Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abscisic Acid 76
Abscisic Acid 76
Uploaded by
vkannanagri0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageAbscisic acid (ABA) stimulates the production of ethene, which causes leaf fall by initiating a series of events: cells at the base of the petiole separate, a protective waxy layer forms, vascular tissue is sealed, and wind breaks the leaf off. ABA also causes stomata to close when water is scarce by binding ABA receptors in guard cell membranes and inhibiting their proton pumps and potassium ion uptake, reducing turgor pressure and closing the pores.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAbscisic acid (ABA) stimulates the production of ethene, which causes leaf fall by initiating a series of events: cells at the base of the petiole separate, a protective waxy layer forms, vascular tissue is sealed, and wind breaks the leaf off. ABA also causes stomata to close when water is scarce by binding ABA receptors in guard cell membranes and inhibiting their proton pumps and potassium ion uptake, reducing turgor pressure and closing the pores.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageAbscisic Acid 76
Abscisic Acid 76
Uploaded by
vkannanagriAbscisic acid (ABA) stimulates the production of ethene, which causes leaf fall by initiating a series of events: cells at the base of the petiole separate, a protective waxy layer forms, vascular tissue is sealed, and wind breaks the leaf off. ABA also causes stomata to close when water is scarce by binding ABA receptors in guard cell membranes and inhibiting their proton pumps and potassium ion uptake, reducing turgor pressure and closing the pores.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Abscisic acid(ABA) is a plant growth substance that
Abscisic acid and leaf fall
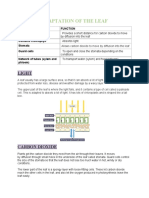
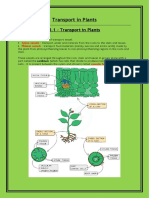
Abscisic acid(ABA) is a plant growth substance that stimulates the production of ethene. Ethene stimulates the fall of leaves or abscission. The following sequence of events leads to leaf fall:
cells in a layer at the base of the petiole separate from one another by the breakdown of the middle lamellae of their cell walls; a protective layer of cells with wax in their walls forms on each side of this abscission layer to prevent infection and water loss, in woody species this layer is cork with suberised cell walls; the vascular tissue is sealed; the leaf is broken off by a mechanical force such as the wind.
Abscisic acid (ABA) and stomata
ABA can help a plant survive stress when water is in short supply. ABA is released from the chloroplasts of mesophyll cells. When ABA reaches the guard cells of a stoma, they lose their turgidity and the stoma closes. When a guard cell takes up water by osmosis, the thick wall adjacent to the stoma resists stretching and becomes more curved. In this way the pore opens. Uptake of water occurs because the water potential of the cell is lowered by addition of potassium ions (K+). An ATP-dependent proton pump transports H+ ions out of the cell. The reduced H+ concentration inside the cells causes potassium ion channels in the plasma membrane to open and K+ ions move down a diffusion gradient into the cell. Guard cells have ABA receptors in their plasma membranes. Binding ABA with these receptors may inhibit the proton pump. Spraying ABA onto crops as an anti-transpirant is not a commercial proposition as the effects are short-lived. A methyl ester of ABA can be used because it is not readily broken down by plants.
You might also like
- Transpiration Lab ReportDocument7 pagesTranspiration Lab ReportG100% (1)
- 06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document24 pages06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Saurabh ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- Water Movement in Plants - Biology Encyclopedia - Cells, Body, Function, Process, Used, Structure, Molecules, Energy 2 PDFDocument4 pagesWater Movement in Plants - Biology Encyclopedia - Cells, Body, Function, Process, Used, Structure, Molecules, Energy 2 PDFDanNo ratings yet
- Stress PhysiologyDocument2 pagesStress PhysiologySmitha AsokNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants HandoutDocument5 pagesTransport in Plants HandoutAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- 8.0 Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages8.0 Transport in Plantskhenso sitholeNo ratings yet
- KLB Biology F3 NoteDocument49 pagesKLB Biology F3 NoteSocdal Abdi100% (2)
- Transport in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesTransport in Flowering PlantsChic BoosterNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Transport in Plants NotesDocument3 pages9.1 Transport in Plants NoteszarahiraniNo ratings yet
- PPH NotesDocument16 pagesPPH Notesvanitar0324No ratings yet
- Plants (HL)Document25 pagesPlants (HL)Boris-Jeremie-Latyr GueyeNo ratings yet
- A Level Transport FinestDocument25 pagesA Level Transport FinestBaguma alexNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Level Transport: Transport in Plants Occurs On Three LevelsDocument5 pagesCellular-Level Transport: Transport in Plants Occurs On Three LevelsTanisha LewisNo ratings yet
- Cohesion-Tension Theory of Transpiration: Seed Banks ZoosDocument4 pagesCohesion-Tension Theory of Transpiration: Seed Banks ZoosRubban KunaNo ratings yet
- Guard Cell - WikipediaDocument42 pagesGuard Cell - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Module/Unit 2B Activity: Instructions: Put Your Answers in A Short Size Paper. Indicate Your Name and SectionDocument2 pagesModule/Unit 2B Activity: Instructions: Put Your Answers in A Short Size Paper. Indicate Your Name and SectionDarlene KrizianNo ratings yet
- BIOL102Alaie NotesDocument93 pagesBIOL102Alaie NotesBarukh B. RohdeNo ratings yet
- II. Parts of The Plant InvolvedDocument3 pagesII. Parts of The Plant InvolvedJoash Carl DiazenNo ratings yet
- Biologyical EssayDocument4 pagesBiologyical Essayruben.debiereNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Transport System in PlantsDocument18 pagesForm 3 Transport System in PlantsachikgaiNo ratings yet
- 9.1 XylemDocument18 pages9.1 Xylemstutireddy1912No ratings yet
- Lec. 06Document15 pagesLec. 06Wilson BhutiaNo ratings yet
- 8 - Plant BiologyDocument16 pages8 - Plant BiologyMohammad Salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantsDocument31 pagesTransportation in PlantssamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- Biology Revision: Plants, Water and MineralsDocument3 pagesBiology Revision: Plants, Water and MineralsMegan Taylor100% (1)
- Bio F5 C4: Transport in PlantsDocument18 pagesBio F5 C4: Transport in PlantsRuksana AshrufNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsDocument17 pages7.2 Gaseous Exchange in PlantsTheresa IzaNo ratings yet
- Plant Behavioural Strategies For SurvivalDocument3 pagesPlant Behavioural Strategies For SurvivalNancyNguyen16No ratings yet
- Lecture Xi - Transport Systems in PlantsDocument14 pagesLecture Xi - Transport Systems in PlantsNeil SNo ratings yet
- Suberin. Suberin Acts As A Barrier To Water and Solute Movement. The EndodermisDocument2 pagesSuberin. Suberin Acts As A Barrier To Water and Solute Movement. The EndodermisHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Water Absorption: Lecture - 3Document32 pagesMechanism of Water Absorption: Lecture - 3Santhosh SanthoshNo ratings yet
- 3.1.2 Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages3.1.2 Transport in PlantssjNo ratings yet
- Topic 9Document7 pagesTopic 9Talia Elan VickeryNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument34 pagesTransport in PlantsYagna LallNo ratings yet
- Pathogen Vs Cell MembraneDocument12 pagesPathogen Vs Cell MembraneHunAin SajjAdNo ratings yet
- LeavesDocument7 pagesLeavesHailey CoutuNo ratings yet
- Stomata-Cornell NotesDocument1 pageStomata-Cornell NotesAnishaNo ratings yet
- ch7 NotesDocument6 pagesch7 Notesisabella cucumberNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plant o Level NotesDocument39 pagesTransport in Plant o Level NotesFangsNo ratings yet
- How Would You Make A Rainbow Rose?Document17 pagesHow Would You Make A Rainbow Rose?Komalsh TheeranNo ratings yet
- OsmosisDocument4 pagesOsmosisSHAN CHAUDHARYNo ratings yet
- Notes 11. Transport in PlantsDocument23 pagesNotes 11. Transport in PlantsBsbdbdbxn ChcbxndndnNo ratings yet
- Plants: QuestionsDocument1 pagePlants: QuestionsAimah SolaimanNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 11Document2 pagesBiology Chapter 11BainsieNo ratings yet
- Topic:: Submitted To: Prof. Hina TariqDocument6 pagesTopic:: Submitted To: Prof. Hina TariqZubair BalouchNo ratings yet
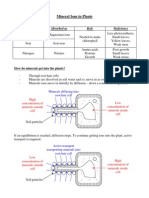
- Mineral Ions in Plants: Ion Absorbed As Role DeficiencyDocument2 pagesMineral Ions in Plants: Ion Absorbed As Role DeficiencyPratheep GsNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants and Transpiration NotesDocument7 pagesTransport in Plants and Transpiration NotesAshleigh JarrettNo ratings yet
- Biology - Leaf ChapterDocument4 pagesBiology - Leaf ChapterWriddhi MononNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesTransport in Plantsoten.temotika02No ratings yet
- Transpiration DR - Rajesh SahuDocument7 pagesTranspiration DR - Rajesh SahuRajesh SahuNo ratings yet
- Bio-Adaptation of The LeafDocument3 pagesBio-Adaptation of The LeafHudaNo ratings yet
- Assigment 2Document5 pagesAssigment 2imanzaid2765No ratings yet
- Biology Form 2 NotesDocument80 pagesBiology Form 2 NotesLutern RayNo ratings yet
- Plant Strss. PhysiologyDocument19 pagesPlant Strss. PhysiologysvaidyaNo ratings yet
- Endodermis and Casparian StripDocument2 pagesEndodermis and Casparian StripYap Hooi CheinNo ratings yet
- Gaseous Exchange Through Stomatal Chamber - : Stomatal Opening and ClosingDocument6 pagesGaseous Exchange Through Stomatal Chamber - : Stomatal Opening and Closingعمیرہ ملکNo ratings yet
- 8.1 - Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages8.1 - Transport in PlantsAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 8 Transport in Plants - CIE Biology IGCSE PDFDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 8 Transport in Plants - CIE Biology IGCSE PDFMd A RAZZAK100% (1)
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet