Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lenzs Law
Uploaded by
Muhammad Bin Anis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views17 pagesLenz's law states that (1) an induced current will flow in a closed conducting loop when the magnetic flux through the loop changes, and (2) the direction of this induced current will be such that it creates its own magnetic field opposing the original change in flux. (3) Examples are given of how the direction of induced current in a coil changes as a magnet passes through it based on Lenz's law.
Original Description:
Original Title
lenzs_law
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLenz's law states that (1) an induced current will flow in a closed conducting loop when the magnetic flux through the loop changes, and (2) the direction of this induced current will be such that it creates its own magnetic field opposing the original change in flux. (3) Examples are given of how the direction of induced current in a coil changes as a magnet passes through it based on Lenz's law.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views17 pagesLenzs Law
Uploaded by
Muhammad Bin AnisLenz's law states that (1) an induced current will flow in a closed conducting loop when the magnetic flux through the loop changes, and (2) the direction of this induced current will be such that it creates its own magnetic field opposing the original change in flux. (3) Examples are given of how the direction of induced current in a coil changes as a magnet passes through it based on Lenz's law.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
LENZ’S LAW
Heinrich F.E. Lenz
• Russian physicist
• (1804-1865)
• 1834 Lenz’s Law
• There is an induced current
in a closed conducting loop
if and only if the magnetic
flux through the loop is
changing. The direction of
the induced current is such
that the induced magnetic
field always opposes the
change in the flux.
There is an induced current in a closed conducting loop if and only if
the magnetic flux through the loop is changing. The direction of the
induced current is such that the induced magnetic field always opposes
the change in the flux.
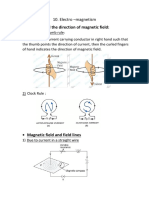
Right Hand Rule
• If you wrap your
fingers around the
coil in the direction
of the current, your
thumb points
north.
If the field of the bar magnet is already in the loop and the
magnet is removed, the induced current is in the direction that
tries to keep the field constant
2 Direction of induced current
b Lenz's law
In both cases, magnet m
oves against a force.
Work is done during th
e motion & it is transferr
ed as electrical energy.
Induced I always flows to oppose the
movement which started it.
Example 1
Current induced along a coil
A bar magnet passes through a coil:
(i) (ii) (iii)
(a) Indicate the direction of the induced I in
each case. Explain briefly.
Example 1
Current induced along a coil
(a) Indicate the direction of the induced I. Explain.
S N
When magnet’s N-pole is moving
I into coil,
(i) induced I flows in such a direction as
to produce a N-pole
Lenz’s
law to oppose the approaching of magnet.
Example 1
Current induced along a coil
(a) Indicate the direction of the induced I. Explain.
(ii)
The induced I become zero
I is about to change direction.
Example 1
Current induced along a coil
(a) Indicate the direction of the induced I. Explain.
N S
(iii)
When magnet’s S-pole is leaving the coil,
induced I flows in such a direction as to
produce a N-pole to oppose the leaving of
magnet.
Lenz’s Law
• Alternating current
through the coil
• What happens to Iron
core?
• What will happen to
the ring?
Lenz’s Law
• The changing magnetic
field in the coil due to the
change in current induces
a current in the metal ring.
Lenz’s Law states that the
magnetic field in the ring
opposes the magnetic field
of the coil and forces the
ring to fly away.
Lenz’s Law
• What just happened?
• How often does this
occur?
Applications of Magnetic Induction
• Magnetic Levitation (Maglev) Trains
• Induced surface (“eddy”) currents produce field in opposite
direction
Repels magnet
Levitates train
S
N
rails
“eddy” current
• Maglev trains today can travel up to 310 mph
Twice the speed of Amtrak’s fastest conventional train!
liner induction
0-70 mph in 3 sec
liner induction
FALLING MAGNET
• the copper tube "sees" a
changing magnetic field
from the falling magnet.
This changing magnetic
field induces a current in
the copper tube.
• The induced current in
the copper tube creates
its own magnetic field
that opposes the
magnetic field that
created it.
You might also like
- Lenzs LawDocument17 pagesLenzs Lawlateh72006No ratings yet
- Lenzs LawDocument17 pagesLenzs LawGanesh LadNo ratings yet
- Lenzs LawDocument17 pagesLenzs LawGanesh LadNo ratings yet
- EMI - Part-1Document33 pagesEMI - Part-1krishoreraj23No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1Document13 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Experiment 1midhunesh41No ratings yet
- Identifying Poles Of An Electromagnet:: Emf = −Dnϕ DtDocument3 pagesIdentifying Poles Of An Electromagnet:: Emf = −Dnϕ DtIntiser RahmanNo ratings yet
- CH 23 EM Induction AC Circuits PDFDocument88 pagesCH 23 EM Induction AC Circuits PDFShane Patrick PanilagNo ratings yet
- CH6 Formula SheetDocument11 pagesCH6 Formula SheetNancy SinghNo ratings yet
- LH111 - 30th Dec - ELL101 Magnetic CouplingDocument23 pagesLH111 - 30th Dec - ELL101 Magnetic CouplingDivyansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic InductionParth GuptaNo ratings yet
- Nagnetic InductionDocument102 pagesNagnetic InductionAyush ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Magnetic Induction, Inductance, Ac and LC CircuitsDocument13 pagesChapter 7 Magnetic Induction, Inductance, Ac and LC CircuitsShara TayonaNo ratings yet
- Walker, Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday's Law of InductionDocument31 pagesWalker, Chapter 23 Magnetic Flux and Faraday's Law of InductionMohsin RazaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics - Stationary ChargesDocument39 pagesElectrostatics - Stationary ChargesmkanwarsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: The Experiments of Faraday and HenryDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: The Experiments of Faraday and HenryNikhil SinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument15 pagesElectromagnetic InductionLaili Fauziah100% (1)
- ElectromagneticInduction 65080Document13 pagesElectromagneticInduction 65080user 003No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument4 pagesElectromagnetic InductionMonica SreeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 PH128 Faraday Law of InductionDocument43 pagesLecture 3 PH128 Faraday Law of InductionKennedy Oswald AikaruwaNo ratings yet
- Induction and The GeneratorDocument56 pagesInduction and The GeneratorGular JabrayilovaNo ratings yet
- Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocument3 pagesLaw of Electromagnetic InductionnonofogoitsemodimoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesElectromagnetic InductionEs ENo ratings yet
- EMI NEW - MergedDocument16 pagesEMI NEW - MergedRabeeh AhmadNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument14 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentREHANNo ratings yet
- Physics Value Based Questions Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction PDFDocument35 pagesPhysics Value Based Questions Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction PDFMohammad HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetism: The Magnetic Effect of A CurrentDocument7 pagesElectro Magnetism: The Magnetic Effect of A CurrentShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- z1 ElectromagneticInduction1Document7 pagesz1 ElectromagneticInduction1Gan PentonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument26 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionqpncsoriano100% (1)
- Electromgnetic InductionDocument5 pagesElectromgnetic InductionGhanshyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Short NotesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetism Short Notespadhaai karoNo ratings yet
- Faradays Law of InductionDocument41 pagesFaradays Law of Inductionashraf_khimaniNo ratings yet
- Notes of Magnetic Effects of Current Class XDocument14 pagesNotes of Magnetic Effects of Current Class Xskshiarora12No ratings yet
- Lenz's Law NotesDocument3 pagesLenz's Law Notesʀᴀᴍᴇʟᴀ ᴍᴀʜɪʟᴜᴍNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction LecturesDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Induction LecturesDoyen DanielNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Circuits and TransformersDocument10 pagesMagnetic Circuits and TransformersSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Year 12 E-Note PhyDocument77 pagesYear 12 E-Note Phyjeffersonawesome28No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thDocument27 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thsyedyaseen39375No ratings yet
- Self InductanceDocument11 pagesSelf Inductanceحفيظو عبدالله100% (1)
- Chapter-13 Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument19 pagesChapter-13 Magnetic Effect of CurrentSuhani GosainNo ratings yet
- 13 Magnetic Effects of Electricity 1Document28 pages13 Magnetic Effects of Electricity 1Ranvijay RajputNo ratings yet
- Airgaps in Magnetic CircuitsDocument20 pagesAirgaps in Magnetic CircuitsLeo WongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Class 10th PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 15 Class 10th PDFMuneer Kaleri75% (4)
- Magnetic Effects of Ec-Part1Document6 pagesMagnetic Effects of Ec-Part1Prisoner FFNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Notes Chpt2Document11 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current Notes Chpt2Sarathrv Rv100% (2)
- Electromagnetic Induction (Topic 11)Document8 pagesElectromagnetic Induction (Topic 11)Daniel ChoiNo ratings yet
- Analysing Electromagnetic InductionDocument21 pagesAnalysing Electromagnetic InductionsazlimanismailNo ratings yet
- Induced Emf.: Faraday's Law. Lenz's LawDocument18 pagesInduced Emf.: Faraday's Law. Lenz's LawDedar RashidNo ratings yet
- Elect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldDocument8 pagesElect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldIsmail MzavaNo ratings yet
- MagnetisumDocument20 pagesMagnetisumPpppNo ratings yet
- 11.2.1 Lenzs Law Part 1Document7 pages11.2.1 Lenzs Law Part 1FishBowl GangNo ratings yet
- Magnetics Main Part 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMagnetics Main Part 1 PDFAnonymousNo ratings yet
- ElectroMagnetic InductionDocument13 pagesElectroMagnetic InductionAndre MorrisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document21 pagesChapter 5badrilaminNo ratings yet
- 10th Standard Science: Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument18 pages10th Standard Science: Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentNANDANA BSNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Document43 pagesMagnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Heidi QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Electromagnetism: Magnetic Field PatternDocument29 pagesChapter 3: Electromagnetism: Magnetic Field PatternNur ArafahNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Analysing Electromagnetic InductionDocument11 pages3.3 Analysing Electromagnetic Inductionpanitiafiziksmkb100% (2)
- Magnetic Field NotesDocument7 pagesMagnetic Field NotesroverstechnicalNo ratings yet
- 2 1 PDFDocument18 pages2 1 PDFالمهندسوليدالطويلNo ratings yet
- Conditions, Switch, While Loop, and For LoopDocument22 pagesConditions, Switch, While Loop, and For LoopM MNo ratings yet
- Attacks Classification in Network Intrusion Detection System Using ANNDocument4 pagesAttacks Classification in Network Intrusion Detection System Using ANNInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- P3M30 32 en M J006 ANSI WebDocument438 pagesP3M30 32 en M J006 ANSI WebUbiratã PaulaNo ratings yet
- MSD Pro-Billet Small Diameter Chevrolet V8 Distributor: ImportantDocument8 pagesMSD Pro-Billet Small Diameter Chevrolet V8 Distributor: ImportantJorgeNo ratings yet
- Fire Fighting Robotic Vehicle: Project OnDocument25 pagesFire Fighting Robotic Vehicle: Project OnRuman Guha NiyogiNo ratings yet
- Ion-Valve Oscillators and Ion-Valve Converters Technologies (Who's Who in Free Energy)Document74 pagesIon-Valve Oscillators and Ion-Valve Converters Technologies (Who's Who in Free Energy)ernieespells1jtkl56100% (19)
- Prescriptive AnalyticsDocument7 pagesPrescriptive AnalyticsAlfredo Romero GNo ratings yet
- How To Investigate and Optimize LTE Throughput in 5 Steps ?: Let's Talk About Throughput OptimizationDocument10 pagesHow To Investigate and Optimize LTE Throughput in 5 Steps ?: Let's Talk About Throughput OptimizationMohamed HaronNo ratings yet
- Arduino Basics - 433 MHZ RF Module With Arduino Tutorial 2Document13 pagesArduino Basics - 433 MHZ RF Module With Arduino Tutorial 2habaoanhNo ratings yet
- CGC Fouling CheckDocument19 pagesCGC Fouling CheckAnonymous KpVxNXs100% (1)
- SMC4-4-16A16B Four-Axis Motion Controller Instruction ManualDocument14 pagesSMC4-4-16A16B Four-Axis Motion Controller Instruction ManuallucaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3Document8 pagesLab 3Mian BlalNo ratings yet
- Material HPLCDocument19 pagesMaterial HPLCIsmil ImamaNo ratings yet
- Sizing of CUCMDocument14 pagesSizing of CUCMgopik85No ratings yet
- Greek Alphabet Made Easy 1-3Document9 pagesGreek Alphabet Made Easy 1-3sakazuluNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Engine Management SystemDocument10 pagesBasic Electronics Engine Management SystemRailyn Tagwalan Timol100% (1)
- Balok 30x50 PDFDocument4 pagesBalok 30x50 PDFdethaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDocument35 pagesChemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDanny Jorge Huicy FernandezNo ratings yet
- 001 Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics Greiner Neise StockerDocument470 pages001 Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics Greiner Neise StockerJose GuerraNo ratings yet
- Page Maker Shortcut KeysDocument4 pagesPage Maker Shortcut KeysVenkata Sri BolaganiNo ratings yet
- NI 6132 6133 SpecificationsDocument8 pagesNI 6132 6133 SpecificationselaineNo ratings yet
- Jobmine ResumeDocument1 pageJobmine ResumeLi XuanjiNo ratings yet
- IEC 62271 202 Standards enDocument27 pagesIEC 62271 202 Standards endineshkrish80% (5)
- 86302152Document2 pages86302152Manuel BoahenNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 GeneralIntroductiontoPLCDocument44 pagesChapter1 GeneralIntroductiontoPLCBùi Văn XêNo ratings yet
- C++ Supermarket Billing Project1Document8 pagesC++ Supermarket Billing Project1Hector TrianaNo ratings yet
- Ballast Vs Ballastless Track Full PDFDocument98 pagesBallast Vs Ballastless Track Full PDFSahan100% (1)
- ArchiveDocument8 pagesArchiveMahmoud MegahedNo ratings yet
- Research On Influence Factors of Landing Gear Retractile HydraulicDocument5 pagesResearch On Influence Factors of Landing Gear Retractile HydraulicPrateek GadagiNo ratings yet