Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Discussion
Uploaded by
santi_su2Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Discussion
Uploaded by
santi_su2Copyright:
Available Formats
DISCUSSION
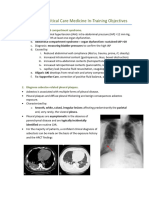
In this case, the patient had been diagnosed as a empyema ec pneumonia community + hypertensi grade 1, already checked cultured and sitology but havent been known the result . Maximal lesiom based on history taking, physical examination, and support examination.
1. The anamnesis : fever, increased body temperature, cough with mucoid sputum, breathlessness and chest pain. 2. Chest examination : a. On inspection, the right lung lag time breathing b. On palpation, pasa fremitus on the right lung is decreased c. On percussion, dullness on the right lung d. On auscultation, vesicular on the right lung is decreased. 3. Taking from support examination, LED 110 mm/hour, WBC 18.700 mm 4. Thorax photo PA appearance show radioopaque at the basal of right lung 5. USG thorax : There was mucoid fluid at the basal of left hemithorax 6. Thoracentesis - Pleural fluid appearance grossly purulent thick, viscous, foul-smelling pus. Foul-smelling fluid indicates an anaerobic infection. Because the diagnostic thoracentesis yields thick pus,definitive pleural drainage is absolutely required. The WSD is attached. 7. Treatment a. Metronidazole Imidazole ring-based antibiotic active against various anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Used in combination with other antimicrobial agents (except for C difficile enterocolitis). Not standard practice to use metronidazole alone because some anaerobic cocci and most microaerophilic streptococci are resistant. a. Meropenem
A carbapenem, not a beta-lactam antibiotic. Bactericidal broad-spectrum carbapenem antibiotic that inhibits cell wall synthesis. Effective against most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Has slightly increased activity against gram-negative bacteria and a slightly decreased activity against staphylococci. b. Methyl prednisolone A steroid medication used to treat inflammatory disorders. Methyl prednisolone decreases inflammation by acting within cells to prevent the release of certain chemicals that are important in the immune system and also decreased the number of white blood cells circulating in the blood.
c. Nifedipine A short acting, calcium channel blocker. Nifedipine prevents calciumdependent mycocyte contraction and vasoconstriction, causing dilatation of the coronary and sytemic arteries. Increased oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue, decreased systemic blood pressure and decreased after load.
8. Prognosis is dubia. Because most patients recover, but the mortality rate remains approximately 10%. Depends on antibiotic therapy and drainage of pleural fluid. 9. Differential diagnose is empyema ec abcess hepar. The result of rivalta test is negative. It means the pleural fluid is doesn`t come from pulmo, but extra pulmo. Besides rivalta test, USG thorax show there was mucoid fluid at the basal of left hemithorax and related to hepar.
You might also like
- Villains 9 Never Never - Serena ValentinoDocument82 pagesVillains 9 Never Never - Serena Valentinoamiratarke82No ratings yet
- IMO Fire Plans Ship Safety SignsDocument61 pagesIMO Fire Plans Ship Safety Signsmercury7k29750100% (3)
- PANCE Prep Pearls Pulmonary Questions PDFDocument8 pagesPANCE Prep Pearls Pulmonary Questions PDFkatNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia: Ang Gobonseng, Ed Gerard R. MedclerkDocument66 pagesCommunity Acquired Pneumonia: Ang Gobonseng, Ed Gerard R. MedclerkRyn Anfone100% (2)
- Staining in Microscopy - Stains and Techniques From WikipediaDocument321 pagesStaining in Microscopy - Stains and Techniques From WikipediaDan Johnson100% (5)
- C-Programming-Class 8Document39 pagesC-Programming-Class 8jack_harishNo ratings yet
- EXP4 The Diels Alder ReactionsDocument3 pagesEXP4 The Diels Alder ReactionsLaura GuidoNo ratings yet
- Pancytopenia Secondary To Bacterial SepsisDocument16 pagesPancytopenia Secondary To Bacterial Sepsisiamralph89No ratings yet
- Acute Bronchitis Case StudyDocument6 pagesAcute Bronchitis Case Studyulka0750% (2)
- Respiratory PathDocument7 pagesRespiratory Pathmoped00No ratings yet
- Bronchitis Obliterans Due To Mycoplasma PneumoniaDocument7 pagesBronchitis Obliterans Due To Mycoplasma Pneumoniawawa chenNo ratings yet
- December09, Paper 1Document16 pagesDecember09, Paper 1Ismail SialaNo ratings yet
- Nbme NotesDocument4 pagesNbme NotesNivedha RajanNo ratings yet
- TMP 155 BDocument7 pagesTMP 155 BFrontiersNo ratings yet
- NBME 1 RatioDocument87 pagesNBME 1 RatioBugs Caslib100% (1)
- A Rare Complication of Acute Appendicitis: Superior Mesenteric Vein ThrombosisDocument4 pagesA Rare Complication of Acute Appendicitis: Superior Mesenteric Vein ThrombosisEsha Putriningtyas SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Cardio & Chest AnswersDocument10 pagesCardio & Chest AnswersVişiön Ac TantaNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine 1Document23 pagesInternal Medicine 1Asif Newaz100% (1)
- A Case of Recurrent Hemoptysis Caused by Pulmonary Actinomycosis Diagnosed Using Transbronchial Lung Biopsy After Bronchial Artery Embolism and A Brief Review of The LiteratureDocument8 pagesA Case of Recurrent Hemoptysis Caused by Pulmonary Actinomycosis Diagnosed Using Transbronchial Lung Biopsy After Bronchial Artery Embolism and A Brief Review of The LiteratureNiatazya Mumtaz SagitaNo ratings yet
- Tuberculous Pericarditis Leading To Cardiac Tamponade Importance of Screening Prior To ImmunosuppressionDocument3 pagesTuberculous Pericarditis Leading To Cardiac Tamponade Importance of Screening Prior To ImmunosuppressionLink BuiNo ratings yet
- RESP MEDICINE For PlabDocument73 pagesRESP MEDICINE For PlabJanie-Vi GorospeNo ratings yet
- Sample Test Questions: Krok 2Document41 pagesSample Test Questions: Krok 2kjkNo ratings yet
- Case Report (Septaecemia) : SummaryDocument3 pagesCase Report (Septaecemia) : Summaryikbal al-lamiNo ratings yet
- A Case of Lupus Pneumonitis Mimicking As Infective PneumoniaDocument4 pagesA Case of Lupus Pneumonitis Mimicking As Infective PneumoniaIOSR Journal of PharmacyNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine Review Class 2010Document65 pagesInternal Medicine Review Class 2010SuNo ratings yet
- Jurding Bedah MuzzamilDocument16 pagesJurding Bedah MuzzamilunknownNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia: Tammy Wichman MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Pulmonary-Critical Care Creighton University Medical CenterDocument80 pagesPneumonia: Tammy Wichman MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Pulmonary-Critical Care Creighton University Medical CenterKartika RezkyNo ratings yet
- RespiratoryDocument57 pagesRespiratoryMuhammad Javed GabaNo ratings yet
- High-Yield Review For The Pulmonary/Allergy/ENT Module Exam and USMLE Step 1Document6 pagesHigh-Yield Review For The Pulmonary/Allergy/ENT Module Exam and USMLE Step 1frabziNo ratings yet
- Medicine RespiratoryDocument80 pagesMedicine Respiratoryan kitNo ratings yet
- Krok2 - Medicine - 2013Document28 pagesKrok2 - Medicine - 2013ashighaNo ratings yet
- Crim Em2013-948071Document2 pagesCrim Em2013-948071m.fahimsharifiNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Round PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPediatric Round PneumoniaSalwa Zahra TsamaraNo ratings yet
- Kr2med 2004engDocument49 pagesKr2med 2004engSuma LathaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine In-Training ObjectivesDocument12 pagesPulmonary and Critical Care Medicine In-Training ObjectiveshectorNo ratings yet
- Soal RespiDocument9 pagesSoal RespiHaidir ArmansyahNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument10 pagesPneumoniaAubrey PerezNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sana Bashir DPT, MS-CPPTDocument46 pagesDr. Sana Bashir DPT, MS-CPPTbkdfiesefll100% (1)
- PertussisDocument6 pagesPertussisMrinal SivadasanNo ratings yet
- Trinity University of Asia St. Luke'S College of Nursing Case Study (Opd) NAME: Marie Deborah Kay B. Chakas CASE: Pneumonia (Pedia)Document19 pagesTrinity University of Asia St. Luke'S College of Nursing Case Study (Opd) NAME: Marie Deborah Kay B. Chakas CASE: Pneumonia (Pedia)MARIE DEBORAH KAY CHAKASNo ratings yet
- MCQ FMS ExamDocument8 pagesMCQ FMS ExamWisnu AdiputraNo ratings yet
- Septic ShockDocument2 pagesSeptic ShockLatifah LàNo ratings yet
- KROK2 2010 Paper (200Qs)Document62 pagesKROK2 2010 Paper (200Qs)Ali Zeeshan100% (1)
- Duran, Kayllien - SGD On CD GRP 14Document11 pagesDuran, Kayllien - SGD On CD GRP 14KAYLLIEN DURANNo ratings yet
- Pulmonology - Cases With AnswersDocument4 pagesPulmonology - Cases With AnswersSimran PiñheiroNo ratings yet
- Case Study Diagnosis and Treatment of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Patient BackgroundDocument2 pagesCase Study Diagnosis and Treatment of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Patient BackgroundHannah BuquironNo ratings yet
- SESSION 3 - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY With AnswersDocument9 pagesSESSION 3 - PATHOPHYSIOLOGY With AnswersSpeed SamNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Pneumonitis Caused by Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Pediatric PatientsDocument4 pagesNecrotizing Pneumonitis Caused by Mycoplasma Pneumoniae in Pediatric Patientswawa chenNo ratings yet
- 2014 Kabir Et Al. - Chronic Eosinophilic Leukaemia Presenting With A CDocument4 pages2014 Kabir Et Al. - Chronic Eosinophilic Leukaemia Presenting With A CPratyay HasanNo ratings yet
- MCQ TestDocument10 pagesMCQ TestWisnu Adiputra100% (1)
- PulmonologyDocument175 pagesPulmonologyJohanna GarciaNo ratings yet
- A Treacherous Course: Clinical Problem-SolvingDocument6 pagesA Treacherous Course: Clinical Problem-SolvingMorocco CandycatyNo ratings yet
- Lower Respiratory Study SheetDocument13 pagesLower Respiratory Study SheetJune Rhoades100% (2)
- My Masterclass Create Exam My History My DetailsDocument100 pagesMy Masterclass Create Exam My History My DetailsMuntasir BashirNo ratings yet
- Case Files® StreptokokusDocument4 pagesCase Files® StreptokokusAHMAD ADE SAPUTRANo ratings yet
- Case 1 - Pneumonia (Final)Document4 pagesCase 1 - Pneumonia (Final)Joegie ArioNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing - RespiratoryDocument15 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - RespiratoryChristian Esteves75% (4)
- 2009Document31 pages2009Pweety Gal PweetheartNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Medicine CME: Lancelot Mark Pinto, Arpan Chandrakant Shah, Kushal Dipakkumar Shah, Zarir Farokh UdwadiaDocument3 pagesRespiratory Medicine CME: Lancelot Mark Pinto, Arpan Chandrakant Shah, Kushal Dipakkumar Shah, Zarir Farokh UdwadiaLintang SuroyaNo ratings yet
- Infections in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Symposium Held at the Institute Jules Bordet, Brussels, BelgiumFrom EverandInfections in Cancer Chemotherapy: A Symposium Held at the Institute Jules Bordet, Brussels, BelgiumNo ratings yet
- AstanDocument4 pagesAstanAbdirahmanNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format Instructional Plan (Iplan) Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Vii, Central VisayasDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format Instructional Plan (Iplan) Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Region Vii, Central VisayasalexNo ratings yet
- Evaluative Commentary: Integrated Language Skills IiiDocument5 pagesEvaluative Commentary: Integrated Language Skills IiiShawn RizalNo ratings yet
- Caustic Soda ProductionDocument33 pagesCaustic Soda Productionrasoul100% (1)
- Eaton Complete Transaxle Repair Guide - Ea11whDocument45 pagesEaton Complete Transaxle Repair Guide - Ea11whSteve Nah100% (1)
- Standing EnukleasiiDocument3 pagesStanding Enukleasiig_meilisaNo ratings yet
- Living With The Himalayan MastersDocument27 pagesLiving With The Himalayan MastersLauren Hughes0% (3)
- A Comparison of The Ideal States of PlatDocument16 pagesA Comparison of The Ideal States of PlatSajid Mahsud100% (1)
- Nsejs Solved Past Paper 2012 PDFDocument22 pagesNsejs Solved Past Paper 2012 PDFJAYESH SHIVARKARNo ratings yet
- Brief History and Development of Traditional Mongolian MedicineDocument8 pagesBrief History and Development of Traditional Mongolian MedicineJim Hertzberg100% (1)
- FW106 Uer ManualDocument73 pagesFW106 Uer ManualDiego Martinez ConteiroNo ratings yet
- RE - 54 - confENc - (Application Manual)Document360 pagesRE - 54 - confENc - (Application Manual)Alexandre MorenoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio EssayDocument3 pagesPortfolio Essayapi-547515381No ratings yet
- Next Generation Firewall Installation GuideDocument251 pagesNext Generation Firewall Installation Guideea.hicham3770No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6Elynn TanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Adsorptive Capacity of Activated Carbon by Aqueous Phase Isotherm TechniqueDocument4 pagesDetermination of Adsorptive Capacity of Activated Carbon by Aqueous Phase Isotherm Techniquemkaseem74No ratings yet
- KZV Newsletter - JanuaryDocument9 pagesKZV Newsletter - JanuaryHasmik MehranianNo ratings yet
- C Programming Functions HomeworkDocument2 pagesC Programming Functions HomeworkAnonymous PDGLsjN1Q5No ratings yet
- Problem Set 6 Fall 2018 With SolutionsDocument5 pagesProblem Set 6 Fall 2018 With SolutionsrickNo ratings yet
- Calculation Storm PipeDocument10 pagesCalculation Storm PipesenghouNo ratings yet
- LKPD 2-Understanding Explanation TextDocument3 pagesLKPD 2-Understanding Explanation TextSabina TuankottaNo ratings yet
- ECA1 - Tests - Language Test 3ADocument1 pageECA1 - Tests - Language Test 3AAneta UrbaniakNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Loss in IndiaDocument15 pagesBiodiversity Loss in IndiaPrena NirolaNo ratings yet
- EDSA People Power RevolutionDocument2 pagesEDSA People Power Revolutionceyavio100% (2)