Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electric Circuit Theory Tut 1: 1. Chapter 2, Problem 8
Uploaded by
Izzat NaserOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electric Circuit Theory Tut 1: 1. Chapter 2, Problem 8
Uploaded by
Izzat NaserCopyright:
Available Formats
EKT 101/4
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY
TUT 1
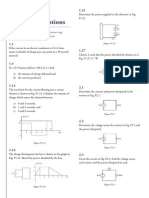
1. Chapter 2, Problem 8.
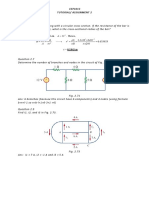
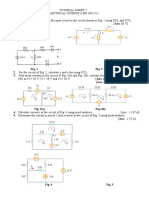
Use KCL to obtain currents i1, i2, and i3 in the circuit shown in Fig. 2.72.
2. Chapter 2, Problem 12.
In the circuit in Fig. 2.76, obtain v1, v2, and v3.
Chapter 2, Problem 14.
Given the circuit in Fig. 2.78, use KVL to find the branch voltages V1 to V4.
Figure 2.78
3. Chapter 2, Problem 23.
Shahadah ahmad
sem1 2010/11
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY
EKT 101/4
TUT 1
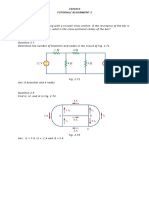
In the circuit shown in Fig. 2.87, determine vx and the power absorbed by the 12-
resistor.
Figure 2.87
4. Chapter 2, Problem 25.
For the network in Fig. 2.89, find the current, voltage, and power associated with the 20k resistor.
Figure 2.89
5. Chapter 2, Problem 34.
Using series/parallel resistance combination, find the equivalent resistance seen by the
source in the circuit of Fig. 2.98. Find the overall dissipated power.
20
12 V
+
_
40
10
40
20
12
10
Figure 2.98 For Prob. 2.34.
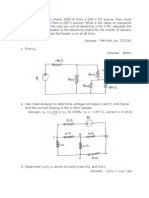
6. Chapter 2, Problem 45.
Shahadah ahmad
sem1 2010/11
EKT 101/4
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY
TUT 1
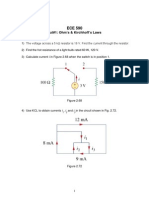
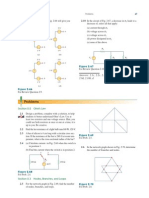
Find the equivalent resistance at terminals a-b of each circuit in
Fig. 2.109.
Figure 2.109
7. Chapter 2, Problem 47.
Find the equivalent resistance Rab in the circuit of Fig. 2.111.
Fig. 2.111.
8. Chapter 2, Problem 53.
Shahadah ahmad
sem1 2010/11
EKT 101/4
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT THEORY
TUT 1
Obtain the equivalent resistance Rab in each of the circuits of Fig. 2.117. In (b), all
resistors have a value of 30 .
Figure 2.117 For Prob. 2.53.
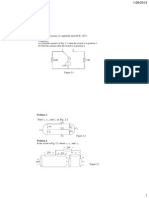
9. Chapter 2, Problem 57.
Find Req and I in the circuit of Fig. 2.121.
Fig. 2.121.
Shahadah ahmad
sem1 2010/11
You might also like
- EE Assignment 23-24 Sem 1Document7 pagesEE Assignment 23-24 Sem 1Triggered CreatorNo ratings yet
- tutorial 1Document3 pagestutorial 1javi.alberto.torrucoNo ratings yet
- KVL KCL Ohm's Law ProblemsDocument3 pagesKVL KCL Ohm's Law Problemsjaspreet964No ratings yet
- TUTO - ASG 02 - JUL2015 - Answer - Electric CircuitDocument4 pagesTUTO - ASG 02 - JUL2015 - Answer - Electric CircuitHasmizar Abd Halim (KTN)No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document9 pagesTutorial 4sreekantha reddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Basic LawsDocument15 pagesChapter 2 Basic LawsChristian Muli0% (1)
- SalinanterjemahanML2F002546 PDFDocument26 pagesSalinanterjemahanML2F002546 PDFsabarullah haliNo ratings yet
- TUTO - ASG 02 - JUL2015 - Electric Circuit - QuestionDocument4 pagesTUTO - ASG 02 - JUL2015 - Electric Circuit - QuestionHasmizar Abd Halim (KTN)No ratings yet
- Activity 2-Circuit ElementsDocument2 pagesActivity 2-Circuit Elementspatrick dgNo ratings yet
- ELECTRO Practice Test 2Document3 pagesELECTRO Practice Test 2Rorisang MolotsiNo ratings yet
- ECE590 - Tutorial 1Document2 pagesECE590 - Tutorial 1NazhammerheartNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1Pasindu PramodNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 PeeeDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 PeeeNick GiiniusNo ratings yet
- Btech CT 1 2017-18 - EndDocument4 pagesBtech CT 1 2017-18 - EndSreenivasaraoDharmavarapuNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of High Voltage Diode 100 KVDocument7 pagesDesign and Construction of High Voltage Diode 100 KVBashir MtwaklNo ratings yet
- Electronic CircuitsDocument2 pagesElectronic CircuitsHossam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial1 8Document9 pagesTutorial1 8Lovish BansalNo ratings yet
- Rechargeable Batteries Applications HandbookFrom EverandRechargeable Batteries Applications HandbookRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- 02_ElectricityDocument5 pages02_Electricitydysonjonas269No ratings yet
- BET Assignment 1 - 2013 Jan BatchDocument2 pagesBET Assignment 1 - 2013 Jan BatchIpshita RanjanaNo ratings yet
- Elec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568Document7 pagesElec2091st Semester Exam Papr20221 - 1705355554568family7482pleaseNo ratings yet
- Test 1 2014 EM2 & EM3 FEBRUARYDocument2 pagesTest 1 2014 EM2 & EM3 FEBRUARYBONGINKOSI DINGAANNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1-Eed1201 Final Havy Feb 12Document6 pagesAssignment 1-Eed1201 Final Havy Feb 12230041601050No ratings yet
- Second Test 2010Document6 pagesSecond Test 2010smisosphamandla30No ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document11 pagesAssignment 1رضا حسن0% (2)
- Circuit problems covering lectures 1-5Document4 pagesCircuit problems covering lectures 1-5Mohammad Al Faiyaz50% (2)
- Chapter 2 ProblemsDocument11 pagesChapter 2 ProblemsVictoria MooreNo ratings yet
- CSET102 - Tutorial-1 - 2023-24 Sem IDocument4 pagesCSET102 - Tutorial-1 - 2023-24 Sem IShreyansh GargNo ratings yet
- Turotial Sheet - 222Document2 pagesTurotial Sheet - 222DR. SUBODH KUMAR SINGHALNo ratings yet
- Problems: Series Resistors 1. For Each Configuration in Fig. 5.85, Find The Individual (NotDocument12 pagesProblems: Series Resistors 1. For Each Configuration in Fig. 5.85, Find The Individual (NotYurany GracianoNo ratings yet
- BEngTech Electrical/Mechanical/Industrial Engineering module testDocument3 pagesBEngTech Electrical/Mechanical/Industrial Engineering module testSims Gift ShibaNo ratings yet
- 201HW2Document3 pages201HW2ojhaaaa0% (1)
- Electrotechnics N4 August 2022 Question Paper PDFDocument9 pagesElectrotechnics N4 August 2022 Question Paper PDFPetro Susan BarnardNo ratings yet
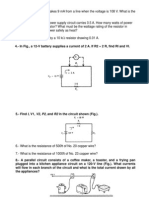
- 4.-In Fig., A 12-V Battery Supplies A Current of 2 A. If R2 2 R, Find RI and VIDocument4 pages4.-In Fig., A 12-V Battery Supplies A Current of 2 A. If R2 2 R, Find RI and VIErnesto MoralesNo ratings yet
- Assignment CTDocument9 pagesAssignment CTdhinojahimeshNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Nov 2019 (Electronics) EngDocument23 pagesElectrical Technology Nov 2019 (Electronics) EngKhathutshelo KharivheNo ratings yet
- ENG1030 Electrical Circuit Tutorial QuestionsDocument3 pagesENG1030 Electrical Circuit Tutorial QuestionsShaun StanleyNo ratings yet
- Aula 4 - Exercise Class 1: Prof. Marcelino AndradeDocument12 pagesAula 4 - Exercise Class 1: Prof. Marcelino AndradeJack Van JhonesNo ratings yet
- EEE (May 2023)Document298 pagesEEE (May 2023)Durjoy SahaNo ratings yet
- EE2001 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesEE2001 Tutorial 1PeiXuan HoNo ratings yet
- 2002UNIT2PAPER2Document16 pages2002UNIT2PAPER2petey78No ratings yet
- 07a1ec05 Network AnalysisDocument8 pages07a1ec05 Network AnalysisSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Circuit AnalysisDocument3 pagesCircuit Analysisiamcrazy1729No ratings yet
- CDocument10 pagesCsoumiaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Booklet IGCSE 1.0Document45 pagesElectricity Booklet IGCSE 1.0Fiona YoungNo ratings yet
- Solar Photovoltaic Technology: Chapter TwoDocument26 pagesSolar Photovoltaic Technology: Chapter TworajapandiyaNo ratings yet
- EE Uptu Old QuesDocument1 pageEE Uptu Old Quesm_mustaqeemNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document3 pagesHW 2gavinilaaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Basic Laws PDFDocument35 pagesChapter 2 - Basic Laws PDFNisha KamelNo ratings yet
- 3rd Sem Electric CircuitDocument57 pages3rd Sem Electric CircuitRajkumarJhapteNo ratings yet
- (A) Determine The Currents I and I of The Circuit Given in Fig. 1 (A) by Using KCLDocument10 pages(A) Determine The Currents I and I of The Circuit Given in Fig. 1 (A) by Using KCLSurya Prakash SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1A AnsDocument4 pagesTutorial 1A AnsRISHABH JAINNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 NETWORK THEOREMSDocument14 pagesUNIT 2 NETWORK THEOREMSlekoringoeNo ratings yet
- 6087.clipper and Clamper 1Document15 pages6087.clipper and Clamper 1Komal ThakurNo ratings yet
- 7Series and Parallel ResistorDocument5 pages7Series and Parallel Resistorleeyuetyu1202No ratings yet
- ELC 260S Tutorial 1 Sem 1 2022Document3 pagesELC 260S Tutorial 1 Sem 1 2022Lehlogonolo MphahleleNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits Analysis 3Document18 pagesElectrical Circuits Analysis 329viswa12No ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsFrom EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovNo ratings yet
- Electric Gas Lighting How to Install Electric Gas Ignition ApparatusFrom EverandElectric Gas Lighting How to Install Electric Gas Ignition ApparatusRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- MITRES 6 007S11 hw09 SolDocument15 pagesMITRES 6 007S11 hw09 SolnicolasamoreiraNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics d203 ReseniDocument90 pagesFluid Mechanics d203 ReseniDennys Fabricio Ramirez100% (1)
- Telephone Network and Computer Interfaces at Communications SitesDocument4 pagesTelephone Network and Computer Interfaces at Communications SitesIzzat NaserNo ratings yet
- 09 3172report0206 53 61Document9 pages09 3172report0206 53 61Izzat NaserNo ratings yet
- Image Retrieval: Importance and Applications: João Augusto Da Silva Júnior Rodiney Elias Marçal Marcos Aurélio BatistaDocument5 pagesImage Retrieval: Importance and Applications: João Augusto Da Silva Júnior Rodiney Elias Marçal Marcos Aurélio BatistaIzzat NaserNo ratings yet
- 09 28 GraceDocument17 pages09 28 GraceIzzat NaserNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer NetworkingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Computer NetworkingIzzat NaserNo ratings yet
- 09 28 GraceDocument17 pages09 28 GraceIzzat NaserNo ratings yet