNo ratings yet
- Components To Be MeasuredDocument43 pagesComponents To Be Measuredarniel antipuestoNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardRodel Romero100% (2)
- Parts and Functions of MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts and Functions of MotherboardJimmySyNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardwares Basic - Inside The BoxDocument31 pagesComputer Hardwares Basic - Inside The BoxEswaran arunachalamNo ratings yet
- Basic Notes 2Document6 pagesBasic Notes 2jivan jyotNo ratings yet
- ItwslabDocument77 pagesItwslabKalyan Reddy AnuguNo ratings yet
- Motherboard PPT Bhupen GargDocument20 pagesMotherboard PPT Bhupen GargBhupen GargNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument44 pagesComputer Hardware ServicingSodnal M. OdeloNo ratings yet
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Basic Input/Output System, The BIOS, ROM BIOS, or System BIOS Is A Chip Located On All Motherboards ThatDocument4 pagesBasic Input/Output System, The BIOS, ROM BIOS, or System BIOS Is A Chip Located On All Motherboards ThatRonnie Oliva MalalisNo ratings yet
- Devesh Kumar 1801227714Document62 pagesDevesh Kumar 1801227714sdhNo ratings yet
- Sir Kyle Perez 1Document2 pagesSir Kyle Perez 1Paulo CelisNo ratings yet
- Itws ManualDocument98 pagesItws Manualapi-291463406No ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument15 pagesMotherboardFredrick MugoNo ratings yet
- Information Technology GRoup 1Document23 pagesInformation Technology GRoup 1Anonymous COMLmKNo ratings yet
- Parts of Mother BoardDocument17 pagesParts of Mother BoardJeza Estaura Cuizon100% (1)
- Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetDocument13 pagesHomework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetJohn Kerby CorralNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Submitted By:-Nisha .R. NairDocument5 pagesMotherboard: Submitted By:-Nisha .R. NairNisha NairNo ratings yet
- Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & Its ComponentsDocument19 pagesChapter No. 1 Motherboard & Its ComponentsSeema swathiNo ratings yet
- PlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12From EverandPlayStation 2 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #12No ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Machine Learning A Z Q ADocument52 pagesMachine Learning A Z Q ADina Garan100% (1)
- Introduction To PID ControlDocument8 pagesIntroduction To PID ControlNooruddin SheikNo ratings yet
- Transformer Per Unit CalculationsDocument19 pagesTransformer Per Unit CalculationsOwais Afzal Jan100% (1)
- Moral DilemmasDocument6 pagesMoral DilemmasOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Engineering & Personal EthicsDocument26 pagesEngineering & Personal EthicsOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Moral DilemasDocument6 pagesMoral DilemasOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Lasing .Lasers Optical FibreDocument10 pagesLasing .Lasers Optical FibreOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Nodal AnalysisDocument13 pagesNodal AnalysisOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Engineering & Personal EthicsDocument26 pagesEngineering & Personal EthicsOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Amplitude Shift Key:: Amplitude Modulation Digital Data Amplitude Carrier WaveDocument4 pagesAmplitude Shift Key:: Amplitude Modulation Digital Data Amplitude Carrier WaveOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- LM565 & LM566Document4 pagesLM565 & LM566Owais Afzal Jan50% (2)
- Introduction To AutoCADDocument18 pagesIntroduction To AutoCADOwais Afzal Jan100% (1)
- LM565 IcDocument3 pagesLM565 IcOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument76 pagesData CommunicationBoran ReklamNo ratings yet
- Data CommunicationDocument76 pagesData CommunicationBoran ReklamNo ratings yet
- Two Nations Theory - DefinitionDocument8 pagesTwo Nations Theory - DefinitionOwais Afzal Jan100% (1)
- System BusDocument11 pagesSystem BusOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- 1973 ConstitutionDocument4 pages1973 Constitutiondjshan143No ratings yet
- Proteus - TutorialDocument11 pagesProteus - TutorialKhairiBudayawanNo ratings yet
- Functions SolutionDocument10 pagesFunctions SolutionOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectiferDocument2 pagesFull Wave RectiferOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- War of IndependenceDocument8 pagesWar of IndependenceOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Pakistan ResolutionDocument2 pagesPakistan Resolutionusmanklodhi100% (1)
- Economy of PakistanDocument10 pagesEconomy of PakistanOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument25 pagesCircular MotionOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Japanese Auction SheetDocument10 pagesJapanese Auction SheetOwais Afzal Jan0% (1)
- LAB 3-Basic Gates: Part 1-AND, OR, NOT Gates: ObjectivesDocument10 pagesLAB 3-Basic Gates: Part 1-AND, OR, NOT Gates: ObjectivesOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Types of Integrated CircuitDocument3 pagesTypes of Integrated CircuitOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet
- Old Map of WorldDocument1 pageOld Map of WorldOwais Afzal JanNo ratings yet