Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calibrate Pressure Gauges with Dead Weight Tester
Uploaded by
Ghulam AbbasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calibrate Pressure Gauges with Dead Weight Tester
Uploaded by
Ghulam AbbasCopyright:
Available Formats
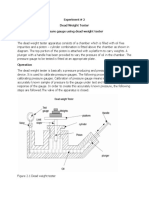
Dead Weight Piston Gauge The deadweight piston gauge (Bell and Howell) is used is to measure pressure in terms
of fundamental units - force and area. A piston is inserted into a close fitting cylinder. Weights are placed on one end of the piston and are supported by fluid pressure applied to the other end. For absolute pressure measurements the assembly is placed inside an evacuated bell jar. Pressure measurements take into account a number of parameters affecting the instrument and its environment. they include the uncertainty of the mass of the weights and the error in the effective area measurement of the cylinder, gravity measurement, air bouyancy and temperature. Measurement units used are Kilopascals (Kpa) or Millibars (Mb). The available range is 20 Kpa. to 300Kpa. The accuracy we feel we have is better than 0.1mb. throughout the full range.
A dead weight tester apparatus uses known traceable weights to apply pressure to a fluid for checking the accuracy of readings from a pressure gauge. A dead weight tester (DWT) is a calibration standard method that uses a piston cylinder on which a load is placed to make an equilibrium with an applied pressure underneath the piston. Deadweight testers are so called primary standards which means that the pressure measured by a deadweight tester is defined through other quantities: length, mass and time. Typically deadweight testers are used in calibration laboratories to calibrate pressure transfer standards like electronic pressure measuring devices.
You might also like
- Calibrating Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument6 pagesCalibrating Bourdon Pressure GaugeKhairil IkramNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight TesterDocument5 pagesDead Weight TesterSoban KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Calibrating Pressure SensorsDocument10 pagesCalibrating Pressure SensorsromasokyNo ratings yet
- Calibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument5 pagesCalibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugeFaizaan EE14No ratings yet
- Ce-271 Fluid Mechanics: Experiment No 05-Calibration of Bourdon GaugeDocument8 pagesCe-271 Fluid Mechanics: Experiment No 05-Calibration of Bourdon Gaugeuthman98No ratings yet
- Pressure Gauge Calliberation ExperimentDocument17 pagesPressure Gauge Calliberation ExperimentTemitayo SolankeNo ratings yet
- Calibrate Pressure Gauges with Dead Weight TesterDocument6 pagesCalibrate Pressure Gauges with Dead Weight TesterdracarysNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document63 pagesChapter 2steven pitchNo ratings yet
- Calibrating a Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument47 pagesCalibrating a Bourdon Pressure Gaugeزياد الحربيNo ratings yet
- Module v. Calibration and Uses of Pressure & Temperature Measuring InstrumentsDocument25 pagesModule v. Calibration and Uses of Pressure & Temperature Measuring InstrumentsDomingo NoverasNo ratings yet
- TF Lab 2Document12 pagesTF Lab 2Mahrukh ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Calibrating Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument9 pagesCalibrating Bourdon Pressure GaugeMuizzuddin Saleh100% (4)
- Calibration of Pressure GaugeDocument4 pagesCalibration of Pressure Gaugeyash ajay kashidNo ratings yet
- Ex 1Document4 pagesEx 120-MCE-63 SYED HASSAN KUMAILNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Bourdon Gauge: Report TitleDocument10 pagesCalibration of Bourdon Gauge: Report Titlewlyan harkiNo ratings yet
- Calibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument4 pagesCalibration of A Bourdon Pressure GaugesubyNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measurement Calibration LabDocument6 pagesPressure Measurement Calibration Labmatjaz555No ratings yet
- Alexandria Universityجامعة الاسكندريةDocument67 pagesAlexandria Universityجامعة الاسكندريةHaneen Safwat ArabNo ratings yet
- Fluids Lab Experiment No:3 Fundamentals of Pressure MeasurementDocument14 pagesFluids Lab Experiment No:3 Fundamentals of Pressure MeasurementDarivan DuhokiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 - Calibration of Pressure Gauge2Document8 pagesExperiment 2 - Calibration of Pressure Gauge2Śūpęr MòÐó60% (5)
- Me Lab. Report 2Document12 pagesMe Lab. Report 2Henry Datangel100% (1)
- BourdonDocument7 pagesBourdonKhairil IkramNo ratings yet
- Calbaration of Pressure GaugeDocument12 pagesCalbaration of Pressure Gaugehamza19792005No ratings yet
- Gauges and Ancillary EquipmentDocument26 pagesGauges and Ancillary EquipmentAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight Calibrator Lab | Group 6Document12 pagesDead Weight Calibrator Lab | Group 6RuHuiNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Bourdon GaugeDocument5 pagesCalibration of Bourdon GaugeShenal Perera0% (1)
- M&MS 2007 453Document17 pagesM&MS 2007 453vijayaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Experiment ListDocument113 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Experiment ListRayhan SaeedNo ratings yet
- LAB No. 08Document3 pagesLAB No. 08M. TahmanNo ratings yet
- To Calibrate A Bourdon Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterDocument3 pagesTo Calibrate A Bourdon Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterMuhammad Arsalan Khan100% (4)
- Dead Weight CalibratorDocument11 pagesDead Weight CalibratorMUHAMMAD SAADULLAH BUTTNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1,2 Me 234 PDFDocument55 pagesExperiment 1,2 Me 234 PDFchinnavenkateswarluNo ratings yet
- Dead Weight TesterDocument6 pagesDead Weight TesterSajithaNo ratings yet
- Bourdon Pressure GaugeDocument7 pagesBourdon Pressure GaugeOneplus entartainmentNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measurement Bench PDFDocument3 pagesPressure Measurement Bench PDFMohammed Cardoza33% (3)
- Chapter - 5 - Pressure Measurements StudentsDocument57 pagesChapter - 5 - Pressure Measurements Studentsprasaad0893% (14)
- Lec 7Document20 pagesLec 7SaadNo ratings yet
- 220s15 ExpB LabManualDocument5 pages220s15 ExpB LabManualMetu Ncc HaberlerNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Pressure Gauge Calibration PDFDocument8 pagesLab 1 Pressure Gauge Calibration PDFbwahahaha67% (6)
- Estimation of Error in Bourdon Type Pressure Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterDocument4 pagesEstimation of Error in Bourdon Type Pressure Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterMohamed TamanNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Error in Bourdon Type Pressure Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterDocument4 pagesEstimation of Error in Bourdon Type Pressure Gauge Using Dead Weight TesterMohamed TamanNo ratings yet
- IME_reportDocument11 pagesIME_reportmatsagarsachin59No ratings yet
- E-Dwt-H Electronic Deadweight Tester-: A Modern Replacement For The Conventional Deadweight TesterDocument4 pagesE-Dwt-H Electronic Deadweight Tester-: A Modern Replacement For The Conventional Deadweight TesterutpalshubhamNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Deadweight Tester.Document22 pagesHydraulic Deadweight Tester.Mayank SinghNo ratings yet
- Exp 2Document4 pagesExp 2Abdul AddaharyNo ratings yet
- Calibration of Pressure GaugeDocument4 pagesCalibration of Pressure GaugeKrish Manglani40% (5)
- Calibration of Pressure GaugeDocument4 pagesCalibration of Pressure Gaugepammy313100% (1)
- Dead Weight Tester ExptDocument2 pagesDead Weight Tester ExptAliceLazar0% (1)
- Dead Weight TesterDocument1 pageDead Weight TesterShrey AnshNo ratings yet
- Determination of Pressure Using Manometers and GaugesDocument5 pagesDetermination of Pressure Using Manometers and GaugesMohammad HajeerNo ratings yet
- EG 232 Mechanical1Document97 pagesEG 232 Mechanical1Anthony MubangaNo ratings yet
- Pmi L3Document52 pagesPmi L3Yom MotiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Pressure Measurements StudentsDocument57 pagesChapter 5 Pressure Measurements StudentsAnurag DavesarNo ratings yet
- Relevant Terms: Importance of The ExperimentDocument1 pageRelevant Terms: Importance of The ExperimentGian CarlyleNo ratings yet
- Me Lab 1Document18 pagesMe Lab 1Richmond OlarteNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Instrument Technology: Measurement of Pressure, Level, Flow and TemperatureFrom EverandInstrument Technology: Measurement of Pressure, Level, Flow and TemperatureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- GasLit 2010Document276 pagesGasLit 2010thawminNo ratings yet
- Thermal OxidationDocument1 pageThermal OxidationGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document18 pagesLec 4Ghulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- 4 Cop VigilanceDocument3 pages4 Cop VigilanceMudassar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Suspension, Dispersion, BlendingDocument20 pagesSuspension, Dispersion, BlendingGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Greg GambleDocument8 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Greg Gambleaj.aquilineNo ratings yet
- Steam BenchDocument2 pagesSteam BenchGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Current Technology of Fuel Cells SystemsDocument5 pagesCurrent Technology of Fuel Cells SystemsGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet