Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sians t1 Latihan
Uploaded by
Nurul Fairuz HusnaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sians t1 Latihan
Uploaded by
Nurul Fairuz HusnaCopyright:
Available Formats
etutorA Tuition Center
SCIENCE MODUL 5 FORM 2
Chapter 1 & 2: The World Through Our Sense & Nutrition
Name:
Date:
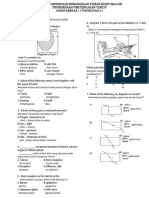
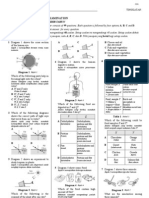
Diagram 6 shows a section through part of a human head containing sensory organ.
Which part of a plant shows positive phototropism?
A
B
C
D
Root
Shoot
Stem
Fruit
PMR 2008
Which of the following sensory organs can detect touch, pain and pressure?
A
Eyes
Diagram 6
B
Nose
C
Ears
Which
of the parts labelled A, B, C or D is a sensory cell?
D
Skin
PMR 2007
PMR 2008
The Following information shows a type of response of a plant due to a stimulus.
-
shoot grows away from the stimulus
enables the plant to obtain water and minerals
roots grow towards gravitional attraction
Which of the following is the response?
A
B
C
D
Geotropism
Phototropism
Thigmotropism
Hydrotropism
PMR 2006
5
6
The diagram shows the path of an impulse after a stimulus is received by the skin.
Stimulus
Nerveof the pupil
The diagram shows Xa change in size
Nerve
Which of the following represents X, Y and Z?
Pupil
A
Brain
Effector
B
Receptor
Effector
C of the
Brain
Receptor
Which
following action will cause
this change?
D
Receptor
Brain
A
Reading a book in a dark room
Z
Receptor
Brain
Effector
Effector
PMR 2005
etutorA Tuition Center
B
C
D
SCIENCE MODUL 5 FORM 2
Chapter 1 & 2: The World Through Our Sense & Nutrition
Entering a darkroom from a bright room
Taking off sun glasses in a bright place
Looking at a distance object after looking at a near object.
PMR 2004
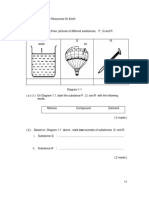
Diagram 1.1 shows how human eye can see. (PMR 2007)
Diagram 1.1
(a) (i) State one difference between object Q and image I.
_________________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
(ii) How does the size of the image I change when the eye is 10 cm from object Q?
________________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
(iii) State one reason for the answer in 1(a)(ii).
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
(b) (i) Complete Diagram 1.2 to show the formation of an image of a distant object on
the retina of the eye of a short sighted person.
Diagram 1.2
(ii) What causes the situation in Diagram 1.2 to happen?
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
(iii) How can the situation in Diagram 1.2 be corrected?
_______________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
etutorA Tuition Center
SCIENCE MODUL 5 FORM 2
Chapter 1 & 2: The World Through Our Sense & Nutrition
NUTRITION
1
Which food pyramid is the best guide to plan a balanced diet?
The calorific value of rice is 15 kJ/g.
Calculate the calorific value in 100g of rice.
PMR 2008
A
B
15 kJ
30 kJ
etutorA Tuition Center
C
D
3
SCIENCE MODUL 5 FORM 2
Chapter 1 & 2: The World Through Our Sense & Nutrition
1500 kJ
3000 kJ
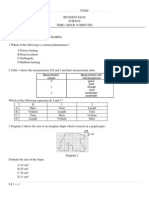
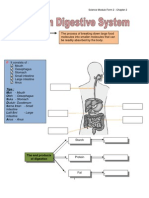
The diagram shows organs in a human digestive system.
Which of the following are the functions of J, K, L and M?
J
A
B
C
D
To digest starch
To digest starch
To digest protein
To digest protein
To perform peristalsis
To digest protein
To perform peristalsis
To digest starch
To digest protein
To digest fat
To digest fat
To perform
peristalsis
To digest fat
To perform peristalsis
To digest starch
To digest fat
The diagram shows a boy who is suffering from kwashiorkor disease.
5 Which of the following pairs of food classes and examples is not correct?
Food class
A
B
C
D
Protein
Carbohydrate
Roughage
Fat
Example
Chicken meat
Noodles
Papaya
Potato
PMR 2004
Which of the following is the cause of the disease?
A
B
C
D
Drinking too much water
Lack of protein in the diet
Lack of calcium in the diet
Too much carbohydrate in the diet
PMR 2005
etutorA Tuition Center
1
SCIENCE MODUL 5 FORM 2
Chapter 1 & 2: The World Through Our Sense & Nutrition
Figure 1.1 shows the human digestive system.( PMR 2004)
Figure 1.1
(a) (i) Label one of the following structures in Figure 1.1.
Pancreas
Liver
Oesophagus
Mouth
(1mark)
(ii) State one function of the structure in (a) (i).
_________________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
(b) A student carried out a food test on sample X.
Table 1.2 shows the results of the test.
Food test
Observation
Sample X is crushed and
added with Millon's reagent
Red precipitate was formed
Sample X tested on filter
paper
Grease spot was formed
Food class
___________________
___________________
TABLE 1.2
(i) Complete Table 1.2 by naming the food classes that are present in sample X.
(1 mark)
(ii) Explain what happens to the food sample X while it is inside structure Q.
___________________________________________________________________
(2 marks)
(iii) State what happens to the final product in (b) (ii).
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
etutorA Tuition Center
2
SCIENCE MODUL 5 FORM 2
Chapter 1 & 2: The World Through Our Sense & Nutrition
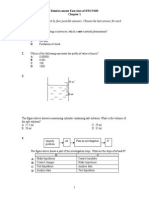
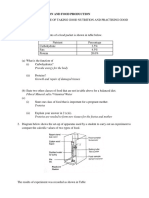
Figure 2.1 shows an experiment to study the action of saliva on starch. The result of the
experiment after 30 minutes is shown in Table 2.2. (PMR 2005)
Figure 2.1
Test tube
X
Presence of starch
No
Yes
Table 2.2
Based on Figure 2.1 and Table 2.2, answer the following questions.
(a) (i) Why must test tubes X and Y be kept in the water bath at 37oC?
_________________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
(ii) State the reason why there is no starch in test tube X.
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
(2 marks)
(iii) In which part of the alimentary canal does the same enzyme action occur as
in the test tube X?
________________________________________________________________
(1 mark)
etutorA Tuition Center
SCIENCE MODUL 5 FORM 2
Chapter 1 & 2: The World Through Our Sense & Nutrition
(b) Figure 2.2 shows pictures of several foods.
Figure 2.2
Based on the pictures, complete the table below by writing the different food classes
and their food samples.
Food classes
Food sample
(i) Carbohydrate
Bread
(ii) ______________________________
______________________________
(iii)_______________________________
______________________________
(iv)_______________________________
______________________________
(v)_______________________________
______________________________
(vi)_______________________________
______________________________
(5 marks)
etutorA Tuition Center
SCIENCE MODUL 5 FORM 2
Chapter 1 & 2: The World Through Our Sense & Nutrition
The world through our senses
PMR 2007
1(a)
(b)
ANSWER:
1. B
2. B
3. D
4. D
5. D
6. C
The image I is smaller. / The image I is inverted.
The image is becomes larger.
The nearer the object to the lens, the larger the image. /
Angle of incidence is larger.
(i)
(ii) The eyeball is longer than normal./ The lens is too thick.
(iii) Use concave lens or diverging lens / Laser surgery
NUTRITION
ANSWER:
1. C
2. C
3. A
4. B
5. D
PMR 20041(a)
(b)
(i) Label one of the following structures:Pancreas, liver, oesophagus or mouth
(ii) State one function of the labelled structure.
Pancreas : Secretes enzyme / examples of enzyme
Secretes hormones / examples of hormone
Liver
: Produces bile / remove toxins from blood / changes
excess amino acids to urea / changes glucose into glycogen
Oesophagus : Moves the food from the mouth to the stomach
Mouth
: Churns food
Starch is broken down by amylase into maltose.
(i) 1. Protein
2. Fats
(ii) Proteins is broken down into amino acids.
Fats is broken down into glycerol and fatty acids
(iii) The digested food is absorbed into the blood capillaries.
PMR 20052(a)
You might also like
- Science Form 2Document6 pagesScience Form 2E's M ZawawiNo ratings yet
- Sains THN 3-Section ADocument13 pagesSains THN 3-Section AMohd Izwan OthmanNo ratings yet
- Soalan Matematik Tahun 5 Mathematics Year 5Document8 pagesSoalan Matematik Tahun 5 Mathematics Year 5RosNani KaRim67% (3)
- Ujian Sains Tingkatan 2Document10 pagesUjian Sains Tingkatan 2SITI ZAIDAH AHMAD50% (6)
- Soalan Matematik Tahun 3 Penilaian 1Document5 pagesSoalan Matematik Tahun 3 Penilaian 1norizan bt awang100% (2)
- f1 Chapter 1Document7 pagesf1 Chapter 1Nurul AzuwinNo ratings yet
- Soalan Science Tingkatan 1Document8 pagesSoalan Science Tingkatan 1Sabri AwangNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 2)Document12 pagesSains Tingkatan 1 (Bab 2)JeyShida73% (11)
- Science Year 5 - Unit 2 Survival of The Species (Notes and Exercise)Document4 pagesScience Year 5 - Unit 2 Survival of The Species (Notes and Exercise)kheshin80100% (3)
- Form 3 - Chapter 9Document9 pagesForm 3 - Chapter 9MARHAINI50% (2)
- SJKT Ladang Senawang, 71450 SG - Gadut: Mid Term Examination Science Year 5 1 Hour 15 MinutesDocument27 pagesSJKT Ladang Senawang, 71450 SG - Gadut: Mid Term Examination Science Year 5 1 Hour 15 MinutesNadarajahNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsDocument11 pagesForm 3 Chapter 1 QuestionsCheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- Soalan Sains Tingkatan 1Document17 pagesSoalan Sains Tingkatan 1RosmizaNo ratings yet
- Ujian Sains Tingkatan 2Document15 pagesUjian Sains Tingkatan 2SITI ZAIDAH AHMAD75% (12)
- SCIENCE FORM 3 Chapter 4 ExerciseDocument7 pagesSCIENCE FORM 3 Chapter 4 ExerciseWan Shuhaimi Wan Ali100% (1)
- Exam Sains Final THN 4Document17 pagesExam Sains Final THN 4mohdyusNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sains Unit 2: Life Processes Tahun 4Document3 pagesSoalan Sains Unit 2: Life Processes Tahun 4ika_nikan0% (1)
- Ujian 1 THN 4Document13 pagesUjian 1 THN 4Che Shuk ShukaNo ratings yet
- Latihan Sains Tahun 5Document8 pagesLatihan Sains Tahun 5Shahruddin Subari60% (5)
- Mathematics Upsr Paper Format Paper Type of Question Type of Answer Number of Questions Time GivenDocument15 pagesMathematics Upsr Paper Format Paper Type of Question Type of Answer Number of Questions Time GivenKhairul Risor Legacy100% (6)
- UPT Matematik Tahun 4 K1 MEI 2019Document14 pagesUPT Matematik Tahun 4 K1 MEI 2019skdkbpNo ratings yet
- Sains Tingkatan 1Document9 pagesSains Tingkatan 1871226No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - The Variety Resources On EarthDocument14 pagesChapter 4 - The Variety Resources On EarthRozaini Othman71% (7)
- Monthly Year 5 Science 2014Document12 pagesMonthly Year 5 Science 2014Ksnithiya GthavanNo ratings yet
- Revision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Document21 pagesRevision Pack Science Form 1 + Form 2Shureen Baskaran100% (1)
- Science Form 1 Chapter 4Document26 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 4Beevy GB73% (11)
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 1Document7 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 1gayathiremathibalanNo ratings yet
- f2 Chapter 2 PDFDocument9 pagesf2 Chapter 2 PDFNurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 Chapter 6Document9 pagesScience Form 1 Chapter 6Syazwani Radzi100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Figure 1 (I) Figure 1 (Ii)Document37 pagesChapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell Organisation: Figure 1 (I) Figure 1 (Ii)Jonathan LingNo ratings yet
- Structured Questions Science Form 2Document12 pagesStructured Questions Science Form 2uminoriah83% (18)
- Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 6Document13 pagesBahasa Inggeris Tahun 6Hayrold LimNo ratings yet
- Bank SoalanDocument11 pagesBank SoalanChe Shuk ShukaNo ratings yet
- Soalan Peperiksaan Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 2Document7 pagesSoalan Peperiksaan Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 2Siti Aqilah100% (1)
- Ujian Mac Matematik Form 1Document4 pagesUjian Mac Matematik Form 1NabilahOthman88100% (1)
- Year 2 Exam Paper 2023 NEWDocument9 pagesYear 2 Exam Paper 2023 NEWMariayee PerumalNo ratings yet
- Topical Test (Integer) BiDocument1 pageTopical Test (Integer) BiRohasniRoslanNo ratings yet
- Soalan Sains Sec A & Sec B Tahun 2Document27 pagesSoalan Sains Sec A & Sec B Tahun 2sasauball75% (8)
- Soalan Peperiksaan Science Tingkatan 1Document6 pagesSoalan Peperiksaan Science Tingkatan 1Aimi Nadia Yusof100% (1)
- Teaching Learning Module KSSR Semakan 2017 Science Year 1 1st EditionDocument98 pagesTeaching Learning Module KSSR Semakan 2017 Science Year 1 1st Editionabq36161713No ratings yet
- Mid Year Exam Science Form 2 2011 - LatestDocument22 pagesMid Year Exam Science Form 2 2011 - LatestTan Phei Ling75% (4)
- Chapter 3 MatterDocument8 pagesChapter 3 Matternaza9775100% (2)
- 1 Which Food Pyramid Is The Best Guide To Plan A Balanced Diet?Document8 pages1 Which Food Pyramid Is The Best Guide To Plan A Balanced Diet?Nurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- Sda Term 2 TestDocument13 pagesSda Term 2 TestHope MaboteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Science Form 4 Module AnswerDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Science Form 4 Module AnswersakinahsulaimanNo ratings yet
- Diagram 6: The World Through Our SensesDocument4 pagesDiagram 6: The World Through Our SensesAnonymous x0kzb3UNo ratings yet
- B Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023Document12 pagesB Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Shyann Kirk - CSEC Biology January 2011 P2Document18 pagesShyann Kirk - CSEC Biology January 2011 P2shyann100% (1)
- Midterm Paper 22008Document10 pagesMidterm Paper 22008husnaihsanNo ratings yet
- Biology MES 2013Document12 pagesBiology MES 2013Al-Ashmal FoolchandNo ratings yet
- Exercise Digestive System PDFDocument22 pagesExercise Digestive System PDFIzudin Hasan86% (7)
- Sce Form 2Document22 pagesSce Form 2williamkong123No ratings yet
- Soalan Ch1-Ch8Document60 pagesSoalan Ch1-Ch8Anonymous x0kzb3UNo ratings yet
- Junior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2000: Do Not Write in This MarginDocument4 pagesJunior Lyceum Annual Examinations 2000: Do Not Write in This MarginPui Pui LamNo ratings yet
- Csec HSB January 2009 p2Document24 pagesCsec HSB January 2009 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNo ratings yet
- Section A: Multiple-Choice Questions (20 Marks) : Put Your Answers Into The Boxes On P.3Document9 pagesSection A: Multiple-Choice Questions (20 Marks) : Put Your Answers Into The Boxes On P.3Aaron LiuNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Exam PaperDocument8 pagesScience Form 2 Exam PaperNorliyana Ali66% (38)
- CHAPTER 2 Nutrition Form 5 ScienceDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 2 Nutrition Form 5 SciencesakinahsulaimanNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Science Form 2 Exam PaperDocument8 pagesScience Form 2 Exam PaperJoanNo ratings yet
- f2 Chapter 2 PDFDocument9 pagesf2 Chapter 2 PDFNurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- Nota Lengkap Sains T4B5Document14 pagesNota Lengkap Sains T4B5Nurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Sains Tingkatan 3Document32 pagesSet 1 Sains Tingkatan 3Nurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Students ManualDocument4 pagesElectricity Students ManualNurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- 1 Which Food Pyramid Is The Best Guide To Plan A Balanced Diet?Document8 pages1 Which Food Pyramid Is The Best Guide To Plan A Balanced Diet?Nurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- RUJUKANDocument3 pagesRUJUKANNurul Fairuz HusnaNo ratings yet
- ICSE-Biology Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperDocument8 pagesICSE-Biology Sample Paper-1-SOLUTION-Class 10 Question PaperFirdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- Kajtez NatCommun 2016Document11 pagesKajtez NatCommun 2016Luka JandricNo ratings yet
- Ontogeny of The Social Brain in Utero and in InfancyDocument7 pagesOntogeny of The Social Brain in Utero and in InfancyFatima LewinnekNo ratings yet
- Vaishnavi Sing: Zulekha Hospital LLC - (SHARJAH)Document1 pageVaishnavi Sing: Zulekha Hospital LLC - (SHARJAH)Abc AbcNo ratings yet
- Alfa Laval Disc Stack Centrifuge TechonologyDocument8 pagesAlfa Laval Disc Stack Centrifuge TechonologyChaitanya B.AndhareNo ratings yet
- Bone and Connective TissueDocument20 pagesBone and Connective TissueKarka PalmaNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project in Science ViDocument21 pagesInvestigatory Project in Science Vijasperrheyhuera100% (2)
- Rumah Sakit Umum Muhammadiyah Siti AminahDocument15 pagesRumah Sakit Umum Muhammadiyah Siti AminahLABRSU MUHANo ratings yet
- Read Up 2 - Word ListsDocument43 pagesRead Up 2 - Word ListsHANANo ratings yet
- Biology P&DDocument5 pagesBiology P&DMakeedaNo ratings yet
- DukeScientificWritingWorkshop PDFDocument61 pagesDukeScientificWritingWorkshop PDFTresfore FungulaniNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Cooling TowersDocument52 pagesPresentation On Cooling TowersMuhammad Haris HamayunNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Blood Glucose Meter & Strip Product Reference - FOR INTERNAL USE ONLYDocument2 pagesDiabetes Blood Glucose Meter & Strip Product Reference - FOR INTERNAL USE ONLYLorie FadolNo ratings yet
- TIMEMANAGEMENTDocument13 pagesTIMEMANAGEMENTPolinda UseroNo ratings yet
- Molecular Genetics: Details Main IdeaDocument8 pagesMolecular Genetics: Details Main IdeaBao HoangNo ratings yet
- Why Are Elephants Less Likely To Get CancerDocument8 pagesWhy Are Elephants Less Likely To Get Canceralicia tNo ratings yet
- LO Week 5 Tutorial 2Document7 pagesLO Week 5 Tutorial 2Hizkia MarlissaNo ratings yet
- Online Test: Nurture X DLP-2012Document15 pagesOnline Test: Nurture X DLP-2012sohan12345No ratings yet
- Makalah SleDocument48 pagesMakalah Slesalini_sadhna17No ratings yet
- GS 631 - Library and Information Services (0+1) : TopicsDocument24 pagesGS 631 - Library and Information Services (0+1) : TopicsVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Reading Practice (Inference 1)Document3 pagesReading Practice (Inference 1)rusman shiddiqNo ratings yet
- History of Surgical ResearchDocument30 pagesHistory of Surgical ResearchOctavian StefanNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Infusa Daun KemuningDocument66 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Infusa Daun Kemuningvidianka rembulanNo ratings yet
- Xtremely Imple: WBC 5 Part DifferentialDocument2 pagesXtremely Imple: WBC 5 Part DifferentialSalah Al-Absi100% (1)
- Hema I Chapter 8 - DiffDocument67 pagesHema I Chapter 8 - DiffderibewNo ratings yet
- Dna Extraction DissertationDocument6 pagesDna Extraction DissertationWhatShouldIWriteMyPaperOnUK100% (1)
- Human and NatureDocument3 pagesHuman and NatureAndreeaNo ratings yet
- S. 3 Biology Paper 1Document9 pagesS. 3 Biology Paper 1Nsaiga RonaldNo ratings yet
- Science SNC2D Grade 10 ExamDocument8 pagesScience SNC2D Grade 10 ExamRiazNo ratings yet
- Plantago Lanceolata (Bio Research)Document8 pagesPlantago Lanceolata (Bio Research)ad3shofNo ratings yet