Professional Documents
Culture Documents
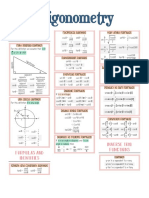
Trig Identities
Uploaded by
Neil Rohit Mallinar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views1 pageThis document provides formulas for trigonometric identities including:
1) Double angle, half angle, sum-difference, and Pythagorean identities.
2) Formulas for trig functions of complementary angles using co-function identities.
3) Formulas showing relationships between trig functions and their inverses, as well as definitions of trig functions in terms of right triangles.
4) Formulas for trig functions of negative angles using even-odd identities.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides formulas for trigonometric identities including:
1) Double angle, half angle, sum-difference, and Pythagorean identities.
2) Formulas for trig functions of complementary angles using co-function identities.
3) Formulas showing relationships between trig functions and their inverses, as well as definitions of trig functions in terms of right triangles.
4) Formulas for trig functions of negative angles using even-odd identities.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views1 pageTrig Identities
Uploaded by
Neil Rohit MallinarThis document provides formulas for trigonometric identities including:
1) Double angle, half angle, sum-difference, and Pythagorean identities.
2) Formulas for trig functions of complementary angles using co-function identities.
3) Formulas showing relationships between trig functions and their inverses, as well as definitions of trig functions in terms of right triangles.
4) Formulas for trig functions of negative angles using even-odd identities.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
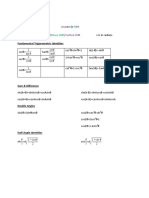
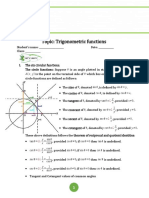
Trig Identities/BASICS
By Neil Mallinar
sin2θ = 2sinθcosθ
cos2θ = cos2 θ - sin2 θ = 1-2sin2 θ = 2cos2 θ-1 Double Angle Formulas
tan2θ = 2tan θ/1-tan2 θ
sinα/2 = ±√(1-cosα/2)
1+cosα
cos α/2 = ±√( /2) Half Angle Formulas
tan α/2 = ±√(1-cosα/1+cosα)
cos(α - β) = cosαcosβ + sinαsinβ
cos(α + β) = cosαcosβ - sinαsinβ
sin(α - β) = sinαcosβ - cosαsinβ
Sum-Difference Formulas
sin(α + β) = sinαcosβ + cosαsinβ
tan(α - β)= tanα - tanβ / 1 + tanαtanβ
tanα + tanβ
tan(α + β) = / 1 - tanαtanβ
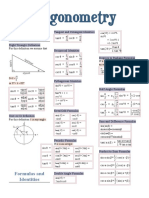
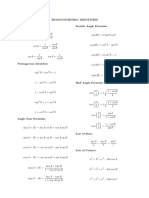
1-cos2θ
sin2θ + cos2θ = 1 sin2 θ = /2 Variations of Double Angle
1+cos2θ
1 + tan2θ = sec2θ Pythagorean Identities cos2 θ = /2 (Power Reducing Formulas)
1-cos2θ
2
1 + cot θ = csc θ 2
tan θ =
2
/1+cos2θ *Derived from Double Angle*
sin(-θ) = -sinθ Sin
cos(-θ) = cos(θ) Opposite tan = sin/cos
tan(-θ) = -tan(θ) Even-Odd Identities Hypotenuse csc = 1/sin
sec(-θ) = sec(θ) Cosine sec = 1/cos
csc(-θ) = -csc(θ) Adjacent cot = 1/tan = cos/sin
cot(-θ) = -cot(θ) Hypotenuse
Tangent
cos (π/2 - θ) = sin θ Opposite
sin (π/2 - θ) = cos θ Adjacent
tan (π/2 - θ) = cot θ Co-Function Identities
cot (π/2 - θ) = tan θ If sinθ = x then θ=sin-1x
sec (π/2 - θ) = csc θ
csc (π/2 - θ) = sec θ
You might also like
- Trig Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageTrig Cheat Sheet: by ViaNeia De JesusNo ratings yet
- Trigo 2Document2 pagesTrigo 2Julie OcolNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometric IdentitiesCarlos Manuel Rodríguez MartínezNo ratings yet
- SMC2 Formula SheetDocument1 pageSMC2 Formula SheetagamdeepNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Function Identities: Quotient Identities Reciprocal IndentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometry Function Identities: Quotient Identities Reciprocal IndentitiesCuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument1 pageTrigArnav MishraNo ratings yet
- TrigoDocument2 pagesTrigoJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument4 pagesTrigonometry: Definition of The Trig FunctionsJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- Math Resources Trigonometric FormulasDocument1 pageMath Resources Trigonometric FormulasMayank GiriNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument7 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesMarjun PachecoNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formulas R3Document3 pagesTrigonometric Formulas R3weird factsNo ratings yet
- Trig IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrig IdentitiesYishan HaiNo ratings yet
- Math 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageMath 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesalyssaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ind EntitiesDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Ind EntitiesSergio CabreraNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Trigonometric Formulas and RelationshipsDocument6 pagesSolutions: Trigonometric Formulas and RelationshipsPreethiNo ratings yet
- Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument2 pagesDefinition of The Trig FunctionsJulie OcolNo ratings yet
- TRIGO IDENTITIES1sssssDocument14 pagesTRIGO IDENTITIES1sssssRaffy CeeNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Radians and DegreesDocument5 pagesRelationship Between Radians and DegreesAlex noslenNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument3 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesAfrazia UmerNo ratings yet
- Pure Math: Topic: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument8 pagesPure Math: Topic: Trigonometric FunctionsKienNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trigo FunctionsDocument5 pagesInverse Trigo FunctionsAjay DuranNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry All Important Formulas ListDocument3 pagesTrigonometry All Important Formulas Listpifaj90517No ratings yet
- Trigonometry Formulas & Identities - Complete List of Trigonometric Formulas (Class 10 To 12)Document6 pagesTrigonometry Formulas & Identities - Complete List of Trigonometric Formulas (Class 10 To 12)ambresh.09No ratings yet
- Summary Trigident PDFDocument1 pageSummary Trigident PDFgebran sarkisNo ratings yet
- Math 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageMath 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesYunz IvensNo ratings yet
- Math 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 pageMath 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesJhan Ray Gomez BarrilNo ratings yet
- Math 126: Calculus IiDocument1 pageMath 126: Calculus IinarasimhacharibabuNo ratings yet
- Griffiths Problems 04.30 PDFDocument4 pagesGriffiths Problems 04.30 PDFdatUPstudentdoeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions and IdentityDocument20 pagesTrigonometric Functions and IdentityClarence PortoNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument19 pagesTrigonometryshwpna1979No ratings yet
- Formula RioDocument4 pagesFormula RioJoséLuisHDZ.No ratings yet
- ProductosDocument2 pagesProductosAndres hurtadoNo ratings yet
- Trigo Formula 20-21Document3 pagesTrigo Formula 20-21ForpdfsNo ratings yet
- Prove The Following. Show Complete Solutions.: SolutionDocument4 pagesProve The Following. Show Complete Solutions.: SolutionRaycelyn Joy CaburnayNo ratings yet
- H Essential TrigDocument1 pageH Essential TriglilxinNo ratings yet
- Corrections Trigo2023Document4 pagesCorrections Trigo2023bentodesaNo ratings yet
- Main Trig Functions Cheat Sheet SlacDocument2 pagesMain Trig Functions Cheat Sheet SlacIvanilson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Basic Cal IdentitiesDocument1 pageBasic Cal IdentitieslanceandreycafeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Trigonometry Summary 1. Basic Trigonometric RatiosDocument2 pagesMathematics Trigonometry Summary 1. Basic Trigonometric RatiosSimran GillNo ratings yet
- Mathematics???Document6 pagesMathematics???DEFRON GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Identities Sheet - S15Document2 pagesIdentities Sheet - S15lucky010428No ratings yet
- Trig Identities Problem SetDocument3 pagesTrig Identities Problem SetMarkudo RikoyaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Identities WorksheetDocument2 pagesTrigonometric Identities WorksheetYuri SamozvanovNo ratings yet
- LAS - Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument2 pagesLAS - Trigonometric IdentitiesJERLYN MACADONo ratings yet
- Trignometry FormulasDocument8 pagesTrignometry FormulasNoobs playNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Functions and Their Relations SL - No Function SL - No FunctionDocument4 pagesTrigonometric Functions and Their Relations SL - No Function SL - No FunctiongfvhgkffgNo ratings yet
- Trig Formula SheetDocument3 pagesTrig Formula SheetNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Trigo IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrigo IdentitiesZyra Kim QuezonNo ratings yet
- MATHS Rappels Formulaire: Institut National Polytechnique de ToulouseDocument6 pagesMATHS Rappels Formulaire: Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouselina meriemNo ratings yet
- Half-Angle identities: rπθ ° cscθDocument2 pagesHalf-Angle identities: rπθ ° cscθkxungsooNo ratings yet
- 1 Trigonom Etria: 1.1 DefinicionesDocument7 pages1 Trigonom Etria: 1.1 DefinicionesJulissaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry SheetDocument4 pagesTrigonometry SheetKelah AligNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: Basic Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument4 pagesFormula Sheet: Basic Trigonometric Identitieschetan temkarNo ratings yet
- Catatan Matematika - TrigonometriDocument1 pageCatatan Matematika - Trigonometri33 SHARA FEBRIANA ANGGRAINI100% (1)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)