Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2.5 Force (Newton 2 Laws) Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Chapter 2.5 Force (Newton 2 Laws) Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Uploaded by
Christopher AuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2.5 Force (Newton 2 Laws) Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Chapter 2.5 Force (Newton 2 Laws) Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Uploaded by
Christopher AuCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2.
5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Chapter 2.5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Chapter 2.5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Chapter 2.5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter 2.5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Force
1.
A force is push or pull exerted on an object.
2.
Force is a vector quantity that has magnitude and direction.
3.
The unit of force is Newton ( or kgms-2).
Unbalanced Force/ Resultant Force
When the forces acting on an object are not balanced, there must be a net force
acting on it. The net force is known as the unbalanced force or the resultant
force.
When a force acts on an object, the effect can change the
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
size,
shape,
stationary state,
speed and
direction of the object.
__________________________________________________________
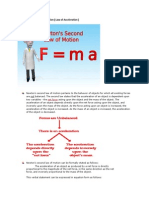
Newton's Second Law
The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the resultant
force acting on the body and is in the same direction.
Implication: When there is resultant force acting on an object, the object will
accelerate (moving faster, moving slower or change direction).
Formula of Force
From Newton's Second Law, we can derived the equation
(IMPORTANT: F Must be the net force)
Chapter 2.5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
1.Example:f=ma
A box of mass 150kg is placed on a horizontal floor with a
smooth surface; find the acceleration of the box when a 300N
force is acting on the box horizontally.
_______________________________________________________________
2. Example: find a, F=ma
A object of mass 50kg is placed on a horizontal floor with a
smooth surface. If the velocity of the object changes from
stationary to 25.0 m/s in 5 seconds when is acted by a force,
find the magnitude of the force that is acting?
Impulsive Force
Example:Impulsive force
A car of mass 1000kg is traveling with a velocity of 25 m/s.
The car hits a street lamp and is stopped in0.05 seconds.
What is the impulsive force acting on the car during the crash?
Chapter 2.5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Chapter 2.5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
Chapter 2.5 Force ( Newton 2nd Laws)
Chapter 2.6 Impulsive Force
You might also like
- 08 - Newtons Laws Practice WorksheetDocument2 pages08 - Newtons Laws Practice WorksheetShiella Mae Baltazar Bulauitan50% (2)
- Newtons 2nd Law NotesDocument23 pagesNewtons 2nd Law NotesJulio Olivos100% (1)
- Laws of MotionDocument24 pagesLaws of MotionAna Marie Renton100% (1)
- Chapter 10-Work Energy and PowerDocument15 pagesChapter 10-Work Energy and PowerLin Xian Xing100% (1)
- Mass and InertiaDocument7 pagesMass and InertiaShafiqah AzuddinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - FBDsDocument24 pagesLecture 5 - FBDsjunedrkaziNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Grade 12 General PhysicsDocument3 pagesModule 4 Grade 12 General PhysicsLaarni Tolete100% (1)
- Newtons 2nd Law Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesNewtons 2nd Law Practice ProblemsJehmmaRosalesCarpisoNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law of Motion WorksheetDocument2 pagesNewtons Law of Motion WorksheetAlyssa Mae DapadapNo ratings yet
- G9 Q4 Melc 21Document5 pagesG9 Q4 Melc 21Klare MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- 2.2 - Forces: Topic 2: MechanicsDocument48 pages2.2 - Forces: Topic 2: MechanicsDaksh LohiaNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws PPTDocument29 pagesNewtons Laws PPTchris estradaNo ratings yet
- CPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 2, Chapter 5Document29 pagesCPO Science Foundations of Physics: Unit 2, Chapter 5farismohNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument29 pagesForce and MotionSalmanNo ratings yet
- Scientific Review of NewtonDocument8 pagesScientific Review of NewtonAnwesh SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document21 pagesChapter 5EyadNo ratings yet
- Newtons 2nd Law CalcsDocument4 pagesNewtons 2nd Law CalcscaitlyntreacyNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion - 1: 5.1. Newtons First LawDocument16 pagesForce and Motion - 1: 5.1. Newtons First Laweka123No ratings yet
- Newton's First Law and Inertial FramesDocument9 pagesNewton's First Law and Inertial FramesPrabawatiUtamiNo ratings yet
- Body ContactDocument22 pagesBody Contactmass1981No ratings yet
- Science Grade9 Q4 LP4Document8 pagesScience Grade9 Q4 LP4Marian GalosoNo ratings yet
- Physics (CETs)Document9 pagesPhysics (CETs)AkiNo ratings yet
- Physics-Law of AccelerationDocument3 pagesPhysics-Law of AccelerationCzarina PotenteNo ratings yet
- Newtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDDocument15 pagesNewtons 1 and 2 Law: ST NDApoorva TalankiNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityDocument26 pagesPhysics Tutorial: Andalas UniversityMiranda Febriani TanjungNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.2 - Forces - StudentDocument48 pagesTopic 2.2 - Forces - Studentyilira4268No ratings yet
- 2ND Law of Motion ReferrenceDocument4 pages2ND Law of Motion ReferrenceROSIEL MANDRIQUENo ratings yet
- Force and Motion - Homework 5Document6 pagesForce and Motion - Homework 5Nithya Lavanya SetlurNo ratings yet
- Study Plan - Brief Activation CE2Document15 pagesStudy Plan - Brief Activation CE2Hebrew TeacherNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Dynamics Pressure 3B 2011Document9 pagesUnit 3 Dynamics Pressure 3B 2011Marshell JonesNo ratings yet
- National Christian Life College Science 8 - Worksheet Newton's Laws of Motion - CDocument3 pagesNational Christian Life College Science 8 - Worksheet Newton's Laws of Motion - CLannayah coNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: "Force, Type of Force and Free Body Diagram For Force"Document9 pagesStrength of Materials: "Force, Type of Force and Free Body Diagram For Force"Lulav BarwaryNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets Science 8-Week 1 and 2Document2 pagesLearning Activity Sheets Science 8-Week 1 and 2Mark Branden Balayo Paranete100% (1)
- Year 10 Physical Sciences Week 3 and 4 AnswersDocument12 pagesYear 10 Physical Sciences Week 3 and 4 AnswersDaniel XuNo ratings yet
- Saman Rizvi - Newton - S Laws WorksheetDocument3 pagesSaman Rizvi - Newton - S Laws Worksheet45375No ratings yet
- Part 2 - CedricsDocument112 pagesPart 2 - CedricsMaria Loresa TumanguilNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Review - Newtons Third Law PDFDocument4 pagesCH 6 Review - Newtons Third Law PDFapi-305977811No ratings yet
- Lecture Week4Document20 pagesLecture Week4Kanade AngelNo ratings yet
- 8science Module 1 Week 1 PDFDocument15 pages8science Module 1 Week 1 PDFAndrew Carmelo A. RubicoNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Effect of Force On Motion NotesDocument8 pages3.2 Effect of Force On Motion NoteskelvinsnancyNo ratings yet
- W2 Three Laws of MotionDocument46 pagesW2 Three Laws of Motionjin.kyron.alonzoNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of Motion ReviewDocument3 pagesNewton Laws of Motion Reviewapi-417027192No ratings yet
- 2nd Law 4Document3 pages2nd Law 4fatpelicanNo ratings yet
- Name: - : ForceDocument10 pagesName: - : ForceGB SoraNo ratings yet
- Physics1 PDFDocument25 pagesPhysics1 PDFClarisse TadeoNo ratings yet
- How Do Bodies MoveDocument28 pagesHow Do Bodies Movedeme2411No ratings yet
- Newtons Second Law and WeightDocument1 pageNewtons Second Law and WeighttasnimNo ratings yet
- NRG Conservation of Energy - Maximize The Mechanical Energy of A Rollercoaster Lab Manual EnglishDocument7 pagesNRG Conservation of Energy - Maximize The Mechanical Energy of A Rollercoaster Lab Manual EnglishDISTOR, JOSH GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Work 2Document18 pagesWork 2elenaNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 9 Chapter 2Document16 pagesPhysics Class 9 Chapter 2om guptaNo ratings yet
- Solution 1:: Class X Chapter 1 - ForceDocument38 pagesSolution 1:: Class X Chapter 1 - ForceVansh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01Document56 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers Chapter 01topwarmachineNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument56 pagesNewton's Lawskoromamoses235No ratings yet
- Article - Newtons 3 Laws - Intro To DynamicsDocument6 pagesArticle - Newtons 3 Laws - Intro To DynamicsRegina Mae Narciso NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Ancy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Document20 pagesAncy C Simon Physical Science Optional Register Number-13971004Mark Jay BongolanNo ratings yet
- Module in Science 8: Self-CheckDocument3 pagesModule in Science 8: Self-CheckEncey Enerva GacasanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title: Laws of Motion: Region I Division of Ilocos SurDocument15 pagesLesson Title: Laws of Motion: Region I Division of Ilocos SurJOHN MAYKALE FARRALESNo ratings yet
- Negative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6From EverandNegative Mass and Negative Refractive Index in Atom Nuclei - Nuclear Wave Equation - Gravitational and Inertial Control: Part 6: Gravitational and Inertial Control, #6No ratings yet
- Pt3 English Special Programme: Date NameDocument4 pagesPt3 English Special Programme: Date NameChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Section D (40 Marks) ) (Time Suggested: 45 Minutes)Document3 pagesSection D (40 Marks) ) (Time Suggested: 45 Minutes)Christopher AuNo ratings yet
- Novel Moby DickDocument1 pageNovel Moby DickChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Diffraction of WavesDocument21 pages1.5 Diffraction of WavesChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Essay IntensiveDocument12 pagesChapter 2 Essay IntensiveChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnet 8.3Document11 pagesElectromagnet 8.3Christopher AuNo ratings yet
- Electromagnet 8.1Document14 pagesElectromagnet 8.1Christopher AuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Light: Normal Reflected Angle Incident AngleDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Light: Normal Reflected Angle Incident AngleChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Voltmeter Reading, E.m.f.: 7.4 Electromotive Force and Internal Resistance Electromotive ForceDocument8 pagesVoltmeter Reading, E.m.f.: 7.4 Electromotive Force and Internal Resistance Electromotive ForceChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- Wave 6.6Document14 pagesWave 6.6Christopher AuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.3 - 1. 4Document22 pagesChapter 1.3 - 1. 4Christopher AuNo ratings yet
- Refraction Is The Bending of A Light Ray at The Boundary of Two Medium As The Light Ray Propagates From A Medium To Another With Difference Optical DensityDocument7 pagesRefraction Is The Bending of A Light Ray at The Boundary of Two Medium As The Light Ray Propagates From A Medium To Another With Difference Optical DensityChristopher AuNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Understanding Total Internal Reflection of Light Critical Angle and Total Internal ReflectionDocument5 pages5.3 Understanding Total Internal Reflection of Light Critical Angle and Total Internal ReflectionChristopher AuNo ratings yet