Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Instructional Objectives:: Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
Uploaded by
scr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pagek
Original Title
41 Pdfsam Conc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentk
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageInstructional Objectives:: Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
Uploaded by
scrk
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Instructional Objectives:
At the end of this lesson, the student should be able to:
categorically state the four common steps to be followed in any method of
design,
define the limit states,
identify and differentiate the different limit states,
state if the structures are to be designed following all the limit states,
explain the concept of separate partial safety factors for loads and material
strengths depending on the limit state being considered,
justify the "size effect" of concrete in its strength,
name the theory for the analysis of structures to be designed by limit states,
name the method of analysis of statically indeterminate beams and frames,
and slabs spanning in two direction at right angles,
justify the need to redistribute the moments in statically indeterminate beams
and frames,
identify four reasons to justify the design of structures or parts of the structure
by limit state method.
2.3.1 Introduction
In any method of design, the following are the common steps to be followed:
(i)
To assess the dead loads and other external loads and forces likely to
be applied on the structure,
(ii)
To determine the design loads from different combinations of loads,
(iii)
To estimate structural responses (bending moment, shear force, axial
thrust etc.) due to the design loads,
(iv)
To determine the cross-sectional areas of concrete sections and
amounts of reinforcement needed.
Version 2 CE IIT, Kharagpur
You might also like
- Strength of Materials - I: Objectives and Out ComesDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials - I: Objectives and Out ComesNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- CE 537 SPRSVDocument5 pagesCE 537 SPRSVCarl Justin AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Steel DesignDocument180 pagesSteel DesignAndrick Alvarez100% (2)
- Structural Lecture1Document6 pagesStructural Lecture1Lyka Mae BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- Introductory ClassDocument14 pagesIntroductory Classpkimani10098No ratings yet
- CE470 Course OutlineDocument10 pagesCE470 Course OutlineYasser Alghrafy100% (1)
- Chapter One: 04/09/2022 1 by Dereje B. (MSC in Structural Engineering)Document9 pagesChapter One: 04/09/2022 1 by Dereje B. (MSC in Structural Engineering)Dereje bedoreNo ratings yet
- Mtech Stru 19 20Document37 pagesMtech Stru 19 20Dhirendra YadavNo ratings yet
- 1 RC 1 Lecture Notes IntroductionDocument52 pages1 RC 1 Lecture Notes IntroductionRajalakshmi MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Review of Statics and Mechanics Introduction To TOSDocument48 pagesWeek 1 Review of Statics and Mechanics Introduction To TOSLEIGHNE GEBRIEL SUINGNo ratings yet
- Design of ConcreteDocument3 pagesDesign of Concretesachin balyanNo ratings yet
- Steel DesignDocument93 pagesSteel DesignSana'a Aamir0% (1)
- Week 1 Review of Statics and Mechanics Introduction To TOSDocument48 pagesWeek 1 Review of Statics and Mechanics Introduction To TOSJHON ROY OLIVANo ratings yet
- ME2233 Spr16 Lecture1igtDocument51 pagesME2233 Spr16 Lecture1igthamzaNo ratings yet
- Basic Education 2008Document24 pagesBasic Education 2008Yasser AlghrafyNo ratings yet
- Modulus No 1Document87 pagesModulus No 1Atif Khan GI CivilNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Structures Analysis and Design of StructuresDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Design of Structures Analysis and Design of StructuresAJNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document41 pagesWa0000.mumtaz4402370No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1Silendrina MishaNo ratings yet
- Design of Offshore StructuresDocument51 pagesDesign of Offshore StructuresBolarinwa100% (3)
- Structural Analysis (FINALS) PDFDocument45 pagesStructural Analysis (FINALS) PDFJunel Torrejos100% (1)
- tHEORY mODULEDocument34 pagestHEORY mODULEJorge DanielleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structural Analysis-Part 1Document30 pagesIntroduction To Structural Analysis-Part 1Hiew Ching YongNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Module 2Document32 pagesEngineering Mechanics Module 2Abigail SiatrezNo ratings yet
- CIV211 - Module1Document49 pagesCIV211 - Module1Dayalan JayarajNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Structural AnalysisDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Structural AnalysisAlyssandra Beatriz AustriaNo ratings yet
- Fhwa Nhi 130102Document2 pagesFhwa Nhi 130102Sana FatimaNo ratings yet
- ToS Lessons MergedDocument150 pagesToS Lessons MergedAlyssandra Beatriz AustriaNo ratings yet
- 7 A These He He Some He These He He He LessDocument1 page7 A These He He Some He These He He He LessjosNo ratings yet
- EM321 TOPIC 1 - Failure Theories and Fatigue Strength PDFDocument180 pagesEM321 TOPIC 1 - Failure Theories and Fatigue Strength PDFJoshua RajNo ratings yet
- Structural Theory (Module 1 - Post Test) - SalamanesDocument3 pagesStructural Theory (Module 1 - Post Test) - SalamanesKinniNo ratings yet
- TDS Lec 5Document114 pagesTDS Lec 5YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Project: For The Design of The Structure, The Deadload, Live Loads, Seismic and Wind LoadDocument6 pagesIntroduction To The Project: For The Design of The Structure, The Deadload, Live Loads, Seismic and Wind LoadAbdul Razzak0% (1)
- Concrete and MasonryDocument14 pagesConcrete and MasonryRegine Kaye TagurdaNo ratings yet
- Sherman Notes PDFDocument213 pagesSherman Notes PDFAbdul Hamid Bhatti100% (1)
- Matrix Approach, Second Edition, Addison-Wesley, 1997Document3 pagesMatrix Approach, Second Edition, Addison-Wesley, 1997Khalid MohammedNo ratings yet
- FDC AssignmentDocument4 pagesFDC AssignmentsumikannuNo ratings yet
- Structural Design: Loads, Dynamic Loads, TransverseDocument2 pagesStructural Design: Loads, Dynamic Loads, TransverseChang NagiNo ratings yet
- RCD1Document6 pagesRCD1Jadrien Mark ImperialNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument17 pagesAnalysisKarim HNo ratings yet
- (Iv) Chain Drives - Roller Chains, Polygonal Effect, Power Rating, Sprocket Wheel, Silent ChainDocument1 page(Iv) Chain Drives - Roller Chains, Polygonal Effect, Power Rating, Sprocket Wheel, Silent ChainArterixpestcontrolNo ratings yet
- Research CH 2Document13 pagesResearch CH 2Hecta KillaNo ratings yet
- Staad-Pro-Ppt InternshipDocument26 pagesStaad-Pro-Ppt Internshipmadhu sreeNo ratings yet
- Ce (Pe) 602BDocument10 pagesCe (Pe) 602BArghya MondalNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectDocument2 pagesLearning ObjectHabtamu NigussieNo ratings yet
- Designing Experiments in A Civil Engineering Curriculum: Session 2526Document9 pagesDesigning Experiments in A Civil Engineering Curriculum: Session 2526Mar WaNo ratings yet
- Bridge Second UnitDocument18 pagesBridge Second UnitFE3056 NAGARAJ.SNo ratings yet
- CEN 315 - Design of Concrete Structures 1 (3.0) : Course Outcomes (CO)Document1 pageCEN 315 - Design of Concrete Structures 1 (3.0) : Course Outcomes (CO)Mehedi Hasan ApuNo ratings yet
- Steel Design To Eurocode 3 University of Sheffield Structural Engineering MastersDocument55 pagesSteel Design To Eurocode 3 University of Sheffield Structural Engineering MastersephremNo ratings yet
- Dynamic-Struct Engineeringconsultant &softwaretraining InstituteDocument38 pagesDynamic-Struct Engineeringconsultant &softwaretraining InstituteArun Varughese Thomas100% (1)
- Frame Idealisation & AnalysisDocument46 pagesFrame Idealisation & AnalysisAnonymous iS33V5100% (1)
- Structural Analysis and Design Tcm4-118204Document140 pagesStructural Analysis and Design Tcm4-118204Evodius RweyemamuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 1Document17 pagesLecture Note 1Fun JinNo ratings yet
- Unit1 2Document7 pagesUnit1 2aswiniNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: Design of Machine Elements MCEN2334Document3 pagesCourse Outline: Design of Machine Elements MCEN2334Jamshed JalilNo ratings yet
- Repair Strengthening of Structures PDFDocument71 pagesRepair Strengthening of Structures PDFAMmarNo ratings yet
- MIE222 Syllabus 2015Document3 pagesMIE222 Syllabus 2015Sourabh DasNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresFrom EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (22)
- 314 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page314 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 318 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page318 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 317 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page317 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 315 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page315 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 316 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page316 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
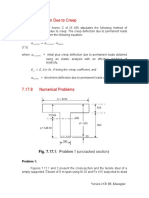
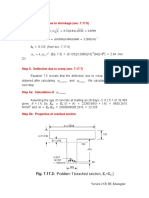
- 7.17.5 Calculation of Short-Term Deflection: I I I I - M / M) (Z / D) (X/D) (B/B) IDocument1 page7.17.5 Calculation of Short-Term Deflection: I I I I - M / M) (Z / D) (X/D) (B/B) IscrNo ratings yet
- 320 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page320 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- Step 6: Checking of The Requirements of IS 456:) (PermDocument1 pageStep 6: Checking of The Requirements of IS 456:) (PermscrNo ratings yet
- Solution 1:: Step 1: Properties of Plain Concrete SectionDocument1 pageSolution 1:: Step 1: Properties of Plain Concrete SectionscrNo ratings yet
- 321 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page321 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 324 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page324 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- Step 5c: Calculation Of: R R EffDocument1 pageStep 5c: Calculation Of: R R EffscrNo ratings yet
- 323 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page323 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 7.17.9 Practice Questions and Problems With Answers: F o W FDocument1 page7.17.9 Practice Questions and Problems With Answers: F o W FscrNo ratings yet
- 328 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page328 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 70 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page70 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 330 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page330 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 333 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page333 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 329 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page329 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 332 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page332 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Deflection: Step 1Document1 pageCalculation of Deflection: Step 1scrNo ratings yet
- 334 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page334 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 57 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page57 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 60 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page60 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 59 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page59 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 58 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page58 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 2.3.8 Summary of This Lesson: TQ.6: Give Four Reasons To Justify The Design of Structures by Limit State MethodDocument1 page2.3.8 Summary of This Lesson: TQ.6: Give Four Reasons To Justify The Design of Structures by Limit State MethodscrNo ratings yet
- 55 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page55 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 56 Pdfsam ConcDocument1 page56 Pdfsam ConcscrNo ratings yet
- 2.3.7 Test 3 With Solutions: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurDocument1 page2.3.7 Test 3 With Solutions: Version 2 CE IIT, KharagpurscrNo ratings yet