Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earthquake Guided Notes
Uploaded by
api-2647562600 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views3 pagesOriginal Title
earthquake guided notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
76 views3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notes
Uploaded by
api-264756260Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Earthquake Guided Notes page494
What is stress? What is strain? How to they compare and
contrast? (make a Venn diagram
Stress Strain
Force per unit Deterioration of materials
caused by stress
Compression, tension, and
shear
Each type causes different types
of strain
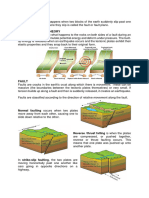
What are the 3 different types of faults? Describe each.
Reverse Fault- Fractures form that form as a result of horizontal
compression
Normal Fault- Fractures caused by horizontal tension
Strike-Slip Fault- Fractures caused by horizontal shear
Materials &
Description
Sketch Movement
Primary
P-Waves
Squeeze and
pull rocks in
the same
direction along
which the
waves are
traveling
Back and forth
Secondary
S-waves
Cause rocks to
move at right
angles in
relation to the
direction of
waves
Right angles
Earthquake Guided Notes page494
Surface
Move in two
directions as
they pass
through rock
Up and
down/side to
side
How do the focus and the epicenter of earthquakes compare and
contrast? The focus is the starting point of the earthquake while
the Earths surface directly above the focus is the epicenter. The
focus is usually deep underground while the epicenter is on the
surface.
The greater the distance between P and S waves on a
seismograph the (longer or shorter) distance away from the
epicenter.
What is the name of the scale used to measure the energy
released during an earthquake? What is the range of the scale?
Seismometers measure earthquakes in seismic waves.
What is the name of the scale used to measure the intensity
(damage done) during and earthquake? What is the range of the
scale? The Richter Scale measures in a scale of one through ten.
Describe the damage caused by earthquakes for a level 1, 5, and
10
Level one earthquakes cant normally be felt, level five
earthquakes are noticeable by all and some dishes and plaster
Earthquake Guided Notes page494
break, and level ten earthquakes causes most ordinary structures
to fall, rails get bent, and landslides are common.
You might also like
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264885511No ratings yet
- The Earth-Shaking Facts about Earthquakes with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Earth-Shaking Facts about Earthquakes with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264090670No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument2 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330300646No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-335690255No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330050095No ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument1 pageEarthquakeapi-269485108No ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330037580100% (1)
- On Earthquake 1Document17 pagesOn Earthquake 1Moshin KhanNo ratings yet
- Ch-2, EarthquakesDocument56 pagesCh-2, EarthquakesAbraham SileshiNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Week 4Document20 pagesModule 4 - Week 4Alice ChanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument2 pagesEarthquake Guided Notesapi-330050027No ratings yet
- 5 - Earthquakes and Related HazardsDocument60 pages5 - Earthquakes and Related HazardsVincent GalleraNo ratings yet
- Danes Kynel G Ricafort ScienceDocument3 pagesDanes Kynel G Ricafort ScienceJenny Ann Mariel ManaladNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design: Seismological AspectsDocument49 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design: Seismological AspectserjuniorsanjipNo ratings yet
- EarthquakesDocument48 pagesEarthquakespascojhonlie62No ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Science 8Document15 pages2nd Quarter Science 8John Ryan PiolNo ratings yet
- 4 - Seismic WavesDocument23 pages4 - Seismic WavesApril ImNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes & FaultsDocument68 pagesEarthquakes & FaultssamNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Introduction To Earthquakes and Earthquakes EngineeringDocument8 pagesChapter One Introduction To Earthquakes and Earthquakes EngineeringAhmed Abd-AlmoujoodNo ratings yet
- Earth Quake DesignDocument13 pagesEarth Quake DesignRanie boy CabanillaNo ratings yet
- Group3 EarthquakeDocument23 pagesGroup3 EarthquakeKiara A.P GajoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021 Second Quarter Geology Module Name: - Shiva Matthew V. Cruz - Section: 11-STEM 5Document7 pagesEarth Science ACADEMIC YEAR 2020-2021 Second Quarter Geology Module Name: - Shiva Matthew V. Cruz - Section: 11-STEM 5Shiva Cruz Jr.No ratings yet
- Lecture No. 15 EarthquakesDocument19 pagesLecture No. 15 EarthquakesZuhair TurkmaniNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes Lesson 1Document11 pagesEarthquakes Lesson 1Diana CosteaNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 SeismologyDocument101 pagesChapter1 SeismologyJulyNo ratings yet
- Earthquake EpicenterDocument50 pagesEarthquake EpicenterWelms NaderzNo ratings yet
- EarthquakesDocument73 pagesEarthquakesMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE Module Quarter 2 Week 1Document5 pagesSCIENCE Module Quarter 2 Week 1MACAINAG, AngelicaNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Gempa2Document43 pagesPengantar Gempa2Aria JonathanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake HazardsDocument16 pagesEarthquake HazardsAlwynMarasiganGamingNo ratings yet
- Group 2 12 STEM B EarthquakeDocument13 pagesGroup 2 12 STEM B EarthquakeAra Hella JordasNo ratings yet
- q2 w1 Earthquakes FaultsDocument41 pagesq2 w1 Earthquakes FaultsAyesha Jan BuenacruzNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument39 pagesEarthquakefalakNo ratings yet
- B1.Seismology - Set 1Document83 pagesB1.Seismology - Set 1syahmi azharNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q2 - Week1 - EarthquakeDocument55 pagesG8 Science Q2 - Week1 - Earthquakewinincepido29No ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Seismic WavesDocument36 pagesEarthquakes and Seismic WavesTeena SeiclamNo ratings yet
- Origin and Occurrence of Earthquake-MarfilDocument3 pagesOrigin and Occurrence of Earthquake-MarfilLyn OzitlamNo ratings yet
- Earthquake 1Document103 pagesEarthquake 1kazimmehdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Earthquake and Its Impact On Roads and BuildingsDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Earthquake and Its Impact On Roads and BuildingsVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14 Tectonic Plates and Earths Internal Structure CSS PMS General Science and AbilityDocument46 pagesLecture 14 Tectonic Plates and Earths Internal Structure CSS PMS General Science and AbilityAsif SardarNo ratings yet
- A Tragedy To Life and PropertyDocument40 pagesA Tragedy To Life and PropertyJocelyn Amen SumalpongNo ratings yet
- Earthquake - Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesEarthquake - Lecture NotesLeandro Remojo JrNo ratings yet
- Eads U1 2MDocument5 pagesEads U1 2Mvidhyakumardec09No ratings yet
- G5 Earthquake ReviewerDocument6 pagesG5 Earthquake ReviewermuhamsumandresNo ratings yet
- Week 9 Disaster and Disaster RiskDocument5 pagesWeek 9 Disaster and Disaster RiskAilyn Uy Laparan DiolataNo ratings yet
- BSC Lecture 3Document36 pagesBSC Lecture 3sansam53No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Propagation of Seismic DisturbanceDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Propagation of Seismic DisturbanceGabriel LopezNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q2 - Week1 - EarthquakeDocument61 pagesG8 Science Q2 - Week1 - EarthquakeIemmee Jane DinglasanNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Engineering2Document147 pagesEarthquake Engineering2Mariz Ellaine Baltazar83% (6)
- Earthquake ReadingsDocument16 pagesEarthquake Readingsapi-251355123No ratings yet
- Earthquakes PDFDocument6 pagesEarthquakes PDFRaphael Ivan FernandezNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument25 pagesEarthquakeSyafiqah AimanNo ratings yet
- On Earthquake 1Document17 pagesOn Earthquake 1Bhey Faune Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Their Destructive EffectsDocument40 pagesEarthquakes and Their Destructive EffectsjoeyNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Awareness AGPDocument103 pagesEarthquake Awareness AGPrameshbabu_1979No ratings yet
- Earthquakes 2Document29 pagesEarthquakes 2Saravana Kumar LakshmananNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument46 pagesEarthquakeMARY GRACE FACULARINNo ratings yet
- Presentation On EarthquakeDocument20 pagesPresentation On EarthquakeManish AroraNo ratings yet
- Eab Wanted PosterDocument2 pagesEab Wanted Posterapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Sec 12 1Document18 pagesSec 12 1api-268159571No ratings yet
- The Atmosphere BasicsDocument22 pagesThe Atmosphere Basicsapi-268159571No ratings yet
- State and Moisture of The AtmosphereDocument110 pagesState and Moisture of The Atmosphereapi-264590160100% (1)
- AirmassandfrontsawebquestDocument5 pagesAirmassandfrontsawebquestapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Global WarmingDocument28 pagesGlobal Warmingapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Honors Ees Post RefelctionDocument1 pageHonors Ees Post Refelctionapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Renewable Energy WebquestDocument3 pagesRenewable Energy Webquestapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Atmosphere Basics WebsquestDocument2 pagesAtmosphere Basics Websquestapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Freshwater Pollution Guided NotesDocument2 pagesFreshwater Pollution Guided Notesapi-330462935No ratings yet
- Hydropower and Water DiversionDocument20 pagesHydropower and Water Diversionapi-268159571No ratings yet
- WaterpollutionDocument33 pagesWaterpollutionapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Water Cycle Webquest 2Document6 pagesWater Cycle Webquest 2api-264756260No ratings yet
- Sewage and SepticDocument24 pagesSewage and Septicapi-264756260100% (1)
- Measuring Water QualityDocument7 pagesMeasuring Water Qualityapi-264756260No ratings yet
- WaterpollutionDocument33 pagesWaterpollutionapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Basin AssignmentsDocument1 pageBasin Assignmentsapi-264756260No ratings yet
- 9-1 Surface WaterDocument38 pages9-1 Surface Waterapi-264150929No ratings yet
- Land UseDocument1 pageLand Useapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Measuring Water QualityDocument7 pagesMeasuring Water Qualityapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Sewage and SepticDocument24 pagesSewage and Septicapi-264756260100% (1)
- GroundwaterDocument16 pagesGroundwaterapi-268159571No ratings yet
- What-Is-A-Watershed-Webquest StudentworksheetDocument5 pagesWhat-Is-A-Watershed-Webquest Studentworksheetapi-268533145100% (1)
- What Is A Solid WasteDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Solid Wasteapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Agriculture NotesDocument4 pagesAgriculture Notesapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Food Production in Europe WebquestDocument2 pagesFood Production in Europe Webquestapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Solid Waste Guided NotesDocument3 pagesSolid Waste Guided Notesapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Nonrenewable Energy NotesDocument3 pagesNonrenewable Energy Notesapi-264756260No ratings yet
- Coastal ProtectionDocument2 pagesCoastal Protectionapi-264756260No ratings yet
- MeatirxtrilogyquestionsDocument2 pagesMeatirxtrilogyquestionsapi-264756260No ratings yet