Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Figure 2
Figure 2
Uploaded by
Yowges YowgesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Figure 2
Figure 2
Uploaded by
Yowges YowgesCopyright:
Available Formats
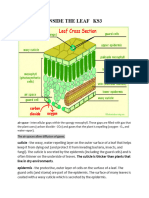
FIGURE 2
Stomata
Stomata are minute aperture structures on plants found typically on the outer leaf skin layer, also known as the epidermis. They consist of two specialized cells, called guard cells that surround a tiny pore called a stoma. The word stomata means mouth in Greek because they allow communication between the internal and external environments of the plant. Their main function is to allow gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor and oxygen to move rapidly into and out of the leaf. Stomata are found on all above-ground parts of plants including the petals of flowers, petioles, soft herbaceous stems and leaves. They are formed during the initial stages of the development of these various plant organs and therefore reflect the environmental conditions under which they grew. Stomata are minute aperture structures on plants found typically on the outer leaf skin layer, also known as the epidermis. They consist of two specialized cells, called guard cells that surround a tiny pore called a stoma. The word stomata means mouth in Greek because they allow communication between the internal and external environments of the plant. Their main function is to allow gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor and oxygen to move rapidly into and out of the leaf. Stomata are found on all above-ground parts of plants including the petals of flowers, petioles, soft herbaceous stems and leaves. They are formed during the initial stages of the development of these various plant organs and therefore reflect the environmental conditions under which they grew.
Stomata
You might also like
- Aquatic Plants: Structure and FunctionsDocument18 pagesAquatic Plants: Structure and FunctionsJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Algae and Land PlantsDocument21 pagesLab 10 Algae and Land Plants13ucciNo ratings yet
- Stomata ExperimentDocument15 pagesStomata Experimentumict100% (1)
- Internal Structure of A LeafDocument20 pagesInternal Structure of A LeafRell Dog100% (1)
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- StomataDocument2 pagesStomataSampriti PandaNo ratings yet
- Inside The Leaf KS3Document2 pagesInside The Leaf KS3Ziya JiwaniNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentHannah CastroNo ratings yet
- AngiospermDocument13 pagesAngiospermTomiwa EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- BS110 Activity1-3b-Boaquiña KianDocument5 pagesBS110 Activity1-3b-Boaquiña KianboaquinakianNo ratings yet
- StomataDocument1 pageStomataMohammad Thooriq RahmawanNo ratings yet
- Stomata OverviewDocument2 pagesStomata Overviewget.aishaaNo ratings yet
- Resume Plants Structure SRI UTAMI 2084205034 2.2 PbioDocument1 pageResume Plants Structure SRI UTAMI 2084205034 2.2 PbioSri Az-zahraNo ratings yet
- 1osc03 PlantkingdomDocument4 pages1osc03 PlantkingdomIrene AragonesesNo ratings yet
- Student Worksheet On StomataDocument2 pagesStudent Worksheet On StomataScribd_is_GreatNo ratings yet
- Laporan 3 StomataDocument18 pagesLaporan 3 StomataRizkaHasanahNo ratings yet
- Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication DataDocument2 pagesLibrary of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication DataMiggy OrticioNo ratings yet
- CASNS 1a Module 4.2Document13 pagesCASNS 1a Module 4.2Maxi VellasNo ratings yet
- Lecture II - MidtermDocument23 pagesLecture II - MidtermENGETS IT7No ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy: Plant Body Organization Short Note.: by @tamiyaDocument25 pagesPlant Anatomy: Plant Body Organization Short Note.: by @tamiyaTeamireab DestaNo ratings yet
- Internal Structure of The LeafDocument27 pagesInternal Structure of The LeafLenaNo ratings yet
- Carandang, Paul Bennedict C. Gr. 9 - St. Gregory The GreatDocument1 pageCarandang, Paul Bennedict C. Gr. 9 - St. Gregory The GreatPaul Benedict CarandangNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of PlantsDocument21 pagesParts and Functions of PlantsRaz QuipedNo ratings yet
- Primary Plant Body Brainiac ?Document6 pagesPrimary Plant Body Brainiac ?davidoluwadimu28No ratings yet
- 30.4C: Leaf Structure, Function, and Adaptation: Key PointsDocument3 pages30.4C: Leaf Structure, Function, and Adaptation: Key PointsTresha CosmeñoNo ratings yet
- Network Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafDocument5 pagesNetwork Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafMarwana SuaibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Notes 2013Document4 pagesLecture 9 Notes 2013Richard HampsonNo ratings yet
- Stomata MechanismDocument6 pagesStomata MechanismSulaiman FairusNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BotanyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To BotanybagongonjeremiasNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesStructure and Functions of Plant Tissuesdina aribahNo ratings yet
- Biology - Leaf ChapterDocument4 pagesBiology - Leaf ChapterWriddhi MononNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Various PlantsDocument8 pagesCharacteristics of Various PlantsSakshi TewariNo ratings yet
- Leaves Are The Powerhouse of PlantsDocument8 pagesLeaves Are The Powerhouse of PlantsBridgette JuarezNo ratings yet
- Reading Guide Answers PlantsDocument9 pagesReading Guide Answers PlantsNirmal PatelNo ratings yet
- Transpiration E - BookDocument18 pagesTranspiration E - BookAkku Tyagi50% (2)
- Biozone 2 PG 342Document3 pagesBiozone 2 PG 342Ji-Soo KimNo ratings yet
- KELOMPOK 6 Offering I: "Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves"Document3 pagesKELOMPOK 6 Offering I: "Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves"Dewi Sekar MiasihNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue SystemsDocument3 pagesPlant Tissue Systemselizabeth shaw gonzalez100% (1)
- Gas Exchange in PlantsDocument6 pagesGas Exchange in PlantsMaria Theresa HerreroNo ratings yet
- Handouts-Lect. 29 - Introduction To Kingdom Plantae PDFDocument6 pagesHandouts-Lect. 29 - Introduction To Kingdom Plantae PDFRizwan BalochNo ratings yet
- Plant Organ - Lab - Rayan AliDocument16 pagesPlant Organ - Lab - Rayan AliRayan AliNo ratings yet
- Transpiration Class 10Document15 pagesTranspiration Class 10shreya morajkarNo ratings yet
- Biology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)Document22 pagesBiology Lecture Notes: (Stemer'S Guide)AbdoNo ratings yet
- Biological ScienceDocument6 pagesBiological ScienceprincexavierfrancismNo ratings yet
- Coursework Bank StomataDocument4 pagesCoursework Bank Stomataujsqjljbf100% (2)
- TRANSPIRATIONDocument20 pagesTRANSPIRATIONMelanie LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Crop Physiology Exercise-2Document7 pagesCrop Physiology Exercise-2Ravikant MishraNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Vegetative Organs of A Seed Plant: Root, Stem and LeavesDocument13 pagesStructure and Functions of The Vegetative Organs of A Seed Plant: Root, Stem and Leaveskarl riveraNo ratings yet
- Yet Another Type of Permanent Tissue Is SclerenchymaDocument2 pagesYet Another Type of Permanent Tissue Is Sclerenchymasanjaydixit9951No ratings yet
- SAT 2 Biology - PlantsDocument22 pagesSAT 2 Biology - PlantsMido MidoNo ratings yet
- Plant Biology Classification of PlantsDocument28 pagesPlant Biology Classification of PlantsAhmet OnaltNo ratings yet
- Epidermis Dan DerivatnyaDocument20 pagesEpidermis Dan DerivatnyaReni Annisa NurhanifahNo ratings yet
- PetalsDocument2 pagesPetalsAnonymous RbkgTBn1K3No ratings yet
- Green Modern Ecology Ecosystem Presentation TemplateDocument22 pagesGreen Modern Ecology Ecosystem Presentation Templatelyka garcia100% (1)
- Gabriel Cruzata - Lecture Activity #4Document5 pagesGabriel Cruzata - Lecture Activity #4Joni Gabriel CruzataNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Plants Organ SystemDocument32 pages1.2 Plants Organ SystemkitsujinnNo ratings yet
- Leaf Anatomy: Cells (E), and They Create A Circle Around The Xylem and The Phloem. On TheDocument3 pagesLeaf Anatomy: Cells (E), and They Create A Circle Around The Xylem and The Phloem. On TheANo ratings yet
- Agronomy Assignment 3Document3 pagesAgronomy Assignment 3Nguyễn Minh ThànhNo ratings yet