Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment: Outline Two Assumptions of The Biological Approach
Uploaded by
YassinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment: Outline Two Assumptions of The Biological Approach
Uploaded by
YassinCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment: Outline Two Assumptions of the Biological
Approach
The biological approach is a theory that is used to describe human
behaviour in terms of biology. This is done by observing physical changes
in the body e.g. heart rate, blood pressure etc. These are physical
responses to a stimulus they are triggered by the nervous system. There
are three assumptions in the biological approach, they are theories that
explain behaviour.
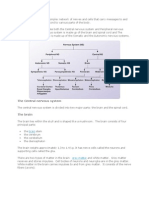
Assumption 1 The Brain
The human brain is divided into 5 main sections called lobes. Each one of
these lobes has a certain function. The frontal lobe is located at the front
of the brain and is responsible for conscious thoughts such as voluntary
movement. It also coordinates certain information from other lobes.
Damage to this part of the brain can result in mood changes. The parietal
lobe is located in the upper-middle section of the brain and plays an
important role in processing sensory information such as temperature,
pressure and pain. The occipital lobe, located at the back of the brain, is
the processing centre of visual information from the eyes, if damaged
hallucinations can be produced. The temporal lobe, is in the lowermiddle part of the brain and is involved in storing memories and
processing emotions.
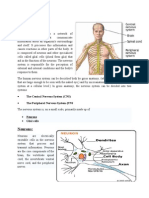
Assumption 2 Neurones and Neurotransmitters
Neurones are a group of nerve cells that are responsible for passing
information around the body in the form of electrical impulses. The
Neurones form a huge network around the body called the Nervous
System. The nervous system consists of the Central Nervous System
(CNS) which acts as a processing centre of the impulses and the
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS).
Neurons pass on information when they receive the impulses from another
neuron which is detected at the receiving end of the neuron on small
branches called dendrites. These impulses are passed on across a small
gap between the dendrites called a synapse. The impulses are passed
across the synapse in the form of chemical messengers called
neurotransmitters. Some examples of neurotransmitters are serotonin
(mood and sleep), adrenaline (heart rate, sweat, blood pressure etc.) and
GABA (anxiety). Neurotransmitter are released from presynaptic vesicles
and travel across the synapse to the receptor site on the dendrite of the
next neurone.
You might also like
- Control, Coordination and Human BrainDocument8 pagesControl, Coordination and Human BrainSakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemCerene denzinNo ratings yet
- The-Nervous-System-Written ReportDocument5 pagesThe-Nervous-System-Written ReportHeileen S. San GabrielNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemalanNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesNervous SystemIhtisham Ul haqNo ratings yet
- KSG-Brain ActivityDocument10 pagesKSG-Brain ActivitySyahirah ZackNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument8 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLaine DerainNo ratings yet
- Questions and AnswersDocument15 pagesQuestions and AnswersTanveerAli01No ratings yet
- NeuropsychologyDocument28 pagesNeuropsychologyFarhan AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Nervous and Endocrine Systems - Science10 PDFDocument84 pagesQ3 - Nervous and Endocrine Systems - Science10 PDFGabriel Pasumbal100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Structure and Function of The Nervous System I. StructuresDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Structure and Function of The Nervous System I. StructuresChielo ZartigaNo ratings yet
- Nervou S System:: NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervou S System:: NeuronsFizzah100% (4)
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument57 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorJAMES ALDRIN CALVEZ PAMPOSANo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument10 pagesThe Nervous Systemhajra0325No ratings yet
- What Is Neuron?Document8 pagesWhat Is Neuron?Shaekh Maruf Skder 1912892630No ratings yet
- Group 1B OutlineDocument3 pagesGroup 1B Outlinejackclaudefajardo15No ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانيةDocument14 pagesالمحاضرة الثانيةNajwa AbdualgaderNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument23 pagesNervous SystemSumaira Noreen100% (1)
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiologyzairis21No ratings yet
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408115Document4 pagesFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408115Misbah NoreenNo ratings yet
- Human BrainDocument17 pagesHuman BrainAkbota KuanishkyzyNo ratings yet
- Preparation in Psychology: Bicol University College of Engineering East Campus LegazpiDocument8 pagesPreparation in Psychology: Bicol University College of Engineering East Campus LegazpiKielNo ratings yet
- The Human Nervous System - 71911Document49 pagesThe Human Nervous System - 71911Rome Voltaire GomezNo ratings yet
- CNS and PNSDocument4 pagesCNS and PNSDeepshikhaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology: Explain The Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology With Pathophysiology: Explain The Functions of The Nervous SystemJay-ar BarquerosNo ratings yet
- 31.2 The Central Nervous SystemDocument28 pages31.2 The Central Nervous Systemmoniaguayo980% (1)
- Biological Basis of BehaviourDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviourSufian Khan100% (1)
- Abpg1103 - Introduction To Psychology. 2Document56 pagesAbpg1103 - Introduction To Psychology. 2Anonymous HK3LyOqR2gNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemTalha KhalidNo ratings yet
- Brain and BehaviourDocument9 pagesBrain and BehaviourKenya BaileyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesNervous SystemRaven MayoNo ratings yet
- PERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASDocument16 pagesPERSONAL DEVELOPMENT - 2nd Batch LASJustin JoshNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Summary NotesDocument9 pagesNervous System - Summary NotesHarshNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System Is A Complex Network of Nerves and Cells That Carry Messages To and From TheDocument18 pagesThe Nervous System Is A Complex Network of Nerves and Cells That Carry Messages To and From TheJanineLingayoCasilenNo ratings yet
- Unit-Two Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument27 pagesUnit-Two Biological Bases of Behaviorरोशन सिग्देलNo ratings yet
- Unit-Two Biological Bases of BehaviorDocument27 pagesUnit-Two Biological Bases of Behaviorरोशन सिग्देलNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument43 pagesControl and CoordinationDukhi InsaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorShermel Joy SolisNo ratings yet
- Nervous System FunctionsDocument10 pagesNervous System FunctionsJovi Leo PunoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Overview: FunctionDocument11 pagesNervous System - Overview: FunctionAadil JuttNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument36 pagesThe Nervous SystemespirituronnierickNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- (Lecture - 4) Neuropsychology of Human BehaviorDocument58 pages(Lecture - 4) Neuropsychology of Human BehaviorN. W. FlannelNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesNervous SystemAdesinasi Cephas AdewunmiNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument21 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorSyed Huzayfah FaisalNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemananthNo ratings yet
- Gen Psych - Chapter 2Document30 pagesGen Psych - Chapter 2Mhild GandawaliNo ratings yet
- 7 Nervous SystemDocument37 pages7 Nervous SystemAthar Habib ShahaniNo ratings yet
- CHP 7 Class 10Document13 pagesCHP 7 Class 10sourabh nuwalNo ratings yet
- The Nervous System-13 Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDocument16 pagesThe Nervous System-13 Dr. Hazim AL-RawiDrAli Al-FendiNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleDocument4 pagesRelationship Between The Brain and The Nervous System - 2328 Words - Term Paper ExampleObi TomaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Week 3 NotesDocument9 pagesPsychology Week 3 Notes01234No ratings yet
- General Psychology Notes Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesGeneral Psychology Notes Nervous SystemRj BengilNo ratings yet
- Bio PsychologyDocument7 pagesBio PsychologyAndrea FleitasNo ratings yet
- CH 7 The Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesCH 7 The Nervous Systemapi-267543553No ratings yet
- Describe The Organization of The Nervous System Including The Central Nervous System and The Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesDescribe The Organization of The Nervous System Including The Central Nervous System and The Peripheral Nervous SystemGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Science NotesDocument45 pagesYear 10 Science NotesAmal VivekNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Physiological Basis of BehaviorDocument37 pagesCHAPTER 2 Physiological Basis of BehaviorIsh Gallito100% (1)
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyNo ratings yet