Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration Is of Two Types
Uploaded by
Kyng GamariOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration Is of Two Types
Uploaded by
Kyng GamariCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration is of two types, aerobic respiration, and anaerobic respiration.
Aerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of
oxygen gas to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants
and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are
produced as end products.
Anaerobic Respiration: It is a process which takes place in the absence of oxygen gas. In this
process, the energy is obtained by the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen. One of
the best examples of anaerobic respiration is the process of fermentation in yeast.
Aerobic Respiration Definition
“Aerobic respiration is the process of producing cellular energy in the presence of
oxygen.”
What is Aerobic Respiration?
Aerobic respiration is a biological process in which food glucose is converted into energy in the
presence of oxygen. The chemical equation of aerobic respiration is as given below-
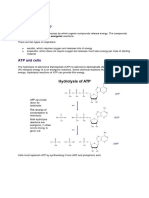
Glucose (C6H12O6) + Oxygen 6(O2) → Carbon-dioxide 6(CO2) + Water 6 (H2O) + Energy (ATP)
According to the above-given chemical equation, energy is released by splitting the glucose
molecules with the help of oxygen gas. At the end of the chemical reaction, energy, water
molecules, and carbon dioxide gas are released as the by-products or end products of the
reactions.
The 2900 kJ of energy is released during the process of breaking the glucose molecule and in
turn, this energy is used to produce ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate molecules which are used by
the system for various purposes.
Aerobic respiration process takes place in all multicellular organisms including animals, plants
and other living organisms.
During the respiration process in plants, the oxygen gas enters the plant cells through the
stomata, which is found in the epidermis of leaves and stem of a plant. With the help of the
photosynthesis process, all green plants synthesize their food and thus releases energy.
Also refer: Respiration
The below-given chemical equation describes the complete process of photosynthesis or the
aerobic respiration in plants.
Carbon-dioxide 6(CO2) + Water 6 (H2O) → Glucose (C6H12O6) + Oxygen 6(O2)
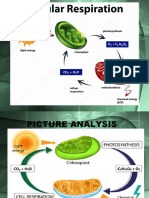
Aerobic Respiration Diagram
The aerobic respiration diagram given below represents the entire process of aerobic respiration.
The different cycles involved in aerobic respiration such as glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron
transport chain are clearly mentioned in the diagram.
Steps of Aerobic Respiration
The complete process of aerobic respiration occurs in four different stages:
Glycolysis
It is the primary step of aerobic respiration is glycolysis and takes place within the cytosol of the
cell. During the glycolysis process, the glucose molecules are splitting and separated into two
ATP and two NADH molecules, which are later used in the process of aerobic respiration.
Formation of Acetyl Coenzyme A
The second step in aerobic respiration is the formation of acetyl coenzyme A. In this process,
pyruvate is oxidized in the mitochondria and 2-carbon acetyl group is produced. The newly
produced 2-carbon acetyl group binds with coenzyme A, producing acetyl coenzyme A.
Citric Acid Cycle
The third step in aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle, which is also called the Krebs cycle. In
this stage of Aerobic respiration, the oxaloacetate combines with the acetyl-coenzyme A and
produces citric acid. The citric acid cycle undergoes a series of reactions and produces 2
molecules of carbon dioxide, 1 molecule of ATP, and reduced forms of NADH and FADH.
Electron Transport Chain
This is the last step in aerobic respiration. In this phase, the large amounts of ATP molecules are
produced by transferring the electrons from NADH and FADH. A single molecule of glucose
creates a total of 34 ATP molecules.
Also refer: Respiratory Quotient
Key Points on Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration is the process of utilisation of oxygen to breakdown glucose, amino
acids, fatty acids to produce ATP.
The pyruvate is then converted into acetyl CoA in the mitochondrial matrix.
The Kreb’s cycle occurs twice per glucose molecule.
The protein complexes are arranged on the inner mitochondrial matrix so that the
electrons pass from one reacting molecule to the other. This is known as the electron
transport chain.
ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
What is anaerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration transfers energy from glucose to cells.
It occurs when oxygen is not present.
It transfers large amounts of energy quickly.
WHEN DOES ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION OCCUR?
Imagine sprinting 100 metres. You need to transfer energy from glucose to your muscles very
quickly. However your body cannot get oxygen to its muscles quickly enough for aerobic respiration
to occur. This is why anaerobic respiration happens instead.
A model of glucose turning into lactic acid.
HOW DOES ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION WORK?
In anaerobic respiration, glucose breaks down without oxygen. The chemical reaction transfers
energy from glucose to the cell. Anaerobic respiration produces lactic acid, rather than carbon
dioxide and water. Unfortunately this can lead to painful muscle cramps.
You might also like
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration in Animals.Document4 pagesAerobic Respiration in Animals.studyklieNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular Respiration ExplainedDocument13 pagesAerobic Cellular Respiration Explainedmanojtbgri5793No ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- Summary of Aerob RespirationDocument3 pagesSummary of Aerob RespirationHenry AndersonNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesAerobic Cellular RespirationlutherlynNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Breathing ExplainedDocument5 pagesMechanics of Breathing ExplainedMark Lyndon M OrogoNo ratings yet
- Jinnah University Women Aerobic AnaerobicDocument13 pagesJinnah University Women Aerobic AnaerobicDEVIL GAMINGNo ratings yet
- CS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsDocument80 pagesCS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsJanrick CabuñasNo ratings yet
- Lab.3 PhysicsDocument4 pagesLab.3 Physicsksoo5118No ratings yet
- Biology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Document3 pagesBiology Lab #12 Discussion (HOW BREATHING RATE CHANGES WITH EXERCISE)Joy-Ann NuptialNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- BioDocument18 pagesBiomarcneil773No ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document10 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Yana LouisseNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Cellular Metabolism ExplainedDocument14 pagesCellular Metabolism ExplainedAndre NesbethNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- Lec 9 Energy of LifeDocument29 pagesLec 9 Energy of LifeFahim AbidNo ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- Teaching Science in Elementary GradesDocument2 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary GradesJenniferChantengcoCatacutan50% (2)
- Cell Respiration: ATP from GlucoseDocument11 pagesCell Respiration: ATP from GlucoseNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- The Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Respiratory SystemPiyush RoyNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismDocument12 pagesRespiration in OrganismopsharpedgeNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeashNo ratings yet
- Las Q4 WK3.1Document8 pagesLas Q4 WK3.1Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument36 pagesCalvin CycleJane Marry IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Measure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerDocument17 pagesMeasure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerTootsie100% (12)
- Chapter 14Document14 pagesChapter 14Yash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument2 pagesRESPIRATIONHaidar RifkiNo ratings yet
- Slide 1Document1 pageSlide 1NickTheTurtleNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument13 pages7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionNor Rafidah Che YusofNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonDocument6 pagesLesson 2: The Reactants For Photosynthesis Are Light Energy, Water, CarbonMarielle RamosNo ratings yet
- respiration cycleDocument1 pagerespiration cycleEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NcellularrespirationDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis NcellularrespirationBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- Downloadfile 15Document23 pagesDownloadfile 15Loren TejonesNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesSummary of Cellular RespirationchiomasingsNo ratings yet
- Respiration 2Document23 pagesRespiration 2api-233649346No ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodDocument28 pagesCellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio W3-5Document9 pagesGen Bio W3-5Alyson EscuderoNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic RespirationDocument34 pagesAnaerobic RespirationArmero, Mariah Sophia V.No ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Key ConceptsDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration Key ConceptsHikaru IshiiNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 14 (PDF)Document12 pagesRespiration in Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 14 (PDF)A. celestianNo ratings yet
- Respiration CHP 7 Biology Form 4Document24 pagesRespiration CHP 7 Biology Form 4Banu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument29 pagesAerobic Respirationleeyaonde123No ratings yet
- The Energy of LifeDocument22 pagesThe Energy of LifeAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- 4Document2 pages4Mohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- 3 7 Cell RespirationDocument3 pages3 7 Cell Respirationapi-296446683No ratings yet
- Gen Bio. 2ND Quarter RespirationDocument3 pagesGen Bio. 2ND Quarter RespirationChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- Cellular respiration stagesDocument7 pagesCellular respiration stagesdickbeater73No ratings yet
- CRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualDocument6 pagesCRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualVanesha AnesNo ratings yet
- Human Alimentary Canal FunctionsDocument3 pagesHuman Alimentary Canal FunctionsKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Cells 4THDocument70 pagesCells 4THKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function PPT 4LRDocument21 pagesCell Structure and Function PPT 4LRKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument2 pagesAnimal and Plant CellKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- In The Poems An African Thunderstorm by Olive Senior and Bird Shooting Season by David Rubadiri The Theme of Nature Is Seen Being Protrayed Throughout The Two Poems Using Literary DevicesDocument1 pageIn The Poems An African Thunderstorm by Olive Senior and Bird Shooting Season by David Rubadiri The Theme of Nature Is Seen Being Protrayed Throughout The Two Poems Using Literary DevicesKyng GamariNo ratings yet
- Gujarat - University PAPERS 2020-2022Document36 pagesGujarat - University PAPERS 2020-2022Shlok RathodNo ratings yet
- Wound HealingDocument44 pagesWound HealingSorin Niky MocanuNo ratings yet
- Physioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsDocument5 pagesPhysioex Lab Report: Pre-Lab Quiz ResultsJoashan Vac100% (2)
- Morphological and anatomical characteristics of seedling plant leaves in different light intensitiesDocument10 pagesMorphological and anatomical characteristics of seedling plant leaves in different light intensitiesAlvie SyahriNo ratings yet
- June 2018 QP - Unit 1 (H) WJEC Biology GCSEDocument28 pagesJune 2018 QP - Unit 1 (H) WJEC Biology GCSEAsni Tunjung ArantikiNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells Practice Exam Questions HigherDocument3 pagesEukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells Practice Exam Questions HigherboneyNo ratings yet
- B TimlogDocument2 pagesB TimlogPriscilla Rosalyna MaranathaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Genetics and ApplicationsDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Genetics and ApplicationsAVINASH VARMANo ratings yet
- Anaphy TransesDocument21 pagesAnaphy Transesfaith A.No ratings yet
- Ara Marie S. Derecho BIO 102 FSH-B Chapter ReviewsDocument24 pagesAra Marie S. Derecho BIO 102 FSH-B Chapter ReviewsLiange FerrerNo ratings yet
- Principles of Microbial BiotechnologyDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Microbial BiotechnologyPS SuryaNo ratings yet
- What Is BiologyDocument3 pagesWhat Is Biologymichellouise17No ratings yet
- The Thorax and Chest WallDocument15 pagesThe Thorax and Chest WallVIRESH VNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDocument15 pagesPhysiology of Respiration: Course Code: BBS01T1008 Course Name: Biology For EngineersDivya TripathyNo ratings yet
- Sectra Education Portal - EN - Medical SimulatorDocument4 pagesSectra Education Portal - EN - Medical SimulatorPol Enrique Trigoso EchaizNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 MCQsDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 MCQsHASSET SHIFERAWNo ratings yet
- 30 Investigations IA IdeasDocument7 pages30 Investigations IA IdeasYasmine Ouled Kaddour El HallaouiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 BloodDocument50 pagesLesson 3 BloodJulius Memeg PanayoNo ratings yet
- CELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE - LysosomesDocument9 pagesCELL-THE UNIT OF LIFE - LysosomesHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4a - Microbial MetabolismDocument29 pagesChapter 4a - Microbial MetabolismNUR BAHIJATUL AKMAL BINTI MOHD ZUL KM-PelajarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 31. Lymph NodesDocument24 pagesLesson 31. Lymph NodesLola PNo ratings yet
- Occular Drug Delivery System - Unit V - NotesDocument17 pagesOccular Drug Delivery System - Unit V - NotesVaishnavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Rotation 4 - DarundayDocument16 pagesRotation 4 - DarundayEzra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Concept of Artava and Artava Chakra An Ayurveda and Modern PerspectiveDocument15 pagesConcept of Artava and Artava Chakra An Ayurveda and Modern Perspectivemanas.horebusiness5No ratings yet
- SCHOOL SUBJECTSDocument15 pagesSCHOOL SUBJECTSAsim KhanNo ratings yet
- Q1 EXAM - Science 9Document3 pagesQ1 EXAM - Science 9Allira Clarion BarazonaNo ratings yet
- Asahina 1983 Domiciliary Cockroach Species in ThailandDocument14 pagesAsahina 1983 Domiciliary Cockroach Species in ThailandDávid RédeiNo ratings yet
- Assay Development Final RevisedDocument38 pagesAssay Development Final RevisedvershaparchaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5Document6 pagesNcert Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 5ppusapatiNo ratings yet
- C. Topic 1 - Types of Tissues (EPITHELIAL TISSUE)Document42 pagesC. Topic 1 - Types of Tissues (EPITHELIAL TISSUE)Rica T. DagosNo ratings yet