Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Full) .: All Questions Are Taken From Chapter 11 in M. Mano/Computer Design and Architecture 3 Ed
Uploaded by
Dana AkermanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Full) .: All Questions Are Taken From Chapter 11 in M. Mano/Computer Design and Architecture 3 Ed
Uploaded by
Dana AkermanCopyright:
Available Formats
4
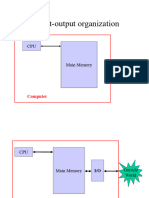
" " Question 1 A commercial interface unit uses different names for the handshake lines associated with the transfer of data from the I/O device into the interface unit. The interface input handshake line is labeled STB (strobe), and the interface output handshake line is labeled IBF (input buffer full). A low-level signal on STB loads data from the I/O bus into the interface data register. A high-level signal on IBF indicates that the data item has been accepted by the interface. IBF goes low after an I/O read signal from the CPU when it reads the contents of the data register. a. Draw a block diagram showing the CPU, the interface, and the I/O device together with the pertinent interconnections among the three units. b. Draw a timing diagram for the handshaking transfer. c. Obtain a sequence-of-events flowchart for the transfer from the device to the interface and from the interface to the CPU. Question 2 How many characters per second can be transmitted over a 1200-baud line in each of the following modes? (Assume a character code of eight bits.) a. Synchronous serial transmission. b. Asynchronous serial transmission with two stop bits. c. Asynchronous serial transmission with one stop bit. Question 3 The bits in the control register of the FIFO shown in Fig. 11-9 (slide 14) are F1F2F3F4 = 0011. Give the sequence of internal operations when an item is deleted from the FIFO and then a new item is inserted. Question 4 Design a parallel priority-interrupt-hardware for a system with eight interrupt sources. Include the truth table of the encoder and the Boolean functions that implement them. Question 5 What programming steps are required to check when a source interrupts the computer while it is still being serviced by a previous interrupt request from the same source?
All questions are taken from Chapter 11 in M. Mano/Computer Design and Architecture 3 Ed.
rd
You might also like
- CA-Assignment 2 - FinalDocument2 pagesCA-Assignment 2 - Finaljixxy jaxNo ratings yet
- COA Assignment - 3Document2 pagesCOA Assignment - 3KomalNo ratings yet
- MPMC EEE Externalkey 2023Document4 pagesMPMC EEE Externalkey 2023srinivas kanakalaNo ratings yet
- COA QuestionBank - 1Document3 pagesCOA QuestionBank - 1itzzsandeshNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Telecommunication ExcercisesDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Telecommunication ExcercisesPhan AnNo ratings yet
- SAP Report Group 2Document14 pagesSAP Report Group 2Chanel Hooper0% (1)
- Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE) : Islamic University of Technology (Iut)Document3 pagesDepartment of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE) : Islamic University of Technology (Iut)Manus HumanNo ratings yet
- 802.11a and 802.16a SimulinkDocument13 pages802.11a and 802.16a SimulinkAkshay KarveNo ratings yet
- 134ak - Computer OrganizationDocument2 pages134ak - Computer Organizationsameeksha chiguruNo ratings yet
- Fabbc9: Convert Hexadecimal To BinaryDocument11 pagesFabbc9: Convert Hexadecimal To BinaryShan NavasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15Document4 pagesLecture 15علي ستار سالم Ali sattar salimNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Mohd Norfitri Nordin Faculty Information Communication TechnologyDocument32 pagesPrepared By: Mohd Norfitri Nordin Faculty Information Communication TechnologyIntan SyuhadaNo ratings yet
- CS401 - Short Notes Chapter 14 PDFDocument3 pagesCS401 - Short Notes Chapter 14 PDFmalikNo ratings yet
- ELEC 2441 - Computer Organization and MicroprocessorsDocument18 pagesELEC 2441 - Computer Organization and MicroprocessorsBillyNo ratings yet
- CA Assignment IIDocument9 pagesCA Assignment IISomesh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Parallel Interfacing With Microprocessor Based SystemDocument32 pagesChapter 2 - Parallel Interfacing With Microprocessor Based SystemAarav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Do Practice CODocument2 pagesDo Practice COSudeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- VL2022230102283 Ast04Document3 pagesVL2022230102283 Ast04UMA MAHESWARI G 20BIT0317No ratings yet
- Important ?Document16 pagesImportant ?ruhipravin352No ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document7 pagesChapter 05John doeNo ratings yet
- Assignments CSE211Document4 pagesAssignments CSE211Raghav JhanjeeNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture (01CE0402) Lab ManualDocument4 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture (01CE0402) Lab ManualrockyNo ratings yet
- Cisco IOS Voice Troubleshooting and Monitoring - E&M Interfaces - DocWikiDocument29 pagesCisco IOS Voice Troubleshooting and Monitoring - E&M Interfaces - DocWikiYs KuoNo ratings yet
- EEE 311 Online Class 1Document8 pagesEEE 311 Online Class 1KhairulNo ratings yet
- 19ecs431 - Embedded SystemsDocument18 pages19ecs431 - Embedded SystemsNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab. 4: Digital DesignDocument11 pagesLab. 4: Digital DesignThịnh PhanNo ratings yet
- Code: 07A4041 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R07) Supplementary Examinations June 2015Document1 pageCode: 07A4041 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R07) Supplementary Examinations June 2015subbuNo ratings yet
- SS07A4041 Digital IC ApplicationsDocument1 pageSS07A4041 Digital IC ApplicationsMahaboob SubahanNo ratings yet
- ADC Through SPIDocument4 pagesADC Through SPIChiquita White100% (1)
- PS2® To Usb Mouse Translator Hardware DiagramDocument10 pagesPS2® To Usb Mouse Translator Hardware Diagramjhenriqueh100% (1)
- 9A04504 Digital IC Applications6Document4 pages9A04504 Digital IC Applications6subbuNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Computer Organization and Architecture - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument15 pagesUnit 4 - Computer Organization and Architecture - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inrk.chakrawartiNo ratings yet
- Shivalik College of Engineering Question Bank Computer Organization B.Tech II Year (IV Semester)Document5 pagesShivalik College of Engineering Question Bank Computer Organization B.Tech II Year (IV Semester)Paras TilaraNo ratings yet
- 9A12301 Digital Logic Design & Computer OrganizationDocument4 pages9A12301 Digital Logic Design & Computer OrganizationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Final Test Example: ET3 301 Embedded SystemsDocument12 pagesFinal Test Example: ET3 301 Embedded SystemsAmin De Rossi SudrajatNo ratings yet
- Final Test Example: ET3 301 Embedded SystemsDocument12 pagesFinal Test Example: ET3 301 Embedded SystemsJagabar SathikNo ratings yet
- Input Output9 6 2021Document53 pagesInput Output9 6 2021zkd9n8f6kfNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Parallel Interfacing With Microprocessor Based SystemDocument32 pagesChapter 2 - Parallel Interfacing With Microprocessor Based SystemSuroj BurlakotiNo ratings yet
- R7410405 Microcontrollers & ApplicationsDocument1 pageR7410405 Microcontrollers & ApplicationssubbuNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 (Microprocessor Internal Architectres)Document18 pagesLecture-3 (Microprocessor Internal Architectres)LHKNo ratings yet
- Instructions: 1. This Examination Consists of FIVE Questions 2. Answer Question ONE (COMPULSORY) and Any Other TWO QuestionsDocument5 pagesInstructions: 1. This Examination Consists of FIVE Questions 2. Answer Question ONE (COMPULSORY) and Any Other TWO QuestionsNjoro officialNo ratings yet
- R07 Set No. 2Document5 pagesR07 Set No. 2Krishna MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Roll No TCS 402/TIT 402: Time: Two (2) Hrs. Maximum Marks: 60Document18 pagesRoll No TCS 402/TIT 402: Time: Two (2) Hrs. Maximum Marks: 60Obsii ChalaNo ratings yet
- Pipelining in Pentium 2Document9 pagesPipelining in Pentium 2amol1agarwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment-II COA2023Document2 pagesAssignment-II COA2023sanjeevani rawatNo ratings yet
- Micro-Controller and Interfacing Exam PaperDocument2 pagesMicro-Controller and Interfacing Exam PaperFenil ModiNo ratings yet
- Chip Neuron Lonworks PDFDocument19 pagesChip Neuron Lonworks PDFCesar PalaciosNo ratings yet
- QbankDocument3 pagesQbankAnanthi RajkumarNo ratings yet
- PC Interfacing Fourth Level Lecture TWO: Parallel (Centronic) Port InterfaceDocument9 pagesPC Interfacing Fourth Level Lecture TWO: Parallel (Centronic) Port Interfaceأسامة المياحيNo ratings yet
- 4.6.2 Universal Serial Bus (USB)Document18 pages4.6.2 Universal Serial Bus (USB)kollavivek_534195858100% (2)
- University of Essex: School of Computer Science andDocument6 pagesUniversity of Essex: School of Computer Science andVlad SimizeanuNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation and ArchitectureDocument2 pagesComputer Organisation and ArchitectureSelin DandpatNo ratings yet
- PC AT Technical Reference Mar84 3 of 3Document246 pagesPC AT Technical Reference Mar84 3 of 3kgrhoadsNo ratings yet
- 01DDT22F2044 Varshaan A/L Puaneswaran: SESI 2 2022/2023Document5 pages01DDT22F2044 Varshaan A/L Puaneswaran: SESI 2 2022/2023Varshaan PuaneswaranNo ratings yet
- 9A04504 Digital IC Applications4Document1 page9A04504 Digital IC Applications4subbuNo ratings yet
- Com OrgDocument39 pagesCom OrgDouaa M. AliNo ratings yet
- Time: 03 Hours Maximum Marks: 100: (Autonomous Institution Under VTU) VI Semester B. E. Examinations, May/Jun 14Document3 pagesTime: 03 Hours Maximum Marks: 100: (Autonomous Institution Under VTU) VI Semester B. E. Examinations, May/Jun 14PrateekMandiNo ratings yet
- Se, All Branches. C A - oDocument2 pagesSe, All Branches. C A - oanuragnair377No ratings yet
- Lab4 - Digital CircuitDocument12 pagesLab4 - Digital CircuitKIÊN ĐẶNG TRUNGNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Serial Communications Interfaces: A Comprehensive Compendium of Serial Digital Input/Output (I/O) StandardsFrom EverandHandbook of Serial Communications Interfaces: A Comprehensive Compendium of Serial Digital Input/Output (I/O) StandardsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (4)