Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Covalent Bonding and Covalent Molecules, Structure and
Covalent Bonding and Covalent Molecules, Structure and
Uploaded by
chelsea555Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Covalent Bonding and Covalent Molecules, Structure and
Covalent Bonding and Covalent Molecules, Structure and
Uploaded by
chelsea555Copyright:
Available Formats
Covalent bonding and covalent molecules, structure and properties.
A covalent bond is a bond between two non-metallic elements. They share electrons inside the molecules.
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule. Covalent bonds are very strong bonds. Covalent bonds are were two atoms share two or more electrons.
Covalent bonds generally have much lower melting points and boiling points than ionic bonding. Covalent bonds are flexible and soft, compared to ionic bonding. Covalent bonds are more flammable than ionic bonds. Covalent bonds dont conduct electricity in water.
Covalent compounds arent soluble in water.
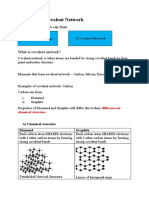
Giant covalent structures
Diamond Diamond is a form of carbon in which each carbon atom is joined to four other carbon atoms, forming a giant covalent structure. As a result, diamond is very hard and has a high melting point. It does not conduct electricity.
Graphite Graphite is a form of carbon in which the carbon atoms form layers. These layers can slide over each other, so graphite is much softer than diamond. It is used in pencils, and as a lubricant. Each carbon atom in a layer is joined to only three other carbon atoms. Graphite conducts electricity.
Silica Silica, which is found in sand, has a similar structure to diamond. It is also hard and has a high melting point, but contains silicon and oxygen atoms, instead of carbon atoms
You might also like
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocument6 pagesDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Giant Molecular StructureDocument2 pagesGiant Molecular StructureMusa ImranNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding: AllotropesDocument7 pagesCovalent Bonding: AllotropesFatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDocument8 pagesNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Engineering: Chemistry Covalent BondingDocument18 pagesDiploma in Engineering: Chemistry Covalent BondingOscar Kelvin NsituNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Vocabulary 1Document6 pagesChemistry Vocabulary 10417979No ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- L10,11 - Covalent Compounds PropertiesDocument21 pagesL10,11 - Covalent Compounds PropertiesKashifNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond NotesDocument8 pagesGiant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond Notesnihan.8558No ratings yet
- A Study On Giant Covalent StructuresDocument3 pagesA Study On Giant Covalent StructuresNicholas TeyNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliDocument11 pagesBonding and Structure: Group: Hammad Rashid Luqman Arshad Moeed AliPro IdiotNo ratings yet
- Yaren ŞahinDocument4 pagesYaren Şahinyaren.sahin200888No ratings yet
- Covalent BondingDocument9 pagesCovalent BondingBite SizeNo ratings yet
- Allotropes of CarbonDocument4 pagesAllotropes of CarbonRoshan Jawad ZafirNo ratings yet
- Giant Ionic and Giant CovalentDocument8 pagesGiant Ionic and Giant CovalentSamuelNo ratings yet
- Discovering Covalent NetworkDocument3 pagesDiscovering Covalent NetworkOng Yun YiNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding v1.0Document45 pagesCovalent Bonding v1.0jt100% (1)
- Chemistry Revision PDFDocument6 pagesChemistry Revision PDFjoud amjadNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding LectureDocument33 pagesCovalent Bonding LectureGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Simple Molecular Covalent StructuresDocument3 pagesProperties of Simple Molecular Covalent Structures908039480No ratings yet
- Types of SubstanceDocument7 pagesTypes of SubstanceTreshan StaynNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding1Document26 pagesCovalent Bonding1BaselNo ratings yet
- Final PDF For Grade 9 PDFDocument5 pagesFinal PDF For Grade 9 PDFmadhuri pawarNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileDocument17 pagesCovalent Bonding, Structure Lecture FileMahi QuaziNo ratings yet
- 5c. CrystalsDocument5 pages5c. CrystalsUnknownKidNo ratings yet
- GIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES-lizDocument8 pagesGIANT COVALENT STRUCTURES-lizKoluoch JrNo ratings yet
- Q2-Org ChemDocument2 pagesQ2-Org ChemMark Joseph LatadeNo ratings yet
- Materials & Macromolecules-OL-NotesDocument3 pagesMaterials & Macromolecules-OL-Notesshlaibat13No ratings yet
- EDEXCEL AS LEVEL COVALENT BOND (Complete) 2019 NEW SPECIFICATIONDocument19 pagesEDEXCEL AS LEVEL COVALENT BOND (Complete) 2019 NEW SPECIFICATIONdrama curiousNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structures (Macromolecules)Document33 pagesGiant Covalent Structures (Macromolecules)ananya.aNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- Elements, Compounds and AtomsDocument12 pagesElements, Compounds and Atomsananya.arumugarajanNo ratings yet
- Diamond and Graphite: by Diyar AlassafDocument9 pagesDiamond and Graphite: by Diyar Alassafdiyar alassafNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding GCSE Review and 10QsDocument5 pagesCovalent Bonding GCSE Review and 10QsPuja DhawanNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondsDocument6 pagesChemical BondsARDIUZNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Structure and BondingDocument5 pagesPresentation On Structure and BondingBaggyNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 States of Matter (Liquidsolid)Document27 pagesTopic 4 States of Matter (Liquidsolid)Siti NuraqidahNo ratings yet
- C2 Revision On Bondings.Document3 pagesC2 Revision On Bondings.malra_97No ratings yet
- Boys' Group 01: Covalent CrystalsDocument14 pagesBoys' Group 01: Covalent Crystalsusman aliNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Document3 pagesCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNo ratings yet
- Effect of Types of Bonding Toward Physical Properties of SubstanceDocument3 pagesEffect of Types of Bonding Toward Physical Properties of SubstanceeilyanaNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of SubstancesDocument3 pagesBonding and Properties of Substancesdan964No ratings yet
- BondsDocument24 pagesBondsPavithran Kamaleswari Year 10No ratings yet
- Privacy Statement Site Map Contact Us: GcseDocument8 pagesPrivacy Statement Site Map Contact Us: GcsetashaNo ratings yet
- The Different Types of Compounds - 240116 - 033252Document5 pagesThe Different Types of Compounds - 240116 - 033252LotusNo ratings yet
- Giant Covalent Structures (SL)Document5 pagesGiant Covalent Structures (SL)Brooks RalphNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelDocument34 pagesChemistry Study Notes Igcse EdexcelAhmed KhalilNo ratings yet
- 04-Lesson 4 Structure of CarbonDocument20 pages04-Lesson 4 Structure of CarbonAnnabel PatarataNo ratings yet
- Che 90308 TypesofsolidsDocument4 pagesChe 90308 Typesofsolidsapi-218511741No ratings yet
- Science March 14Document1 pageScience March 14josefbonifacioleeNo ratings yet
- Bonding TheoriesDocument31 pagesBonding TheoriesMatthew HallNo ratings yet
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 pageBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302No ratings yet
- Lesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFDocument6 pagesLesson3 - Chemical Bonding PDFMia ChanNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Properties of Solids StudentDocument7 pages3.2 Properties of Solids StudentZachary Daniel UyNo ratings yet
- Notes On Bonding and StructureDocument5 pagesNotes On Bonding and Structurefletcherberryheath2006No ratings yet
- Metallic Ionic and Covalent BondingDocument3 pagesMetallic Ionic and Covalent BondinglesarouNo ratings yet
- Chemical StructureDocument6 pagesChemical StructuremonkeysaltaccNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry - Unit 4 - Bonding Study GuideDocument7 pagesIB Chemistry - Unit 4 - Bonding Study GuideHamzah JoharNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.From EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.No ratings yet