Professional Documents
Culture Documents
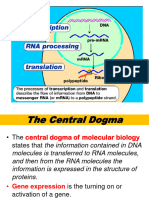
Translation
Uploaded by
faiyeeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Translation
Uploaded by
faiyeeCopyright:
Available Formats
Translation
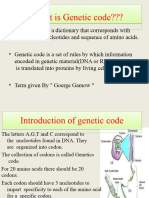
The Genetic Code
- The genetic code is a dictionary identifying the link between a sequence of nucleotides and a sequence of amino acids. - The genetic code is degenerate, specific, universal, and non-overlapping. D-SUN - The genetic code consists of 3 nucleotide codons. - AUG is the initiation codon signaling the start of the open reading frame. - UAA, UAG, and UGA are termination codons, signaling the end of an open reading frame. - The open reading frame is usually a gene encoding a protein
Wobble Hypothesis
-This explains how the 61 codons out of the 64 possible codons, can still be translated even though there are less tRNA than the expected 61. - There are 64 possible codons for the genetic code. - Three of these 64 codons on the mRNA are stop codons, which terminate translation by binding to release factors rather than tRNA molecules. - Each of the remaining 61 codons requires their own tRNA to be read, however fewer than 61 tRNA exist. - The Wobble Hypothesis is used to explain how few tRNA can actually read all the codons on mRNA. - A minimum of 32 tRNAs are needed to translate all 61 codons.
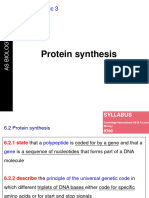
Protein synthesis
-Occurs in 5 steps 1) Amino acid activation 2) Initiation 3) Elongation 4)Termination and Release 5) Folding and posttranslational processing. a.a + tRNA + ATP Mg2+ aminoacyltRNA + AMP + PPi
AminoacyltRNA synthetases adds the 20 amino acids to their corresponding tRNA
Amino Acid Activation Ribosome Mechanism
You might also like
- Syllabus of EnglishDocument7 pagesSyllabus of EnglishAshuNo ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument2 pagesGenetic CodekvictoNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma Transcription Raza PDFDocument19 pagesCentral Dogma Transcription Raza PDFMD ANIMO HASANNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Fatty AcidsDocument2 pagesBiosynthesis of Fatty AcidsAyeshaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code. A Comprehensive Overview.Document32 pagesGenetic Code. A Comprehensive Overview.Mughal Gumar Farooq100% (1)
- Lec4 Genetic Code & RNA TripletsDocument28 pagesLec4 Genetic Code & RNA TripletsSITI BAZILAH BINTI BILAK KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Protein Metabolism: Presented By: Danica Alyssa Cruz, RMTDocument39 pagesProtein Metabolism: Presented By: Danica Alyssa Cruz, RMTDanica Alyssa CruzNo ratings yet
- 5.the Genetic CodeDocument8 pages5.the Genetic CodeCharm BatiancilaNo ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument16 pagesGenetic CodeSivagami Satish kumarNo ratings yet
- BCH 404 TranslationDocument12 pagesBCH 404 TranslationKendra FouetsopNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument21 pagesUntitledPINTO, KATE JUSTINE RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Turn in SheetDocument45 pagesTurn in Sheet25210580No ratings yet
- Genetic Code and Its CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesGenetic Code and Its CharacteristicsFasiha MushadiNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Guided Notes #2Document45 pagesUnit 6 Guided Notes #225210580No ratings yet
- Lecture # 20 The Genetic CodeDocument41 pagesLecture # 20 The Genetic CodethomasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.3 - Protein SynthesisDocument107 pagesChapter 6.3 - Protein Synthesisnie20060301No ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument3 pagesGenetic Codenitesh.th15005No ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument4 pagesGenetic Codeavilashabas39No ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument36 pagesGenetic CodeYashNo ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument15 pagesGenetic Codekratikaagrawal50No ratings yet
- Genetic CodeDocument47 pagesGenetic CodeAsha Bandhe0% (1)
- L14 BioDocument7 pagesL14 BioAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- 6.2 - TranslationDocument21 pages6.2 - TranslationAna JuatasNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: DECEMBER 13, 2010 Cape Biology Unit 1 Mrs. HaughtonDocument45 pagesProtein Synthesis: DECEMBER 13, 2010 Cape Biology Unit 1 Mrs. HaughtonAshley MorganNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance 2Document6 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance 2VARSHAN GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Genetic CodonDocument21 pagesModule 8 - Genetic CodonAllan SigangaNo ratings yet
- Information Transfer - Part1Document8 pagesInformation Transfer - Part1Avirup RayNo ratings yet
- Animation 22: DNA Words Are Three Letters LongDocument2 pagesAnimation 22: DNA Words Are Three Letters Longkiper.valNo ratings yet
- Information Transfer: Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument22 pagesInformation Transfer: Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyAvirup RayNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis Worksheet PART A. Read The FollowingKent100% (2)
- The Genetic CodeDocument5 pagesThe Genetic CodeNathaniel CamangonNo ratings yet
- SYBT Sem III Unit II TranslationDocument56 pagesSYBT Sem III Unit II TranslationMeir SabooNo ratings yet
- Genetic Code: Maria Septiana Parmonang AroeanDocument15 pagesGenetic Code: Maria Septiana Parmonang AroeanGe'sh Na'shy TyneNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis RevisionDocument22 pagesProtein Synthesis RevisionKrishnendu RoyNo ratings yet
- BIO353 Lecture 10 mRNA SplicingDocument8 pagesBIO353 Lecture 10 mRNA SplicingMina KoçNo ratings yet
- Module - 3&4 NotesDocument42 pagesModule - 3&4 Notesums.fsc.2020No ratings yet
- Translation Notes SheetDocument5 pagesTranslation Notes SheetKelsey BakerNo ratings yet
- RNA Transcription and TranslationDocument138 pagesRNA Transcription and Translationnoeme babiaNo ratings yet
- Translation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanDocument30 pagesTranslation: By: Nathaniel Craig G. de GuzmanCristie Ann GuiamNo ratings yet
- 6-RNA TranslationDocument43 pages6-RNA TranslationAlainNo ratings yet
- Genatic CodesDocument25 pagesGenatic CodeszzzNo ratings yet
- Transcription Is The First Step in Gene Expression. It InvolvesDocument8 pagesTranscription Is The First Step in Gene Expression. It InvolvesrendezvousfrNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis: Dr. Gertude Kiwanuka Biochemistry Dept MustDocument41 pagesProtein Synthesis: Dr. Gertude Kiwanuka Biochemistry Dept MustRonnieNo ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 pagesProtein SynthesisEverly Joy JingcoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 Translational, Protein Synthesis and Post Translational Modifications MD 2 2023 by DR Mohamed AbdelbakyDocument56 pagesLecture 9 Translational, Protein Synthesis and Post Translational Modifications MD 2 2023 by DR Mohamed Abdelbakysoushinelall2007No ratings yet
- Practice Problems HourlyDocument2 pagesPractice Problems Hourlyjls tjhNo ratings yet
- Rna and TranscriptionDocument46 pagesRna and TranscriptionReyana BaderNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis (Translation) : IlosDocument14 pagesProtein Synthesis (Translation) : Ilosghost beastNo ratings yet
- Gp501-Priniciple of Genetics: Genetic CodeDocument29 pagesGp501-Priniciple of Genetics: Genetic Codeprejan rajaNo ratings yet
- BC Lec M6 Lesson 3Document21 pagesBC Lec M6 Lesson 3Mershonthel MarquezNo ratings yet
- Human Genetic Inheritance LabDocument5 pagesHuman Genetic Inheritance LabAntonov MikalisNo ratings yet
- Lab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021Document11 pagesLab 8 - Transcription-Translation-ONLINE VERSION - 2021thesoccerprince.10No ratings yet
- Transcription and Translation 2014Document32 pagesTranscription and Translation 2014Shilpa KantariaNo ratings yet
- Cells Translate DNA Mrna Proteins Ribosome Amino Acids Messenger RNA Transfer RNA NucleotidesDocument3 pagesCells Translate DNA Mrna Proteins Ribosome Amino Acids Messenger RNA Transfer RNA NucleotidesQura Tul AinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Translation and Mutations Learning GoalsDocument10 pagesLecture 3: Translation and Mutations Learning GoalsAngelica SmithNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis WorksheetDocument4 pagesProtein Synthesis WorksheetDen RoixNo ratings yet
- Unit 6. Proteins SynthesisDocument57 pagesUnit 6. Proteins Synthesismunyanezaolivier422No ratings yet
- Protein SynthesisDocument54 pagesProtein SynthesisGemmie Jn PierreNo ratings yet
- SMT Top v1 36inchDocument15 pagesSMT Top v1 36inchfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- Topik WishDocument3 pagesTopik WishfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- CODeL ASSIGNMENT LETTER UNAM Core ModuleDocument22 pagesCODeL ASSIGNMENT LETTER UNAM Core ModulefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- Pattern 1Document12 pagesPattern 1faiyeeNo ratings yet
- Topik WishDocument1 pageTopik WishfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- Topik WishDocument1 pageTopik WishfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument3 pagesDefinitionfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- This Is PaperDocument1 pageThis Is PaperfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- MCQ'S: ItraconazoleDocument10 pagesMCQ'S: ItraconazolefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- ItraconazoleDocument10 pagesItraconazolefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- This Is PaperDocument1 pageThis Is PaperfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- D FileDocument1 pageD FilefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- E FileDocument1 pageE FilefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- C FileDocument1 pageC FilefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- A FileDocument1 pageA FilefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- How Many Species of Tsetse Flies Are Under Genus GlossinaDocument19 pagesHow Many Species of Tsetse Flies Are Under Genus GlossinafaiyeeNo ratings yet
- A FileDocument1 pageA FilefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- A True StoryDocument3 pagesA True StoryfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- B FileDocument1 pageB FilefaiyeeNo ratings yet
- SBB - Blood Composition & Functions of Plasma ProteinsDocument4 pagesSBB - Blood Composition & Functions of Plasma ProteinsfaiyeeNo ratings yet
- Abg Practice QuizDocument13 pagesAbg Practice QuizPatty Romero0% (1)
- Anti Aging MagazineDocument65 pagesAnti Aging MagazineSava1988100% (1)
- Protein Digestion in RuminantsDocument12 pagesProtein Digestion in RuminantsJ Jesus Bustamante GroNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis PastPaper QuestionsDocument24 pagesPhotosynthesis PastPaper QuestionsEva SugarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry - WikipediaDocument14 pagesBiochemistry - WikipediaAchilles ManthosNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps of GlycolysisDocument2 pages10 Steps of GlycolysisMay TN0% (1)
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 2Document23 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 2Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- SEP2009-410004-Biochemistry & Clinical Pathology PDFDocument1 pageSEP2009-410004-Biochemistry & Clinical Pathology PDFArif Misbahi100% (1)
- Nitrogen Metabolism Tutorial QuestionsDocument4 pagesNitrogen Metabolism Tutorial QuestionsImmanuel LashleyNo ratings yet
- 02 Plant EcophysiologyDocument49 pages02 Plant Ecophysiologylam lamNo ratings yet
- Class 12 THB CH-5 SPORTS AND NUTRITIONDocument12 pagesClass 12 THB CH-5 SPORTS AND NUTRITIONpillalastudyNo ratings yet
- Enzyme InhibitionDocument17 pagesEnzyme InhibitionazwelljohnsonNo ratings yet
- June 2016 MS - Unit 4 AQA Biology A-LevelDocument11 pagesJune 2016 MS - Unit 4 AQA Biology A-Levelrohin athavaleNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument73 pagesBioenergeticsJiela Mae MamaatNo ratings yet
- Darlene Krizian G. Dayuha: Bio100 - General BotanyDocument2 pagesDarlene Krizian G. Dayuha: Bio100 - General BotanyDarlene KrizianNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Features of The Cell Danger ResponseDocument11 pagesMetabolic Features of The Cell Danger ResponseLau RaNo ratings yet
- Advances of Glycometabolism Engineering in Chinese Hamster Ovary CellsDocument11 pagesAdvances of Glycometabolism Engineering in Chinese Hamster Ovary Cellsip87JCNo ratings yet
- C4 Plants Past Paper Question CIEDocument3 pagesC4 Plants Past Paper Question CIESevilay CaferogluNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology 5Document20 pagesPlant Physiology 5avita rukmanaNo ratings yet
- Human Energy Expenditure During Rest and Physical ActivityDocument46 pagesHuman Energy Expenditure During Rest and Physical ActivityKamyab Sadeghzadeh100% (2)
- Cellular EnergyDocument3 pagesCellular EnergyEvelyn KimNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid SynthesisDocument70 pagesAmino Acid SynthesisBhavesh BatraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Drug Action 2 Barbiturate Analogs and Other Sedative Hypnotics - DeRuiter - Lecture Fall (2003) PDFDocument12 pagesPrinciples of Drug Action 2 Barbiturate Analogs and Other Sedative Hypnotics - DeRuiter - Lecture Fall (2003) PDFdextroenantiomerNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Kmk22004 Industrial MicrobiologyDocument4 pagesAssignment 1 Kmk22004 Industrial Microbiologyaliaanis386No ratings yet
- High Yield MCQs - Dr. Nikita NanwaniDocument10 pagesHigh Yield MCQs - Dr. Nikita NanwaniDeeksha BhardwajNo ratings yet
- B.sc. II Biotechnology Entire Sem - III & IVDocument29 pagesB.sc. II Biotechnology Entire Sem - III & IVGayatriNo ratings yet
- Advanced BIochemistry PPT I SemDocument469 pagesAdvanced BIochemistry PPT I Semkratikaagrawal50No ratings yet
- Desai 2008Document3 pagesDesai 2008Raul GamiñoNo ratings yet
- 1 Historical Overview and Future Perspective: Bernhard Eikmanns, Marcella Eikmanns, and Christopher J. PaddonDocument22 pages1 Historical Overview and Future Perspective: Bernhard Eikmanns, Marcella Eikmanns, and Christopher J. PaddonDr. Laxman RautNo ratings yet
- Phy Med Scien Tech Revised Syllabus Mar 2019 2Document100 pagesPhy Med Scien Tech Revised Syllabus Mar 2019 2AshokNo ratings yet