Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transformation
Uploaded by
pop0008Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Transformation
Uploaded by
pop0008Copyright:
Available Formats
Mao Yuan Liu Kambrya College
Notes on Transformation
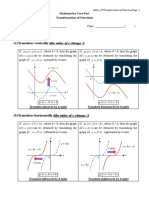
Interpreting equations Absolute: a f (b ( ) x + d ) + c Order: Horizontal translation (d) Horizontal dilation and reflection from the y axis (b) Vertical dilation (a) Vertical translation (c) Relative: a f (b ( x + d )) + c Order: Horizontal translation (d) Horizontal dilation and reflection from (-d, 0) (b) Vertical dilation (a) Vertical translation (c)
Transformation to x values: Always substitute x for transformed expressions Dilation and reflection are absolute from the y axis. Translations are always relative to current position. Transformation to y values: Always dilate/reflect first, and then translate. Dilations and reflections are absolute from the x axis. Translations are always relative to current position.
1. 2. 3. 4.
1. 2. 3. 4.
Terms in transformation 1 Dilation by a factor of in the y direction (or parallel to x) or reflection in the y axis n (absolute from y axis):
If translation is performed first, dilation and reflection has to be performed on a relative scale unless otherwise specified.
f ( x + b) f ( n x + b)
1 in the y direction (or parallel to x) or reflection in the y axis n (relative to graph position): Dilation by a factor of
f ( x + b) f ( n ( x + b))
Translation of n units to the right (in the x direction) (always translated relative to graph position):
f (b x) f (b ( x n))
Dilation by a factor of n in the x direction (or parallel to y) or reflection in the x axis (relative to graph position):
f ( x) + c n f ( x) + c
Dilation by a factor of n in the x direction (or parallel to y) or reflection in the x axis (absolute from x axis):
f ( x) + c n ( f ( x) + c) f ( x) f ( x) + n
Translation n units upwards (always translated relative to graph position):
Relative (translation first) transformations in x: yc =x b
y = bx + c
Absolute (dilation first) transformations in x: y c = x b
y = b( x + c )
Page 4 of 54
You might also like
- Properties of Function NotesDocument11 pagesProperties of Function NoteswelcometotheswampNo ratings yet
- 04 Transformation of Function NotesDocument3 pages04 Transformation of Function Notesm100% (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Function Transformations: Just Like Transformations in Geometry, We Can Move and Resize The Graphs of FunctionsDocument8 pagesFunction Transformations: Just Like Transformations in Geometry, We Can Move and Resize The Graphs of FunctionsKez MaxNo ratings yet
- 03 2D-3D GeometryDocument77 pages03 2D-3D GeometryTuseeq RazaNo ratings yet
- Translation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation: Course Offered byDocument20 pagesTranslation, Reflection, Dilation, and Rotation: Course Offered byemiliaroslanNo ratings yet
- Transformation Parent FunctionsDocument15 pagesTransformation Parent Functionsqqvhc2x2prNo ratings yet
- Sec Math Functions FunctiontransformationsDocument31 pagesSec Math Functions Functiontransformationsnellymanganyi62No ratings yet
- 1.2 Transformations of Linear andDocument63 pages1.2 Transformations of Linear andanbarasu tutorNo ratings yet
- Key Ideas Week 8Document2 pagesKey Ideas Week 8shadowosNo ratings yet
- Transformations 1Document32 pagesTransformations 1KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Transformations of Graphs: Name Description What To Look For in The Function How The Function ChangesDocument2 pagesTransformations of Graphs: Name Description What To Look For in The Function How The Function ChangesMindy DyarNo ratings yet
- Exponential Functions Part 2Document17 pagesExponential Functions Part 2Will AbarisoNo ratings yet
- Maths Notes (Graphing Techniques)Document3 pagesMaths Notes (Graphing Techniques)Teo Jia Ming NickolasNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus ReviewDocument45 pagesVector Calculus ReviewJoshua CookNo ratings yet
- Functions and Their Transformations 2010Document1 pageFunctions and Their Transformations 2010Khaik Yong LeeNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Transformation Matrices Example: Puma 560: ©2017 Max DonathDocument19 pagesHomogeneous Transformation Matrices Example: Puma 560: ©2017 Max DonathchrisNo ratings yet
- 2.5.2 Equation of Translated LinesDocument1 page2.5.2 Equation of Translated Linespataset329No ratings yet
- Homogeneous Transformation Matrices Example: Puma 560: ©2018 Max DonathDocument19 pagesHomogeneous Transformation Matrices Example: Puma 560: ©2018 Max Donathbendali nadirNo ratings yet
- Many FormulasDocument11 pagesMany FormulasDillep NandaNo ratings yet
- Transformations of FunctionsDocument4 pagesTransformations of FunctionsCaribNo ratings yet
- Crib Sheet PDFDocument4 pagesCrib Sheet PDFHadarNo ratings yet
- Diploma Prep 1 - TransformationsDocument18 pagesDiploma Prep 1 - TransformationsU.KNo ratings yet
- Core 3 Revision Guide: OCR SyllabusDocument3 pagesCore 3 Revision Guide: OCR SyllabusRichardTudor96No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Dragged)Document1 pageLecture Notes (Dragged)yawas50511No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Dragged)Document1 pageLecture Notes (Dragged)yawas50511No ratings yet
- Block 1 PPTDocument273 pagesBlock 1 PPTprince JiNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Function Investigation - Maria AncutaDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Function Investigation - Maria Ancutaapi-515654558No ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document11 pagesLecture 5ewewewNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes (Dragged) 2Document1 pageLecture Notes (Dragged) 2yawas50511No ratings yet
- in This Section, We Will Study The Following Topics:: Families of GraphsDocument15 pagesin This Section, We Will Study The Following Topics:: Families of GraphsHenriel TambioNo ratings yet
- AphketchingDocument10 pagesAphketchinghoangngocphanduy187No ratings yet
- Handouts D8 1 PDFDocument8 pagesHandouts D8 1 PDFVed Vrat AryaNo ratings yet
- CG 3Document10 pagesCG 3sefefe hunegnawNo ratings yet
- A Few Standard Graphs: F (X) X F (X) XDocument8 pagesA Few Standard Graphs: F (X) X F (X) XDesyilalNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Part 1Document74 pagesUnit 2 - Part 1A1FA MSKNo ratings yet
- Final RevisionDocument21 pagesFinal Revisionsprinklesdb16No ratings yet
- ZTZMGob JDocument7 pagesZTZMGob JObert MupomokiNo ratings yet
- Maths Quadratic GraphsDocument10 pagesMaths Quadratic GraphshaniaNo ratings yet
- Math 141 Exam Summary SheetDocument2 pagesMath 141 Exam Summary SheetjackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument24 pagesChapter 4 PDFirusha100% (1)
- 2D Geometrical Transformations: Foley & Van Dam, Chapter 5Document34 pages2D Geometrical Transformations: Foley & Van Dam, Chapter 5Ashutosh JhaNo ratings yet
- Transformations SummaryDocument8 pagesTransformations SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Math 19 Summer 2012: June 27Document2 pagesMath 19 Summer 2012: June 27Ganesh KumarNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument9 pagesExamplesTANVI78No ratings yet
- 电动力学 课件:Course1 Vector AnalysisDocument29 pages电动力学 课件:Course1 Vector AnalysisJUN LAINo ratings yet
- The Difference Between Relation and FunctionDocument15 pagesThe Difference Between Relation and Functionbjkhaw75No ratings yet
- Lecture 199 623Document17 pagesLecture 199 623Ravi TejaNo ratings yet
- Ch1a (Compatibility Mode)Document80 pagesCh1a (Compatibility Mode)Shakthi VinayaNo ratings yet
- Hodder GraphsDocument28 pagesHodder GraphsHoa Dinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- CAD GM KJHA 2d TransformationDocument91 pagesCAD GM KJHA 2d TransformationAnu SinghNo ratings yet
- EEE241: Fundamentals of Electromagnetics: Introductory Concepts, Vector Fields and Coordinate SystemsDocument80 pagesEEE241: Fundamentals of Electromagnetics: Introductory Concepts, Vector Fields and Coordinate SystemsRamo KissNo ratings yet
- Cim 23.6Document81 pagesCim 23.6RajeshKumarNo ratings yet
- Geom2d PDFDocument13 pagesGeom2d PDFstalin1227No ratings yet
- Homogeneous TransformDocument10 pagesHomogeneous TransformAaqib KhanNo ratings yet
- Concavity or Convexity FinalDocument18 pagesConcavity or Convexity Finalkumarvishal192004No ratings yet
- 04.TwoDimensional Transformations MCADocument67 pages04.TwoDimensional Transformations MCAashwiniNo ratings yet
- Materi 03. 2D Geometric Transformation: Komputer GrafikDocument33 pagesMateri 03. 2D Geometric Transformation: Komputer GrafikFauzi RahadianNo ratings yet