Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LPG Installation Tips
Uploaded by
ShyBokxCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LPG Installation Tips
Uploaded by
ShyBokxCopyright:
Available Formats
Liquid petroleum Gas (LPG) Systems
LPG installations are covered by BS 5482: parts 1, 2 &3. LPG is stored in tanks that range in size from domestic tonne to commercial 1,3,5,7 and 12 tonne tanks. Another method of sizing tanks is to use their water capacity i.e. 450 litres. The diagram below shows a typical schematic layout of a LPG system.
Installation Notes
1. A prime requirement is that storage vessels must not be installed within buildings particularly basements, LPG being heavier than air. 2. Storage pressure for propane is 6.9 bar.
3. This is reduced to about 0.70 bar at the first stage regulator, which supplies the primary distribution main running up to the outside of the building. 4. A second stage regulator fitted on the outside wall of the building will have an output pressure of 0.037 bar (37 millibar) to suit the standard low pressure rating of appliances such as cookers, boilers,etc.
The storage of LPG fixed installations.
1. At normal temperature commercial propane has a vapour pressure of about 7 bar. 2. LPG vapour is denser than air. 3. All piping over 13mm should be made of steel. 4. Copper piping should be seamless and only used under 13mm diameter. 5. LPG tanks over 9000 litres water capacity should be enclosed by a 1.8metre fence. 6. Tanks should be installed with pressure relief valve, drain, contents gauge, and if the tank is over 2250 litres water capacity, a pressure gauge. 7. All connections should have a shut-off valve.
Installation notes for Liquefied Petroleum Gas plants.
1. Tanks up to 1 tonne product capacity must be sited at least 3 metres (10 feet) away from any building. 2. Tanks greater than 1 tonne capacity must be sited at greater distances from buildings. 3. Special jointing compound for pipe fittings should be used. 4. Special P.T.F.E. tape may be used. 5. For most cases pipework from the first stage of pressure regulation is of heavyweight class C galvanised steel. 6. 12.5mm water gauge (0.5 in. w.g.) pressure drop is the maximum permitted pressure drop on pipelines. 7. A shut-off valve must be positioned in the gas line immediately before it enters a building and a second isolating valve should be installed before second stage pressure regulation.
Preventing Gas Leaks
A scenario of gas leaking slowly into a cavity wall or other enclosed space is very dangerous. The gas leak may not be detected for some time and an explosion may occur if the gas quantity builds up and a source of ignition is present. To prevent gas leaks the following points should be noted; 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Gas pipes to run outside as much as possible. Minimal joints in pipework. Test pipes after installation for leaks. If gas pipes have to run in an enclosed space install a Gas leak detection system with sensors, alarm and automatic gas shut off valve. If gas pipes have to run in an enclosed vertical shaft install an extract fan so that the shaft is continuously fully vented. Movement allowances should be made for Gas pipes laid in cement floor screeds. Periodic checks (by competent person) to ensure there are no leaks. Use correct pipes and jointing methods MDPE (yellow plastic) underground, galvanised steel and copper above ground. Most gas leaks occur at pipe joints. Ensure correct jointing method for pipe system such as fusion joints for large MDPE pipes, screwed joints for steel pipes and compression and capillary jointing methods for copper pipes. Also Gas PTFE tape (thicker than normal) is used for screwed and compression fittings.
You might also like
- LPG InstallationDocument24 pagesLPG InstallationHaris LatifNo ratings yet
- Specification LPG ServicesDocument12 pagesSpecification LPG ServicesDak SerikNo ratings yet
- Gas Piping Building Services 1Document21 pagesGas Piping Building Services 1abinayaNo ratings yet
- Guide to Safe Domestic Gas PipingDocument30 pagesGuide to Safe Domestic Gas Pipingmitasyahu50% (2)
- LPG Pipe Sizing ChartDocument1 pageLPG Pipe Sizing ChartJohnt1260% (5)
- LPG Pipe SizingDocument2 pagesLPG Pipe Sizingimtiyaz94No ratings yet
- Fire Safety Requirements For Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) Cylinder InstallationsDocument26 pagesFire Safety Requirements For Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) Cylinder Installationspitong_manning100% (2)
- LPG Pipe SystemDocument10 pagesLPG Pipe SystemHansika RajapakshaNo ratings yet
- LPG SystemDocument12 pagesLPG Systemmzma1971No ratings yet
- Layout Plans For Installation of LPG Autogas StationsDocument15 pagesLayout Plans For Installation of LPG Autogas StationsEjaz Ahmed RanaNo ratings yet
- Gas Pipe SizingDocument17 pagesGas Pipe Sizingcentaury2013100% (2)
- LPG Piping SizeDocument13 pagesLPG Piping SizeSopi LabuNo ratings yet
- LPGDocument67 pagesLPGraritylim100% (3)
- Gas Installation PDFDocument31 pagesGas Installation PDFNelson VargasNo ratings yet
- Vol 4 SNG and LPG Systems OverviewDocument57 pagesVol 4 SNG and LPG Systems OverviewHenry Suarez100% (3)
- 5000m3 LPG Tank FarmDocument2 pages5000m3 LPG Tank FarmLpgTankFarmNo ratings yet
- LPG SpecificationsDocument18 pagesLPG SpecificationsAtef Mohameden100% (1)
- LPG Project 3Document13 pagesLPG Project 3Jehirul IslamNo ratings yet
- BS 6172 - 2010Document30 pagesBS 6172 - 2010thegasengineer50% (4)
- Designing Fire Fighting System For LPG Bottling Plant - Pavan EditedDocument12 pagesDesigning Fire Fighting System For LPG Bottling Plant - Pavan Editedpavan50% (2)
- Mobile LPG Cylinder Filling PlantsDocument13 pagesMobile LPG Cylinder Filling PlantsASKOKONo ratings yet
- LPG 106 Schematic Diagram Gas LayoutDocument1 pageLPG 106 Schematic Diagram Gas Layoutkhawaldeh jamal0% (1)
- LPG Distribution For High Rise BuildingsDocument10 pagesLPG Distribution For High Rise Buildingskmas16120% (1)
- MED GAS PROD STOR TRANS DELDocument67 pagesMED GAS PROD STOR TRANS DELsantosh100% (2)
- Stair Pressurization CalculationDocument9 pagesStair Pressurization CalculationHaymanot BaynesagnNo ratings yet
- Standard Codes Followed in LPG IndustriesDocument41 pagesStandard Codes Followed in LPG Industriesaarunsnair100% (2)
- Automatic Fire Sprinkler SystemDocument16 pagesAutomatic Fire Sprinkler SystemArnel ArnaoNo ratings yet
- SPRINKLER Zone Control ValveDocument4 pagesSPRINKLER Zone Control ValveIonut SomneaNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Systems for BuildingsDocument70 pagesFire Protection Systems for BuildingsZezo Abdallah100% (1)
- LPG SpecificationDocument4 pagesLPG SpecificationAdeniyi Alese50% (2)
- Gas Piping Design and InstallationDocument75 pagesGas Piping Design and Installationboron97100% (2)
- LPG Handbook PDFDocument50 pagesLPG Handbook PDFAhmed Sherif100% (1)
- Day 04 Maintenance of LPG SystemDocument11 pagesDay 04 Maintenance of LPG Systemkmas1612No ratings yet
- Deluge System Definition Working Applications and Advantages With PDFDocument4 pagesDeluge System Definition Working Applications and Advantages With PDFSiwaNo ratings yet
- Gas Reticulation Project Group 8Document13 pagesGas Reticulation Project Group 8Mohd Hafiz50% (2)
- B o Q - LPGDocument3 pagesB o Q - LPGHemn Rafiq Tofiq100% (3)
- LPG Piped Gas Systems For Residential Flats-1Document32 pagesLPG Piped Gas Systems For Residential Flats-1tannu singh0% (3)
- Smoke Extraction in BuildingsDocument59 pagesSmoke Extraction in Buildingskonan2007100% (1)
- Kid de Wet ChemicalDocument110 pagesKid de Wet Chemicalbhima irabatti100% (1)
- Fire Protection Requirements For High Rise Building 15 M in Height or AboveDocument40 pagesFire Protection Requirements For High Rise Building 15 M in Height or AboveNishant Sharma100% (1)
- Statutory LPG standardsDocument4 pagesStatutory LPG standardsalwacsNo ratings yet
- Technical Journal Fire PumpDocument7 pagesTechnical Journal Fire PumpIzallmachineNo ratings yet
- LPG PipingDocument20 pagesLPG PipingLelosPinelos123100% (2)
- Chap5 Gas Reticulation SystemDocument188 pagesChap5 Gas Reticulation SystemNorafiqah Ismail100% (3)
- Medical Gas Pipeline SystemDocument16 pagesMedical Gas Pipeline Systemshivangiis0796511No ratings yet
- LPG Design Guiudliines DubaiDocument15 pagesLPG Design Guiudliines Dubairiyas100% (3)
- LPG 102 Ground Floor PlanDocument1 pageLPG 102 Ground Floor Plankhawaldeh jamalNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For LPG Systems Work Installation, Testing & CommissioningDocument6 pagesMethod Statement For LPG Systems Work Installation, Testing & CommissioningDong Vanra100% (1)
- Sprinkler Sizing en v1Document12 pagesSprinkler Sizing en v1CristianDumitru0% (1)
- Fire Drencher System - Base-Engineer PDFDocument2 pagesFire Drencher System - Base-Engineer PDFpequenita34100% (1)
- 1.1.1 LPG 1.1.2viscosity 1.1.3 Vapor Pressure 1.1.4 Specific Gravity 1.1.5 Flame Temperature 1.1.6 Flash Point 1.1.7 Odorization of LPG 1.1.8 Colour 1.1.9 ToxicityDocument6 pages1.1.1 LPG 1.1.2viscosity 1.1.3 Vapor Pressure 1.1.4 Specific Gravity 1.1.5 Flame Temperature 1.1.6 Flash Point 1.1.7 Odorization of LPG 1.1.8 Colour 1.1.9 ToxicityzeyadNo ratings yet
- Minimum Maximum LPG Energy Content (Btu/f)Document5 pagesMinimum Maximum LPG Energy Content (Btu/f)Mirza Aatir SalmanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Design BriefDocument5 pages3.1 Design BriefRaj KamalNo ratings yet
- Standards: (Comment Based On Propane)Document3 pagesStandards: (Comment Based On Propane)zorro21072107No ratings yet
- Refrigeration PipelinesDocument2 pagesRefrigeration PipelinesDavidB1206No ratings yet
- M.engineering - Piping SystemsDocument55 pagesM.engineering - Piping SystemsKordalhs KyriakosNo ratings yet
- GENERIC GENERATOR INSTALLATION MANUAL - Sections 7 and 8.pdf TIMBLEDocument6 pagesGENERIC GENERATOR INSTALLATION MANUAL - Sections 7 and 8.pdf TIMBLEBenedict john SabaleNo ratings yet
- Inspection of The SystemsDocument12 pagesInspection of The SystemsTulen CabuldinNo ratings yet
- Chlorine Supply ContainersDocument6 pagesChlorine Supply ContainersDaniel Puello RodeloNo ratings yet
- Gas SupplyDocument9 pagesGas SupplyDennis GichuruNo ratings yet
- Sample IsometricDocument1 pageSample IsometricShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect MatrixDocument1 pageCause and Effect MatrixShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Deepstar - Chevron Multiphase Design Guide PT 1Document105 pagesDeepstar - Chevron Multiphase Design Guide PT 1Smile M75% (4)
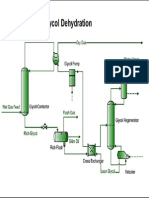
- Gas Processing and Products SchematicDocument1 pageGas Processing and Products SchematicShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Engineering ChecklistDocument4 pagesEngineering ChecklistShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Auto LPG Dispensing Station SpecificationDocument5 pagesAuto LPG Dispensing Station SpecificationShyBokxNo ratings yet
- P&ID ChecklistDocument4 pagesP&ID ChecklistShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Summary:: Steitoff Dyatt Engineering LimitedDocument4 pagesSummary:: Steitoff Dyatt Engineering LimitedShyBokxNo ratings yet
- DPR Guidelines N Procedures For The Design Construction Operation N Maintenance of Oil N Gas Pipeline SysDocument39 pagesDPR Guidelines N Procedures For The Design Construction Operation N Maintenance of Oil N Gas Pipeline SysShyBokx75% (4)
- Alumina Production ProcessDocument1 pageAlumina Production ProcessShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop Equivalents PDFDocument1 pagePressure Drop Equivalents PDFShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Glycol Gas-DehydrationDocument1 pageGlycol Gas-DehydrationShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection and Corrosion DefintionsDocument13 pagesCathodic Protection and Corrosion DefintionsShyBokx100% (1)
- Selection, Sizing, and Operation of Control Valves For Gases and LiquidsDocument7 pagesSelection, Sizing, and Operation of Control Valves For Gases and LiquidsAshish ShahNo ratings yet
- Sample Line ListDocument1 pageSample Line ListShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Gas Processing SchematicDocument1 pageGas Processing SchematicShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Tuning TheoryDocument8 pagesInstrumentation Tuning TheoryShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Cathodic Protection PDFDocument13 pagesCathodic Protection PDFShyBokxNo ratings yet
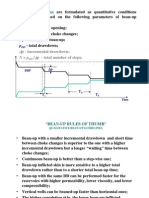
- Bean-Up Rules of ThumbDocument3 pagesBean-Up Rules of ThumbShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Slam Shut ValveDocument0 pagesSlam Shut ValveShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Mist Extractor PDFDocument1 pageMist Extractor PDFShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Pressure Drop Equivalent TableDocument1 pagePressure Drop Equivalent TableShyBokxNo ratings yet
- C-27-2008 Thrust Block DesignDocument26 pagesC-27-2008 Thrust Block Designeagle411No ratings yet
- NPSH Definition and CalculationDocument7 pagesNPSH Definition and CalculationShyBokxNo ratings yet
- Thrust and Anchor Blocks DesignDocument26 pagesThrust and Anchor Blocks DesignShyBokx100% (4)
- LPG Technical ProposalDocument5 pagesLPG Technical ProposalShyBokx80% (5)
- Mist Extractor PDFDocument1 pageMist Extractor PDFShyBokxNo ratings yet
- C-27-2008 Thrust Block DesignDocument26 pagesC-27-2008 Thrust Block Designeagle411No ratings yet
- Piping Best PracticesDocument43 pagesPiping Best PracticesShyBokx100% (1)
- Protection of Reinforcement With Corrosion Inhibitors, PhaseDocument137 pagesProtection of Reinforcement With Corrosion Inhibitors, Phasealwan61No ratings yet
- Design - Part 4 - Job Knowledge 93Document4 pagesDesign - Part 4 - Job Knowledge 93Billy TanNo ratings yet
- COE10102, Forms of CorrosionDocument60 pagesCOE10102, Forms of CorrosionامينNo ratings yet
- Pds - Floor Hardener NMDocument2 pagesPds - Floor Hardener NMkasivisanadhNo ratings yet
- Soleal PYn Door Brochure /PUIGMETAL®Document9 pagesSoleal PYn Door Brochure /PUIGMETAL®PUIGMETAL®No ratings yet
- Hiap Teck Steel CatalogueDocument82 pagesHiap Teck Steel CatalogueYoke Mei Tang71% (7)
- Rebar Shape CodesDocument1 pageRebar Shape CodesRUDDY DE JESÚS ALMÁNZAR CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Protek Etl: Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageProtek Etl: Technical Data SheetArnel G. PetalioNo ratings yet
- Burao Water Supply Expansion Sub-Project LOT - Install two 1000m3 Reservoirs on the GroundDocument19 pagesBurao Water Supply Expansion Sub-Project LOT - Install two 1000m3 Reservoirs on the Groundmustafe0% (1)
- Physical and Chemical DataDocument2 pagesPhysical and Chemical DataPermesh GoelNo ratings yet
- Maxytone TDS enDocument24 pagesMaxytone TDS enMatrix DesamparadosNo ratings yet
- Synaxis Prequalification (2018)Document82 pagesSynaxis Prequalification (2018)Synaxis ReadymixNo ratings yet
- ASTM D3754 Tuberia de Fibra de VIdirio para Sistemas Industriales y A PresiónDocument14 pagesASTM D3754 Tuberia de Fibra de VIdirio para Sistemas Industriales y A PresiónalexagoNo ratings yet
- Amphenol: Amphenol /pyle Industrial Connectors Star-Line, Star-Line EX, Star-LokDocument85 pagesAmphenol: Amphenol /pyle Industrial Connectors Star-Line, Star-Line EX, Star-Lokrolando laffontNo ratings yet
- OJT-Initial-Report (2) As of Sept 16Document50 pagesOJT-Initial-Report (2) As of Sept 16Ralph GalvezNo ratings yet
- WOOD As A BUILDING MATERIAL 2Document9 pagesWOOD As A BUILDING MATERIAL 2Jays Tioxon IIINo ratings yet
- CASTING Design GuideDocument54 pagesCASTING Design GuideXin Yu75% (4)
- Highly stressed die forgings technical termsDocument22 pagesHighly stressed die forgings technical termsLeo AislanNo ratings yet
- MS 01 180Document88 pagesMS 01 180DucVikingNo ratings yet
- E.2.2 Sheet Metal WorkingDocument18 pagesE.2.2 Sheet Metal WorkingMesfin SisayNo ratings yet
- Carbon Steel ENG 5 ArtikelnrsDocument5 pagesCarbon Steel ENG 5 ArtikelnrsNenadNo ratings yet
- Use of Plastic Waste in Road ConstructionDocument3 pagesUse of Plastic Waste in Road ConstructionriyaNo ratings yet
- McMaster - About Plastics Doc 8574KACDocument3 pagesMcMaster - About Plastics Doc 8574KACkristechnikNo ratings yet
- RENOVATION COSTDocument18 pagesRENOVATION COSTRohit BawaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2, Flat Slab Flexural DesignDocument1 pageAssignment 2, Flat Slab Flexural DesignKelly Obrien0% (1)
- Cutting Tool and Tool GeometryDocument58 pagesCutting Tool and Tool Geometry18033 S.M RahatNo ratings yet
- Estimation and EstimatesDocument61 pagesEstimation and EstimatesShaheryar AhmadNo ratings yet
- AISI 10B22 Steel DatasheetDocument2 pagesAISI 10B22 Steel DatasheetMaria Teresa Fernández OlavarrietaNo ratings yet
- Mill Scale 2Document7 pagesMill Scale 2viswaprasad005No ratings yet
- Struktur Baja I 7Document25 pagesStruktur Baja I 7Latifah Meda FerlytaNo ratings yet
- The Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingFrom EverandThe Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Gentle Art of Swedish Death Cleaning: How to Free Yourself and Your Family from a Lifetime of ClutterFrom EverandThe Gentle Art of Swedish Death Cleaning: How to Free Yourself and Your Family from a Lifetime of ClutterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (467)
- Plan and Organize Your Life: Achieve Your Goals by Creating Intentional Habits and Routines for SuccessFrom EverandPlan and Organize Your Life: Achieve Your Goals by Creating Intentional Habits and Routines for SuccessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (19)
- Kintsugi Wellness: The Japanese Art of Nourishing Mind, Body, and SpiritFrom EverandKintsugi Wellness: The Japanese Art of Nourishing Mind, Body, and SpiritRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Nobody Wants Your Sh*t: The Art of Decluttering Before You DieFrom EverandNobody Wants Your Sh*t: The Art of Decluttering Before You DieRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Success at Home with ADHD.: Practical Organization Strategies to Make Your Life Easier.From EverandSuccess at Home with ADHD.: Practical Organization Strategies to Make Your Life Easier.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Survival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosFrom EverandSurvival Mom: How to Prepare Your Family for Everyday Disasters and Worst-Case ScenariosRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- The Buy Nothing, Get Everything Plan: Discover the Joy of Spending Less, Sharing More, and Living GenerouslyFrom EverandThe Buy Nothing, Get Everything Plan: Discover the Joy of Spending Less, Sharing More, and Living GenerouslyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (40)
- How to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingFrom EverandHow to Keep House While Drowning: A Gentle Approach to Cleaning and OrganizingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- Martha Stewart's Very Good Things: Clever Tips & Genius Ideas for an Easier, More Enjoyable LifeFrom EverandMartha Stewart's Very Good Things: Clever Tips & Genius Ideas for an Easier, More Enjoyable LifeNo ratings yet
- The Joy of Less: A Minimalist Guide to Declutter, Organize, and SimplifyFrom EverandThe Joy of Less: A Minimalist Guide to Declutter, Organize, and SimplifyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (276)
- Dwelling: Simple Ways to Nourish Your Home, Body, and SoulFrom EverandDwelling: Simple Ways to Nourish Your Home, Body, and SoulRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- The Life-Changing Magic of Tidying Up: The Japanese Art of Decluttering and OrganizingFrom EverandThe Life-Changing Magic of Tidying Up: The Japanese Art of Decluttering and OrganizingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2993)
- Extraordinary Projects for Ordinary People: Do-It-Yourself Ideas from the People Who Actually Do ThemFrom EverandExtraordinary Projects for Ordinary People: Do-It-Yourself Ideas from the People Who Actually Do ThemRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Declutter Like a Mother: A Guilt-Free, No-Stress Way to Transform Your Home and Your LifeFrom EverandDeclutter Like a Mother: A Guilt-Free, No-Stress Way to Transform Your Home and Your LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (164)
- Tortoise and Hare Decluttering: The Whats, Whys, and Hows of Every Angle of DeclutteringFrom EverandTortoise and Hare Decluttering: The Whats, Whys, and Hows of Every Angle of DeclutteringRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- Identity Clutter: The Whats, Whys, and Hows of Every Angle of DeclutteringFrom EverandIdentity Clutter: The Whats, Whys, and Hows of Every Angle of DeclutteringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (44)
- How to Manage Your Home Without Losing Your Mind: Dealing with Your House's Dirty Little SecretsFrom EverandHow to Manage Your Home Without Losing Your Mind: Dealing with Your House's Dirty Little SecretsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (338)
- M.O.M. Master Organizer of Mayhem: Simple Solutions to Organize Chaos and Bring More Joy into Your HomeFrom EverandM.O.M. Master Organizer of Mayhem: Simple Solutions to Organize Chaos and Bring More Joy into Your HomeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (25)
- Homegrown & Handmade: A Practical Guide to More Self-Reliant LivingFrom EverandHomegrown & Handmade: A Practical Guide to More Self-Reliant LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Furniture Makes the Room: Create Special Pieces to Style a Home You LoveFrom EverandFurniture Makes the Room: Create Special Pieces to Style a Home You LoveRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Home Economics: Vintage Advice and Practical Science for the 21st-Century HouseholdFrom EverandHome Economics: Vintage Advice and Practical Science for the 21st-Century HouseholdRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Let It Go: Downsizing Your Way to a Richer, Happier LifeFrom EverandLet It Go: Downsizing Your Way to a Richer, Happier LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (67)
- A Contractor Tells All: A Guide to Saving Money & Avoiding Trouble On Your Next Home ProjectFrom EverandA Contractor Tells All: A Guide to Saving Money & Avoiding Trouble On Your Next Home ProjectRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Everything Organize Your Home Book: Eliminate clutter, set up your home office, and utilize space in your homeFrom EverandThe Everything Organize Your Home Book: Eliminate clutter, set up your home office, and utilize space in your homeRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Decluttering at the Speed of Life: Winning Your Never-Ending Battle with StuffFrom EverandDecluttering at the Speed of Life: Winning Your Never-Ending Battle with StuffRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (578)