Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pipe Rack / Ways & Rack Piping: Akshaya Sharma
Pipe Rack / Ways & Rack Piping: Akshaya Sharma
Uploaded by
Hafiz Muhammad Ayaz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views23 pagesPiping Rack concepts
Original Title
piperackrackpiping-140118082457-phpapp02.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPiping Rack concepts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views23 pagesPipe Rack / Ways & Rack Piping: Akshaya Sharma
Pipe Rack / Ways & Rack Piping: Akshaya Sharma
Uploaded by
Hafiz Muhammad AyazPiping Rack concepts
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 23
PIPE RACK / WAYS
&
RACK PIPING
By,
Akshaya Sharma
Associate Engineer
Piping Department
Date 16th Nov 2006
Contents
INTRODUCTION
PIPE RACK
Pipe Rack design criteria
Shapes
Future Space
Width of Pipe Rack
Clearance
Pipe Rack Loading
RACK PIPING
Positions of Lines (Process & Utilities)
Hot Lines & Cold Lines
Bigger Size Lines
Pipe Spacing
Anchor Bay
Unit Battery Limit
Expansion Loops
Pipe Route
Trays
INTRODUCTION
A pipe rack is the main artery of a process unit. It connects
all equipment with lines that cannot run through adjacent
areas. Because it is located in the middle of the most plants,
the pipe rack must be erected first, before it becomes
obstructed by rows of equipment. Pipe racks carry process,
utility piping and also include instrument and electrical
cable trays as well as equipment mounted over all of these.
The primary data required for detailed development of a
pipe rack :
Plot Plan
P&IDs
Client Specification
Construction Materials
Fire proofing requirements
Statutory requirements
3
PIPE RACK DESIGN CRITERIA
Shapes
Future Space
There are various shapes of pipe rack like L/T/U/H/Z.
These shapes shall be considered based on the area
available.
The total width of the pipe rack shall include 25%
extra space for future expansion/modification in unit
for rack-width upto 16m and 10% for rack-width above
16m. The future space %age is normally based on the
client requirements.
Width of Pipe rack
The width of the rack shall be 6m, 8m or 10m for
single bay and 12m, 16m or 20m for double bay
having 4 tiers maximum. The spacing between pipe
rack portals shall be taken as 6m in general. However
it can be increased to 8m depending on the size of the
5
pumps to be housed below pipe rack.
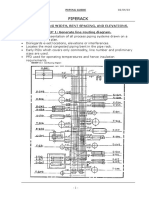
RACK WIDTH SELECTION CRITERIA
DIFFERENT SHAPES OF PIPE RACKS
DEAD END YARD LINES ENTER &
LEAVE ONE END OF THE RACK
L-SHAPED YARD LINES CAN
ENTER & LEAVE NORTH & EAST
OF THE RACK
STRAIGHT THROUGH YARD LINES
CAN ENTER & LEAVE BOTH ENDS
OF THE RACK
T-SHAPED RACK PIPING CAN
ENTER & LEAVE THREE SIDES OF
THE RACK
DIFFERENT SHAPES OF PIPE RACKS
COMPBINATION OF I & T SHAPED
RACK
U-SHAPED YARD LINE CAN ENTER
& LEAVE ALL FOUR SIDES OF THE
RACK
COMPLEX RACK PIPING ARRANGEMENT
FOR VERY LARGE CHEMICAL PLANT
PIPE RACK DESIGN CRITERIA
Clearance
For units, clearance beneath pipe rack
shall be 4m minimum both in longitudinal
and transverse directions.
For Offsite, clearance beneath pipe rack
shall be 2.2m minimum both in
longitudinal and transverse directions.
Road clearance shall be 7m for main road
and 5m for secondary road.
PIPE RACK LOADING
Pipe rack loads shall be given by stress group to
Civil & structural discipline for pipe rack design.
Sustain Load (Dead Load)
Thermal Laod
Load by thermal expansion of piping & Reaction
force by internal pressure of expansion bellows
Dynamic Laod
Weight of piping, valve and load insulation
Load by vibration of piping & by wind and
earthquake
Sustained Load (Live Load)
Liquid load for hydrostatic pressure test
10
RACK PIPING
Position of Lines
Predominantly process lines are to be kept at
lower tier and, utility & hot process lines on
upper tier.
Hot Lines & Cold Lines
Generally hot lines & cold lines are to kept at
different tiers or at different groups on a tier.
Pipe Spacing
Minimum spacing between adjacent lines shall be
decided based on O.D. of bigger size flange (minimum
rating 300# to be considered), O.D. of the smaller pipe,
individual insulation thickness and additional 25mm
clearance. Even if flange is not appearing the min.
spacing shall be based on above basis only. Actual line
spacing, especially at L bend and loop locations, shall
take care thermal expansion/thermal contraction/nonexpansion of adjacent line. Non-expansion/thermal
contraction may stop the free expansion of the
11
adjacent line at L bend location.
RACK PIPING
Bigger Size Lines
Anchor Bay
Large size lines (14 and larger) shall be arranged
close to the column in order to decrease the bending
moment of beam. Water lines more than 30 shall not
be routed over pipe rack, these shall be routed
underground.
Anchors on the racks are to be provided on the anchor
bay if the concept of anchor bay is adopted. Otherwise
anchor shall be distributed over two to three
consecutive bays.
Anchors shall be provided within unit on all hot lines
leaving the unit.
Pipe Route
Racks shall be designed to give the piping shortest
possible run and to provide clear head rooms over
main walkways, secondary walkways and platforms.
12
RACK PIPING
Trays
Generally top tier is to be kept for Electrical cable
trays (if not provided in underground trench) and
Instrument cable ducts/trays. Cable tray laying to
take care of necessary clearances for the fire proofing
of structure.
Battery Limit (ISBL)
Process lines crossing units (within units or from unit
to main pipeway) are normally provided with a block
valve, spectacle blind and drain valve. Block valves
are to be grouped and locations of block valves in
vertical run of pipe are preffered. If the block valves
have to be located in an overhead pipe-way, staircase
access to a platform above the lines shall be provided.
13
RACK PIPING
14
RACK PIPING
15
RACK PIPING
16
EXPANSION LOOPS
Expansion loop is provided on the high
temperature lines. This information shall be
given by stress group. All the loops shall be
located around one column only.
MAKE LINES INTO A GROUP AND INSTALL A
LARGE SIZE PIPING AND HIGH TEMPERATURE
PIPING TO THE EDGE OF THE RACK
17
EXPANSION LOOPS
When necessary to install an expansion loop on
the condensate line, do it horizontally to
prevent water hammering. But do as above if
horizontal loop is impossible.
18
PIPE RACK DESIGN CRITERIA
19
PIPE RACK DESIGN CRITERIA
20
PIPE RACK DESIGN CRITERIA
21
PIPE RACK DESIGN CRITERIA
22
THANK YOU
23
You might also like
- Workover Tubing DesignDocument120 pagesWorkover Tubing DesignMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack Design PhilosophyDocument13 pagesPipe Rack Design Philosophyप्रभु नाथ सिंहNo ratings yet
- Design Practice For Piping Arangement (Pipe Rack)Document53 pagesDesign Practice For Piping Arangement (Pipe Rack)Chairul Anwar100% (2)
- Pipe Supports DesignDocument29 pagesPipe Supports Designpbao_12No ratings yet
- OxidationDocument47 pagesOxidationskgarg04100% (1)
- Pipe Rack LAYOUTDocument25 pagesPipe Rack LAYOUTSAMI UR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Pipe RackDocument33 pagesPipe RackSaid Ahmed Salem100% (1)
- Pipe RackDocument20 pagesPipe RackKehinde AdebayoNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack & Rack PipingDocument22 pagesPipe Rack & Rack PipingOmar MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Pipe Racks ArrangementDocument42 pagesPipe Racks ArrangementShailin ShahNo ratings yet
- Pipe SupportsDocument87 pagesPipe SupportsVeeramanikandanNo ratings yet
- PVE Piping Layout Presentation - Part 1Document68 pagesPVE Piping Layout Presentation - Part 1Nguyen Quang Nghia100% (1)
- 1 PiperackDocument8 pages1 PiperackDinesh Kumar JdNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack Rack PipingDocument23 pagesPipe Rack Rack PipingAlessandro1975No ratings yet
- Piperack Planning GuideDocument4 pagesPiperack Planning GuideryncscNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Piperack DesignDocument70 pagesAspects of Piperack Designdhdahanuwala100% (3)
- Pipe RackDocument25 pagesPipe RackVernie SorianoNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack PresentationDocument19 pagesPipe Rack Presentationkaushalacharya67% (3)
- Modular Pipe Rack ConceptDocument29 pagesModular Pipe Rack ConceptPhilippe LAVOISIERNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack Sizing and Loading DataDocument5 pagesPipe Rack Sizing and Loading DataAnand.5No ratings yet
- Pipe SupportsDocument18 pagesPipe SupportsdwipaNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis Slug Flow PulsationDocument18 pagesStress Analysis Slug Flow Pulsationbhavesh shuklaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Expansion in Piping SystemsDocument55 pagesThermal Expansion in Piping SystemsDivyaShethNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack Sizing and Loading DataDocument6 pagesPipe Rack Sizing and Loading DataapirakqNo ratings yet
- Pipe SupportsDocument31 pagesPipe SupportsAnonymous sLRlLlu100% (1)
- Pipe Supports DesignDocument29 pagesPipe Supports DesignkarunaNo ratings yet
- 903-10004-SPC-M-001 Piping Material SpecificationDocument15 pages903-10004-SPC-M-001 Piping Material SpecificationChitradeep FalguniyaNo ratings yet
- Piping Stress Critical Lines - Basis For Piping Critical Line List PDFDocument3 pagesPiping Stress Critical Lines - Basis For Piping Critical Line List PDFanup15balagarhNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack Loading Calculation Forflare UnitDocument35 pagesPipe Rack Loading Calculation Forflare UnitYethish Maroli100% (1)
- Pipe RoutingDocument4 pagesPipe RoutingJaykumarNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack Sizing and Loading DataDocument7 pagesPipe Rack Sizing and Loading DataRambabuNo ratings yet
- 11 Pipe RacksDocument24 pages11 Pipe RacksKusailaNo ratings yet
- Piping Stress SpecificationDocument23 pagesPiping Stress Specificationpourang1361100% (1)
- Piping InformationDocument201 pagesPiping Informationroyalcom100% (1)
- Caesar GuidelineDocument152 pagesCaesar Guidelineraghib_afzal0% (1)
- Allowable Pipe Spans LoadsDocument84 pagesAllowable Pipe Spans LoadsMalcolm Hutton100% (5)
- Pipe RackDocument1 pagePipe RackJinu JacobNo ratings yet
- Pipe SupportDocument162 pagesPipe Supportsurendar100% (1)
- Presentation On PiperackDocument27 pagesPresentation On Piperackabdussalam_zahrani100% (1)
- Pipeline Stress Analysis With Caesar IIDocument16 pagesPipeline Stress Analysis With Caesar IIPugel YeremiasNo ratings yet
- Piperack Guide2 (7 May, 02)Document61 pagesPiperack Guide2 (7 May, 02)adnan_kasaloNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack / Ways & Rack Piping: Akshaya SharmaDocument23 pagesPipe Rack / Ways & Rack Piping: Akshaya SharmaWahyu IrwansyahNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack 1Document17 pagesPipe Rack 1bipin_pmkNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack and Rack Piping Considerations With Online Course With PDFDocument5 pagesPipe Rack and Rack Piping Considerations With Online Course With PDFSaidFerdjallahNo ratings yet
- Pipe Rack and Rack Piping Considerations With Online Course With PDFDocument5 pagesPipe Rack and Rack Piping Considerations With Online Course With PDFAmjadali ChoudhariNo ratings yet
- DBR For PipingDocument50 pagesDBR For Pipingrajachem100% (1)
- Chapter 12 - Pipe Ra - 2018 - The Engineer S Guide To Plant Layout and Piping deDocument21 pagesChapter 12 - Pipe Ra - 2018 - The Engineer S Guide To Plant Layout and Piping deezeabrilNo ratings yet
- UG Vs AG PipingDocument9 pagesUG Vs AG PipingRahul Lavand100% (3)
- PIPEDocument10 pagesPIPEJoshua SykamNo ratings yet
- Facility ManagementDocument7 pagesFacility ManagementTajudeen IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Pipeline EngineeringDocument52 pagesPipeline Engineeringhamid sobirinNo ratings yet
- Rack DesignDocument8 pagesRack DesignMayank Sethi100% (1)
- ESCHandbook Chapter3 3.18Document12 pagesESCHandbook Chapter3 3.18Larry Wayne Sumpter, JrNo ratings yet
- Bends - Route SelectionDocument6 pagesBends - Route SelectionanishsrNo ratings yet
- Manual in DepthNEC PDFDocument31 pagesManual in DepthNEC PDFdamanpb3633No ratings yet
- Pipeline DesignDocument46 pagesPipeline Designprisen24No ratings yet
- DG260543Document7 pagesDG260543Ahmed OsamaNo ratings yet
- Sub Station DesignDocument43 pagesSub Station DesignZIPDASH86% (7)
- General Pipe Rack Configuration 0 DivDocument2 pagesGeneral Pipe Rack Configuration 0 DivhumshkhNo ratings yet
- 2-Plant Layout - Pipeway DesignDocument25 pages2-Plant Layout - Pipeway DesignLaxmikant Sawleshwarkar100% (1)
- Underground Piping (U/G) : Cooling Tower PipelineDocument9 pagesUnderground Piping (U/G) : Cooling Tower PipelineMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects: Ganesan V Assistant Manager-TSD D&H Secheron Electrodes PVT - LTDDocument49 pagesWelding Defects: Ganesan V Assistant Manager-TSD D&H Secheron Electrodes PVT - LTDPrakash RajNo ratings yet
- A Numerical Model For The Simulation of External Gear Pumps: P P T VDocument6 pagesA Numerical Model For The Simulation of External Gear Pumps: P P T Vbullshit sitesNo ratings yet
- ServomotorDocument25 pagesServomotorAbhirajNo ratings yet
- Etextbook 978 0321939968 Natural Hazards Earths Processes As Hazards Disasters and CatastrophesDocument61 pagesEtextbook 978 0321939968 Natural Hazards Earths Processes As Hazards Disasters and Catastrophesbenjamin.vega423100% (55)
- Diffraction Notes - Question AnswerDocument13 pagesDiffraction Notes - Question AnswerSuchetaNo ratings yet
- Pipe Work Guidelines Expansion BellowsDocument15 pagesPipe Work Guidelines Expansion BellowsAnkith100% (1)
- Fan AcousticsDocument99 pagesFan Acousticsjacob chexNo ratings yet
- Coastal Planning Management Lesson1-OverviewDocument57 pagesCoastal Planning Management Lesson1-OverviewshirleyNo ratings yet
- Analysis Laporan PKLDocument10 pagesAnalysis Laporan PKLAnonymous qWGYhGtiKbNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MSDocument7 pagesChemistry MSaneeshNo ratings yet
- Flo 17SDocument8 pagesFlo 17SVictor GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Phys2 Ch2 Templaw0 NewDocument52 pagesPhys2 Ch2 Templaw0 NewQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- HVAC NotesDocument4 pagesHVAC NotesameerNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Temperature Experiments - MDocument11 pagesLab Report - Temperature Experiments - MAliyu AbdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and Mettlurgy QBDocument12 pagesEngineering Materials and Mettlurgy QBSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Summer Practice Test 2 AnswersDocument24 pagesSummer Practice Test 2 AnswersLisa Dea SaryNo ratings yet
- Optik: Francis Segovia-Chaves, Herbert Vinck-PosadaDocument6 pagesOptik: Francis Segovia-Chaves, Herbert Vinck-PosadaAnonymous Ov7mv0AlVNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 3 (Explanation Text)Document4 pagesEXERCISE 3 (Explanation Text)Nur Hidayah HarahapNo ratings yet
- Watershed WebquestDocument5 pagesWatershed Webquestapi-264590160No ratings yet
- Lab Report 5Document5 pagesLab Report 5mamoona noreenNo ratings yet
- Chemicals Zetag DATA LDP Zetag 7878 FS 40 - 0410Document2 pagesChemicals Zetag DATA LDP Zetag 7878 FS 40 - 0410PromagEnviro.comNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2: Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawDocument7 pagesGeneral Physics 2: Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawMarlon TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Registro C22-S3-PPDocument13 pagesRegistro C22-S3-PPAndres ViasusNo ratings yet
- Application of Nanotechnology in Civil EngineeringDocument2 pagesApplication of Nanotechnology in Civil EngineeringChetan MunnaNo ratings yet
- Lattice Energy CIE Chemistry A2 Chemical EnergeticsDocument2 pagesLattice Energy CIE Chemistry A2 Chemical EnergeticsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Crankshaft Balance: Practical ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesCrankshaft Balance: Practical ConsiderationsTarek MohamedNo ratings yet
- Iit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1Document48 pagesIit - JEE Syllabus: RSM79 PH I AS CH 1MD IMRAN100% (1)
- Band-Selective Holstein Polaron in Luttinger Liquid Material A Moo (A K, RB)Document7 pagesBand-Selective Holstein Polaron in Luttinger Liquid Material A Moo (A K, RB)Scribd ScribdNo ratings yet
- KaplanDocument43 pagesKaplanKamran AliNo ratings yet