Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aerobic Respiration in Animals.
Uploaded by
studyklie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAerobic Respiration in Animals
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals.
Uploaded by
studyklieAerobic Respiration in Animals
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Aerobic Respiration in Animals
What is Aerobic respiration
Aerobic respiration is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the
presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is
common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, water and carbon
dioxide are produced as end products.
Aerobic respiration is a biological process in which food glucose is converted
into energy in the presence of oxygen.
The 2900 kJ energy is released during the process of breaking the glucose
molecule and in turn, this energy is used to produce ATP- Adenosine
Triphosphate molecules which are used by the system for various purposes.
Aerobic respiration process takes place in all multicellular organisms including
animals, plants and other living organisms. During the respiration process in
plants, the oxygen gas enters the plant cells through the stomata, which is found
in the epidermis of leaves and stem of a plant with the help of the
photosynthesis process, all green plants synthesize their food and thus releases
energy.
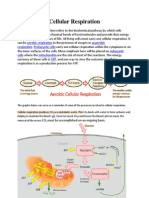
Aerobic respiration Diagram
The aerobic respiration diagram given below represents the entire process of
aerobic respiration. The different cycles involved in aerobic respiration such as
glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain are clearly mentioned in the
diagram
Steps of aerobic Respiration
The complete process of aerobic respiration occurs in four different stages.
Glycolysis
The primary step of aerobic respiration is glycolysis and takes place within the
cytosol of the cell. During the glycolysis process, the glucose molecules are split
and separated into two ATP and two NADH molecules which are later used in the
process of aerobic respiration.
Formation of Acetyl Coenzyme A
The second step in aerobic respiration is the formation of acetyl coenzyme A. In
this process, pyruvate is oxidized in the mitochondria and 2-carbon acetyl group is
produced. The newly produced 2-carbon acetyl group binds with coenzyme A,
producing acetyl coenzyme A.
Critical Acid Cycle
The third stage in aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle which is also called the
Krebs cycle. In this stage of Aerobic respiration the oxaloacetate combines with
the acetyl coenzyme A and produces citric acid. The citric acid cycle undergoes a
series of reactions and produces 2 molecules of carbon dioxide, 1 molecule of ATP
and reduced forms of NADH and FADH.
Electron Transport Chain
This is the last step in aerobic respiration. In this phase the large amount of ATP
molecules are produced by transferring the electrons from NADH. A single
molecule of glucose creates a total of 34 ATP molecules.
Key Points on Aerobic Respiration
• Aerobic respiration is the process of utilization of oxygen to breakdown
glucose, amino acids, fatty acids to produce ATP.
• The pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA in the mitochondrial matrix.
• The Krebs cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule.
The protein complexes are arranged on the inner mitochondrial matrix so that
the electrons pass from one reacting molecule to the other. This is known as
the electron transport chain.
• ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
Where does aerobic and anaerobic respiration take place?
Aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondrial matrix of the cell. On the
contrary, anaerobic respiration occurs in the fluid portion of the cytoplasm.
What is the importance of aerobic respiration?
Aerobic respiration provides energy to the living organisms to perform all the
essential functions of life. That is why aerobic respiration is important.
What are the different types of aerobes?
The different types of aerobes include:
• Obligate aerobes that strictly need oxygen to grow.
Facultative aerobes can grow in the presence as well as the absence of
● Microaerophiles grow in the presence of oxygen but cannot survive in
the atmospheric concentrations of oxygen.
Advantage of aerobic respiration
The main advantages of the aerobic respiration are;
1. Large amount of ATP production takes place during aerobic respiration.
2. The byproducts of aerobic respiration are not harmful, since they are carbon
dioxide and water.
3. During aerobic respiration; the respiratory substrate is completely oxidized.
4. Aerobic respiration involves the process of exchange of gasses between the
living organisms and the environment.
You might also like
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument6 pagesRespiration in Plants-NotesAnirudh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationChristian BaleNo ratings yet
- Grade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialDocument19 pagesGrade 11: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialJake LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument28 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationGlena MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 Energy of LifeDocument29 pagesLec 9 Energy of LifeFahim AbidNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Foods Experimental Perspectives 8th Edition Mcwilliams Test BankDocument23 pagesFoods Experimental Perspectives 8th Edition Mcwilliams Test BankSeanBishoppkyc100% (10)
- MCQs Veterinary ToxicologyDocument11 pagesMCQs Veterinary ToxicologySunil100% (15)
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration ExplainedDocument13 pagesAerobic Cellular Respiration Explainedmanojtbgri5793No ratings yet
- Respiration Is of Two TypesDocument3 pagesRespiration Is of Two TypesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Summary of Aerob RespirationDocument3 pagesSummary of Aerob RespirationHenry AndersonNo ratings yet
- Jinnah University Women Aerobic AnaerobicDocument13 pagesJinnah University Women Aerobic AnaerobicDEVIL GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Downloadfile 15Document23 pagesDownloadfile 15Loren TejonesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document14 pagesChapter 14Yash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4Mohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14 Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesLesson 14 Cellular RespirationGinalyn QuimsonNo ratings yet
- BioDocument18 pagesBiomarcneil773No ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 14 (PDF)Document12 pagesRespiration in Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 14 (PDF)A. celestianNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument2 pagesRESPIRATIONHaidar RifkiNo ratings yet
- GB 1 NotesDocument10 pagesGB 1 Notesrenlie jane pedronanNo ratings yet
- Plant Respiration ExplainedDocument6 pagesPlant Respiration ExplainedAadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class-11 Biology Revision - Respiration in PlantsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class-11 Biology Revision - Respiration in PlantsSHRAVYA K REDDYNo ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Document5 pagesReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Measure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerDocument17 pagesMeasure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerTootsie100% (12)
- 11 Biology Notes ch14 Respiration in PlantsDocument8 pages11 Biology Notes ch14 Respiration in Plantssanjay kannaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonDocument6 pagesLesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonMarielle RamosNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in Elementary GradesDocument2 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary GradesJenniferChantengcoCatacutan50% (2)
- Biology 2nd QRTR Exam - OutlineDocument5 pagesBiology 2nd QRTR Exam - OutlineLouie Joice MartinezNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 3Document19 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 3Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Q2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesQ2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationRaph tsuNo ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument29 pagesAerobic Respirationleeyaonde123No ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesAerobic Cellular RespirationlutherlynNo ratings yet
- CIE Biology A-level NotesDocument5 pagesCIE Biology A-level NotesbeiyuNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument33 pagesCellular RespirationAndres MarotoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Metabolism ExplainedDocument14 pagesCellular Metabolism ExplainedAndre NesbethNo ratings yet
- 3 7 Cell RespirationDocument3 pages3 7 Cell Respirationapi-296446683No ratings yet
- Slide 1Document1 pageSlide 1NickTheTurtleNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 1Document21 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic Respiration 1LP May JaymeNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration in PlantsDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration in PlantsMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1Document50 pagesQuarter 2 Week 3 Lesson 2 Week 4 Lesson 1champimiloNo ratings yet
- biologydictionary.net-Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument6 pagesbiologydictionary.net-Cellular Respiration Definitionsumeshp664No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - The Energy-Producing Process in Living CellsDocument21 pagesCellular Respiration - The Energy-Producing Process in Living CellsAbirami SankarNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants class 11 Notes Biology summaryDocument5 pagesRespiration in Plants class 11 Notes Biology summaryMANDAL VIKRAMNo ratings yet
- CS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsDocument80 pagesCS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsJanrick CabuñasNo ratings yet
- Las Q4 WK3.1Document8 pagesLas Q4 WK3.1Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismDocument12 pagesRespiration in OrganismopsharpedgeNo ratings yet
- Inbound 9168743087088869744Document9 pagesInbound 9168743087088869744MarkNo ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides & Aryl Halides: (Subjective Problems) (Objective Problems)Document68 pagesAlkyl Halides & Aryl Halides: (Subjective Problems) (Objective Problems)Debayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication NotesDocument11 pagesDna Replication NotesJanine San LuisNo ratings yet
- Melting Point Determination (Final)Document3 pagesMelting Point Determination (Final)2022473608No ratings yet
- COSMETICS - Bleaching AgentsDocument3 pagesCOSMETICS - Bleaching AgentsBENCYNo ratings yet
- Fourth Unit-EditedDocument5 pagesFourth Unit-EditedS. C.No ratings yet
- Experimental Studies On The Contribution of Solar Energy As A Source For Heating Biogas Digestion UnitsDocument16 pagesExperimental Studies On The Contribution of Solar Energy As A Source For Heating Biogas Digestion UnitsBadr OUHAMMOUNo ratings yet
- LAMP Protocols For Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Genomic RNA - Odb - 25M2020Document8 pagesLAMP Protocols For Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Genomic RNA - Odb - 25M2020Daniel EidNo ratings yet
- Soil Genesis, Composition & Dev. - RJ GavilenoDocument37 pagesSoil Genesis, Composition & Dev. - RJ GavilenorjbgavilenoNo ratings yet
- Ion-Exchange Membranes: Preparative Methods For Electrodialysis and Fuel Cell ApplicationsDocument23 pagesIon-Exchange Membranes: Preparative Methods For Electrodialysis and Fuel Cell ApplicationsJose Antonio Siñani VilteNo ratings yet
- Effective Extraction of Quinine and Gramine From Water by Hydrophobic Ionic Liquids: The Role of AnionDocument8 pagesEffective Extraction of Quinine and Gramine From Water by Hydrophobic Ionic Liquids: The Role of AnionCarlos CordobaNo ratings yet
- Valorization of Spent Brewers Yeast For The ProduDocument18 pagesValorization of Spent Brewers Yeast For The ProduHarshad Vinay SavantNo ratings yet
- FICHA TECNICA HIDROXIPROPILMENTIL CELULOSA Kimicell KMP40000SDocument1 pageFICHA TECNICA HIDROXIPROPILMENTIL CELULOSA Kimicell KMP40000SCarlos SiuNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesDocument2 pagesExperiment 9 - Hydrolysis of CarbohydratesJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- 3 Transcription-From - DNA - To - RNADocument7 pages3 Transcription-From - DNA - To - RNACHIARA ANDREINA ALFARO PURISACANo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Chemical ReactionDocument13 pagesGrade 10 Chemical ReactionSheendy Claire BeljotNo ratings yet
- Muddy ShoreDocument16 pagesMuddy ShorePratyush NahakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 EM MCQ Unit Test-ANSWERSDocument2 pagesChapter 2 EM MCQ Unit Test-ANSWERSSudhan RNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id3439618Document10 pagesSSRN Id3439618firtaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Treatment Technologies For E-WasteDocument49 pagesAdvanced Treatment Technologies For E-WasteJayvin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- DPP 1 Optical Isomerism VKP Sir-3706Document3 pagesDPP 1 Optical Isomerism VKP Sir-3706Sanjay Mani TripathiNo ratings yet
- Remodeling in Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) Design and Parameters For The Sustained Production of ElectricityDocument14 pagesRemodeling in Microbial Fuel Cell (MFC) Design and Parameters For The Sustained Production of ElectricityMamta AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Aha Extract 44 Glycerin - TDSDocument2 pagesAha Extract 44 Glycerin - TDSlakshmi0vinayNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde & KetoneDocument40 pagesAldehyde & KetoneSaqib HussainNo ratings yet
- Product Range: Plastics For Every Day LifeDocument56 pagesProduct Range: Plastics For Every Day LifeHabteyes AbateNo ratings yet
- Question Bio P1Document14 pagesQuestion Bio P1Rohana PaimanNo ratings yet
- Zymogen, Isozymes, Abzymes, RibozymesDocument9 pagesZymogen, Isozymes, Abzymes, Ribozymesr6jxkkg7nqNo ratings yet
- Nhung Van de Ly Thuyet THPT Thuong GapDocument126 pagesNhung Van de Ly Thuyet THPT Thuong Gaptuấn cường trần nguyễnNo ratings yet
- Evaluación de Shampoo ComercialesDocument9 pagesEvaluación de Shampoo ComercialesEladio MendozaNo ratings yet