Professional Documents
Culture Documents
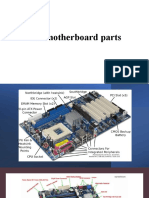
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & Its Components
Uploaded by
Seema swathiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & Its Components
Uploaded by
Seema swathiCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C.
Rathod
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components
What is Motherboard?
• The main circuit board of a microcomputer.
• The motherboard contains the connectors for attaching additional boards.
• It contains the CPU, BIOS, memory, mass storage interfaces, USB, SATA, serial & parallel ports,
expansion slots, & all controllers required to control standard peripheral devices, such as the
display screen, keyboard, & the disk drive.
• CPU is the main component on the motherboard or computer system. CPU is the brain of the
computer.
• All these chips that reside on the motherboard are known as the motherboard’s chipset.
• It also known as a mainboard, system board or logic boards.
Types of motherboards
• There are two types of motherboards
1. Non-integrated motherboards.
2. Integrated motherboards.
1. Non-integrated motherboards :-( it means old motherboards) have assemblies such as the I/O port
connectors (serial & parallel ports), hard drive connectors, floppy controllers & connectors, joystick
connections, network interface card (NIC) etc. installed as expansion boards.
2. Integrated motherboards: -it also called as all in one motherboard.
• Integrated system board has multiple components integrated into the board itself. These may
include the CPU, video card, sound card, and various controller cards.
• These types of motherboards has all I/O ports other peripheral connectors on the motherboard such
as network RJ45 connectors, USB port, audio jack,& SATA HDD connector, DVD ROM
connector, etc. all connect directly to the motherboard.
Motherboard form factors:
Q. What is form factor? List any two form factors of the motherboard
• The shape & layout of motherboard are called the form factor.
• It refers to the physical dimensions (size & shape) as well as certain connecters, screw hole &
other position of that the board will fit.
• FF is related to the configurations of the pc.
Types of form factors:-
There are 12 official form factors.
PC/XT, AT, BabyAT, ATX, Mini-ATX, Micro-ATX, FlexATX, LPX, Mini LPX, NLX,
BTX, PicoBTX, Micro-BTX.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 1
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
Components of motherboard (List):-
1. CPU(processor)
2. System clock
3. Chipset(north bridge & south bridge)
4. ROM BIOS
5. RAM & RAM cache(memory)
6. ATX power connector
7. PCI & PCI express slot
8. USB slot
9. SATA/IDE connector
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 2
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
1. CPU Internal Structure
• The CPU was first developed at Intel with the help of Ted Hoff in the early 1970’s.
• It is also called as processor, Computer Processor, Microprocessor, central processor, & “thebrains of the
computer.”
• It is responsible for interpreting & executing most of the commands from the computer’s hardware&
software.
• The major CPU manufacturers are Intel, Motorola, IBM, Advanced Micro Devices(AMD), & Cyrix
Fig. CPU Internal Structure
System Bus
1. Address Bus:-
• A collection of wires connecting the CPU with main memory that is used to identify particular
locations (addresses) in main memory.
• It is a unidirectional bus means data travels only one way, from the CPU to memory.
• Modern PCs have 36 address lines.
2. Data Bus:-
• It is group of electrical wires used to send data back & forth between two or more components. i.e.
the connections between & within the CPU, memory,& peripherals used to carry Data.
• It is bidirectional bus.
• Data bus to carry actual data or information, an address bus to determine where it should be sent.
3. Internal Registers:-
• There are 16 general, control & system registers in the CPU.
• Program counter, stack pointer, Accumulator (A), index register, flag register.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 3
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
CPU/Processor Modes (Q. What is processor mode?)
• It also called CPU modes or CPU privilege level.
• All modern CPUs can run in different modes of operation.
• The mode of operation determines how the CPU manages applications & memory.
• The processor modes are used by processor to create an operating environment for itself.
• There are 3 different modes of operation
1. Real Mode
2. Protected Mode
3. Virtual Real Mode.
1. Real Mode (Q. Describe real mode processor?)
Real mode, also called real address mode, is an operating mode of all x86compatible CPUs.
• Real mode is characterized by a 20-bit segmented memory address space (giving exactly 1 MB of
addressable memory).
• Real mode provides no support for memory protection, multitasking, or code privilege levels.
• In real-mode, only the first 1 M bytes of memory can be addressed with the typical segment: offset
logical address. Each segment is 64K bytes long.
• Real mode is of course used by DOS & standard DOS applications.
2. Protected Mode (Q. Describe protected mode of processor?)
• This mode was first introduced with the 80286 processor.
• The differences between this mode and real address mode are Protection and a larger address space.
• This is much more powerful mode of operation than real mode, & used in all modern multitasking
operating system.
• An address line has 24 bits on an 80286 CPU, limiting the available address space to 16 megabytes.
• Used: - Window 9X, OS/2, Linux. Even DOS.
• Advantages:-
1. Full access to all system memory. There is no 1MB limit in protected mode.
2. Ability to multitask –meaning execution of multiple programs simultaneously.
3. Support for virtual memory.
4. Faster (32 bit) access to memory &faster 32 bit drivers to do input or outout transfers.
3. Virtual Real (8086) Mode (Q. Describe Virtual Real (8086) mode of processor?)
Also called virtual 8086 mode
It is an additional capability, an enhancement, of protected mode.
There is often a desire to be able to run DOS programs under Windows, to solve this problem this
mode is used.
It emulates real mode from within protected mode allowing DOS programs to run.
A protected mode operating system such as Windows can in fact create multiple virtual real mode
machines, each of which appear to the software running them.
Each virtual machine gets its own 1MB address space, an image of the real hardware BIOS routines,
everything.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 4
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
Q. Compare Real Mode & Protected mode
Process Technologies:-
• It used to improve the performance of the processor.
• The design complexity of CPUs increased as various technologies facilitated building smaller & more
reliable electronic devices.
• 1st such improvement came with the advent of the transistor.
• Operating speed & power requirements are affected by transistor size.
• There are two types of technologies are used.
1. The Dual Independent Bus (DIB) architecture.
2. Hyper Threading Technology.
Processor Socket & Slots
• Processor socket is a connection that allows computer processors to be connected to a motherboard.
• A CPU socket or CPU slot is a mechanical component that provides mechanical & electrical
connections between a microprocessor & a printed circuit board (PCB).
• It is the connector that interfaces between a computers motherboard & processor itself.
Chipset Architecture
• Chipset is a collection of several intelligent controllers & programmable chips.
• Use of chipset simplifies the motherboard design.
• In pc, the chipset represents the connection between the processor & everything else.
• It controls the features & abilities of the motherboard.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 5
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
• Chipset usually contains the processor bus interface called Front-side bus (FSB), memory controller,
bus controller, I/O controller & more.
• Two types of Chipset architecture
1. North/south bridge architecture
2. Hub architecture
1. North/South Bridge Architecture: [W-09,S-13]
Intel’s earlier chipset were broken into multi-tiered architecture known as North Bridge and South
Bridge components as well as Super I/O chip.
North Bridge: it is the connection between the high speed processor bus and the slower AGP & PCI
buses.
South Bridge: it is the bridge between PCI bus and even slower ISA bus.
Super I/O chip: contains commonly used peripheral items all combined in single chip.
Fig.North/South Bridge Architecture
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 6
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
North Bridge
Northbridge is also referred to as PAC (PCI-AGP) controller is the main component of the motherboard and
only motherboard circuit (besides the processor) that runs at the full motherboard speed. It serves as the four
way connection between CPU, Memory, Video card and south bridge.
South Bridge
The Southbridge is the lower speed component of the chipset. The south bridge connects to the 33MHz PC and
contains the interface to ISA bus. It also contains dual ATA/IDE hard disk controller interfaces, one or more
USB interfaces, CMOS RAM, real time clock functions, interrupt controller, DMA controller.
Super I/O chip contains serial port, floppy controller, keyboard & mouse interface.
Functions of South Bridge
It is a chip on the motherboard.
It is also known as I/O controller hub (ICH).
It incorporates a number of different controller functions.
It looks after the transfer of data to and from the hard disk and all the other I/O devices, & passes this
data into the link channel which connects to the north bridge.
It connects to the 33 MHz PCI bus & contains the interface or bridge to the 8 MHz ISA bus.
It also contains dual ATA/IDE hard disk controller interfaces, one or more USB interfaces.
It also contains DMI (Direct Memory Interface), Matrix storage, audio, AC97 modem, Ethernet.
Function of North Bridge
It is also knows as memory controller hub (MCH).
It is a controller which controls the flow of data between the CPU (processor) & RAM, & to the AGP
port.
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) is I/O card used for the video card.
In new motherboards in replacement of AGP the PCI Express x16 port is used.
Fig: Connection of North/South Bridge
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 7
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
1. Hub Architecture: [W-08]
Fig. Hub Architecture
Intel Hub Architecture (IAH) is also known as Accelerated Hub Architecture.
It is Intel’s architecture for the 8xx family of chipsets.
In fig, the Memory controller hub (MCH) is connected to I/O controller hub (ICH) via 266 MB/s bus.
This connection is called Direct Media Interface (DMI).
MCH chip Provides connectivity for memory & AGP.
ICH chip provides connectivity for PCI, USB, sound, IDE/ATA & LAN
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 8
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
Latest Chipset for PC
• Intel X79, Z87, H87 chipset will be the latest & greatest Chipset available until the second quarter 2014.
1. Intel X79 Express Chipset:-
Feature:-
1. Processor
2. Storage Technology
3. Protection Technology
4. PCI Express 2.0 interface
5. High definition audio
6. USB
7. SATA- 6 GBPS, eSATA
8. Green Technology
Motherboard Buses:-
• Bus is a shared linear pathway that connects multiple devices on M/B.
• Bus provides communication Bi-directionally.
• Processor, cache, RAM, expansion cards, disks, & other communicate using one or more buses
that exist in the computer.
• The external bus is also referred to as the expansion bus.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 9
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
• The common types of buses are ISA, PCI, AGP, USB and IDE/SATA.
1. PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect)
• PCI specifies a computer bus for attaching peripheral devices to a computer motherboard.
• PCI bus adds another tier to the interface between CPU & I/O devices.
• It is high speed bus that connects high performance peripherals like video adaptors, disk adaptors
& network adaptors to the chipset processor & memory.
• Specifications of PCI:-
• Speed:-33.33MHz.
• Data transfer Speed:-133mb/s for 32 bit, 266mb/s for 64 bit.
• Bus size Supported: - 32 bit or 64 bit.
• 5V/ 3.3V signaling.
• Supporting of multi-processor systems.
• Features of PCI Bus
• Extremely high-speed data transfer:-133mb/s for 32 bit, 266mb/s for 64 bit.
• Plug & Play Facility:-PCI board inserted in any PCI slot is automatically detected &
required I/O & memory resources are allotted by system.
• It can work with 32 bit or 64 bit bus width.
• It uses 3.3V or 5V for operations.
• It is device independent which means it can be used to connect different types of devices
such as hard disk controllers, sound cards, multimedia controllers, LAN cards etc.
• Full multi-master capability:-this allows any PCI master to communicate directly with
other PCI master/slave.
2. PCI-X(Peripheral Component Interconnect Extended)
PCI-X (Peripheral Component Interconnect Extended) is a computer bus & expansion card
standard designed to supersede PCI.
It is essentially faster version of PCI, running at twice the speed.
PCI-X was developed jointly by IBM, HP, & Compaq.
Features of PCI-X:-
• 1. Up to 133MHz bus Speed.
• 2. 64 bit bandwidth.
• 3. 1GB/s throughput.
• 4. More efficient bus operation for easier interface.
• 5. Backwards compatibility.
3. PCI-E (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) or PCIE
It is a computer expansion card interface format.
It was designed to replace PCI, PCI-X &AGP (graphics card interface).
PCI-E as newer motherboards & computers being made today are supporting this new connection.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 10
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
PCI-E is a point to point topology.
It increases the available bandwidth from 133 MB/s to 8 GB/s.
It provides each device with its own dedicated data pipeline.
• Advantages:-
• Software compatibility with old version.
• High throughput (up to >4GB/s)
• Scalable bandwidth.
• Dedicated bandwidth per slot.
• Peer to peer communication
• Long life (20 + yrs).
Accelerated graphics port (AGP)
•It is also called as advanced graphics port.
•AGP designed by Intel & introduced in august 1997. It uses dedicated point to point channel that
allows the graphics controller card to direct access to s/m memory
• It is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a graphics card to motherboard.
• Primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics.
• It is currently being phased out in favor of PCI Express.
• It is designed to accept an AGP video card.
• It transfers are 32 bit wide.
• Clock speed 66.66 MHz.
• AGP 1x transferred 1 bit per data line per clock cycle yielding 266.66 Mb/s.
• AGP 2x & 4x transferred 2 & 4 bits per data line per clock cycle yielding 533.33 & 1066.66Mbps
respectively.
• AGP 8x transfers 8 bits per line per clock cycle yielding 2133.28 Mbps.
• AGP 8x is used in graphics intensive applications like video editing, 3-dimensional mapping, etc.
Logical Memory Organization
• My PC has 512 MB of memory.
• The system memory in the PC it is often referred to as single number is in fact broken into several
different areas.
• 1. Conventional Memory
• 2. Extended Memory
• 3.Expanded Memory
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 11
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
Fig. Logical memory organization
1. Conventional Memory
First 640 kb of system memory is called conventional memory.
This area is available for use by standard DOS programs, device drivers, command.com, and
interrupt vector.
It available to all PCS.
Limited to 640 kb.
Virtually every program can use this memory.
By default DOS, device drivers, in conventional memory.
Originally this was the only place that programs could run.
Conventional memory occupies addresses 00000h to 9FFFFh.
Fig: Conventional Memory
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 12
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
2. Extended Memory
All of the memory above 1MB is called extended memory.
This is all the memory above the high memory area until the end of system memory.
It is used for programs & data when using an OS running.
It is found from address 10FFF0h to the last address of system memory.
The most commonly used manager is HIMEM.SYS, which sets up extended memory according to
the extended memory specification (XMS).
XMS is the standard that PC programs use for accessing extended memory.
3. Expanded Memory
• An older standard for accessing memory above 1 MB which is called expanded memory.
• It uses a protocol called the expanded memory specification or EMS.
• EMS was originally created to overcome the 1MB addressing limitations of the 8088 & 8086
CPUs.
• Expanded memory is not directly addressable by the processor.
• Instead, it can only be accessed through a small 64K window established in upper memory area.
• Expanded memory is a segment or bank switching scheme in which custom memory adapter has
large number of 64K segments on board combined with special switching & mapping hardware.
• Expanded memory specification developed by Lotus, Intel & Microsoft (LIM).
RAM (Random Access Memory)
• Random-access memory, or RAM, provides large quantities of temporary storage in a computer
system.
• Remember the basic capabilities of a memory:
– It should be able to store a value.
– You should be able to read the value that was saved.
– You should be able to change the stored value.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 13
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
• There are two basic types of RAM
1. Static RAM (SRAM)
2. Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Dynamic Memory
Dynamic memory is built with capacitors.
– A stored charge on the capacitor represents a logical 1.
– No charge represents logic 0.
However, capacitors lose their charge after a few milliseconds. The memory requires constant
refreshing to recharge the capacitors. (That’s what’s “dynamic” about it.)
Dynamic RAMs tend to be physically smaller than static RAMs.
– A single bit of data can be stored with just one capacitor and one transistor, while static RAM
cells typically require 4-6 transistors.
– This means dynamic RAM is cheaper and denser—more bits can be stored in the same
physical area.
Types of RAM
Static RAM (SRAM)
– Each cell stores bit with a six-transistor circuit.
– Retains value indefinitely, as long as it is kept powered.
– Relatively insensitive to disturbances such as electrical noise.
– Faster (8-16 times faster) and more expensive (8-16 times more expensive as well) than DRAM.
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
– Each cell stores bit with a capacitor and transistor.
– Value must be refreshed every 10-100 ms.
– Sensitive to disturbances.
– Slower and cheaper than SRAM.
1. SDRAM
• Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) SDRAM replaced DRAM, FPM (fast page mode), and EDO
(extended data o/p).
• SDRAM is an improvement because it synchronizes data transfer between the CPU and memory.
• SDRAM allows the CPU to process data while another process is being queued.
• Features of SDRAM:-
• 1. All SDRAM chips for desktop Pcs have 168 pins.
• 2. Speed of SDRAM is 100 MHz & 133 MHz.
• 3. generally available in size 32mb, 64mb, 128mb,256mb, 512mb,1GB etc.
• 4. Operating voltage 3.3V.
• 5. The architecture used synchronous.
• 6. Operation Max temperature -85 degree c.
• 7. It pre fetches 1 bit at a time.
2. DDR( Double Data Rate SDRAM)
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 14
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
• Double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory (DDR SDRAM) is a class of
memory integrated circuits used in computers.
• It basically doubles the rate of data transfer of standard SDRAM by transferring data on the up &
down tick of a clock cycle.
• DDR memory operating at 333 MHz actually operates at 166 MHz * 2.
DDR (double data rate synchronous dynamic RAM)
• Features of DDR:-
• 1. All DDR RAM chips have 184 pins.
• 2. DDR RAM comes different speeds. i.e. 100mhz, 133mhz, 166mhz, 200mhz.
• 3. DDR RAM is twice as fast as SDRAM.
• 4. Operating voltage 2.5V.
• 5. The architecture used source-synchronous.
• 6. Operation Max temperature -85 degree c.
• 7. It pre-fetches 2 bits at a time.
DDR2 (double data rate two synchronous dynamic RAM)
• Features of DDR2:-
• 1. All DDR2 chips have 240 pins.
• 2. DDR2 RAM to operate at data rates of 400 MHz, 533 MHz, 667 MHz, & above.
• 3. Higher bandwidth.
• 4. Lower power 1.8V.
• 5. The architecture used source-synchronous.
• 6. Operation Max temperature 95 degree c.
• 7. It pre-fetches 4 bits at a time.
DDR3 (double data rate three synchronous dynamic RAM)
• DDR3 (double data rate three synchronous dynamic RAM is a RAM technology used high speed
storage of the working data of computer.
• Features of DDR3:-
• 1. Introduction of asynchronous RESET pin.
• 2. Support of system level flight time compensation.
• 3. On- DIMM mirror friendly DRAM pin out.
• 4. DDR3 RAM to operate at data rates of 800 MHz, 1066 MHz, 1333 MHz, 1600 MHz & above.
• 5. READ & WRITE calibration.
• 6. It works on lower power 1.5V.
• 7. It pre-fetches 8 bits at a time.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 15
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
Concept of cache memory
• Processor does all memory operations with cache.
• It is a high speed memory kept in between the processor & RAM to increase the data execution
speed. It is kept near to the processor.
• It is smaller, faster memory which stores copies of data from the most frequently used main
memory locations.
• When the processor needs to read from or write to a location in main memory, it first checks
whether a copy of that data is in cache.
• CPU uses cache memory to store instructions that are repeatedly required to run programs,
improving overall system speed.
• Advantages of cache memory is that CPU does not use the motherboard system bus for data
transfer.
Need of cache memory
• When a program executes, the cache memory is searched first.
• To increase the speed of processes to store frequently accessed memory location in cache so that
the CPU can access immediately.
• It is directly accessible memory to CPU or processor.
• It is a fastest memory as compared to all other memory.
• It increases the speed of the CPU or processor.
Level of cache memory or types of cache or Cache Hierarchy
There are different levels of cache:-
1. L1 cache or internal cache
2. L2 cache or external cache
3. L3 cache or shared cache
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 16
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
L1 Cache or Internal Cache
• Cache built into CPU itself is referred to as level 1 (L1) cache or Internal cache.
• It is a small, high speed cache incorporated right into the processor chip.
• L1 cache typically ranges in size from 8kb to 64kb & uses the high speed SRAM(static RAM) .
L2 Cache or External Cache
• Cache that resides on a separate chip next to CPU is called Level 2(L2) cache or external cache.
• L2 cache is between main memory & CPU.
• It provide higher data bandwidth interface between the L2 cache & processor core.
L3 Cache or Shared Cache
• L3 cache has come into trend with the advent of multi-core CPUs.
• These chips will have both L1 & L2 caches for each separate core, there is a common fairly large
L3 shared by all cores.
• It is usually the size of all other caches combined or few multiples of all other caches combined.
• Advantages:
1. Speed of system or improving performance.
2. It lies on the same chip the access time is very small.
3. It is intelligent memory.
4. It reduces wait state or no wait states.
• Disadvantages:
1. Size is very small.
2. Cost is very high.
Q. Compare between internal & External cache
Sr. No. L1 or Internal Cache L2 or External Cache
Cache that resides on separate chip next to
1 Cache built into chipset itself
the CPU
2 Directly accessible to processor Resides between processor & RAM
3 Small in size Bigger in size
4 Faster than external Slower cache
5 Cost is more Cost is less
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 17
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
6 Waiting delay is less Waiting delay is more
Features of Intel Processor
1) Features of Pentium processor
• Superscalar architecture – Pentium has two data paths (U & V pipelines) that allow it to
complete more than one instruction per clock cycle.
• It is RISC processor Design
• 64–bit data path – This doubles the amount of information pulled from the memory on each fetch.
• Clock speed of Pentium available in 75, 90, 100, 120, 133, 150, 166, 200 & 233MHz.
• 32-bit microprocessor – 32-bit addressing
• Pipelined Floating Point Unit
• Separate code (8K) & data (8K) cache
• Advance Design Features: Branch Prediction 237-pin PGA package
What is BIOS ? (Basic Input Output System)? [W-08, W-10, S-11]
• It is also called as ROM BIOS, PC BIOS, System BIOS.
• It is software program that tests the computer hardware components.
• Serves as a standardized communication interface between the computer’s hardware and the operating
system.
• Is a small ROM chip on the PC’s motherboard.
• A basic software program containing all BIOS functions is permanently stored in the ROM.
• This software functions as a basic operating system.
• Is responsible for starting the PC.
• This hardware integrated with software is also referred to as firmware.
Functions of the BIOS
• When you first turn on your PC
– Your PC requires information
• to detect PC components
• To find the operating system(floppy disk, hard drive, or a CD-ROM)
– This information is stored in the BIOS
• To give instructions for the POST (power-on self test).
• This self test ensures that the computer has all of the necessary parts & functionality needed to
successfully start itself, such as use of memory, a keyboard & other parts.
• If errors are detected during the test, the BIOS instruct the computer to give a code that reveals the
problem.
• Error codes are typically a series of beeps heard shortly after startup.
• The BIOS also works to give the computer basic information about how to interact with some critical
components, such as drives & memory that it will need to load the OS.
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 18
Chapter No. 1 Motherboard & its Components Prof. Vilas C. Rathod
Motherboard Selection Criteria [S-10, S-11]
• Processor: A Pentium motherboard should use as minimum the second-generation 3.3v Pentium
processor with 296-pin socket 5 or 7 configuration.
• Processor Socket: Pentium motherboard should have at least one ZIFF socket that follows the
Intel Socket 7 specification. VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) socket will allow the best selection
of future Pentium processors.
• Motherboard speed: Pentium motherboard speeds are start from 66MHz onwards.
• Cache memory: All Pentium motherboards should have 256K to 512K or more of L2 cache on-
board.
• SIMM/DIMM memory: All Pentium or Pentium Pro motherboards should use either 72 pin
SIMMs or 168 pin DIMMs. Today all motherboard use DIMM type of memory.
• Bus type: Today on the motherboard PCI Express bus is used.
• Form Factor: Different types of form factors are like AT for 80286 onwards, ATX for P-IV
motherboards onwards, NLX improvement over ATX.
• Built-in interfaces: A motherboard should contain as many built-in standard controllers &
interfaces (FDC, HDC, UART, LPT, PS/2, USB, and SCSI) as possible (except video).
• Motherboard Chipset: Different types of chipset are Intel Triton II (430HX), Orion (450 KX &
450 GX), and Natoma (440FX).
• Plug & Play
• Power management
Computer Hardware & Maintenance (17428) Page 19
You might also like
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- CHM Topic 1 Notes Motherboard Its ComponentsDocument20 pagesCHM Topic 1 Notes Motherboard Its Componentsraymund12345No ratings yet
- Motherboard. CompDocument16 pagesMotherboard. Compfrp60658No ratings yet
- A++ Note For SECE by TamiratDocument60 pagesA++ Note For SECE by TamiratHenock TadesseNo ratings yet
- MGU-TASFA-EDSI-IT-101 - Module 2 - Hardware and Operating SystemsDocument33 pagesMGU-TASFA-EDSI-IT-101 - Module 2 - Hardware and Operating SystemsTesNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To Personal Computer System - 02Document82 pagesCH1 - Introduction To Personal Computer System - 02Pastor Roy Onyancha CyberNo ratings yet
- ChipsetsDocument24 pagesChipsetsJonald BualNo ratings yet
- 2 Computer Components With Their FunctionsDocument58 pages2 Computer Components With Their FunctionsPatrick L. RondinaNo ratings yet
- PC ComponentsDocument57 pagesPC ComponentsbronxkieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Fundamentals (Lab) : Engr. Muhammad BilalDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Computer Fundamentals (Lab) : Engr. Muhammad Bilalbilal wadudNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Mother BoardDocument28 pagesParts of A Mother BoardReilina KylaNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument41 pagesMotherboardjoseph rey ybiosaNo ratings yet
- Technology ICT: By: Aljohn D. EsplanaDocument58 pagesTechnology ICT: By: Aljohn D. EsplanaAljohn Duran EsplanaNo ratings yet
- PC ComponentsDocument56 pagesPC ComponentsAmit Bikram GogoiNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument2 pagesMotherboardGrace BravoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PC ComponentsDocument56 pagesIntroduction To PC ComponentsAkmad AliNo ratings yet
- Cpe111-Lesson-5 Parts of ComputerDocument81 pagesCpe111-Lesson-5 Parts of ComputerLance AsioNo ratings yet
- cHIPSET AND CONTROLLERDocument9 pagescHIPSET AND CONTROLLERMelody MwhengwereNo ratings yet
- Motherboardppt41 160905161959Document39 pagesMotherboardppt41 160905161959Adrian Yan Yan DelaraNo ratings yet
- Gilas PC MaintenanceDocument97 pagesGilas PC MaintenanceEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol SciNo ratings yet
- Inside the Computer: A Guide to Basic Hardware ComponentsDocument31 pagesInside the Computer: A Guide to Basic Hardware ComponentsEswaran arunachalamNo ratings yet
- Motherboard PPT Bhupen GargDocument20 pagesMotherboard PPT Bhupen GargBhupen GargNo ratings yet
- 1 - Microcontroller VS Microprocontroller TechnologyDocument35 pages1 - Microcontroller VS Microprocontroller TechnologyVinnoth SrikumarNo ratings yet
- PC Components PartsDocument38 pagesPC Components PartsLeira Mae Vasquez RacalNo ratings yet
- Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument90 pagesTypical Configuration of Computer Systemgani100% (1)
- IT Fundamentals Assignment on Microcomputer ComponentsDocument6 pagesIT Fundamentals Assignment on Microcomputer ComponentsFlores Carl JosephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemSohum VenkatadriNo ratings yet
- Know your computer system components and memory typesDocument41 pagesKnow your computer system components and memory typesomviskarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Computer Hardware - Part 2Document44 pagesChapter 1 Computer Hardware - Part 2abinissri rajamuniswaranNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - IcsDocument70 pagesCHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - Icsruzanna abu bakarNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motherboard ComponentsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Motherboard ComponentsallamNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardwares Basic - Inside The BoxDocument33 pagesComputer Hardwares Basic - Inside The BoxSaima Binte IkramNo ratings yet
- The MotherboardDocument39 pagesThe MotherboardGenevev Reyes100% (1)
- Parts of A ComputerDocument15 pagesParts of A ComputerAnnie Rose MahinayNo ratings yet
- Components of A MotherboardDocument114 pagesComponents of A Motherboarddeejhay14100% (1)
- Part 1 MOTHERBOARDDocument45 pagesPart 1 MOTHERBOARDOrlando FelixNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 HIDocument32 pagesUnit 1 HIAchsah S. ThomasNo ratings yet
- Bab-1 Pengantar Personal Computer (PC) 1Document30 pagesBab-1 Pengantar Personal Computer (PC) 1haniNo ratings yet
- Computer Components and SpecificationsDocument3 pagesComputer Components and SpecificationsdonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Typical Configuration of Computer System: IntroductionDocument13 pagesChapter-1 Typical Configuration of Computer System: IntroductionFaizal KhanNo ratings yet
- Parts of a Computer System ExplainedDocument36 pagesParts of a Computer System ExplainedBushra zamanNo ratings yet
- ITE PC v41 Chapter1Document28 pagesITE PC v41 Chapter1Legesse SamuelNo ratings yet
- Computer Parts: by HmsDocument34 pagesComputer Parts: by HmssadiaNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument21 pagesMotherboardYash KumarNo ratings yet
- Internal Components of a ComputerDocument63 pagesInternal Components of a ComputerLester MagallonesNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Name - Sachin Roll No - 20156 Branch - CseDocument39 pagesMotherboard: Name - Sachin Roll No - 20156 Branch - CseSachin DhamiNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument60 pagesMotherboardAlbert Magno CaoileNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 PC Components Lesson 2Document57 pagesLesson 1.2 PC Components Lesson 2Kaye CorNo ratings yet
- Final Notes of Second Yr 2022Document269 pagesFinal Notes of Second Yr 2022RAM KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Passing Package CSDocument20 pagesPassing Package CSbharathkumar900845No ratings yet
- Motherboard HandoutDocument5 pagesMotherboard HandoutJudea SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 8051 Microcontroller Architecture & Interfacing GuideDocument178 pages8051 Microcontroller Architecture & Interfacing Guidesivar22No ratings yet
- Computer ICTDocument20 pagesComputer ICTmobilelegendshelpcenter2022No ratings yet
- Configure Computer SystemsDocument17 pagesConfigure Computer SystemsRyuNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Refers To The Physical Machine That Make Up The Computer Installation. These Are TheDocument5 pagesComputer Hardware Refers To The Physical Machine That Make Up The Computer Installation. These Are Thekariukipoly0% (1)
- CSS Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesCSS Lesson Planirene cadizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 MotherboardDocument102 pagesChapter 2 MotherboardratZ_trgNo ratings yet
- To Study MOTHERBOARD.: HistoryDocument6 pagesTo Study MOTHERBOARD.: Historyshyam ranaNo ratings yet
- Parts of the Computer and its Components ExplainedDocument38 pagesParts of the Computer and its Components ExplainedMark Ivan AbrizaNo ratings yet
- Dbms TextbookDocument109 pagesDbms TextbookSeema swathiNo ratings yet
- Solved SSC MTS 9 October 2017 Shift 1 Paper With Solutions PDFDocument42 pagesSolved SSC MTS 9 October 2017 Shift 1 Paper With Solutions PDFSeema swathiNo ratings yet
- TALLY MODEL COMPANY TRAININGDocument39 pagesTALLY MODEL COMPANY TRAININGKingg2009100% (1)
- Number SeriesDocument11 pagesNumber SeriesSeema swathiNo ratings yet
- Amulet Felicia Brochure 1Document2 pagesAmulet Felicia Brochure 1emrenj50% (2)
- Tom TomDocument10 pagesTom Tomzascribdot0% (1)
- Central Fire Station Project BriefDocument80 pagesCentral Fire Station Project Briefahmad.alatawnehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1to 4 NewDocument169 pagesChapter 1to 4 NewSunita ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- Clark W Edwin Elementary Number TheoryDocument129 pagesClark W Edwin Elementary Number TheoryDireshan Pillay100% (1)
- Business meeting workshopDocument3 pagesBusiness meeting workshopEdison David GuapachoNo ratings yet
- Mortgage Credit Loss DistributionDocument25 pagesMortgage Credit Loss DistributionSwayambhu MandalNo ratings yet
- Measures of Impact of Science and Technology on Indian AgricultureDocument318 pagesMeasures of Impact of Science and Technology on Indian AgricultureVikrant RaghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Spatial DataDocument10 pagesCharacteristics of Spatial DataSohit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Accenture SAP General Ledger PDFDocument12 pagesAccenture SAP General Ledger PDFmageshjayapaul6149No ratings yet
- Understanding Community Dynamics and ActionsDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Community Dynamics and ActionsChristian Guimban100% (2)
- YogasDocument4 pagesYogasHoracio TackanooNo ratings yet
- Aristotle's Physics (Barnes)Document187 pagesAristotle's Physics (Barnes)Carlos CortésNo ratings yet
- Right brain left brain harmony Dieter RamsDocument31 pagesRight brain left brain harmony Dieter RamsAhmad Hafiz QifliNo ratings yet
- U Wu Dkczu Fodkl: Low Carbon Development in China and IndiaDocument406 pagesU Wu Dkczu Fodkl: Low Carbon Development in China and IndiamaveryqNo ratings yet
- Context Analysis and Source EvaluationDocument97 pagesContext Analysis and Source EvaluationAnali BarbonNo ratings yet
- Girl UndergroundDocument52 pagesGirl UndergroundJuan Alberto GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Ancient Quarrel Between Philosophy and Poetry, Raymond B.Document16 pagesAncient Quarrel Between Philosophy and Poetry, Raymond B.Amiya Bhushan SharmaNo ratings yet
- 099CYUT5512017 001卵礫石Document212 pages099CYUT5512017 001卵礫石ruizhou04 wuNo ratings yet
- Eee 2018Document4 pagesEee 2018kesavantNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Cycle: Refrigeration & Air-Conditioning by Wilbert F. Stoecker / Jerold W. Jones (Chapter 10)Document16 pagesVapor Compression Cycle: Refrigeration & Air-Conditioning by Wilbert F. Stoecker / Jerold W. Jones (Chapter 10)nauman khanNo ratings yet
- In-Situ Fermentors CatalogueDocument4 pagesIn-Situ Fermentors CatalogueVineet GuptaNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy in AdolescentsDocument6 pagesPregnancy in AdolescentsMayerli MelissaNo ratings yet
- Creating and Maintaining An Effective Filling Record System - 9-10 November, 2017Document1 pageCreating and Maintaining An Effective Filling Record System - 9-10 November, 2017Muhamad Fadli HarunNo ratings yet
- Composites in Aerospace PresentationDocument19 pagesComposites in Aerospace PresentationJithin Devan PadincharayilNo ratings yet
- ISCOM2824G Conifuguration20090519Document378 pagesISCOM2824G Conifuguration20090519Svetlin IvanovNo ratings yet
- Ways to Earn Money LessonDocument3 pagesWays to Earn Money LessonSyarifahSyarinaSheikhKamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Kyocera FS-C5350DN Kyocera Command Center Operation Guide Rev. 6.3 (Manual)Document66 pagesKyocera FS-C5350DN Kyocera Command Center Operation Guide Rev. 6.3 (Manual)Anonymous pp0zmS2oNo ratings yet
- The Power Reiki SymbolDocument3 pagesThe Power Reiki SymbolSeema QureshiNo ratings yet
- Integration of A Radiation Sensor With A Mobile Robot Under ROSDocument17 pagesIntegration of A Radiation Sensor With A Mobile Robot Under ROSEdmund LeongNo ratings yet
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionFrom Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Hacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxFrom EverandHacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxNo ratings yet
- Model-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodFrom EverandModel-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodNo ratings yet
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XFrom EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Dancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldFrom EverandDancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Computer Science: A Concise IntroductionFrom EverandComputer Science: A Concise IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionFrom EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- From Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionFrom EverandFrom Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionNo ratings yet
- The No Bull$#!£ Guide to Building Your Own PC: No Bull GuidesFrom EverandThe No Bull$#!£ Guide to Building Your Own PC: No Bull GuidesNo ratings yet
- 2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersFrom Everand2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersNo ratings yet
- Kindle Fire Owner's Manual: The ultimate Kindle Fire guide to getting started, advanced user tips, and finding unlimited free books, videos and apps on Amazon and beyondFrom EverandKindle Fire Owner's Manual: The ultimate Kindle Fire guide to getting started, advanced user tips, and finding unlimited free books, videos and apps on Amazon and beyondRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)