Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trig Identities and Derivatives
Uploaded by
joepepphhh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageTrigonometric identities and derivative rules are presented. The basic trig identities relate sin, cos, tan, sec, csc functions. Product rules define trig function products in terms of sums. Double/half angle formulas express double and half angle functions as products of single angle functions. Derivative rules give the derivatives of sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, cot, inverse sin, inverse cos, and inverse tan functions.
Original Description:
yeah
Original Title
Trig Identities
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTrigonometric identities and derivative rules are presented. The basic trig identities relate sin, cos, tan, sec, csc functions. Product rules define trig function products in terms of sums. Double/half angle formulas express double and half angle functions as products of single angle functions. Derivative rules give the derivatives of sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, cot, inverse sin, inverse cos, and inverse tan functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageTrig Identities and Derivatives
Uploaded by
joepepphhhTrigonometric identities and derivative rules are presented. The basic trig identities relate sin, cos, tan, sec, csc functions. Product rules define trig function products in terms of sums. Double/half angle formulas express double and half angle functions as products of single angle functions. Derivative rules give the derivatives of sin, cos, tan, csc, sec, cot, inverse sin, inverse cos, and inverse tan functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
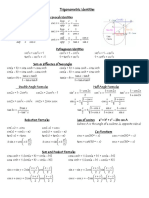
Trig Identities and Derivatives
GSI: Rob Bayer, Math 1B, Fall 2007
There are a lot more identities here than you probably need to know by memory, and there may be some
missing from here that would be good to know, but hopefully this will be helpful. FYI: For the most part,
you wont be using much of csc or cot, but Ive included them here anyways just in case.
Identities
The Basics: sin
2
x + cos
2
x = 1 tanx = sinx/ cos x
sec x = 1/ cos x sec
2
x = 1 + tan
2
x
csc x = 1/ sinx csc
2
x = 1 + cot
2
x
sin(x) = sin(x) cos(x) = cos(x)
Product Rules: sinAcos B =
1
2
(sin(AB) + sin(A+B))
sinAsinB =
1
2
(cos(AB) cos(A+B))
cos Acos B =
1
2
(cos(AB) + cos(A+B))
Double/Half Angle: sinxcos x =
1
2
sin(2x) sin(2x) = 2 sin(x) cos(x)
sin
2
x =
1
2
(1 cos(2x)) cos(2x) = 1 2 sin
2
(x)
cos
2
x =
1
2
(1 + cos(2x)) cos(2x) = 2 cos
2
(x) 1
tan(2x) =
2 tan(x)
1tan
2
(x)
cos(2x) = cos
2
(x) sin
2
(x)
Note that the double/half angle formulas are just the Product Rule ones, with A = B = x plugged in.
Derivatives
d
dx
sinx = cos x
d
dx
cos x = sinx
d
dx
tanx = sec
2
x
d
dx
csc x = csc xcot x
d
dx
sec x = sec xtanx
d
dx
cot x = csc
2
x
d
dx
sin
1
x =
1
1x
2
d
dx
cos
1
x =
1
1x
2
d
dx
tan
1
x =
1
1+x
2
1
You might also like
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Proving Identities and Other ApplicationsDocument13 pagesProving Identities and Other ApplicationsJonnifer QuirosNo ratings yet
- Percentile: ClassesDocument18 pagesPercentile: ClassesVIBHANSHU SINGHNo ratings yet
- Have A Great Summer!Document18 pagesHave A Great Summer!CKNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 01Document20 pagesTrigonometry 01vinayakkanchalNo ratings yet
- Chuyendeluonggiac 3Document3 pagesChuyendeluonggiac 3thanhhiendhktNo ratings yet
- Functions FormulasDocument3 pagesFunctions FormulasmrbubosNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageTrig Cheat Sheet PDFsolikan45No ratings yet
- 5.1 Part 1 GroupworkDocument5 pages5.1 Part 1 GroupworkPeytonNo ratings yet
- Trig Cheat Sheet 2Document1 pageTrig Cheat Sheet 2Jin HyungNo ratings yet
- Algebra and Trigonometry 6th Edition Blitzer Test BankDocument37 pagesAlgebra and Trigonometry 6th Edition Blitzer Test Bankjeffreywesttwnekpscxq100% (29)
- Formula ListDocument15 pagesFormula ListAdithya SampathNo ratings yet
- Important NotesDocument9 pagesImportant NotesSatyanneshi ERNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 2nd Edition Blitzer Test Bank 1Document36 pagesTrigonometry 2nd Edition Blitzer Test Bank 1MrsPamelaSmithajzkqogp100% (15)
- Trigonometric Identities: Math 142Document5 pagesTrigonometric Identities: Math 142Joe NasalitaNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument32 pagesTrigonometrySriram_V100% (1)
- Mathematics 17: Algebra and Trigonometry Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageMathematics 17: Algebra and Trigonometry Trigonometric IdentitiesSanny Domingo AfableNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Integrals-Solutions: ReviewDocument3 pagesTrigonometric Integrals-Solutions: ReviewMarCheLinaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 2nd Edition Blitzer Test Bank 1Document43 pagesTrigonometry 2nd Edition Blitzer Test Bank 1Doris Golden100% (39)
- E3Qtri XDocument12 pagesE3Qtri XRevelationNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry 1st Edition Blitzer Test Bank 1Document48 pagesTrigonometry 1st Edition Blitzer Test Bank 1Ramon Mcclure100% (40)
- Trigonometry 2nd Edition Blitzer Test BankDocument37 pagesTrigonometry 2nd Edition Blitzer Test Bankclitusquanghbz9up100% (22)
- 109 Topic8Document12 pages109 Topic8vishal_bokaroNo ratings yet
- Formula To MerorizeDocument2 pagesFormula To MerorizeFakhrur RaziNo ratings yet
- Ebook College Algebra and Trigonometry 3Rd Edition Ratti Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument64 pagesEbook College Algebra and Trigonometry 3Rd Edition Ratti Test Bank Full Chapter PDFrosakien8871yc100% (10)
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Inverse Trigonometry HWT - 1Document8 pagesSolutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Inverse Trigonometry HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document15 pagesUnit 3api-220078930No ratings yet
- Qa TrigonometryDocument10 pagesQa TrigonometryManikandan MNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Simplifying ExpressionsDocument8 pagesLesson 2 - Simplifying Expressionsiminathi ndlovuNo ratings yet
- More Trigonometric SubstitutionDocument35 pagesMore Trigonometric SubstitutionArsalan JumaniNo ratings yet
- On Tap Luong Giac THPTDocument11 pagesOn Tap Luong Giac THPTngocha91No ratings yet
- Basic Trig IdentitiesDocument2 pagesBasic Trig IdentitiesGkou DojkuNo ratings yet
- TipsDocument5 pagesTipsShivara ShivarajNo ratings yet
- Trignometry Basic QuestionsDocument18 pagesTrignometry Basic Questionsdev1996100% (1)
- CivE 222 Course Outline - 2018SDocument8 pagesCivE 222 Course Outline - 2018SRyan LeeNo ratings yet
- Trig Integrals: Things We Know AlreadyDocument6 pagesTrig Integrals: Things We Know AlreadyJuanes SkaterNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Tutorial - 2sDocument3 pagesAMA1110 Tutorial - 2sBrian LiNo ratings yet
- BasicTrigonometry PDFDocument5 pagesBasicTrigonometry PDFCruise_IceNo ratings yet
- Formulario Matematicas 2009Document0 pagesFormulario Matematicas 2009JJOCNo ratings yet
- Math12-1 - Lesson 7 - Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument15 pagesMath12-1 - Lesson 7 - Trigonometric IdentitiesKobe MartinezNo ratings yet
- FormulaeDocument15 pagesFormulaeProf. M. C. RajuNo ratings yet
- Senior Class FormulaeDocument8 pagesSenior Class FormulaeOP GuptaNo ratings yet
- Limits: ObjectivesDocument19 pagesLimits: ObjectivesRaviTejaPonukupatiNo ratings yet
- Type The Document SubtitleDocument16 pagesType The Document SubtitleNguyễn Trọng QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-04-16 at 2.26.24 PMDocument2 pagesScreenshot 2023-04-16 at 2.26.24 PMt6cqcr2qx7No ratings yet
- Trigonometry For LeafletDocument2 pagesTrigonometry For LeafletSantoshNo ratings yet
- Basic Trig IdentitiesDocument1 pageBasic Trig IdentitiesMadeleine LohNo ratings yet
- Trig No Metric FormulasDocument4 pagesTrig No Metric FormulasZee Shan100% (1)
- Trigonometric Identities and EquationsDocument9 pagesTrigonometric Identities and EquationsOla Sowemimo-CurrencyNo ratings yet
- Derivative of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument1 pageDerivative of Trigonometric Functionsmike capitoNo ratings yet
- Trig ReviewDocument3 pagesTrig ReviewSayee SaranNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument6 pagesTrigonometrylee_yi_5No ratings yet
- Tan X Sin X Cos X Cot X Cos X Sin X CSC X 1 Sin X Sec X 1 Cos X Cot X 1 Tan X Sin Tan CotDocument3 pagesTan X Sin X Cos X Cot X Cos X Sin X CSC X 1 Sin X Sec X 1 Cos X Cot X 1 Tan X Sin Tan CotAudrey LeeNo ratings yet
- Trig Identities 2Document8 pagesTrig Identities 2Buddy OverthinkerNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Trigonometric Ratio & Equation HWT - 1Document6 pagesSolutions To Home Work Test/Mathematics: Trigonometric Ratio & Equation HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- Sin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsDocument10 pagesSin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsChetnaNo ratings yet
- 1.3. Integration of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument5 pages1.3. Integration of Trigonometric FunctionsRandy Cham AlignayNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet