Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Menghitung Roof Ceiling Reflection
Menghitung Roof Ceiling Reflection
Uploaded by
Riski SaraswatiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Menghitung Roof Ceiling Reflection
Menghitung Roof Ceiling Reflection
Uploaded by
Riski SaraswatiCopyright:
Available Formats
LIGHTING DESIGN LIGHTING LEVEL CALCULATIONS
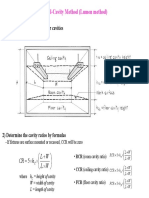
The Zonal Cavity approach to calculate average illumination levels is based on the concept
of dividing any room into three cavities. (1) The space between the ceiling and the luminaires is the ceiling cavity. (2) The space between he luminaires and the work plane is the
room cavity. (3) The space between the work plane and the floor is the floor cavity.
Room Cavity = Volume bounded by walls, luminaire plane and work plane.
hrc = height of room cavity.
Cavity Ratio = Dimensions of Cavity Expressed as Mathematical Relationship;
RCR = Room Cavity Ratio;
CCR = Ceiling Cavity Ratio;
FCR = Floor Cavity Ratio;
Room Cavity Ratio (RCR)
RCR =
5 hrc (L+W)
10 hrc
For Square Rooms RCR =
LxW
2.5 (Cavity Height x Cavity Perimeter)
For Irregular
Shaped Rooms RCR =
Room Surface Reflectances:
pc = Ceiling
pw = Walls
pf = Floor
(L=W)
Area of Cavity Base
Ceiling Cavity Ratio (CCR)
Effective Cavity Reflectances:
The combination of actual reflectances within a given cavity into one reflectance at the
face of the cavity.
pcc = Effective Ceiling Cavity Reflectance
pfc = Effective Floor Cavity Reflectance
5 hcc (L+W)
CCR =
LxW
= RCR
hfc
hrc
Floor Cavity Ratio (FCR)
5 hfc (L+W)
hfc
FCR =
= RCR
LxW
hrc
Coefficient of Utilization: (CU)
Portion of lamp lumens which reach the work plane. Affected by fixture design, room pro- For square rooms or irregular rooms calculate RCR then use the ratio of the cavity heights
portions, and room-surface reflectances.
to determine CCR and FCR.
Light Loss Factor: (LLF)
The approximate average illumination level or number of luminaires may be calculated as
Depreciation of initial lighting level due to Lamp Lumen Depreciation (LLD) and accumulafollows:
tion of dirt on the lamp and luminaire surface (Luminaire Dirt Depreciation LDD).
1. Determine Room Cavity Ratio (RCR)
Affected by fixture design, lamp choice, number of burning hours and type of interior.
2. Determine Reflectances
Ballast Factor: (BF)
The commercial ballast performance relative to reference ballast.
Typical approximate reflectances:
Other Factors:
See IES Lighting Handbook for recurring and non-recurring factors that lead to still greater
accuracy, including the determination of effective cavity reflectances.
Ceiling:
Standard White Paint
Rough White Pain
Rough Light Paint
80%
50%
30%
Walls:
White Paint
Rough Light Paint
80%
30%
Floors:
Dark Concrete
Carpet Average
20%
15%
3. Find Coefficient of Utilization
Knowing the ceiling. walls and floor reflectances and the room cavity ratio (calculated
in step 1), the coefficient of utilization may be found from the manufacturers published
data or typical data found in the current IES Handbook. See Table 1 below for example.
For a room cavity ratio of1.0 and reflectances of 30 (ceiling), 30 (wall), and 20 (floor) the
CU equals 0.63 for this luminaire.
W = Room Width
L = Room Length
Ceiling Cavity = Volume bounded by walls, ceiling and luminaire plane.
hcc = height of ceiling cavity. *For surface mounted or recessed fixtures
4. Compute Average Footcandle Level or Number of Luminaires using formulas A and/or B.
hcc = 0.
Floor Cavity = Volume bounded by walls. floor and work plane.
hfc = height of floor cavity.
B.Maintained
A.Number of
(Maintained Illuminance (FC) Desired) x (Area in Square Feet)
Illuminance (Number of Luminaires) x (Lamp Lumens Per Luminaire) x (CU) x (LLD) x BF)
Luminaires =
(Lamp Lumens/Luminaire) x (CU) x (LLD) x (BF)
(Area in Square Feet)
(FC) =
COEFFICIENTS OF UTILIZATION FOR 20 PERCENT EFFECTIVE FLOOR CAVITY REFLECTANCE
Effective Ceiling
Cavity Reflectance
Wall Reflectance
80
50
30
70
10
Room Cavity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
50
30
50
10
50
30
30
10
10
50
30
10
50
30
10
65
57
49
43
37
33
29
26
24
21
63
53
45
38
32
28
24
21
19
16
61
50
41
34
28
24
20
17
15
12
62
54
47
41
36
32
28
25
23
20
61
51
43
36
31
27
23
20
18
15
59
48
40
33
27
23
20
17
15
12
57
47
38
31
26
22
18
15
13
10
COEFFFICIENTS OF UTILIZATIONZONAL CAVITY
75
64
56
48
42
37
33
29
26
23
71
59
49
41
35
30
26
22
20
17
68
54
44
36
30
25
21
18
15
12
73
63
54
47
41
36
32
29
26
23
69
58
48
40
34
30
25
22
20
17
66
53
43
35
29
25
21
18
15
12
69
60
52
45
39
35
31
27
25
22
66
55
47
39
33
29
25
21
19
16
64
51
42
35
29
24
20
17
15
12
See manufacturers published data for actual coefficients of utilization.
T 12
1/98
You might also like
- Zonal Cavity Method For Indoor CalculationsDocument3 pagesZonal Cavity Method For Indoor CalculationsJoniel Rosal Jayag80% (5)
- Artificial Lighting CalculationDocument40 pagesArtificial Lighting CalculationSonisha Aryal100% (1)
- LED Technology Presentation (Rev Kuwait)Document63 pagesLED Technology Presentation (Rev Kuwait)AV Shrinivas100% (3)
- Cahier Technique: Discrimination With LV Power Circuit BreakersDocument10 pagesCahier Technique: Discrimination With LV Power Circuit BreakersAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 1-Lumen Method PDFDocument11 pages1-Lumen Method PDFRADHIKANo ratings yet
- TransLine 1 ConclusionDocument2 pagesTransLine 1 ConclusionmultisporkyNo ratings yet
- Illumination AdditionalDocument80 pagesIllumination Additionalbutohpakang100% (1)
- Lumen MethodDocument11 pagesLumen Methodgiziew belay100% (1)
- 10 Lighting - CU and CR CalculationDocument28 pages10 Lighting - CU and CR CalculationNatalie CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Zonal Cavity CalcDocument23 pagesZonal Cavity Calcmaulia farahNo ratings yet
- Zonal Cavity Method For Calculating The Number of Lamps in An AreaDocument9 pagesZonal Cavity Method For Calculating The Number of Lamps in An AreaAbdulyekini Ahmadu100% (1)
- Lighting: CHAPTER - 1: Building Electrical Installation CalculationDocument13 pagesLighting: CHAPTER - 1: Building Electrical Installation CalculationMr NobodyNo ratings yet
- Supplementary ProblemsDocument3 pagesSupplementary Problems白銀0% (1)
- 2 - Low Intensity Discharge Lamps Part 3Document41 pages2 - Low Intensity Discharge Lamps Part 3Miko F. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document19 pagesChapter 3Lëlîså DébālkéNo ratings yet
- Electric LightingDocument10 pagesElectric LightingSarah FrazierNo ratings yet
- IlluminationDocument43 pagesIlluminationlee robert olivar67% (3)
- Illumination Engineering: Utilization, Traction, Heating & Drives - Unit-1Document59 pagesIllumination Engineering: Utilization, Traction, Heating & Drives - Unit-1suvo dasNo ratings yet
- ILLUMINATIONDocument12 pagesILLUMINATIONjohncedrixbNo ratings yet
- Calculate Lighting Fixture's Beam Angle and Lumen - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument5 pagesCalculate Lighting Fixture's Beam Angle and Lumen - Electrical Notes & ArticlesRahul ItaliyaNo ratings yet
- Lighting Design by Lumen MethodDocument11 pagesLighting Design by Lumen MethodAmos Korme100% (1)
- Zonal CavityDocument32 pagesZonal CavityarkidechNo ratings yet
- Zonal Cavity & Lumen MethodDocument36 pagesZonal Cavity & Lumen MethodAnanda DuttaNo ratings yet
- Illumination EngineeringDocument7 pagesIllumination EngineeringSumit GawareNo ratings yet
- Illumination NotesDocument16 pagesIllumination NotesANIL KUMAR100% (1)
- Thesis of JhoweeDocument25 pagesThesis of JhoweeTrüth SeekerNo ratings yet
- 0501 Eu1 RJR PPT IllumDocument17 pages0501 Eu1 RJR PPT IllumAlexNo ratings yet
- Lumen Method Lighting CalculationDocument9 pagesLumen Method Lighting CalculationAdisuNo ratings yet
- Lighting DesignDocument2 pagesLighting DesignKhay SaadNo ratings yet
- Zonal Cavity RatioDocument3 pagesZonal Cavity RatioPrecious AdeboboyeNo ratings yet
- Calculations and The Laws of IlluminationDocument3 pagesCalculations and The Laws of Illuminationbrijesh varshneyNo ratings yet
- IlluminationDocument130 pagesIlluminationsavvymovNo ratings yet
- Interior Lighting: M CM V FDocument33 pagesInterior Lighting: M CM V FHassen LazharNo ratings yet
- AdU Illumination Problem Set 1Document1 pageAdU Illumination Problem Set 1Andrew NibungcoNo ratings yet
- Solar GeometryDocument55 pagesSolar GeometrySwamy Venkata Udayagiri100% (2)
- Statistical Intervals For A Single SampleDocument31 pagesStatistical Intervals For A Single SampleBui Tien DatNo ratings yet
- Low Intensity Discharge Lamps: Group 1Document69 pagesLow Intensity Discharge Lamps: Group 1Ronald James DiazNo ratings yet
- Swes Unit 3Document64 pagesSwes Unit 3pradeepNo ratings yet
- Light System and Design Calculations ExampleDocument9 pagesLight System and Design Calculations ExampleMark Anthony GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lighting Design BasicsDocument25 pagesLighting Design BasicsPooja PundeerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document9 pagesChapter 12m_michael_cNo ratings yet
- Lighting Building Service SystemsDocument5 pagesLighting Building Service SystemsPrincess Morales TyNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Illumination EngineeringDocument30 pagesLecture Notes For Illumination EngineeringVishal Narkhede83% (12)
- Lecture - 4 - Artificial - Lighting - CalculationDocument40 pagesLecture - 4 - Artificial - Lighting - Calculationsamuel seyoumNo ratings yet
- Revision Qns 2Document1 pageRevision Qns 2Colesha BarukaNo ratings yet
- D'Alembert's Principle: REF Ma REF W GDocument2 pagesD'Alembert's Principle: REF Ma REF W GGianne Karl AlmarinesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2Melkamu BirlewNo ratings yet
- Elementary Idea of The Special Features Required andDocument13 pagesElementary Idea of The Special Features Required andnikhil100% (1)
- FinalDocument21 pagesFinalMohammed Arshad AliNo ratings yet
- Lumen Method: Illuminance: The Quantity of Light Reaching A Certain Surface. It'sDocument15 pagesLumen Method: Illuminance: The Quantity of Light Reaching A Certain Surface. It'sSarah Al-MutlaqNo ratings yet
- Sheet2 - SolutionsDocument17 pagesSheet2 - SolutionsMöstafa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics (Statics) : A B A B A B BDocument2 pagesEngineering Mechanics (Statics) : A B A B A B BMallene EhurangoNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument9 pagesSolutionDaaniyyee Abdiisaa100% (1)
- VejigDocument2 pagesVejigMiner TPNo ratings yet
- Zonal Cavity Method: Laguna State Polytechnic University Sta Cruz, LagunaDocument12 pagesZonal Cavity Method: Laguna State Polytechnic University Sta Cruz, LagunaEeeeeeNo ratings yet
- GROUP-9 - 2.8-Lighting Application and Design (REVISED)Document58 pagesGROUP-9 - 2.8-Lighting Application and Design (REVISED)Von ToledoNo ratings yet
- Reading The CU TableDocument1 pageReading The CU TableelectworldNo ratings yet
- Lumen Man!Document18 pagesLumen Man!bukit_guestNo ratings yet
- Lighting Calculation PresentationDocument9 pagesLighting Calculation PresentationSuhandri AndryNo ratings yet
- Cavity Method VirtudazoDocument25 pagesCavity Method VirtudazoJoshua TupasNo ratings yet
- Lumen Method Calculation WorksheetDocument1 pageLumen Method Calculation WorksheetDonald Gabriel100% (1)
- 10 Piano-2023-2024-Grade-1Document1 page10 Piano-2023-2024-Grade-1Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 7 Piano-2023-2024-Grade-1Document1 page7 Piano-2023-2024-Grade-1Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 6 Piano-2023-2024-Grade-1Document1 page6 Piano-2023-2024-Grade-1Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 2 Piano-2023-2024-Grade-1Document1 page2 Piano-2023-2024-Grade-1Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Transportation Research Procedia 25 (2017) 4529-4543Document1 pageTransportation Research Procedia 25 (2017) 4529-4543Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 3 Discrimination With Power Circuit-BreakersDocument9 pages3 Discrimination With Power Circuit-BreakersAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Techno-Economic Analysis of Intermittent Renewable Energy Penetration With The Proposed India-Sri Lanka HVDC InterconnectionDocument13 pagesTechno-Economic Analysis of Intermittent Renewable Energy Penetration With The Proposed India-Sri Lanka HVDC InterconnectionAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 4 Examples of Circuit-Breaker Selections For An LV InstallationDocument9 pages4 Examples of Circuit-Breaker Selections For An LV InstallationAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- SL Energy Policy 2019Document3 pagesSL Energy Policy 2019Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Color Measurements: RGB Value Tristimulus Value Chromaticity Coordinate CCTDocument3 pagesColor Measurements: RGB Value Tristimulus Value Chromaticity Coordinate CCTAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Lightning: 1% of Strokes Exceed 200 KaDocument1 pageLightning: 1% of Strokes Exceed 200 KaAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Colorimetry & StandardsDocument4 pagesColorimetry & StandardsAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Radiant Energy: Capable of Exciting The Retina and Producing A Visual SensationDocument1 pageRadiant Energy: Capable of Exciting The Retina and Producing A Visual SensationAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Transient Over VoltagesDocument5 pagesTransient Over VoltagesAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Semester 1: Curriculum - B.Sc. Engineering Honours in Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesSemester 1: Curriculum - B.Sc. Engineering Honours in Electrical EngineeringAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Non Linear Model For Bi-Color LED: Two LED Sets From Two Different Colors Warm White and Cool WhiteDocument4 pagesNon Linear Model For Bi-Color LED: Two LED Sets From Two Different Colors Warm White and Cool WhiteAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- RH TechPaperIESL Oct06Document9 pagesRH TechPaperIESL Oct06Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- 1-2006Document8 pages1-2006Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Writing Tips: Thesis: Which SectionsDocument4 pagesWriting Tips: Thesis: Which SectionsAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Applying 61000-5-2 To Cable Shield Bonding and Earthing, 21 May 04Document6 pagesThe Benefits of Applying 61000-5-2 To Cable Shield Bonding and Earthing, 21 May 04Asanka RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Overcurr Ent Protection: Location 2 Phase A Instantaneous Cur Rent I 1aDocument1 pageOvercurr Ent Protection: Location 2 Phase A Instantaneous Cur Rent I 1aAsanka RodrigoNo ratings yet