Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sinusoidal Pulse-Width Modulation
Sinusoidal Pulse-Width Modulation
Uploaded by
tba1509900 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views13 pagesOriginal Title
3870.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views13 pagesSinusoidal Pulse-Width Modulation
Sinusoidal Pulse-Width Modulation
Uploaded by
tba150990Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
ECE 442 Power Electronics 1
Sinusoidal Pulse-Width Modulation
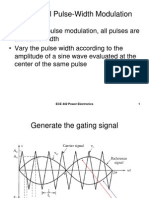
In multiple-pulse modulation, all pulses are
the same width
Vary the pulse width according to the
amplitude of a sine wave evaluated at the
center of the same pulse
ECE 442 Power Electronics 2
Generate the gating signal
2 Reference Signals, v
r
, -v
r
ECE 442 Power Electronics 3
Comparing the carrier and reference signals
Generate g
1
signal by comparison with v
r
Generate g
4
signal by comparison with -v
r
ECE 442 Power Electronics 4
Comparing the carrier and reference signals
ECE 442 Power Electronics 5
Potential problem if Q
1
and Q
4
try to turn ON
at the same time!
ECE 442 Power Electronics 6
If we prevent the problem
Output voltage is low when g
1
and g
4
are
both high
ECE 442 Power Electronics 7
This composite signal is difficult to generate
ECE 442 Power Electronics 8
Generate the same gate pulses with one
sine wave
ECE 442 Power Electronics 9
Alternate scheme
ECE 442 Power Electronics 10
rms output voltage
Depends on the modulation index, M
2
1
p
m
o S S
m
p
V V V
o o
t t
=
=
Where
m
is the width of the mth pulse
ECE 442 Power Electronics 11
Fourier coefficients of the output voltage
( ) ( )
2
1
4 3
sin sin sin
4 4 4
1, 3, 5, ..
p
S m m m
n m m
m
V n
B n n
n
n
o o o
o t o
t
=
(
= + + +
(
=
ECE 442 Power Electronics 12
Harmonic Profile
ECE 442 Power Electronics 13
Compare with multiple-pulse case for p=5
Distortion Factor is considerably less
You might also like
- Passive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2From EverandPassive and Discrete Circuits: Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Unit 4 InvertersDocument86 pagesUnit 4 InvertersHaritha RkNo ratings yet
- Eead422 TransformerDocument183 pagesEead422 TransformerRenzJohnAmpostaNo ratings yet
- ELEX3 Differential AmplifiersDocument38 pagesELEX3 Differential AmplifiersJacklyn Kate Caballero Garduque100% (1)
- Sinusoidal Pulse-Width ModulationDocument13 pagesSinusoidal Pulse-Width ModulationengrarNo ratings yet
- Voltage Control of Single-Phase Inverters - Commonly-Used TechniquesDocument14 pagesVoltage Control of Single-Phase Inverters - Commonly-Used TechniquesShakir HussainNo ratings yet
- Directional Coupler - Bathe Hole Coupler PDFDocument21 pagesDirectional Coupler - Bathe Hole Coupler PDFvbhamini94100% (3)
- Lecture 4 Differential AmplifiersDocument21 pagesLecture 4 Differential Amplifierstranhieu_hcmutNo ratings yet
- A7838087 Electronic Devices For Gate Ec Study Notes On Semiconductor PhysicsDocument10 pagesA7838087 Electronic Devices For Gate Ec Study Notes On Semiconductor PhysicsAvinash KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 05Document5 pagesLab 05Lovely JuttNo ratings yet
- Modul 11 Mesin Listrik 11 PDFDocument33 pagesModul 11 Mesin Listrik 11 PDFaswardiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Guide For Electronics 3 OperaDocument114 pagesLaboratory Guide For Electronics 3 Opera1553No ratings yet
- Lab 05Document3 pagesLab 05Juan TarquiNo ratings yet
- OFC - Lec - LEDDocument27 pagesOFC - Lec - LEDfatmagulkerim19No ratings yet
- Current SourcesDocument17 pagesCurrent SourcesJesse StoutNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ExperimentDocument5 pagesLaboratory ExperimentMark Jomel MangampoNo ratings yet
- Ayush ProjectDocument16 pagesAyush ProjectAYUSH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Semiconductors: Basic PropertiesDocument20 pagesSemiconductors: Basic PropertiesR Brent MattisNo ratings yet
- Power Mosfets: - Two TypesDocument13 pagesPower Mosfets: - Two TypesDiane Bonilla LacenaNo ratings yet
- Band Gap in A SemiconductorDocument11 pagesBand Gap in A Semiconductorabhishek1205choudharyNo ratings yet
- Eead422 Transformer PPT UpdatedDocument190 pagesEead422 Transformer PPT UpdatedFrinz Mardie GañoNo ratings yet
- Voltage Control of Single-Phase Inverters - Commonly-Used TechniquesDocument17 pagesVoltage Control of Single-Phase Inverters - Commonly-Used TechniquesMariam MugheesNo ratings yet
- LIC M-III PPTsDocument51 pagesLIC M-III PPTsDEEPTHE S 20BEC1171No ratings yet
- Phy PotentiometerDocument20 pagesPhy PotentiometerDanyRaj100% (3)
- High Voltage Lecture - 8Document33 pagesHigh Voltage Lecture - 8Mansoor SarwarNo ratings yet
- 8-Port Power CombinerDocument21 pages8-Port Power CombinerTharakram KorripatiNo ratings yet
- Ehb 222e Lecture 6 - Mosfet DC AnalysisDocument30 pagesEhb 222e Lecture 6 - Mosfet DC Analysisanil052001No ratings yet
- Wien Bridge.Document11 pagesWien Bridge.Enock OmariNo ratings yet
- Experiment Experiment Experiment Experiment Experiment: Aboratory AnualDocument7 pagesExperiment Experiment Experiment Experiment Experiment: Aboratory AnualChinmaya SahuNo ratings yet
- ENGD1103 Lab1 2022Document9 pagesENGD1103 Lab1 2022ellaismaewebbNo ratings yet
- 4.4 MOSFETS in IC CSA CGA Biasing and AmplificationDocument33 pages4.4 MOSFETS in IC CSA CGA Biasing and AmplificationKesani Venkat Narsimha ReddyNo ratings yet
- UNIT I and II NewDocument171 pagesUNIT I and II Newdinesh.vNo ratings yet
- Chap 4: RadiationDocument40 pagesChap 4: RadiationOng Teck ChongNo ratings yet
- Manual NewDocument41 pagesManual NewShobha AnchanNo ratings yet
- Ecgr3155 Experiment 8 Mosfet Amplifiers Configurations and Input Output ImpedancesDocument9 pagesEcgr3155 Experiment 8 Mosfet Amplifiers Configurations and Input Output ImpedancesdrhammoudaNo ratings yet
- ECE3013 - Linear Integrated Circuits: Module-IiiDocument50 pagesECE3013 - Linear Integrated Circuits: Module-IiiWINORLOSENo ratings yet
- Mother'S Public School Unit-1, Bhubaneswar: Factors Affecting The Internal Resistance of A CellDocument15 pagesMother'S Public School Unit-1, Bhubaneswar: Factors Affecting The Internal Resistance of A CellAyush MishraNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument112 pagesBasic ElectronicsoomganapathiNo ratings yet
- Exp 4Document3 pagesExp 4Chinmoy GhoshNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits: 0.1 Series RLC Circuit Series RLC Circuit - PhasorsDocument6 pagesAC Circuits: 0.1 Series RLC Circuit Series RLC Circuit - PhasorsMahmudul HasanNo ratings yet
- To Investigate The Relation Between The Ratio ofDocument15 pagesTo Investigate The Relation Between The Ratio ofvirendernyk3No ratings yet
- Ring Attenuator Matched Load Twist Bend CornerDocument24 pagesRing Attenuator Matched Load Twist Bend CornerpadmaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier.Document37 pagesPower Electronics Single-Phase Half-Wave Rectifier.Hassan technologist0% (1)
- Akhilphysics 1Document10 pagesAkhilphysics 1sumathi0576No ratings yet
- To Investigate A Self Designed TransformerDocument18 pagesTo Investigate A Self Designed TransformerSheen93% (15)
- BooksDocument30 pagesBooksHabib IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- Electro Handout (Jaan Kalda)Document48 pagesElectro Handout (Jaan Kalda)hfhfhss chuppiNo ratings yet
- Ex05 Lim OpampDocument9 pagesEx05 Lim OpampLIM Sheryl M.No ratings yet
- Expt Write-UpDocument37 pagesExpt Write-UpTushar PatwaNo ratings yet
- Diode ReviewDocument34 pagesDiode ReviewM Madan GopalNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document25 pagesModule 4siddharth jainNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Parameters of AntennasDocument16 pagesFundamental Parameters of AntennasShrivishal TripathiNo ratings yet
- Bio Amps NotesDocument9 pagesBio Amps Notesagmnm1962No ratings yet
- Rayleigh PotDocument10 pagesRayleigh PotNikhilesh ShajiNo ratings yet
- Series Resonant Inverter With Bidirectional Switch: ECE 442 Power Electronics 1Document27 pagesSeries Resonant Inverter With Bidirectional Switch: ECE 442 Power Electronics 1mrboyedNo ratings yet
- Practical Procedure - Term 1Document9 pagesPractical Procedure - Term 1Ammar ZaminNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project HesDocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project HesBk ShreyaNo ratings yet
- PEC DC DC ConvertersDocument60 pagesPEC DC DC ConvertersJoshua HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project, Physics On Internal ResistanceDocument11 pagesInvestigatory Project, Physics On Internal ResistanceKavya PatelNo ratings yet