Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounting Case
Uploaded by
Manas Ranjan KarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accounting Case
Uploaded by
Manas Ranjan KarCopyright:
Available Formats
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
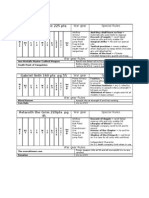
Question 1: REPORT ON OPERATIONS OF MARIA HERNANDEZ & ASSOCIATES THROUGH AUGUST 31,2001 BALANCING ACCOUNT Cash 12,000 40,000
(0) (1)
Cash 12,000 (2) 40,000 (3) (3) (4)
900 6,000 33,000 5,500
52,000 Balance 6,600
900 6,000 33,000 5,500 6,600 52,000
Equity (0)
30,000
BALANCING ACCOUNT Equity 0 30,000 30,000 30,000 30,000 Balance 30,000
Note payable (0)
20,000
BALANCING ACCOUNT Note payable 0 20,000 20,000 20,000 20,000 Balance 20,000
(0)
Prepaid expenses 12,000
BALANCING ACCOUNT Prepaid expenses 12,000 12,000 Balance 12,000
0 12,000 12,000
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
(0) (4)
Equipment 27,000 11,000
BALANCING ACCOUNT Equipment 27,000 11,000 38,000 Balance 38,000
0 0 38,000 38,000
(0) (2)
Inventory 5,000 (2) 900
1,700
BALANCING ACCOUNT Inventory 5,000 900 5,900 Balance 4,200
1,700 4,200 5,900
Sales revenue (1) (1)
40,000 7,000
BALANCING ACCOUNT Sales revenue 0 40,000 0 7,000 47,000 47,000 47,000 Balance 47,000
(1)
Account receivable 7,000
BALANCING ACCOUNT Account receivable 7,000 7,000 Balance 7,000
0 7,000 7,000
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
(2)
Cost of sales 1,700
BALANCING ACCOUNT Cost of sales 1,700 1,700 Balance 1,700
0 1,700 1,700
(3)
Rent expenses 6,000
BALANCING ACCOUNT Rent expenses 6,000 6,000 Balance 6,000
0 6,000 6,000
(3)
Utility expenses 33,000
BALANCING ACCOUNT Utility expenses 33,000 33,000 Balance 33,000
0 33,000 33,000
Account payable (4)
5,500
BALANCING ACCOUNT Account payable 5,500 5,500 Balance
5,500 0 5,500 5,500
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
TRIAL BALANCE Balance Debit Credit 6,600 7,000 6,000 38,000 4,200 5,500 20,000 30,000 47,000 1,700 33,000 6,000 102,500 102,500
Cash Accounts receivable Prepaid rent Equipment Inventory Accounts payable Note payable Paid in capital Sales revenue Cost of sales Utility expenses Rent expenses Total
ADJUSTING PROCESS Depreciation expenses 1,500 Accumulated Depreciation (5) 1,500 Interest expenses 200 Accrued Expense (6)
(5)
(6)
200
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
CLOSING ENTRIES Income Summary Cost of sales 1,700 Rent expenses 6,000 Utility expenses 33,000 Depreciation expenses 1,500 Interest expenses 200 42,400 (7) 1,380 3,220 Income Tax Liability (7) Retained Earning Balance 3,220 Balance
47,000
47,000
1,380
To balance
0 3,220 3,220
Maria started her own business with $50,000 in cash and in two months later she had only $6,600 left. There was a significant decline in cash of $45,400 because this is the first year of business and as the owner, Maria had to invest an considerable sum of money in starting up, for example Maria had to purchase equipment and software, which are extremely important tool in her industry, equip her office with stationery and office supplies, moreover she also had to hire good designers to support her with projects and pay them, pay all the bills including renting expenses, utility expenses But she did manage to bring customers to company and increase the company s sales revenue, and we could say that the company did make profit because just in two months from establishment with a great deal of investment, the company was still able to capture $3,220 as retained earnings. Besides, Maria did not depend do much on debt to run her own business and this gives her an advantage to generate more profit as soon as she finishes the investment. However, there are a lot of risks for Maria to face. Firstly, with only $6,600 left, there is a risk that she can or she cannot pay the salary or any extra operation cost next month, in the worst case there is no projects coming in anymore. Secondly, with such a young business, can she borrow money from the bank, when she wants to expand her business? Finally, there is a collection risk from the customers side, can Maria manage to collect $7,000 accounts receivable fast to supply the operation. It might be very sensitive for her, because of course when she has just opened her company, every customer is very precious, so she cannot take any risk to lose them either.
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
Question 2: REPORT OF STATUS OF THE BUSINESS ON AUGUST 31, 2001 Maria Hernandez & Associates August 31, 2001 Balance Sheets Assets Current assets: Cash Account receivable Inventories Total current assets Net fixed assets Equipment Other fixed assets Total net fixed assets Total assets Liabilities and Equity Current liabilities Account payable Accrued interest Accrued taxes Notes payable Accumulated Depreciation Total current liabilities Long-term bonds Total debt Common equity Capital stock Retained earnings Total common equity Total liabilities and equity
6,600 7,000 4,200 17,800 38,000 6,000 44,000 61,800
5,500 200 1,380 20,000 1,500 28,580 0 28,580 30,000 3,220 33,220 61,800
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
Maria Hernandez & Associates Income Statement for 2001 Net sales Operating cost Depreciation Total operating costs EBIT Interest EBT Taxes (30%) Net income 47,000 40,700 1,500 42,200 4,800 200 4,600 1,380 3,220
Maria Hernandez & Associates Statement of Cash flow for 2001 I. Operating Activities Net income Depreciation Increase in inventories Increase in accounts receivable Increase in accounts payable Increase in accrued wage and taxes Net cash provided by operating activities II. Long-term investing activities Cash used to acquire fixed assets III. Financing activities Increase in notes payable Increase in bonds outstanding Payment of dividends to stockholders Net cash provided by financing activities IV. Summary Cash and equivalent at the beginning Cash and equivalent at the end 50,000 6,600 3,220 1,500 1,700 7,000 5,500 1,380 20,300
42,500
20,000 0 0 20,000
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
Question 3: ANALYSIS THE REPORTS LIQUIDITY RATIOS Firstly, we begin to test the Liquidity ratios, which give us an idea of the firm s ability to pay off debts that are maturing within a year FCF = EBIT(1-T) + Depreciation Capital Expenditures - NWC = $3,220 + $1500 ($1500 + $44,000) (-$10,780) = $58,000 Free cash flow (FCF) of the company shows the cash that a company is able to generate after laying out the money required maintaining or expanding its asset base. So after finishing investing, it is the chance for Maria to increase the profit margin. Also this positive FCF indicates the company s ability to pay its debt, dividends (in this case Maria is the only owner of the company so she does not have to pay any dividends). (1) CF for operating / NI = $20,300/ $3,220 = 6.3 This ratio is greater than 1, indicating that the company is generating profit. (2) CF for operating / Debt = $20,300 / 28,580 = 71% However this ratio is smaller than 100%, indicating that the company s profit still be impacted by its debt. Net working capital = Current assets Current liabilities = $17,800 - $28,580 = -$10,780 This working capital deficit show a shortage of liquidity, the company s assets cannot readily be converted into cash. Therefore it cannot ensure that the company is able to continue its operations and that it has sufficient funds to satisfy both maturing short-term debt and upcoming operational expenses. Current ratio = Current assets / Current liabilities = $17,800 / $28,580 = 0.62x
The company s current liabilities are rising faster than its current assets that can tell us the company may have financial difficulty, it may force Maria to begin to pay her account payable more slowly and borrow more from the other source if she does not figure out a way to speed up her account receivable to have more cash.
8
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
ASSET MANAGEMENT RATIOS:
Secondly, we turn to asset management ratios, which give us an idea of how efficiently the firm is using its assets.
Inventory turnover ratio = Sales / Inventories = $47,000 / $4,200 = 11.19x
The company s inventory turnover ratio is high, indicating that it do not hold so many inventories.
Fixed assets turnover ratio = Sales / Net fixed assets = $47,000 / $44,000 = 1.06x
From this ratio we can indicate that this company is using its fixed assets not so intensively, if Maria does not know how to manage her assets effectively, that may cause her to let out her profit.
Total assets turnover ratio = Sales / Total assets = $47,000 / $61,800 = 0.76x
This can indicate that this company is not generating enough sales given its total assets. So the problem is with its current assets and accounts receivable. Lucky for Maria that in this case there are no inventories for her to worry about so the solution might be faster collection of receivables or increase of sale or both of them in order to improve operation.
DEBT MANAGEMENT RATIOS:
Then, we turn to debt management ratios, which give us an idea of how the firm has financed its assets as well as the firm s ability to repay its long-term debt
Debt ratio = Total debt / Total assets = $28,580 / $61,800 = 46%
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
The Debt ratio means almost half of the company s total assets are generating from debt. With quite high debt ratio, it may cause the company relatively costly to borrow additional funds without first raising more equity. Creditors will be reluctant to lend the firm more money, and management would probably be subjecting the firm too high a risk of bankruptcy if it sought to borrow a substantial amount of additional funds.
PROFITABILITY RATIOS
Then, we calculate the profitability ratios, which reflect the net result of all of the financing policies and operating decision in order to have an idea of how profitably the firm is operating and utilizing its assets.
Operating margin = Operating income (EBIT) / Sales = $4,600 / $47,000 = 9.7%
The company s operating margin is quite low indicating that the operation cost is quite high. This is consistent which the fact that in the first year of business Maria had to invest a lot of money in startup process.
Profit margin = Net income / Sales = $3,220/ $47,000 = 6.8%
The company s profit margin is quite low and this result occurred because its operating margin is also low due to high operation cost. Maria can raise her profit margin by reducing her debt because the interest will pull down her net income, besides high depreciation cost might be also the problem.
Return on total assets (ROA) = Net income / Total assets = $3,220 / $61,800 = 5.2%
This low ROA is not good this can result from a conscious decision to use of debt, in this case like mentioned above, high interest expenses will cause net income to be relatively low.
Return on common equity (ROE) = Net income / Common equity = $3,220 / $33,220 = 9.6%
10
Case study: Maria Hernandez & Associates
Group 1
The company s ROE is low and this is a result from the company s use of debt, that the company uses investment funds inefficiently to generate earnings growth.
FINAL THOUGHT:
Summary of Financial Ratios Ratio Current ratio FCF NWC Fixed assets turnover ratio Total assets turnover ratio Inventory turnover ratio Debt ratio Operating margin Profit margin ROA ROE Ratio 0.62x $58,000 -$10,780 1.06x 0.76x 11.19 46% 9.7% 6.8% 5.2% 9.6% Comment Poor OK Poor Poor Poor OK High (risky) Poor Poor Poor Poor
All of our calculations have shown one thing, the company has virtually risk. Almost half of the company s total assets are generating from debt, and extremely weak current and quick ratios, indicating its financial problems in paying debts. Besides, it uses its plant and equipment ineffectively and collection risk of its accounts receivable.
11
You might also like
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 9 - Acctg Cycle of A Service BusinessDocument52 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 9 - Acctg Cycle of A Service Businesscan't yujout80% (5)
- Christine Sousa BagsDocument8 pagesChristine Sousa BagsKaila Clarisse Cortez100% (5)
- Simple Compound Complex and Compound Complex SentencesDocument7 pagesSimple Compound Complex and Compound Complex SentencesRanti HarviNo ratings yet
- (Bloom's Modern Critical Views) (2000)Document267 pages(Bloom's Modern Critical Views) (2000)andreea1613232100% (1)
- Crime and Punishment Vocabulary 93092Document2 pagesCrime and Punishment Vocabulary 93092Rebeca Alfonso Alabarta50% (4)
- Acctg Problem 7Document4 pagesAcctg Problem 7Salvie Perez Utana57% (14)
- Ily Abella Surveyors - WorksheetDocument2 pagesIly Abella Surveyors - WorksheetNeilan Jay FloresNo ratings yet
- Starmada House RulesDocument2 pagesStarmada House Ruleshvwilson62No ratings yet
- Afar Partnership LiquidationDocument42 pagesAfar Partnership LiquidationKrizia Mae Uzielle PeneroNo ratings yet
- PDF-Afar CompressDocument128 pagesPDF-Afar CompressCharisse VisteNo ratings yet
- Ae 100 Section L Navarro, LainaDocument14 pagesAe 100 Section L Navarro, LainaLaina Recel NavarroNo ratings yet
- A) Show The Effects of The Above Transactions On The Accounting Equation Using The Following FormatDocument4 pagesA) Show The Effects of The Above Transactions On The Accounting Equation Using The Following FormatMark CalimlimNo ratings yet
- PTE GURU - Will Provide You Template For Following SST, SWT, RETELL, DI and ESSAY and at The End Some Good Knowledge of Scoring SystemDocument6 pagesPTE GURU - Will Provide You Template For Following SST, SWT, RETELL, DI and ESSAY and at The End Some Good Knowledge of Scoring Systemrohit singh100% (1)
- Project ManagementDocument37 pagesProject ManagementAlfakri WaleedNo ratings yet
- Maria Hernandez & Associates: Case Study #1Document6 pagesMaria Hernandez & Associates: Case Study #1Susy CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Maria Hernandez SolutionDocument13 pagesMaria Hernandez SolutionShashank PatelNo ratings yet
- Accounts Unadjusted Trial Balance Adjustments Ajusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Debit Credit Debit Credit DR CR DR CR DR CRDocument4 pagesAccounts Unadjusted Trial Balance Adjustments Ajusted Trial Balance Income Statement Balance Sheet Debit Credit Debit Credit DR CR DR CR DR CRGIDEON, JR. INESNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 (Suggested Solution)Document2 pagesTutorial 2 (Suggested Solution)DyksterNo ratings yet
- Fund Flow Statement NumericalsDocument9 pagesFund Flow Statement Numericalsjaydeep kriplaniNo ratings yet
- Assets, Liabilities and Equity of ARA Galleries Pty LTD As at 30 June 2017Document4 pagesAssets, Liabilities and Equity of ARA Galleries Pty LTD As at 30 June 2017BáchHợpNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1 (Chapter 9)Document3 pagesAccounting 1 (Chapter 9)angel cao100% (2)
- Activities and Assesment 2Document4 pagesActivities and Assesment 2Mante, Josh Adrian Greg S.No ratings yet
- Accounting - Trial BalanceDocument1 pageAccounting - Trial Balancefranchesca.dejesus.educNo ratings yet
- Vending Machines SolutionDocument6 pagesVending Machines SolutionizquierdofacturaNo ratings yet
- Transaction Analysis Janelle'SRESTAURANTDocument2 pagesTransaction Analysis Janelle'SRESTAURANTReana ReyesNo ratings yet
- 2021 SM2 Tutorial 02 InClass SolutionDocument3 pages2021 SM2 Tutorial 02 InClass SolutionZhu ZiRuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Partnership Liquidation Practice ExercisesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 - Partnership Liquidation Practice ExercisessanjoeNo ratings yet
- FAR Chapter 4Document5 pagesFAR Chapter 4Celine Therese BuNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SFM AnswerDocument4 pagesQuiz 1 SFM Answerangelicacas063No ratings yet
- 17 - Accounting For Incomplete Records (Single Entry)Document7 pages17 - Accounting For Incomplete Records (Single Entry)KAMAL POKHRELNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Basics of AccountingDocument1 pageAssignment - Basics of AccountingSamadhi KatagodaNo ratings yet
- FA2 - CFS SOlutionDocument1 pageFA2 - CFS SOlutionKc SevillaNo ratings yet
- Consolidation FP ExampleDocument4 pagesConsolidation FP ExampleYoooNo ratings yet
- Consolidation FP ExampleDocument4 pagesConsolidation FP ExampleYAUHANo ratings yet
- Accounting EquationDocument4 pagesAccounting Equationunknown PersonNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument1 pageWorksheetjoygie124apigoNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1Document5 pagesFabm 1Lady Aleah Naharah P. AlugNo ratings yet
- Jawaban CH 5 - TM 11Document3 pagesJawaban CH 5 - TM 11ahmad shinigamiNo ratings yet
- Rico - Assignment IaDocument18 pagesRico - Assignment IaGwen TimoteoNo ratings yet
- Accn 101 Assignment Group WorkDocument8 pagesAccn 101 Assignment Group WorkkumbiraidavidNo ratings yet
- Worksheet J. P. Peralta Computer ClinicDocument2 pagesWorksheet J. P. Peralta Computer ClinicMinjin lesner ManalansanNo ratings yet
- Profit 220,333.3 3 220,333.33Document1 pageProfit 220,333.3 3 220,333.33CookiemonsterNo ratings yet
- SBR1 Dummy With Cash FlowDocument15 pagesSBR1 Dummy With Cash Flowakansha.associate.workNo ratings yet
- Mahusay, Bsa 315, Module 1-CaseletsDocument9 pagesMahusay, Bsa 315, Module 1-CaseletsJeth MahusayNo ratings yet
- Indirect MethodDocument4 pagesIndirect MethodjustinreyNo ratings yet
- Exercise 8-7 Page 319Document3 pagesExercise 8-7 Page 319Dianne Jane LirayNo ratings yet
- Assignment TwoDocument10 pagesAssignment TwoTeke TarekegnNo ratings yet
- J. P. Peralta Computer Clinic Worksheet For The Month Ended December 31, 2020Document2 pagesJ. P. Peralta Computer Clinic Worksheet For The Month Ended December 31, 2020Minjin lesner ManalansanNo ratings yet
- Account Name Trial Balance Income Statement Capital Statement Balance SheetDocument2 pagesAccount Name Trial Balance Income Statement Capital Statement Balance SheetMeryl BinoNo ratings yet
- Actbfar Exercise #2Document8 pagesActbfar Exercise #2Janela Venice SantosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Problem 1 SolutionDocument8 pagesChapter 9 Problem 1 SolutionAustin Coles83% (6)
- Hotel Abc Hotel Abc Balance Sheet Cash Flow Statement As Per 31 December 2020 As of 31 December 2020Document2 pagesHotel Abc Hotel Abc Balance Sheet Cash Flow Statement As Per 31 December 2020 As of 31 December 2020Yoga SaputraNo ratings yet
- Perpetual Answer KeyDocument11 pagesPerpetual Answer KeyRichelle Janine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Partnership Operations PROBLEM 6 and 8 With Worksheet 6.)Document12 pagesChapter 2 - Partnership Operations PROBLEM 6 and 8 With Worksheet 6.)sanjoeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - Joint VentureDocument10 pagesCHAPTER 6 - Joint VentureminmenmNo ratings yet
- Dzaky Farhansyah - V1620034 - E5-19 - P5-8A - P5-7ADocument15 pagesDzaky Farhansyah - V1620034 - E5-19 - P5-8A - P5-7ADzaky FarhansyahNo ratings yet
- Revenue History ChartDocument2 pagesRevenue History ChartjsweigartNo ratings yet
- Accounting English Medium: Paper Based Revision Programme Marking Guide - Revision Paper - 34Document6 pagesAccounting English Medium: Paper Based Revision Programme Marking Guide - Revision Paper - 34Malar SrirengarajahNo ratings yet
- Consolidation FP ExampleDocument4 pagesConsolidation FP ExampleSuryaRaoNo ratings yet
- Zabala Auto Supply Worksheet JANUARY 31, 2021 Unadjusted Trial Balance DebitDocument24 pagesZabala Auto Supply Worksheet JANUARY 31, 2021 Unadjusted Trial Balance DebitIphegenia DipoNo ratings yet
- DB6 - Worksheet & FS Prep For Merchandising BusinessDocument4 pagesDB6 - Worksheet & FS Prep For Merchandising BusinessArrianeNo ratings yet
- Test Bank 3 - Ia 3Document25 pagesTest Bank 3 - Ia 3jessaNo ratings yet
- Unit NDocument1 pageUnit NjharithpalaciosNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Kunci Jawaban Minggu 5 Lap Konsol 15 - 19 Feb 2016Document6 pages5.1 Kunci Jawaban Minggu 5 Lap Konsol 15 - 19 Feb 2016agustadivNo ratings yet
- FADM Assignment SolvedDocument12 pagesFADM Assignment SolvedAnujain JainNo ratings yet
- Restrictive Covenants - AfsaDocument10 pagesRestrictive Covenants - AfsaFrank A. Cusumano, Jr.No ratings yet
- Depreciated Replacement CostDocument7 pagesDepreciated Replacement CostOdetteDormanNo ratings yet
- Dda 2020Document32 pagesDda 2020GetGuidanceNo ratings yet
- Depreciation, Depletion and Amortization (Sas 9)Document3 pagesDepreciation, Depletion and Amortization (Sas 9)SadeeqNo ratings yet
- MAKAUT CIVIL Syllabus SEM 8Document9 pagesMAKAUT CIVIL Syllabus SEM 8u9830120786No ratings yet
- 14CFR, ICAO, EASA, PCAR, ATA Parts (Summary)Document11 pages14CFR, ICAO, EASA, PCAR, ATA Parts (Summary)therosefatherNo ratings yet
- Business Enterprise Simulation Quarter 3 - Module 2 - Lesson 1: Analyzing The MarketDocument13 pagesBusiness Enterprise Simulation Quarter 3 - Module 2 - Lesson 1: Analyzing The MarketJtm GarciaNo ratings yet
- HelpDocument5 pagesHelpMd Tushar Abdullah 024 ANo ratings yet
- Blood Angels Ref SheetsDocument4 pagesBlood Angels Ref SheetsAndrew ThomasNo ratings yet
- Travisa India ETA v5Document4 pagesTravisa India ETA v5Chamith KarunadharaNo ratings yet
- Financial Report: The Coca Cola Company: Ews/2021-10-27 - Coca - Cola - Reports - Continued - Momentum - and - Strong - 1040 PDFDocument3 pagesFinancial Report: The Coca Cola Company: Ews/2021-10-27 - Coca - Cola - Reports - Continued - Momentum - and - Strong - 1040 PDFDominic MuliNo ratings yet
- WFP AF Project Proposal The Gambia REV 04sept20 CleanDocument184 pagesWFP AF Project Proposal The Gambia REV 04sept20 CleanMahima DixitNo ratings yet
- An Introduction: by Rajiv SrivastavaDocument17 pagesAn Introduction: by Rajiv SrivastavaM M PanditNo ratings yet
- Facts:: Topic: Serious Misconduct and Wilfull DisobedienceDocument3 pagesFacts:: Topic: Serious Misconduct and Wilfull DisobedienceRochelle Othin Odsinada MarquesesNo ratings yet
- GOUP GO of 8 May 2013 For EM SchoolsDocument8 pagesGOUP GO of 8 May 2013 For EM SchoolsDevendra DamleNo ratings yet
- Variable Costing Case Part A SolutionDocument3 pagesVariable Costing Case Part A SolutionG, BNo ratings yet
- Thesis RecruitmentDocument62 pagesThesis Recruitmentmkarora122No ratings yet
- Christian Biography ResourcesDocument7 pagesChristian Biography ResourcesAzhar QureshiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Quranic Studies PDFDocument19 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Quranic Studies PDFtaha zafar100% (3)
- Internship Report Mca Audit Report InternshipDocument33 pagesInternship Report Mca Audit Report InternshipJohnNo ratings yet
- Trifles Summary and Analysis of Part IDocument11 pagesTrifles Summary and Analysis of Part IJohn SmytheNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument44 pagesThesisjagritiNo ratings yet
- Dam Water SensorDocument63 pagesDam Water SensorMuhammad RizalNo ratings yet
- 2 Quiz of mgt111 of bc090400798: Question # 1 of 20 Total Marks: 1Document14 pages2 Quiz of mgt111 of bc090400798: Question # 1 of 20 Total Marks: 1Muhammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet