Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Peperiksaan Percubaan Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2011 1511/Sj
Uploaded by
Mhafiz AhmadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Peperiksaan Percubaan Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2011 1511/Sj
Uploaded by
Mhafiz AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
SULIT
JABATAN PELAJARAN PERAK
PEPERIKSAAN PERCUBAAN SIJIL PELAJARAN MALAYSIA 2011
Science Kertas 1 & Kertas 2 Skema Jawapan September
1511/SJ
UNTUK KEGUNAAN PEMERIKSA SAHAJA SCIENCE Paper 1 and Paper 2 MARKING SCHEME
This marking scheme contains 9 printed pages 1511 (PP)
SULIT [Lihat halaman sebelah SULIT
SULIT Science SPM Paper 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 B B A D A D A C A B 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 C B D C D D B C B C 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 C B A D C A B D A D 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 D B A A B C D C C B 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 C A A C D A B C D C
SULIT
SULIT Paper 2 Question
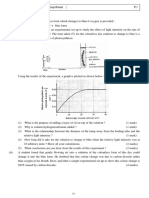
(a) Volume of gas (collected) (b)
Volume of gas (cm 3) Isipadu gas (cm3) X 40 X X X
Answer
Mark 1
Marks 1
30
20 X 10
1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Time (minute) Masa (minit)
(c) (i)
Volume of gas collected is directly proportional to the reaction time.
1 1 Total 2 5 1
(ii) 48 cm3
(a) 1.5 0.1 cm (b) 1. Near object from the pin-hole camera produce large image. 2. Further object from the pin-hole camera produce small image. 3. The size of image in Diagram 2.1 is larger than the size of image in Diagram 2.2. 2 (c) 1. The nearer the distance of the object, the larger the size of the image. 2. The further the distance of the object, the smaller the size of the image. (d) 1. The size of the object // The height of the object 2. The size of the hole. // Number of pin hole. (e) The image is sharper // A sharper image is produce.// Sharp image on the screen. 3 (a) Bacteria cannot grow under white light/light/ sunlight/bright light SULIT 3
1 1 Total 1
1 1 5 1
SULIT Bacteria growth well in the dark place. (b) (i) Manipulated variable: Light intensity// presence of light (ii) Responding variable: Growth of bacteria// Bacterial growth // Cloudiness of nutrient broth (c) In the dark (d) Bacterial growth is a process that causes the nutrient broth becomes cloudy. (a) 1. Green pea seedling with complete culture solution have more roots than that of culture solution without phosphorous. 2. Green pea seedling with complete culture solution produce more roots than culture solution without phosphorous. 4 (b) Complete culture solution contains phosphorous for the growth of roots. (c) (i) Type of seedling// Volume of culture solution // Size of seedling// (ii) The number of roots // Growth rate (d) Algae will growth in the solution. Total (a) Radioactive decay (b) Ray M : Beta rays Ray N : Gamma rays (c) 1. Lead 2. Concrete 5 (d) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cause cancer Kills / damage body cells / tissues Causes infertility / sterility Causes death Causes mutation Causes deformity of newborn babies 1 2 1 1 1 1 5 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 Total 1 2 1 1 5 1
1 2 [Any two] 1 Total 6
6 (a) (i) SULIT Mitosis 4 1
SULIT (ii) 1. To increa s e the numb er of body / som a tic cells. 2. Replace worn out / dead cells. 3. Reproduc e asexu ally in unicellular organis m s / fungi/ ferms/ moss e s . (b) 1. Each chromos o m e s doubles (to beco m e a pair of chrom a tid e s ). 2. Chromos o m e s replicat e (to form two chrom a tid e s) (c) 1 1 (d) Tips of shoot / roots. (e) 2 (a) X: Kernel Y: Mesocarp (b) Mesocarp // Y (c) Vitamin A / E 7 (d) 1. It is resistant to high temperature // 2. Does not produce unpleasant odours. (e) Sterilisation , Separation , Extraction , Filtration , Purification 1 1 Total (a) (i) Chilli sauce Y. (ii) Has expiry date. (b) (i) Monosodium glutamate (ii) 1. Cancer 2. Mental retardation in chlidren 8 (c) To slows down the action of bacteria // To avoid the bacterial growth in food. (d) Net weight // Quantity of food 1 1 1 1 1 1 Total 6 (a) 3 SULIT 5 1 1 1 1 6 Total 1 1 1 1 1 1 6 2 1 1
1 1 1
2 1 1
3 1 1 1
SULIT
(b) 1. Informations is not affected by the change of wheather/ condition in the atmosphere. 9 2. More information can be transmitted. (c) (i) P : Gamma ray (ii) Radio waves (iii) Microwaves 10 (a) Hypothesis: 1. The presence of salt increases the boiling point of distilled water. 2. Presence of impurities will increase the boiling point of distilled water. (b) (i) Aim: To study the effect of impurities on the boiling point of distilled water. (ii) Variables : 1. Manipulated : The presence of impurities / table salt 2. Responding : Boiling point (of distilled water / mixture) 3. Fixed : Volume of distilled water // Quantity of salt // Type of salt. (Any 2) (iii)Apparatus: 1. Distilled water 2. Table salt 3. Beaker 4. Wire gauze 5. Tripod stand, 6. Bunsen burner 7. Thermometer (iv) Procedure : 1. Pour 100 cm3 of distilled water into a beaker. 2. Heat up distilled water until it boils. 3. Observe and record the boiling point by using thermometer. 4. Repeat the experiment with mixture of distilled water and salt. OR: Functional and labelled diagram
1 1 1 1 1 Total 3 6 2 1
1 1
1 1
1 1 2 (max)
1 1 1 1 4
1 (v) Result : SULIT 6
SULIT
The presence of impurities Without salt With salt
Boiling point / oC
Total
10
(a) Two differences between chemical and physical changes: Chemical changes 1. New substance is formed. 2. Not reversible // Difficult to reverse Example of physical changes: 1. Melting ice 2. Evaporation of water. 3. Dissolving sugar in water. (b) (i) Common characteristics: 1. New substance is formed. 11 2. Not reversible // Difficult to reverse (ii) Other example of chemical changes: 1. Heating iron with sulphur 2. Burning magnesium in presence of air. 3. Heating copper (II) carbonate. (iii) Two example of physical changes: 1. Melting ice 2. Evaporation of water. 3. Dissolving sugar in water. and not reversible. [Any two] 1 1 Total 2 1 10 (iv) Chemical changes is a process which is new substance is formed 1 [Any one] 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 4 Physical changes 1. No new substance is formed. 2. Reversible // Easy to reverse. 1 1
SULIT
SULIT
(a) Type of plastic Thermoplastics Thermosets Example Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) / nylon / polythene / perspex / polystyrene / polypropene Bakelite / melamine / epoxy glue / 2 2 (b) Identify the problem: Environmental pollution Clarification of the problem: Improper disposal of plastics wastes. 12 Methods to overcome the problem: 1. Recycling the plastics 2. Reuse the plastics 3. Burning the plastics in incinerators. 4. Bury the plastics in the ground. 5. Use biodegradable plastics. [Any three methods] Best method and reason: e.g: Method: Burning the plastics in incinerators. Reason: Prevent the release of carbon dioxide or poisonous gases. [Any one method with correct reason] 1 1 4 1 1
1 1 1
Total ENDS OF SCHEMES
10
SULIT
You might also like
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Plant NutritionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Peperiksaan Percubaan Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2011 1511/SjDocument8 pagesPeperiksaan Percubaan Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia 2011 1511/SjDavid SwanggerboyNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Ecology And Our Impact On The EcosystemNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Solaf 2 SainsDocument10 pagesSkema Jawapan Solaf 2 SainsFidaNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan SOLAF 3 Sains SPM 2011F PDFDocument9 pagesSkema Jawapan SOLAF 3 Sains SPM 2011F PDFRoxus ThamNo ratings yet
- Microbiological Aspects of Pollution Control: Fundamental Aspects of Pollution Control and Environmental ScienceFrom EverandMicrobiological Aspects of Pollution Control: Fundamental Aspects of Pollution Control and Environmental ScienceNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan SOLAF 1 Sains SPM 2011Document9 pagesSkema Jawapan SOLAF 1 Sains SPM 2011Muhd Shahir Salleh100% (1)
- Marking Scheme Sains SPM Diagnostik Kertas 2Document16 pagesMarking Scheme Sains SPM Diagnostik Kertas 2Nirmala JosephineNo ratings yet
- Skema Kertas 1 Sains SPMDocument9 pagesSkema Kertas 1 Sains SPMSurie Di Hati AreyonNo ratings yet
- Skema Solaf2 Kertas2Document10 pagesSkema Solaf2 Kertas2Leong LaichuoNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Sains Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2Document3 pagesSkema Jawapan Sains Tingkatan 5 Kertas 2riyashree100% (1)
- Skema Paper 2 ChemDocument11 pagesSkema Paper 2 ChemFarah Shafiqah AmiruddinNo ratings yet
- Skema Set 6Document9 pagesSkema Set 6Azian MusaNo ratings yet
- Skema Set 2 Kertas 2Document7 pagesSkema Set 2 Kertas 2Man Yang PandaiNo ratings yet
- Total 9: Na Na ODocument8 pagesTotal 9: Na Na Osamsu41520No ratings yet
- Biology Paper 2 by Andy Tse: InstructionsDocument8 pagesBiology Paper 2 by Andy Tse: InstructionsnonameNo ratings yet
- Science: Kertas 1 Dan Kertas 2 OgosDocument5 pagesScience: Kertas 1 Dan Kertas 2 OgospiyabaikNo ratings yet
- Jabatan Pelajaran TerengganuDocument8 pagesJabatan Pelajaran TerengganuAzian MusaNo ratings yet
- 2011 SBP Kimia SkemaDocument22 pages2011 SBP Kimia SkemaCarmen Km ﺕNo ratings yet
- Answer ATSDocument17 pagesAnswer ATSkembara08No ratings yet
- 4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Document22 pages4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Robert HicksNo ratings yet
- HPCCSS F1 Is 2021 Hye QPDocument15 pagesHPCCSS F1 Is 2021 Hye QPxXCORG1GUCC1XxNo ratings yet
- 0620 w11 Ms 32Document6 pages0620 w11 Ms 32skglkNo ratings yet
- SPM Trial 2011 Chemistry A PahangDocument22 pagesSPM Trial 2011 Chemistry A Pahangyin_soon_1No ratings yet
- Scicent SQ U2 5-6 SetA Final eDocument4 pagesScicent SQ U2 5-6 SetA Final esteve LNo ratings yet
- Bio 3.1 PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesBio 3.1 PhotosynthesisSuzuko YukinoNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah Chemistry SPM 2013 K2 SKEMADocument12 pagesTrial Kedah Chemistry SPM 2013 K2 SKEMACikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Perlis Biologi Skema K2 SPM 09Document15 pagesPerlis Biologi Skema K2 SPM 09kanmanikandaNo ratings yet
- 2016 P2S1 F5 Chemistry Paper 2 Answer Scheme:: Answer Sub Mark MarksDocument9 pages2016 P2S1 F5 Chemistry Paper 2 Answer Scheme:: Answer Sub Mark MarksCt NurNo ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle MCQDocument23 pagesCarbon Cycle MCQHʌɩɗɘʀ Aɭɩ0% (1)
- Paper 2 Marking Scheme 2013Document18 pagesPaper 2 Marking Scheme 2013Jaaizah JaafarNo ratings yet
- 2016 P6 FSC Mendaki PSLE AnswersDocument4 pages2016 P6 FSC Mendaki PSLE AnswersAaron HeeNo ratings yet
- Science Solved-Sample-Paper-Class-7-SA1-Set-1Document5 pagesScience Solved-Sample-Paper-Class-7-SA1-Set-1SushilNo ratings yet
- Https Doc 0c 0c Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentDocument9 pagesHttps Doc 0c 0c Apps Viewer - GoogleusercontentAhmad RezaNo ratings yet
- SOTA Worksheeet ScienceDocument18 pagesSOTA Worksheeet ScienceShannon OngNo ratings yet
- Civil Questions and Answers-Other-Major-TopicsDocument39 pagesCivil Questions and Answers-Other-Major-TopicsAkd Deshmukh100% (1)
- SPM Trial 2015 Chemistry A2 PerlisDocument10 pagesSPM Trial 2015 Chemistry A2 PerlisagilenNo ratings yet
- SA-1 Science 7thDocument5 pagesSA-1 Science 7thAmrita SenNo ratings yet
- Ecw568 Test Question 5 Feb 2021Document4 pagesEcw568 Test Question 5 Feb 2021Syalmira LovetobelovedNo ratings yet
- F.3 1st Term Bio Exam (16-17) - TV ShortDocument2 pagesF.3 1st Term Bio Exam (16-17) - TV Shortjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Sagam 2nd Term Sec Quest.Document60 pagesSagam 2nd Term Sec Quest.akinmadeayomide095No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper-08 (For 2013)Document11 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper-08 (For 2013)cbsesamplepaperNo ratings yet
- SBP 2011 Mid Year AnswerDocument17 pagesSBP 2011 Mid Year AnswerSaya MenangNo ratings yet
- Biology: James Ruse Agricultural High SchoolDocument17 pagesBiology: James Ruse Agricultural High SchoolAlexCuiNo ratings yet
- STFALKKC F2IS AnsDocument3 pagesSTFALKKC F2IS AnsVic KyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Science SA1 Set 2Document4 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 7 Science SA1 Set 2Manogna ChembetiNo ratings yet
- BCA-445-18, BCA-445-20, BCA-CS-445-20 Environmental StudiesDocument2 pagesBCA-445-18, BCA-445-20, BCA-CS-445-20 Environmental StudiesnbrcodingaddaNo ratings yet
- EPC 312 Final Exam (June2015)Document13 pagesEPC 312 Final Exam (June2015)kalasa roydNo ratings yet
- Summer 2023 Biology Mock 1BDocument23 pagesSummer 2023 Biology Mock 1Bbsc1280No ratings yet
- F.3 17-18 1st Term Bio Exam AnswersDocument4 pagesF.3 17-18 1st Term Bio Exam Answersjonas hoNo ratings yet
- Environmental Issues: SolutionsDocument26 pagesEnvironmental Issues: SolutionsvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Env Module 4 QuestionsDocument19 pagesEnv Module 4 QuestionsDeepti KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 9701 s02 QP 6Document12 pages9701 s02 QP 6Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Science Annual 20-21 Answer KeyDocument6 pagesScience Annual 20-21 Answer KeyVIMLA BNo ratings yet
- Environmental Issues: SolutionsDocument26 pagesEnvironmental Issues: SolutionsPrakshit TyagiNo ratings yet
- NTSE - II-2014: Scholastic Ability TestDocument20 pagesNTSE - II-2014: Scholastic Ability TestShorya KumarNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Law. Application To AirDocument12 pagesIdeal Gas Law. Application To AirJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Equipment Made of 2.25 Cr-1 Mo Steel in Quenched and Tempered ConditionDocument37 pagesEquipment Made of 2.25 Cr-1 Mo Steel in Quenched and Tempered ConditionNayibet Quintero DíazNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Work SheetDocument28 pagesChemical Bonding Work Sheetkrishna priyaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Answers Q6-Q11Document6 pagesTutorial 1 Answers Q6-Q11A/P SUPAYA SHALININo ratings yet
- MCQ S-1Document8 pagesMCQ S-1kavisanjurohillaNo ratings yet
- Review On Adsorption of Heavy Metal in Wastewater by Using GeopolymerDocument8 pagesReview On Adsorption of Heavy Metal in Wastewater by Using GeopolymerJanine Rose MendozaNo ratings yet
- Laser Marking FundamentalsDocument4 pagesLaser Marking FundamentalsJosé Cassina100% (1)
- Thermal Spray Coatings: Ads Ta, E'Document6 pagesThermal Spray Coatings: Ads Ta, E'Darryl007No ratings yet
- Silicone As A Moulding Material For LossDocument3 pagesSilicone As A Moulding Material For LossDan Octavian PaulNo ratings yet
- Msds Cleaning SolventDocument4 pagesMsds Cleaning SolventMoineeNo ratings yet
- Cathodic ProtectionDocument12 pagesCathodic ProtectionIndhumathi BabusenanNo ratings yet
- 10-Coagulation and PrecipitationDocument34 pages10-Coagulation and PrecipitationAnu NNo ratings yet
- Nanomaterials What Are Nanomaterials?Document6 pagesNanomaterials What Are Nanomaterials?ASHKRIT TIWARINo ratings yet
- wch12 01 Que 20221015Document22 pageswch12 01 Que 20221015Sifat OffeyNo ratings yet
- Survey Form For Collecting Reverse Osmosis Plant Operation DataDocument2 pagesSurvey Form For Collecting Reverse Osmosis Plant Operation DataJendayiNo ratings yet
- Laws of Chemical CombinationDocument78 pagesLaws of Chemical Combinationharry metuNo ratings yet
- BIOFUELS ACT of 2006RA 9367Document6 pagesBIOFUELS ACT of 2006RA 9367Jem VadilNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Stability and Excipient CompatibilityDocument12 pagesPhysical and Chemical Stability and Excipient CompatibilityRebecca ChenNo ratings yet
- Common & Chemical Names: Dr. Gaurav GargDocument12 pagesCommon & Chemical Names: Dr. Gaurav GargATUL SINGHNo ratings yet
- Eksoy ZDHC Level3Document6 pagesEksoy ZDHC Level3Waqas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Httppostedfile Track Eqp 1feb11 23393Document12 pagesHttppostedfile Track Eqp 1feb11 23393dorao80No ratings yet
- Test # 3 Redox RreactionsDocument2 pagesTest # 3 Redox RreactionsAzain CardenasNo ratings yet
- Rhenogran mbt80 en RCRDocument2 pagesRhenogran mbt80 en RCRsaadNo ratings yet
- Consumer Chemistry Grade 9Document27 pagesConsumer Chemistry Grade 9Roxanne Sioco100% (2)
- A Review On Design and Fabrication of Fuel Fired Crucible FurnaceDocument12 pagesA Review On Design and Fabrication of Fuel Fired Crucible FurnaceJamilu TankoNo ratings yet
- Regulation 2013 Me 6352 Manufacturing Technology Notes - PmsDocument164 pagesRegulation 2013 Me 6352 Manufacturing Technology Notes - PmsSubramanian PmNo ratings yet
- Feed Ingredients and Fertilizers For Farmed Aquatic Animals: Sources and Composition.Document222 pagesFeed Ingredients and Fertilizers For Farmed Aquatic Animals: Sources and Composition.DARAVELLA100% (2)
- 61510008Document1 page61510008Krishna Vacha100% (1)
- Coating-Failure-Defects 2 PDFDocument10 pagesCoating-Failure-Defects 2 PDFaahil ahmadNo ratings yet
- April 11 - Gas Sweetening ProcessDocument95 pagesApril 11 - Gas Sweetening Processhoangduy7696No ratings yet