Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To SDH
Uploaded by
Deepayan Choudhury0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views9 pagesSDH STM1
Original Title
Introduction to SDH
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSDH STM1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views9 pagesIntroduction To SDH
Uploaded by
Deepayan ChoudhurySDH STM1
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Introduction to the Synchronous Digital
Hierarchy (SDH)
The History of Digital Transmission
z 70s - introduction of PCM into Telecom networks
z 32 PCM streams are Synchronously Multiplexed to 2.048
Mbit/s (E1)
z Multiplexing to higher rates via PDH
z 1985 Bellcore proposes SONET
z 1988 SDH standard introduced.
PDH: Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy
z Multiplex levels:
2.048 Mbit/s
8.448 Mbit/s
34.368 Mbit/s
139.264 Mbit/s
z Uses Positive justification to adapt frequency differences
z Overheads: CRC
z Defects: LOS, LOF, AIS
Plesiochronous Multiplexing
z Before SDH transmission networks were based on the
PDH hierarchy.
z Plesiochronous means nearly synchronous.
z 2 Mbit/s service signals are multiplexed to 140 Mbit/s for
transmission over optical fiber or radio.
z Multiplexing of 2 Mbit/s to 140 Mbit/s requires two
intermediate multiplexing stages of 8 Mbit/s and 34 Mbit/s.
z Multiplexing of 2 Mbit/s to 140 Mbit/s requires multiplex
equipment known as 2, 3 and 4 DME.
z Alarm and performance management requires separate
equipment in PDH.
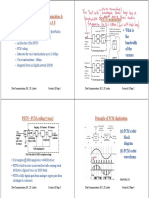
PDH vs. SDH Hierarchy
z PDH transmission rates:
z SDH is designed to unify all transmission rates into a
single Mapping hierarchy
Japan
North
America
Europe
274.176 M bit/s
139.264Mbit/s
397.2 M bit/s
x4
97.728 M bit/s
x3
x6
32.084 M bit/s
44.738 M bit/s
x5
x7
6.312 M bit/s
6.312 Mbit/s
x4
x 4
34.368 Mbit/s
x 4
8.448 M bit/s
x4
x 4
1.544 M bit/s
2.048 M bit/s
PDH Multiplexing
z PDH Multiplexing of 2 Mbit/s to 140 Mbit/s requires 22
PDH multiplexers:
16 x 2DME
4 x 3DME
1 x 4DME
z Also a total of 106 cables required.
2 Mb it/s
8 Mbi t/s
2
D
M
E
3 4 Mb it/s
140 Mbi t/s
3
D
M
E
4
D
M
E
64
2
D
M
E
3
D
M
E
PDH Add/Drop
z If a small number of 2 Mbit/s streams passing through a
site need to be dropped then in PDH this requires large
amount of equipment to multiplex down to 2Mbit/s.
What is SDH?
z The basis of Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH) is
synchronous multiplexing - data from multiple tributary
sources is byte interleaved.
z In SDH the multiplexed channels are in fixed locations
relative to the framing byte.
z Demultiplexing is achieved by gating out the required
bytes from the digital stream.
z This allows a single channel to be dropped from the data
stream without demultiplexing intermediate rates as is
required in PDH.
SDH Rates
z SDH is a transport hierarchy based on multiples of 155.52
Mbit/s
z The basic unit of SDH is STM-1:
STM-1
155.52 Mbit/s
STM-4
622.08 Mbit/s
STM-16
2588.32 Mbit/s
STM-64
9953.28 Mbit/s
z Each rate is an exact multiple of the lower rate therefore
the hierarchy is synchronous.
You might also like
- PDH SDH PresentationDocument67 pagesPDH SDH PresentationDanish Ahmed100% (2)
- Hand Outs of SDH Basics (1) IntroductionDocument32 pagesHand Outs of SDH Basics (1) IntroductionKarthikeyan PandianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: SONET/SDHDocument100 pagesChapter 5: SONET/SDHrahul_mhatre_26No ratings yet
- Payload 4 02Document232 pagesPayload 4 02rahul_mhatre_26No ratings yet
- Introduction To The Synchronous DigitalDocument10 pagesIntroduction To The Synchronous DigitalVarun KothariNo ratings yet
- Broadband Network and Technologies PART1Document100 pagesBroadband Network and Technologies PART1Amin Hajj MohamadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Optical Transmission System (PDH) : Plesiochronous Digital HierarchyDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Optical Transmission System (PDH) : Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchyv_mangaloreNo ratings yet
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GFrom EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SDH IntroductionDocument44 pagesSDH IntroductionQuan HoangNo ratings yet
- Non-Linearities in Passive RFID Systems: Third Harmonic Concept and ApplicationsFrom EverandNon-Linearities in Passive RFID Systems: Third Harmonic Concept and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- PRI DocumentationDocument19 pagesPRI Documentationmathur_mayurNo ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- Chapter ThreeDocument73 pagesChapter ThreeAbenezer BedluNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Introduction To SDHDocument44 pagesIntroduction To SDHCaring PankajNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Digital Hierarchy: Muhammad ZeeshanDocument85 pagesSynchronous Digital Hierarchy: Muhammad ZeeshanRehman AkramNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabFrom EverandSimulation of Digital Communication Systems Using MatlabRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- SDH TechnologyDocument2 pagesSDH Technologymmathur_9No ratings yet
- Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) EvolutionDocument29 pagesPublic Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) EvolutionleangsimNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document11 pagesLecture 1Christop22No ratings yet
- Advances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsFrom EverandAdvances in Analog and RF IC Design for Wireless Communication SystemsGabriele ManganaroRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Transmission FundamentalsDocument93 pagesTransmission FundamentalsMark MatingNo ratings yet
- E CarrierDocument19 pagesE CarrierElmarie RecorbaNo ratings yet
- Digital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemFrom EverandDigital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- What Is Meant by "Plesiochronous" ?Document13 pagesWhat Is Meant by "Plesiochronous" ?ranjeetsumanNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication Systems: PDH, SDH, SONET Multiplexing ProtocolsDocument32 pagesOptical Communication Systems: PDH, SDH, SONET Multiplexing ProtocolsrashiborgohainNo ratings yet
- Transmission Is The Act of Transporting Information From One Location To Another Via A SignalDocument55 pagesTransmission Is The Act of Transporting Information From One Location To Another Via A SignalDeepesh TrivediNo ratings yet
- IT Y3 NewDocument187 pagesIT Y3 NewShreerama Samartha G BhattaNo ratings yet
- Γηαλδξζ 6 Δπηγδηα Μηκροκτμασηκζ Εδτξζ (Mw Link) - ΒαΗκδ ΔννοηδDocument53 pagesΓηαλδξζ 6 Δπηγδηα Μηκροκτμασηκζ Εδτξζ (Mw Link) - ΒαΗκδ ΔννοηδEnder SaliNo ratings yet
- 1.digital Signal HierarchyDocument21 pages1.digital Signal HierarchymumerbuttNo ratings yet
- PSTN-PCM Coding and Data Communication PrinciplesDocument7 pagesPSTN-PCM Coding and Data Communication PrinciplesJai GaizinNo ratings yet
- PDH Vs SDHDocument18 pagesPDH Vs SDHMuhammad KashifNo ratings yet
- SDHDocument91 pagesSDHbrightmsfstarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SDHDocument44 pagesIntroduction To SDHmojtaba_2000No ratings yet
- Concept of PDH MultiplexingDocument27 pagesConcept of PDH MultiplexingRohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of SDH TechnologyDocument467 pagesFundamental of SDH TechnologyNishad Patil100% (1)
- Capacity and ModulasiDocument20 pagesCapacity and ModulasiRizka Nurhasanah0% (1)
- Technical Tutorial: Subject: SDH Date: Prepared byDocument9 pagesTechnical Tutorial: Subject: SDH Date: Prepared bySanjeev Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- SDH Basics OverviewDocument71 pagesSDH Basics OverviewNagdath100% (7)
- Modem Basics: Types, Standards, and Error CorrectionDocument14 pagesModem Basics: Types, Standards, and Error CorrectionKrishnaKumarNo ratings yet
- PDH to SDH: Introduction to Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy and Synchronous Digital HierarchyDocument10 pagesPDH to SDH: Introduction to Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy and Synchronous Digital HierarchyMonikaRaniNo ratings yet
- SDH Network Topologies ExplainedDocument13 pagesSDH Network Topologies ExplainedKuldeep KumarNo ratings yet
- PDH SDH Presentation 1Document67 pagesPDH SDH Presentation 1Mhamad DannawiNo ratings yet
- Data Signaling RateDocument10 pagesData Signaling RatepraveenNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication 1JOHNDocument35 pagesTelecommunication 1JOHNABHILASH C NNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1A-PDHDocument21 pagesLecture 1A-PDHReg NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SDHDocument44 pagesIntroduction To SDHAhmed YunesNo ratings yet
- Digital Network - Lecturer1Document38 pagesDigital Network - Lecturer1Jumanne AllyNo ratings yet
- WDMWDMDocument40 pagesWDMWDMAbrar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Swa Mimo BasicsDocument12 pagesSwa Mimo BasicsabdelNo ratings yet
- Ims RegistrationDocument4 pagesIms Registrationtempgp100% (1)
- Ims RegistrationDocument22 pagesIms RegistrationDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- TM50020 LTE20 Single 20 UEIss 1Document8 pagesTM50020 LTE20 Single 20 UEIss 1Deepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- 860 PDFDocument275 pages860 PDFDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Moshell CommandsDocument76 pagesMoshell CommandsIsac Lima75% (12)
- Introduction To Wireless MIMO - Theory and ApplicationsDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Wireless MIMO - Theory and Applicationskokusz76100% (2)
- P 2telDocument26 pagesP 2telGokul KrishNo ratings yet
- Hetnet/Small Cells: WiseharborDocument8 pagesHetnet/Small Cells: Wiseharborrakeshksaraf-1No ratings yet
- LTE and LTE-Advanced Factsheet: The "Long Term Evolution" of UMTSDocument16 pagesLTE and LTE-Advanced Factsheet: The "Long Term Evolution" of UMTSDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Moshell CommandsDocument76 pagesMoshell CommandsIsac Lima75% (12)
- Carrier Aggregation InfographicDocument1 pageCarrier Aggregation InfographicDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- New OpenDocument SpreadsheetDocument4 pagesNew OpenDocument SpreadsheetDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- 01 Fundamentals of Telecommunications PDFDocument40 pages01 Fundamentals of Telecommunications PDFRonald GreavesNo ratings yet
- TC General and TCIFDocument27 pagesTC General and TCIFDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Transfer ModeDocument10 pagesAsynchronous Transfer ModeDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Household Expenses Calculator V1.0Document3 pagesHousehold Expenses Calculator V1.0Deepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- 3MN 00467 1011 RJZZAi1Document112 pages3MN 00467 1011 RJZZAi1Deepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Lapdm: Asynchronous Transfer ModeDocument4 pagesLapdm: Asynchronous Transfer ModeDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SDHDocument9 pagesIntroduction To SDHDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- IJSCE Paper2Document4 pagesIJSCE Paper2Deepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent Trdu2X40-08 Lte 3Gpp Band 20: Lte FDD Transmit Receive Duplexer Unit - 800 MHZ EddDocument2 pagesAlcatel-Lucent Trdu2X40-08 Lte 3Gpp Band 20: Lte FDD Transmit Receive Duplexer Unit - 800 MHZ EddFouzan SaeedNo ratings yet
- 9YZ 03803 0210 RJZZAi6a TC Commissioning ManualDocument134 pages9YZ 03803 0210 RJZZAi6a TC Commissioning ManualDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- LTE Resource Allocation Types ExplainedDocument5 pagesLTE Resource Allocation Types ExplainedDeepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- S1Document21 pagesS1Deepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Twin TRX PDFDocument8 pagesTwin TRX PDFanon_264233933No ratings yet
- DCT General User Guide GSM v1 17Document90 pagesDCT General User Guide GSM v1 17Deepayan ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- 04 - Ims OverviewDocument20 pages04 - Ims OverviewSilvio CadeteNo ratings yet
- Aug12 SridharDocument44 pagesAug12 SridharFrost IceNo ratings yet