Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bond
Uploaded by
Don LeeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bond
Uploaded by
Don LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
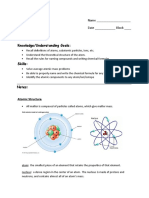
Bond: come together Charge: there is either a positive or negative charge Compound: two or more elements coming together.
Electrons: negative charged Electron clouds: a visible model of the most likely locations for the electrons in an atom. Electron level: A quantum-mechanical concept for energy levels of electrons about the nucleus; electron energies are functions of each particular atomic species. Family: Fission: a nuclear reaction in which an atomic nucleus is split into two smaller parts. Formula Unit: the chemical formula with the least number of elements outof the set of empirical fo rmulas having the same proportion of ions as elements.
Fusion: a nuclear reaction in which the nuclei of which atoms combine to form of two atoms combine to form a larger nucleus Group: a column of elements in a periodic table Half-Life: The time required for one half of a sample of radioactive isotope to decay Ion: an atom or a group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge Ionic Bond: The force that holds cautions and anions together Isotope: Atoms of a given element that have different numbers of neutrons and different mass number. Mass number: The sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom Metal: Elements that are good conductors of heat and electric current Molecule: A neutral group of atoms that is joined together by one or more covalent bond. Monomer: A small organic molecule that joins with other monomers to form a polymer Neutron: neutral charge Nucleus (nuclei): The dense, positively charged mass located in the center of an atom: Oxidation number Period: A row in a periodic table of elements the time required for one complete cycle of a periodic motion Periodic table: An arrangement of elements in columns based on a set of properties that repeat from row to row Polar: Pertaining to a compound exhibiting polarity or dipole moment, that is a compound bearing a partial positive charge on one side and a partial negative charge on the other.
You might also like
- Unit 1 - GlossaryDocument3 pagesUnit 1 - GlossaryNisal Nuwan SenarathnaNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Physical Chemistry I - AQA Chemistry A-LevelDocument9 pagesDefinitions - Physical Chemistry I - AQA Chemistry A-LevelÏt's RîçkgãrçīäNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Edexcel As Keywords Unit 1Document4 pagesChemistry Edexcel As Keywords Unit 1Ashan BopitiyaNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 1 Principles of Chemistry - Edexcel Chemistry IGCSEDocument5 pagesDefinitions - Topic 1 Principles of Chemistry - Edexcel Chemistry IGCSEReem MazarNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument27 pagesChemistryErica LeNo ratings yet
- SC 2Document3 pagesSC 2diyasanjeev13No ratings yet
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 1 DefinitionsDocument2 pagesAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 1 DefinitionsMuadh ChatiNo ratings yet
- Rebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamDocument5 pagesRebyuwer Sa Asignaturang AghamjoshuaNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Topic 3 Atoms Elements and Compounds - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument2 pagesDefinitions - Topic 3 Atoms Elements and Compounds - CAIE Chemistry IGCSEAtif BakhshNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry NotesDocument44 pagesAs Chemistry NotesRamesh IyerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Atomic StructureMelissa ChaiNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Unit 1: Structure, Bonding and Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument11 pagesEdexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Unit 1: Structure, Bonding and Introduction To Organic ChemistryDefaults rulezNo ratings yet
- Notebook 2 RevisedDocument1 pageNotebook 2 Revisedapi-329476755No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure KeywordsDocument1 pageAtomic Structure KeywordsWafa OsmanNo ratings yet
- Key TermsDocument9 pagesKey TermsLayan HalasaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 105, Glossary: Chapter 1, Matter and MeasurementsDocument4 pagesChemistry 105, Glossary: Chapter 1, Matter and MeasurementsmuhammadyousufkhanNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument14 pagesBasic ChemistryPitherNo ratings yet
- Edenglen Physical Science DefinitionsDocument17 pagesEdenglen Physical Science DefinitionsTanaka ChirawuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Teacher 2Document13 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Teacher 2noNo ratings yet
- Chemistry For PhysiciansDocument14 pagesChemistry For PhysiciansenzlibraryNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Chapter 2: The Structure of The Atom: No. TermDocument1 pageChapter 2: The Structure of The Atom: No. TermAnderlisz HoneyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2Document24 pagesChemistry Unit 2Auvan HilarioNo ratings yet
- Acid: Is That Substance That Donates A Hydrogen Cation To Another Substance Called BaseDocument3 pagesAcid: Is That Substance That Donates A Hydrogen Cation To Another Substance Called BaseKIMBERLY ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Required IB Physics DefinitionsDocument7 pagesRequired IB Physics DefinitionsКатерина ДьомкінаNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesAtomic StructureRamchandran IyerNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument4 pagesChemistryKent RosimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 VocabDocument2 pagesChapter 2 VocababNo ratings yet
- InformationDocument2 pagesInformationScarleth PortilloNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry DefinitionsDocument5 pagesIb Chemistry DefinitionsChe Jen Wang100% (1)
- FAD1005 Chemistry 1 Definition ListDocument3 pagesFAD1005 Chemistry 1 Definition ListmuhammadNo ratings yet
- Chap 2 ChemistryDocument20 pagesChap 2 ChemistryLina AnberNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument9 pagesChemistry NoteslunaNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument14 pagesBasic ChemistryAtul DwivediNo ratings yet
- Esp Answer KeyDocument2 pagesEsp Answer KeyAslan MorgadoNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry - Definitions (V.1) Topic 1 - StoichiometryDocument9 pagesIb Chemistry - Definitions (V.1) Topic 1 - StoichiometryNikole GualdrónNo ratings yet
- Notebook 2Document1 pageNotebook 2api-340425056No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Electronic Structure of The Atom Rz29fmDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure and Electronic Structure of The Atom Rz29fmkerri “Kerri” samNo ratings yet
- Early Chemistry: Early Chemists Only Believed in 1 Element: Dirt Later Chemists Believed in 4 ElementsDocument14 pagesEarly Chemistry: Early Chemists Only Believed in 1 Element: Dirt Later Chemists Believed in 4 ElementsDili Apriana AksariNo ratings yet
- Definitions PDFDocument9 pagesDefinitions PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- All Matter in Universe Is Composed Of: AtomsDocument11 pagesAll Matter in Universe Is Composed Of: AtomsmNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1atomic StructureDocument10 pagesChemistry 1atomic StructureRosely PaquiteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Vocabulary: Jake Sherman Chemistry PAP-FDocument2 pagesChapter 3 Vocabulary: Jake Sherman Chemistry PAP-FBobbi BooneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - PeriodicityDocument3 pagesChapter 3 - PeriodicitySimran Pamela ShahaniNo ratings yet
- 2 Repaso de ChemestryDocument7 pages2 Repaso de ChemestryLuciana AbudNo ratings yet
- 2 Matter Notes - TeacherDocument3 pages2 Matter Notes - Teacherapi-251355123No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Chemical Level of OrganizationDocument17 pagesChapter 2 The Chemical Level of OrganizationO AfolabiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LifeDocument25 pagesChemistry of LifeEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec Notes CompletedDocument36 pagesChem Lec Notes Completedaliaaplarisan647No ratings yet
- Unit 1 3 Periodic TrendsDocument30 pagesUnit 1 3 Periodic Trendsaudrey.sengeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes: Subatomic Particle Relative Mass Relative Charge Symbol Proton Neutron ElectronDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Notes: Subatomic Particle Relative Mass Relative Charge Symbol Proton Neutron ElectronAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Important DefinitionsDocument6 pagesImportant DefinitionsicedgoblinNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesTopic 1 - Atomic Structurejulian maltoNo ratings yet
- Keywords (F332)Document2 pagesKeywords (F332)minato05No ratings yet
- 3.classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Some Important Points and Terms of The ChapterDocument7 pages3.classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Some Important Points and Terms of The ChapterShivaNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry Chapter 3 - Atomic StructureDocument5 pagesCsec Chemistry Chapter 3 - Atomic Structurechelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends VocabDocument2 pagesPeriodic Trends Vocabyufeimou2007No ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1Document1 pageInformation Sheet 1mas510bdNo ratings yet
- Important As DefinitionsDocument3 pagesImportant As DefinitionsmiammyNo ratings yet