Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conditional Sentences Formula
Conditional Sentences Formula
Uploaded by
riarifOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conditional Sentences Formula
Conditional Sentences Formula
Uploaded by
riarifCopyright:
Available Formats
CONDITIONAL SENTENCES FORMULA
Conditional sentences are built of two sentences, they are;
1. If Clause
2. Main Clause
Conditional sentences are divided into three types, they are;
1. Type I (probable condition)
2. Type II (present unreal)
3. Type III (past unreal)
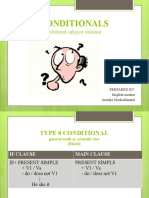
TYPE I
IF + SIMPLE PRESENT (S + VERB1 + S/ES), SIMPLE FUTURE (S + WILL/SHALL + VERB1)
T Y P E II
IF + SIMPLE PAST (S + VERB2), PAST FUTURE (S + WOULD/SHOULD + VERB1)
T Y P E III
IF + PAST PERFECT (S + HAD + VERB3), PAST FUTURE PERFECT (S + WOULD/SHOULD + HAVE + VERB3)
Example:
- If I have a car, I will go to Balikpapan. (Type I)
- If I had a car, I would go to Balikpapan. (Type II)
- If I had had a car, I would have gone to Balikpapan (Type III)
There will be three possible questions occur for Conditional, they are;
1. If clause,………. (It means, we have to find the main clause of the sentence)
2. ………., main clause (It means, we have to find the If clause of the sentence)
3. If clause, main clause (It means, we have to find the meaning of the sentence)
TYPE I
MAYBE/PERHAPS/PROBABLY + SIMPLE PRESENT (S + VERB1 + S/ES)
T Y P E II
SIMPLE PRESENT (S + VERB1 + S/ES) (The fact of the sentence is contradictive to the real
condition)
T Y P E III
SIMPLE PAST (S + DIDN’T + VERB1) (The meaning is always negative)
Example:
1. If I have a car, I will go to Balikpapan.
- Maybe I have a car, so I go to Balikpapan.
2. If I had a car, I would go to Balikpapan.
- I don’t have a car, so I don’t go to Balikpapan.
3. If I had had a car, I would have gone to Balikpapan.
- I didn’t have a car, so I didn’t go to Balikpapan
You might also like
- Conditional SentenceDocument4 pagesConditional SentenceAmelia SaphiraNo ratings yet
- Untuk Bahasa Inggris Conditional SentenceDocument4 pagesUntuk Bahasa Inggris Conditional SentenceAnnisaIstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Conditional Class Full NotesDocument13 pagesConditional Class Full NotesThangavel Raj JNo ratings yet
- Conditionals: Download My Infographic!Document2 pagesConditionals: Download My Infographic!Bogdan Victor FeresteanuNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument1 pageGrammarYou NesNo ratings yet
- Type 0, Type 1, Type 2 and Type 3.: Conditionals ConditionalsDocument6 pagesType 0, Type 1, Type 2 and Type 3.: Conditionals ConditionalsAnca ȘtefănescuNo ratings yet
- Conditionals ToeflDocument3 pagesConditionals Toeflseb_streitenbergerNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALs I, II, III-theoryDocument4 pagesCONDITIONALs I, II, III-theoryRandom EditzNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences All TypesDocument14 pagesConditional Sentences All TypessirtayyabNo ratings yet
- What Are Conditionals in English Grammar?: The Zero ConditionalDocument3 pagesWhat Are Conditionals in English Grammar?: The Zero ConditionalSamina ShamimNo ratings yet
- Conditionals CheatsheetDocument1 pageConditionals Cheatsheetmr.rudyNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence: V1+s/es / (-) Does Not+v1 Is/am/are+ A/N/ADocument2 pagesConditional Sentence: V1+s/es / (-) Does Not+v1 Is/am/are+ A/N/AIkaHesti PratiwiNo ratings yet
- DirectionDocument2 pagesDirectionYUMRINo ratings yet
- If ClausesDocument13 pagesIf ClausesYunanda Alya MustikaNo ratings yet
- Trik Rahasia Tes Potensi AkademikDocument13 pagesTrik Rahasia Tes Potensi AkademikZonia febianiNo ratings yet
- If Clause Main Clause: Conditional Sentences Important Points To Remember: I. Conditional Sentences Type 1Document10 pagesIf Clause Main Clause: Conditional Sentences Important Points To Remember: I. Conditional Sentences Type 1Chuong VoNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument9 pagesConditional SentencesManal CherifNo ratings yet
- If ClausesDocument4 pagesIf Clausesadriandobre2014No ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences / If-Clauses Type I, II, IIIDocument2 pagesConditional Sentences / If-Clauses Type I, II, IIIBobby ZNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument40 pagesConditionalshakimNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences (Kalimat Pengandaian)Document4 pagesConditional Sentences (Kalimat Pengandaian)gn_X00No ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument21 pagesConditional Sentencesherrys79100% (1)
- Conditional Clause and Main ClauseDocument5 pagesConditional Clause and Main ClauseRatnaNo ratings yet
- Xercise Conditional Sentences Type 1,2,3Document9 pagesXercise Conditional Sentences Type 1,2,3FlashNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument5 pagesConditional SentenceSelina MardiyanaNo ratings yet
- Nama: Wa Ode Nursakinah NIM: A201901086 Kelas: E3 Tugas: Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesNama: Wa Ode Nursakinah NIM: A201901086 Kelas: E3 Tugas: Bahasa InggrisWdnursakinahNo ratings yet
- (If + Present Simple, ... Present Simple) : The Zero ConditionalDocument3 pages(If + Present Simple, ... Present Simple) : The Zero ConditionalJonat ChNo ratings yet
- The Conditional Sentence (IF Clause) : First TypeDocument2 pagesThe Conditional Sentence (IF Clause) : First TypeNaailRiaamNo ratings yet
- 6a Hè Conditional SentencesDocument4 pages6a Hè Conditional SentencesLin TranNo ratings yet
- Ly Thuyet - Cau Dieu KienDocument2 pagesLy Thuyet - Cau Dieu Kienchâm thanhNo ratings yet
- Conditionals RulesDocument2 pagesConditionals RulesAngelo DaraziNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument4 pagesConditional SentencesSnakegreemNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences (Type Ii)Document11 pagesConditional Sentences (Type Ii)Arief Hyuk JaeNo ratings yet
- If Clauses EnglishDocument13 pagesIf Clauses EnglishMaiden DiNo ratings yet
- Conditional Clause and Main ClauseDocument3 pagesConditional Clause and Main ClauseYoga IputuNo ratings yet
- Teori Conditional SentencesDocument3 pagesTeori Conditional SentencesamelianiNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences "IF" and "Wish": (Kalimat Pengandaian)Document12 pagesConditional Sentences "IF" and "Wish": (Kalimat Pengandaian)Jd HermawanNo ratings yet
- Lesson On Conditional SentencesDocument2 pagesLesson On Conditional SentencesMarina PeshovskaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Three Types Lesson EasyDocument5 pagesConditional Three Types Lesson EasyHassan Ait AddiNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences Kelas XII SMT 2Document5 pagesConditional Sentences Kelas XII SMT 2bondan iskandarNo ratings yet
- Conditional Sentences: By: Ms. Nensi Arfika Dewi, S.PDDocument7 pagesConditional Sentences: By: Ms. Nensi Arfika Dewi, S.PDnensi ArdeNo ratings yet
- 1.a.IF-CLAUSES (0,1,2,3.types) - 2-2Document2 pages1.a.IF-CLAUSES (0,1,2,3.types) - 2-2joanaNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentenceDocument30 pagesConditional SentenceNeltza SiregarNo ratings yet
- Maryati (Tugas B.Inggris)Document3 pagesMaryati (Tugas B.Inggris)Riska AdeyanaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Advan 1Document6 pagesConditional Advan 1mariaeoiNo ratings yet
- BachillerDocument5 pagesBachillerFatima VazquezNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument2 pagesConditionalSylvie ChamberlandNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument15 pagesConditional Sentencesmikayla septiaNo ratings yet
- Conditionals FinalDocument9 pagesConditionals FinalAnastasija DavlesevicNo ratings yet
- 2 - Fce - Conditional 0123 Rules 2015Document10 pages2 - Fce - Conditional 0123 Rules 2015Alba Fortuny HueteNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument6 pagesConditionalswara2030No ratings yet
- Passive VoiceDocument4 pagesPassive VoicevelwynallectiusNo ratings yet
- Ud4 Comunicacion Prof InglesDocument19 pagesUd4 Comunicacion Prof InglesJose Miguel Ortega AndresNo ratings yet
- Conditionals PatternsDocument6 pagesConditionals PatternsOleseaNo ratings yet
- First, Second, Third ConditionalDocument12 pagesFirst, Second, Third ConditionalGünel BayramovaNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument5 pagesConditionalDiya GarciaNo ratings yet
- Conditional Clause and Main ClauseDocument22 pagesConditional Clause and Main ClauseTita RashidaNo ratings yet
- If (Conditional) ClauseDocument2 pagesIf (Conditional) ClauseRiza LuthfiNo ratings yet
- If Clauses Conditional With QuestionsDocument22 pagesIf Clauses Conditional With QuestionsAroshani LiyanageNo ratings yet