Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Expiration / Exhalation:: Inspiration / Inhalation
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Expiration / Exhalation:: Inspiration / Inhalation
Uploaded by
Danial AsyraafOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Expiration / Exhalation:: Inspiration / Inhalation
Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Expiration / Exhalation:: Inspiration / Inhalation
Uploaded by
Danial AsyraafCopyright:
Available Formats
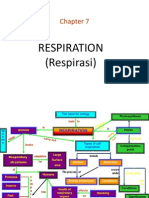
CHAPTER 7-RESPIRATION (FORM 4)
www.sureshkumarbio.wordpress.com
Main substrate needed
Surface
Protozoa
membrane
Gills Fishes
RESPIRATION
Lungs Humans
Tracheal system Insects
Lungs, skin, Amphibians
Respiratory
Structures
Of Animals
1.External:
-a mechanical process
-also known as breathing
-maintains a continuous
exchange of CO2 and O2.
Divided into
2. Internal:
-also called cellular respiration.
-a biochemical process.
-energy released from ATP.
Divided into
2. Aerobic respiration:
-requires O2.
-breakdown of glucose is complete.
-large amount of energy .
-energy is used toform ATP.
-occur in mitochondria.
-CO2 released as waste products.
1.Anaerobic respiration:
- require O2.
-breakdown of glucose is not
complete.
-less amount of energy.
-occur in cytoplasm.
-by products are:
i)lactic acid in animals.
ii)ethanol in yeast&plants.
glucose
Divided into
Inspiration / Inhalation:
-O2 taken in through
mouth / nostrils
(b) yeast / plants:
-glucose is converted into ethanol
+ energy + CO2.
process is also called
fermentation.
-ethanol is converted back to CO2
and energy when O2 is present.
Occur in
Expiration / Exhalation:
-CO2 released through
mouth / nostrils
(a) Human muscle:
-happens during vigorous exercise.
-lactic acid builds up in muscle
causes muscle fatigue.
-after exercise, deep and fast breathing
occurs
to break down lactic acid.(in muscle
and liver)
-amount of O2 needed for the
breakdown is called Oxygen debt.
-lactic acid is broken down to form CO2
and energy.
-energy from this process is less.
You might also like
- Apologia Biology Class Module 6 NotesDocument4 pagesApologia Biology Class Module 6 Noteschickfilamom100% (2)
- Smart Module 1 SPM 1119Document131 pagesSmart Module 1 SPM 1119fattahjamal100% (25)
- Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationDocument1 pageChapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationXuan Deng FamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / ExhalationDocument1 pageChapter 7-Respiration (Form 4) : Inspiration / Inhalation: Expiration / Exhalationmentos999No ratings yet
- II. Aerobic RespirationDocument4 pagesII. Aerobic RespirationJenness VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Module p3 BiologyDocument16 pagesModule p3 BiologyRaj GobalNo ratings yet
- Living Organisms Require Energy: The Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument38 pagesLiving Organisms Require Energy: The Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionWen Shan ChuaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Essay QuestionsDocument4 pagesCellular Respiration Essay QuestionsLaila Abdul100% (1)
- Biomas Power PlantDocument19 pagesBiomas Power PlantPrabir Kumar PatiNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration IB BIoDocument27 pages2.8 Cell Respiration IB BIoPerson Anonymous100% (1)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Faida Hamid87% (23)
- Respiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4Document90 pagesRespiration Chapter 7 Biology Form 4edain84No ratings yet
- Module 3 Gas Exchange and Transport CirculationDocument22 pagesModule 3 Gas Exchange and Transport Circulationwillowpill02No ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationDocument22 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationChew Han Hoong0% (2)
- 4 4 CR ReinforcementDocument2 pages4 4 CR Reinforcementapi-242765774No ratings yet
- Biology Topic One Maintaining A BalanceDocument22 pagesBiology Topic One Maintaining A BalanceHolly GlennNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATION Notes 2ADocument9 pagesRESPIRATION Notes 2AGeorginah NjambiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map 2013-2014Document18 pagesCurriculum Map 2013-2014api-233653042No ratings yet
- SPM Bio F4 C7 (Incomplete)Document2 pagesSPM Bio F4 C7 (Incomplete)Wenan Chooi Wen HanNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- A Set of Things So Related As To Form A Whole: Matter and EnergyDocument2 pagesA Set of Things So Related As To Form A Whole: Matter and EnergyMaria MarieNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lecture NotesDocument108 pagesCell Biology Lecture Notesjnsengupta100% (1)
- Today's Objective: SOL 3.dDocument11 pagesToday's Objective: SOL 3.dzameershahNo ratings yet
- NegOr Q4 GenBio2 SLKWeek2 v2Document22 pagesNegOr Q4 GenBio2 SLKWeek2 v2albazeervaNo ratings yet
- 10th Biology New Book 2021-22 Latest2Document86 pages10th Biology New Book 2021-22 Latest2kaziamna62No ratings yet
- General Biology II q4 Week 2Document26 pagesGeneral Biology II q4 Week 2Educhamp Learning CenterNo ratings yet
- Production of Oxygen Using Pressure Swing Adsorption TechnologyDocument10 pagesProduction of Oxygen Using Pressure Swing Adsorption TechnologyGAGAN SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document15 pagesQ2 Module 5margudo.tchiNo ratings yet
- Apr 2010PYPDocument19 pagesApr 2010PYPDarsyaNo ratings yet
- Biology End of Course Exam 2012 - Study Guide and Review Biological Concept Resources and QuestionsDocument12 pagesBiology End of Course Exam 2012 - Study Guide and Review Biological Concept Resources and Questionsrpatel1989No ratings yet
- Life Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFDocument4 pagesLife Processes - Respiration QB - 2019 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Cod Removal of Slaughter Wastewater by Expanded Granular Sludge Bed (Egsb) With Polyvinyl Alcohol (Pva) As A Biomass CarrierDocument6 pagesCod Removal of Slaughter Wastewater by Expanded Granular Sludge Bed (Egsb) With Polyvinyl Alcohol (Pva) As A Biomass CarrierChinh Nguyen DangNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasDocument7 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasParasNo ratings yet
- Development of A Simulation Model For The Hybrid Solar Dryers As Alternative Sustainable Drying System For Herbal and Medicinal PlantsDocument21 pagesDevelopment of A Simulation Model For The Hybrid Solar Dryers As Alternative Sustainable Drying System For Herbal and Medicinal PlantsAdel BahnasawyNo ratings yet
- Ethanol From Cellulose: A General ReviewDocument5 pagesEthanol From Cellulose: A General ReviewRahmat YousdarNo ratings yet
- General Biology II Q4 Week 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology II Q4 Week 2Rose MoselaNo ratings yet
- Cyclonic Separation (REVISED)Document8 pagesCyclonic Separation (REVISED)maryroseallinegNo ratings yet
- SNAB Bio Unit 5 Summary Power PointDocument71 pagesSNAB Bio Unit 5 Summary Power Pointbfdboii100% (2)
- Group Challenge 3Document7 pagesGroup Challenge 3Acel PeñalozaNo ratings yet
- 2.8 - Cell RespirationDocument27 pages2.8 - Cell Respirationmarisa colegateNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 PDFDocument25 pagesChapter9 PDFsgw67No ratings yet
- IB Biology Study GuideDocument38 pagesIB Biology Study GuideDesny SaldateNo ratings yet
- General Biology II Q4 Week 2Document19 pagesGeneral Biology II Q4 Week 2Alex BlancoNo ratings yet
- Winogradsky Column ProjectDocument3 pagesWinogradsky Column Projectampaynz1No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument68 pagesRespirationNorhidayah IsmailNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration in Animals.Document4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals.studyklieNo ratings yet
- Resume HartDocument2 pagesResume Hartapi-255441847No ratings yet
- Biology STPM Trial 1Document3 pagesBiology STPM Trial 1Shah RinNo ratings yet
- Biogeochemical Cycle Notes - Science - Catherine DoyleDocument3 pagesBiogeochemical Cycle Notes - Science - Catherine DoyleCatherine DoyleNo ratings yet
- Respiration Labco 5Document5 pagesRespiration Labco 5smithsashay74No ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document10 pagesLecture 3Marvin JeaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document138 pagesChapter 7Bëar MëNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Document24 pagesBiology Form 4 Notes Chapter 7Nitya Dewi100% (2)
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaeDocument29 pagesAerobic Cellular Respiration: Pea Plants Zophobus Morio LarvaezulaikhaabdrahmanNo ratings yet
- Struktur Sistem RespirasiDocument2 pagesStruktur Sistem RespirasisahatmanurungNo ratings yet
- Hal 00895375Document12 pagesHal 00895375muyodi yahayaNo ratings yet
- Bio-Batteries: Energy Storage Based On Flexible Nanocomposite PaperDocument1 pageBio-Batteries: Energy Storage Based On Flexible Nanocomposite Paperdivya1587No ratings yet
- Bio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Document17 pagesBio 5 - Cellular Respiration 2022-2023Gillion lordNo ratings yet
- Solar-Hydrogen Energy Systems: An Authoritative Review of Water-Splitting Systems by Solar Beam and Solar Heat: Hydrogen Production, Storage and UtilisationFrom EverandSolar-Hydrogen Energy Systems: An Authoritative Review of Water-Splitting Systems by Solar Beam and Solar Heat: Hydrogen Production, Storage and UtilisationNo ratings yet
- Provision Food Support Life: Nutrition Is The of Materials, Usually in Form Of, To in OrganismsDocument38 pagesProvision Food Support Life: Nutrition Is The of Materials, Usually in Form Of, To in OrganismsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Biologyform5 Chapter6 130716042847 Phpapp01Document2 pagesBiologyform5 Chapter6 130716042847 Phpapp01Sharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- ActivityseriesSolubilitiesPolyatomic IonsReference SheetDocument1 pageActivityseriesSolubilitiesPolyatomic IonsReference SheetSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Itchemf4topicaltest2bl 121017213209 Phpapp02Document8 pagesItchemf4topicaltest2bl 121017213209 Phpapp02Sharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- Bab 3Document5 pagesBab 3Sharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 - Plant NutritionDocument6 pagesBiology Form 4 - Plant NutritionSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- 01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsDocument21 pages01 Interaction Between Biotic ComponentsSharmini Rajagopal100% (1)
- Bio f4 Chap 5 Cell DivisionDocument30 pagesBio f4 Chap 5 Cell DivisionGula MelakaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument25 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- EndocrineDocument10 pagesEndocrineSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument25 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDocument25 pagesChemistry Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Short NotesDocument31 pagesChemistry Short NotesSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet
- RCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl GroupsDocument6 pagesRCOOR Where R and R Represented The Same or Different Alkyl GroupsSharmini RajagopalNo ratings yet