Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit1 Network Parameters
Uploaded by
rohinishalini47Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit1 Network Parameters
Uploaded by
rohinishalini47Copyright:
Available Formats
Unit -1
Network parameters
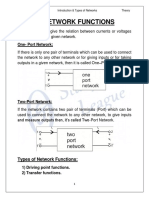
A network may be used for representing either source or load. A pair of
terminals at which a signal may enter or leave a network is called a port. A port is
defined as any pair of terminals into which energy is supplied,or from which energy
is withdrawn or where the network variables may be measured.
A two port network is simple a network inside a black box and the network has two
pairs of accessible terminals.one pair represents the input ant the other represents
the output.such building block is very common in electronic systems,communication
systems,transmission and distribution systems.
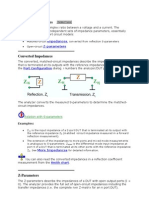
OPEN CIRCUIT IMPEDANCE OR [Z] PARAMETERS
Now if I 1 = 0 means the input port is an open circuit
and
if
I 2 = 0 means the output port is an open circuit
and
Figure 1: Determination of Z-parameters
[Z] parameters are known as open circuit impedance parameters because, in both the cases, one port is
open (i.e., I 1 = 0 and I 2 = 0)
Z 11 and Z 22 are driving-point impedance at port 1 and port 2. In the case of driving-point function the data
should be from the same port.
Z 12 and Z 21 are transfer impedance because in Z
from port 2,
12
and Z 21; one data is from port 1 and the other data is
Z 12 [ V 1/ I 1] [V 1 from port 1 and I 2 from port 2] = reverse transfer impedance.
Z 21 [V 2 /I 1] [I 1 from port 1 and V 2 from port 2] = forward transfer impedance.
It is seen that dimensionally each parameter is an impedance (ratio voltage and current), therefore, the
impedance parameters may be either calculated or measured by first opening port 2 and then determining
the ratios [ V 1/ I 1] and [V 2 /I 1] , and then opening port 1 and determining the ratios[V 1 / I
2] and [V 2 /I 2]. But in this chapter we will solve all problems using the comparing method.
You might also like
- Unit V - 2 - Two Port NetworksDocument39 pagesUnit V - 2 - Two Port NetworksShirisha marasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Two Port Netw All in OneDocument53 pagesChapter 3 Two Port Netw All in OneAbdi Jote100% (1)
- Lec10 Microwave Network Analysis (II)Document20 pagesLec10 Microwave Network Analysis (II)Mohammed AbbasNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Two Port NetworksDocument73 pagesUnit - 1 Two Port NetworksHema DarshanaNo ratings yet
- Two-Port Measurements and S-ParametersRev0.1 PDFDocument18 pagesTwo-Port Measurements and S-ParametersRev0.1 PDFRostam DastanNo ratings yet
- Two-Port Measurements and S-ParametersRev0.1 PDFDocument18 pagesTwo-Port Measurements and S-ParametersRev0.1 PDFRostam DastanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Single & Multi-Port NetworksDocument27 pagesLecture 4 - Single & Multi-Port NetworksAnubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- 3947Document7 pages3947Dei PehNo ratings yet
- Two Port Networks محول 1Document9 pagesTwo Port Networks محول 1aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document16 pagesChapter 18EL DrickNo ratings yet
- Chp3-Microwave Network Analysiswithexamples - Part1Document36 pagesChp3-Microwave Network Analysiswithexamples - Part1Ahmad MuzayyinNo ratings yet
- Two Port Networks - Impedance and Admitance Parameters-1Document50 pagesTwo Port Networks - Impedance and Admitance Parameters-1SAJJAD AHMAD Jalozai Electrical - Batch 20No ratings yet
- Network Analysis-Two Port Network & Network FunctionsDocument34 pagesNetwork Analysis-Two Port Network & Network Functionsanjugadu100% (2)
- Chapter 8 Two Port Network & Network Functions: Learning OutcomesDocument34 pagesChapter 8 Two Port Network & Network Functions: Learning OutcomesKarim Ullah PW ELE BATCH 22No ratings yet
- NETWORK ANALYSIS Chap.8 TWO PORT NETWORK & NETWORK FUNCTIONS PDFDocument34 pagesNETWORK ANALYSIS Chap.8 TWO PORT NETWORK & NETWORK FUNCTIONS PDFsudarshan poojaryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To S-Parameters: Abstract: This Paper Mainly Talks About The SDocument3 pagesIntroduction To S-Parameters: Abstract: This Paper Mainly Talks About The SMaulik MehtaNo ratings yet
- EIE324 2portDocument30 pagesEIE324 2portEmmanuel OkoroNo ratings yet
- Two Port Network Notes by An Indian ProfessorDocument54 pagesTwo Port Network Notes by An Indian ProfessorBabul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Two Port NetworksDocument74 pagesTwo Port NetworksDheesha GNo ratings yet
- Two Port NetworkDocument51 pagesTwo Port NetworkPranzal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chap 1, 2, 3,4,5,6,7Document76 pagesChap 1, 2, 3,4,5,6,7ERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- UNIT I, II, III, IV, V Notes PDFDocument93 pagesUNIT I, II, III, IV, V Notes PDFThiagu RajivNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Two Port NetworksDocument19 pagesUnit 5-Two Port NetworksMoorthiNo ratings yet
- Two PortNetworkDocument40 pagesTwo PortNetworkyuk69No ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit AnalysisDocument40 pagesElectrical Circuit AnalysisRamalingeswar JNo ratings yet
- Two Port NetworksDocument12 pagesTwo Port NetworksAmitava BiswasNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document44 pagesUnit 5Chirantan BiswasNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument7 pagesResearch Articlevlad vNo ratings yet
- Two-Ports NetworksDocument24 pagesTwo-Ports NetworksMohammadNo ratings yet
- Two-Port Networks and Amplifiers: EECS 142Document49 pagesTwo-Port Networks and Amplifiers: EECS 142Elessaid SaadNo ratings yet
- Properties of (S) MatrixDocument5 pagesProperties of (S) MatrixSyed Zafar Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Two Port NetworksDocument45 pagesChapter 17 Two Port Networksmahnoor238705No ratings yet
- ParametersDocument2 pagesParameterssamisvineetNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineerin1Document13 pagesFaculty of Engineerin1maged mohamedNo ratings yet
- Microwave Note 11Document94 pagesMicrowave Note 11Rayan NezarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document77 pagesChapter 5chalaNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Types of NnetworksDocument4 pagesIntroduction & Types of NnetworksPrashant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits 3Document42 pagesElectrical Circuits 3akramul alimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document12 pagesChapter 1ERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- PPP PP P"PP PP PP PPPPDocument35 pagesPPP PP P"PP PP PP PPPPsugunapriyaaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter FiveDocument31 pagesChapter FiveERMIAS AmanuelNo ratings yet
- Osnove ElektrotehnikeDocument178 pagesOsnove Elektrotehnikevegacg100% (1)
- Lecture 15: S Parameters and The Scattering MatrixDocument7 pagesLecture 15: S Parameters and The Scattering MatrixDinda NurhayatiNo ratings yet
- Two Port Networks - UploadDocument16 pagesTwo Port Networks - UploadkarthikhrajvNo ratings yet
- Module2 15EC71Document23 pagesModule2 15EC71Priyanka PrakashNo ratings yet
- Lecture Slides-Network AnalysisDocument35 pagesLecture Slides-Network Analysisaසිල්වාNo ratings yet
- Two Port CircuitsDocument13 pagesTwo Port CircuitsSandaruwan WanninayakaNo ratings yet
- S ParametersDocument36 pagesS ParametersRegginNo ratings yet
- 2 Port NetworkDocument3 pages2 Port NetworkManojav YVNo ratings yet
- Section 4 2 Impedance and Admittance Matricies PackageDocument25 pagesSection 4 2 Impedance and Admittance Matricies PackageMohammed AlhakeemiNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet