Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes: Training Objectives
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes: Training Objectives
Uploaded by
rajjsmit1989Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes: Training Objectives
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes: Training Objectives
Uploaded by
rajjsmit1989Copyright:
Available Formats
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes
Training Objectives
After watching the video and reviewing this printed material, the viewer will
gain knowledge and understanding of the stamping process and the die systems
used to form sheet metal.
• the terms “ductility” and “formability” are explained
• the essential components of the stamping process are detailed
• basic stamping terms are defined
• progressive and transfer die technology is illustrated
• die lubrication is addressed
• circle grid analysis is explained
Sheet Metal Stamping
Stamping presses and stamping dies are tools used to produce high volume sheet
metal parts. These parts achieve their shape through the effects of the die
tooling.
Production stamping is generally performed on materials .020” to .080” thick,
but the process also can be applied to foils as thin as .001” or to plate stock
with thickness' approaching 1.000”.
Formability is the primary attribute of sheet metal material. Formability is
further defined as the materials ability to be:
• bent
• stretched
• drawn
The metallurgical term for these qualities is “ductility”. Ductility is the
materials ability to deform and elongate without fracture. The extent to which a
stamping is subjected to such deformation is directly related to the part’s
overall shape and geometry. Other factors also influence the material’s
formability. They include:
• the die design
• the press
• the press speed
• lubrication
• sheet metal feeding mechanisms
• monitoring and control systems
The word “die” is a generic term used to describe the tooling used to produce
stamped parts. A die set assembly consisting of a male and female component is
the actual tool that produces the shaped stamping. The male and female
components work in opposition to both form and punch holes in the stock. The
upper half of the die set, which may be either the male or female, is mounted on
the press ram and delivers the stroke action. The lower half is attached to an
intermediate bolster plate which in turn is secured to the press bed. Guide pins
are used to insure alignment between the upper and lower halves of the die set.
Fundamental Manufacturing Processes Video Series Study Guide - 1 -
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes
The most common types of dies perform cutting and forming. Cutting dies are used
to shear sheet material into what is called a blank. These blanks are then
exposed to blanking dies which cut the entire perimeter of the part, or to
forming dies where the blank is stamped into a part. Punching is another
function of cutting dies. Punching is the cutting of a slug from the sheet metal
stock to produce a hole or slot. Cutting dies are also used to trim excess metal
from around a formed part.
Hole punching and other cutting operations require specific and carefully
maintained clearances between the punch (male component) and the die (female
component). The setting of the required clearances is determined by both the
stock thickness and temper. In general, die clearances increase as the stock
thickness increases. The depth of punch penetration into the sheet metal stock
will also increase as softer stock is used.
Forming is a general term used to describe a stamped part whose shape and
contour is reproduced directly from the shape and contour of a die set. The main
forming operations accomplished with press mounted dies are:
• drawing
• bending
• flanging
• hemming
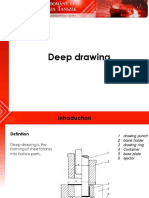
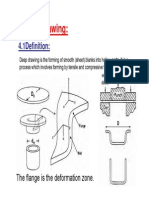
Drawing, or draw forming, involves forcing a blank deeply into a die cavity and
shaping it into the shape and contour of the punch face and sides. Without
sufficient formability qualities, drawn blanks are subject to wrinkling,
thinning, and fracturing. Draw forming requires an addition to the die set
called a blankholder. The function of the blankholder, usually a ring through
which the punch and ram pass, is to control the metal flow as it is forced into
the die cavity. In practice, the blankholder must exert less pressure against
the blank than the punch, so metal can flow into the die; yet it must exert
enough pressure to prevent the material from wrinkling.
Bending is a relatively simple forming operation which provides rigidity and
shape to sheet metal parts. Similar to bending is flanging. However a flange is
significantly smaller in dimension than the rest of the part. The functions of a
flange include:
• giving a more finished appearance
• rigidity
• edge strengthening
• providing a fastening or attachment surface
Hemming is the folding over of a short flange upon itself to form a smooth,
rounded edge and to facilitate the attachment of mating parts.
Multiple stamping operations may be performed within a single die, or at a
number of die stations within a die set and with a single stroke of the press.
Single station dies can be either compound dies or combinations dies. A compound
die performs basic cutting operations such as blanking and hole punching to
produce parts. Combination dies combine shaping and forming functions with
cutting operation to manufacture parts.
Fundamental Manufacturing Processes Video Series Study Guide - 2 -
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes
Multiple station dies are arranged so that a series of sequential operations are
accomplished with each press stroke. Two die types are used; progressive and
transfer. With progressive dies, coil stock is fed into the press. Individual
stampings are connected with a carrier strip as they progress through the
various die operations and are ultimately separated and then discharged from the
press. In transfer die operations individual stock blanks are mechanically moved
from die station to die station within a single die set. Large stampings are
done with tandem press lines where the stock is moved from press to press in
which specific operations, such as drawing or trimming, are performed.
The resistance of the sheet metal stock to the forces exerted by the moving dies
creates friction. For this reason, lubrication is vital for successful sheet
metal forming. A lubrication's function is to minimize contact between the
tooling and the work piece. This results in reduced tonnage requirements, longer
tooling life, and improved product quality.
Lubricants range from light mineral oils to high viscosity drawing compounds.
They may be oil base, water soluble, or synthetic materials. These lubricants
may be applied in a variety of ways, including:
• manually by roller or brush
• drip
• machine roller
• spraying
• flooding
Die making is as much of an art as a science. When all the dynamics of stamping
are taken into account, the resulting part may not meet all expectations. To
help fine tune the stamping process and finalize die design, die makers use an
analytical tool called Circle Grid Analysis, or CGA. The application of CGA
involves the etching of a pattern of small circles on the surface of the blank.
This pattern deforms along with the blank as it is formed, providing point-to-
point calculations of the deformation that occurred. Analyzing this stamped grid
pattern suggests the location and type of rework that must be performed on the
dies to produce easily manufactured parts. The CGA process is repeated on the
die until an acceptable part is produced.
Fundamental Manufacturing Processes Video Series Study Guide - 3 -
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes
Review Questions
1. Most sheet metal stamping uses materials:
a. .020 to .080 thick
b. .050 to .125 thick
c. .001 to 1.000 thick
d. .010 to .100 thick
2. Ductility refers to a material’s ability to:
a. resist penetration
b. resist corrosion
c. bend over upon itself
d. deform and elongate
3. A compound die is a die that performs:
a. hemming and flanging
b. blanking and hole punching
c. bending only
d. hole punching only
4.. The device(s) used to insure die component alignment are called:
a. roller bearings
b. ways
c. guide pins
d. "v" grooves
5. The terms drawing, flanging, and hemming are examples of:
a. forming
b. punching
c. slitting
d. extruding
6. A carrier strip is used with:
a. transfer dies
b. progressive dies
c. tandem presses
d. combination dies
7. The principle function of a lubricant in press stamping is to:
a. cool the dies
b. enable easy stack removal
c. prevent wrinkling
d. minimize tool contact to the work
8. Circle Grid Analysis, or CGA, is used to:
a. calculate tonnage exerted on the work
b. predict deformation distances
c. finalize die design
d. determine optimum press speed
Fundamental Manufacturing Processes Video Series Study Guide - 4 -
Sheet Metal Stamping Dies & Processes
Answer Key
1. a
2. d
3. b
4. c
5. a
6. b
7. d
8. c
Fundamental Manufacturing Processes Video Series Study Guide - 5 -
You might also like
- Punch and DieDocument16 pagesPunch and DieNani DatrikaNo ratings yet
- Deep DrawDocument4 pagesDeep DrawBalvinder PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Progressive Die DesignDocument1 pageProgressive Die DesignRodrigo Iyomasa0% (1)
- Design and Calculations of Piercing & Blanking DieDocument89 pagesDesign and Calculations of Piercing & Blanking DieVipul MetaNo ratings yet
- Press Tool Design PPT Module 1Document48 pagesPress Tool Design PPT Module 1janak100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Tool and Die DesignDocument70 pagesChapter 4 Tool and Die Designdawit solomonNo ratings yet
- 3 Die CuttingDocument41 pages3 Die CuttingNarendrareddy RamireddyNo ratings yet
- Types of DiesDocument17 pagesTypes of DiesJayditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Die DesignDocument102 pagesChapter 4 Die DesignTamirat Nemomsa100% (3)
- Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume III: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #3From EverandPlastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume III: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #3No ratings yet
- 04 Cutting ClearanceDocument18 pages04 Cutting Clearancegaurav deshmukhNo ratings yet
- DiesDocument4 pagesDiesjohan pambudiNo ratings yet
- Tool Design - Chapter 4 (Part 4)Document22 pagesTool Design - Chapter 4 (Part 4)Fiq IFTNo ratings yet
- Tool Design - Chapter 4 (Part 3)Document59 pagesTool Design - Chapter 4 (Part 3)Fiq IFT100% (1)
- Sheet Metal Forming (2) - 2Document30 pagesSheet Metal Forming (2) - 2Wakahare PtahNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Press ToolsDocument31 pages01 Introduction To Press ToolsNiranjan HalgarNo ratings yet
- DieDocument6 pagesDieAditya GoelNo ratings yet
- Presstool MasterDocument111 pagesPresstool MasterRajesh Kumar100% (2)
- Sheet Metal Processes BendingDocument11 pagesSheet Metal Processes BendingYashvir SinghNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal FormingDocument25 pagesSheet Metal Formingankushkapoor2003No ratings yet
- Stock Strip LayoutDocument3 pagesStock Strip LayoutSwaran Singh67% (3)
- 5 Strip LayoutDocument28 pages5 Strip LayoutNarendrareddy Ramireddy67% (3)
- Computing Die Thickness and MarginsDocument3 pagesComputing Die Thickness and MarginsAnand PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- 03 Cutting ForceDocument3 pages03 Cutting ForceAhmad Mustaghfiri Asrar100% (1)
- Fine Blanking PDFDocument33 pagesFine Blanking PDFClaudineiFerreiraAndréNo ratings yet
- Fine BlankingDocument26 pagesFine BlankingHarish Ks100% (1)
- Metal Forming LabDocument57 pagesMetal Forming LabRohitGuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 ShearingDocument29 pages1 ShearingSriram MuruganNo ratings yet
- EIN 3390 Chap 17 Sheet-Forming Processes Part 1 Spring 2012Document50 pagesEIN 3390 Chap 17 Sheet-Forming Processes Part 1 Spring 2012sudharsans88No ratings yet
- Deep Drawing: Deep Drawing Is A Sheet Metal Forming Process in Which A Sheet Metal Blank Is Radially DrawnDocument4 pagesDeep Drawing: Deep Drawing Is A Sheet Metal Forming Process in Which A Sheet Metal Blank Is Radially DrawnbrahimNo ratings yet
- Deep Drawing UhuyyyyDocument20 pagesDeep Drawing UhuyyyyeltonNo ratings yet
- Strip LayoutDocument35 pagesStrip LayoutJay PatelNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Design of Blanking Tool For Washer Special: Nandish Harti DR D. RamegoudaDocument4 pagesConceptual Design of Blanking Tool For Washer Special: Nandish Harti DR D. Ramegoudaaravindan476No ratings yet
- Press ToolDocument12 pagesPress ToolJitendra Bhole100% (2)
- Press Working TerminologyDocument16 pagesPress Working TerminologyAadrika UmashankarNo ratings yet
- Fine BlankingDocument9 pagesFine BlankingElaine JohnsonNo ratings yet
- E2 Deep DrawingDocument43 pagesE2 Deep DrawingAllen MarshNo ratings yet
- Press ToolDocument71 pagesPress Toolamolnjainajgmail.com 7507254906No ratings yet
- Flowforming or Metal Spinning (Spin Forming)Document2 pagesFlowforming or Metal Spinning (Spin Forming)ShivajiNo ratings yet
- Broaching BasicsDocument5 pagesBroaching Basicssaritha0003No ratings yet
- Sheet MetalDocument21 pagesSheet MetalRam Janm Singh100% (2)
- T&D - Core 4 Tool & DieDocument44 pagesT&D - Core 4 Tool & Dietisha revillaNo ratings yet
- Press Tool CalculationDocument76 pagesPress Tool CalculationPrashant AmbadekarNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal-Cup DrawingDocument25 pagesSheet Metal-Cup DrawingCADTDD100% (1)
- Side CutterDocument7 pagesSide Cutterbabuty100% (2)
- Course Material TwoDay Workshop Sheetemetal DHIO GTTCDocument132 pagesCourse Material TwoDay Workshop Sheetemetal DHIO GTTChsvjvv100% (1)
- SHEARINGDocument6 pagesSHEARINGanmol6237No ratings yet
- MLD TheoryDocument96 pagesMLD TheorySheik Abdullah100% (1)
- PressWorking SDocument49 pagesPressWorking SRafiqueNo ratings yet
- Types of Press Tools - Wikipedia PDFDocument24 pagesTypes of Press Tools - Wikipedia PDFAvula VinayNo ratings yet
- 4 Deep DrawingDocument26 pages4 Deep Drawingmck_medo100% (1)
- Seminar On Split Cavity MouldDocument43 pagesSeminar On Split Cavity MouldasgrutuNo ratings yet
- Compound Die Design: A Case Study: Sneha S. Pawar, R. S. DaluDocument4 pagesCompound Die Design: A Case Study: Sneha S. Pawar, R. S. DaluchupchapNo ratings yet
- DV11PUB9 Study GuideDocument5 pagesDV11PUB9 Study Guider_saniosNo ratings yet
- DV11PUB9 Study Guide PDFDocument5 pagesDV11PUB9 Study Guide PDFEnriqueGDNo ratings yet
- StampingDocument2 pagesStampingKapiel KatariaNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal OperationsDocument27 pagesSheet Metal OperationsbmvinayNo ratings yet
- Die Basics 101: Intro To Stamping: Stamping (Metalworking) Stamping PressingDocument30 pagesDie Basics 101: Intro To Stamping: Stamping (Metalworking) Stamping PressingAmitNo ratings yet
- Six Weeks Industrial Training ReportDocument27 pagesSix Weeks Industrial Training ReportGagan Deep100% (2)
- Design Guidelines: Basic OperationsDocument2 pagesDesign Guidelines: Basic OperationsLokesh NarasimhaiahNo ratings yet
- SM PDF Chapter2Document28 pagesSM PDF Chapter2kyara906No ratings yet
- Slope Stability in Slightly Fissured Claystones and MarlsDocument25 pagesSlope Stability in Slightly Fissured Claystones and MarlsrullyirwandiNo ratings yet
- Gprprinciplescomponents 161126115646Document26 pagesGprprinciplescomponents 161126115646arunNo ratings yet
- What Is Filtration?Document17 pagesWhat Is Filtration?Muhammad Awais SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Burkert Type2000, PneumaticDocument29 pagesBurkert Type2000, PneumaticGL Thiết Bị Công NghiệpNo ratings yet
- Specification: WEW Series Computer Display Hydraulic Universal Testing MachineDocument2 pagesSpecification: WEW Series Computer Display Hydraulic Universal Testing MachinecathyNo ratings yet
- Iso 21940 1 2019Document12 pagesIso 21940 1 2019Inspección refamecaNo ratings yet
- Agitator DesignDocument8 pagesAgitator DesignCMEngineersNo ratings yet
- A. 77.65% B. 87.6% C. 97 TR D. 68.65%Document94 pagesA. 77.65% B. 87.6% C. 97 TR D. 68.65%LordesNo ratings yet
- Module Exercise 3 - KTG and Thermodynamics 1677647248245Document4 pagesModule Exercise 3 - KTG and Thermodynamics 1677647248245shiladityabarua072No ratings yet
- G-Tech Rotary Lobe Pump OIM Manual PDFDocument23 pagesG-Tech Rotary Lobe Pump OIM Manual PDFGiorgiana Rosu100% (1)
- 9.2 Electrochemical CellsDocument31 pages9.2 Electrochemical Cells昊元No ratings yet
- Simulating Electrohydraulic Soft Actuator Assemblies Via Reduced Order ModelingDocument8 pagesSimulating Electrohydraulic Soft Actuator Assemblies Via Reduced Order Modelingblrrrgh333No ratings yet
- Study of Reliability Analysis of CVT SystemDocument13 pagesStudy of Reliability Analysis of CVT Systemswapnil pandeNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument43 pagesSound WavesAyush SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Surface Properties and Surface Characterization-2-1Document61 pagesSurface Properties and Surface Characterization-2-1a.vidhya 12345No ratings yet
- Materials System SpecificationDocument9 pagesMaterials System SpecificationHandri YantoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S092422441730818X MainDocument18 pages1 s2.0 S092422441730818X MainTanakorn RachapilaNo ratings yet
- Ajme 1 7 24Document6 pagesAjme 1 7 24Hoai Anh VuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Mod. 7.Document23 pagesFluid Mechanics Mod. 7.Rianie Taguiam CiprianoNo ratings yet
- Screening 7Document4 pagesScreening 7Ramon Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Kulkarni's Academy All India Scholarship Test Paper Answer Key and Solutions PDFDocument33 pagesKulkarni's Academy All India Scholarship Test Paper Answer Key and Solutions PDFMurali Krishna TNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 285 Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: Lecture Notes Assoc. Prof. Joel R. SalazarDocument102 pagesChemistry 285 Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: Lecture Notes Assoc. Prof. Joel R. SalazarAlyssa BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Basics of Hydrostatic Level Measurement Instrumentation ToolsDocument7 pagesBasics of Hydrostatic Level Measurement Instrumentation ToolsAbarajithan RajendranNo ratings yet
- Reboiler and VaporiserDocument56 pagesReboiler and Vaporiserjihad jamareiNo ratings yet
- Williamson HallDocument8 pagesWilliamson HallAnvay ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- BASF Plastic Material DatasheetDocument24 pagesBASF Plastic Material DatasheetshafiqNo ratings yet
- B 80 - 01 - Qjgwltax PDFDocument11 pagesB 80 - 01 - Qjgwltax PDFessai expertiseNo ratings yet
- Test CertificateDocument2 pagesTest CertificatePRITESH100% (2)
- Case Study: CSTR StabilizationDocument8 pagesCase Study: CSTR StabilizationΜιχάλης ΝικολάουNo ratings yet