Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Wheat Plant: Origins of Flour
The Wheat Plant: Origins of Flour
Uploaded by
Ryan SorianoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Wheat Plant: Origins of Flour
The Wheat Plant: Origins of Flour
Uploaded by
Ryan SorianoCopyright:
Available Formats
Origins of Flour Wheat flour was first domesticated about 10.
0.000 years ago It is a cultivated grass from the Levant region in the Middle East.
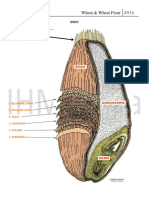
The Wheat Plant
Head / Beard, Kernel Stem Root
Make up of White Flour
Starch (sugars) Protein (gluten) Moisture Carbohydrates (absorbs moisture) Lipids Ash (mineral particles) Carotenoids (off-white color)
Functions of Flour
1. It provides structure. 2. It absorbs liquids. 3. It contributes flavor and color 4. It adds nutritional value. - proteins, carbohydrates, dietary fiber, iron,folic acid, Vitamin B
a.) Whole-Wheat-Flour : The whole grain is used. - Graham flour (Sylvester Graham) - high in protein, but does not form as much gluten due to bran particles & wheat germ - short shelf life
b.) White flour : Only the endosperm is used. High-gluten flour (13.5-14.5 % protein) Bread flour (11.5-13.5% protein) All-purpose flour (9.5-11.5% protein) Pastry flour (7-9.5% protein) Cake flour (6-8% protein)
c.) Rye Flour : from whole rye berries and grains of rye grass d.) Soy Flour - made from roasted soybeans that have been - ground into a powder - gluten-free e.) Nut flours : made from raw or dried nuts that have been ground to a powdery meal f.) Rice flour from the endosperm of the rice kernel; low in protein, no gluten g.) Potato flour not a grain but is cooked, dried and milled into flour h.) Cornmeal : coarsely ground corn the whole dried corn kernel is used
i.) Cornstarch: finely ground corn; only endosperm of the corn kernel is used
Storage and Preservation
Store no more than 6 months. Keep airtight and in a cool, dry place. Keep away from direct sunlight. Observe FIFO --- do not add new flour to old flour.
Flour Chart (Classifications) Ash Protein Wheat flour type US ~0.4% ~9% pastry flour all-purpose flour high gluten flour first clear flour 1050 405 550 812 T110 T150 German T45 T55 T80 French
~0.55% ~11% ~0.8% ~1% >1.5% ~14% ~15% ~13%
white whole wheat 1600
You might also like
- About WFC Flour Types BookletDocument3 pagesAbout WFC Flour Types BookletMie YaNo ratings yet
- Cereal Technology NotesDocument45 pagesCereal Technology Notesgrace mwenjeNo ratings yet
- Cereals and Pasta CookeryDocument48 pagesCereals and Pasta CookeryJoshua Guiriña100% (3)
- Cereals and Cereal ProductsDocument3 pagesCereals and Cereal ProductsGlenda Jaca100% (1)
- Bakrey 3rd YrDocument10 pagesBakrey 3rd YrWasim ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Cereal ProcessingDocument23 pagesCereal ProcessingAnjar CoolNo ratings yet
- Cereals and StarchDocument25 pagesCereals and StarchRonnell Arlan Arranguez EñegoNo ratings yet
- Technology OF Wheat Milling: Nimisha K OST-2015-24-13 M.Sc. FS&TDocument32 pagesTechnology OF Wheat Milling: Nimisha K OST-2015-24-13 M.Sc. FS&Traja singamNo ratings yet
- Types of Grains, Whole Grains, and CerealsDocument33 pagesTypes of Grains, Whole Grains, and CerealsPia Isabel Vargas100% (2)
- Grains2190 PowerpointDocument35 pagesGrains2190 Powerpointapi-245680208100% (1)
- Cereals and GrainsDocument29 pagesCereals and GrainsJoan Eda De Vera100% (1)
- Ppt... Preparation of Cereals Starch DishesDocument48 pagesPpt... Preparation of Cereals Starch DishesJesse Mae Grace Jaum67% (3)
- CH 2 Cereal GrainsDocument82 pagesCH 2 Cereal GrainsshahidNo ratings yet
- Processing and Value Addition of CerealsDocument56 pagesProcessing and Value Addition of Cerealsprinceej79% (14)
- CerealsDocument27 pagesCerealsJuliet MalasNo ratings yet
- Ignou PGDFT Notes On WheatDocument83 pagesIgnou PGDFT Notes On WheatPreeti Joshi Sachdeva100% (1)
- Cereals and Cereals by ProductsDocument28 pagesCereals and Cereals by ProductsDr-Shoaib MeoNo ratings yet
- Flour and It's CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesFlour and It's CharacteristicsGessel AdlaonNo ratings yet
- CerealsDocument5 pagesCerealsifioksunday52No ratings yet
- Seeds of Cultivated GrassesDocument40 pagesSeeds of Cultivated GrassesUUVVNo ratings yet
- 8 Bakey TechnologyDocument103 pages8 Bakey TechnologyPawan CoomarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Preparation of Cereals and Starch DishesDocument11 pagesLesson 1: Preparation of Cereals and Starch DishesMaria Andrea Eunice RicarroNo ratings yet
- Let's Explore!: Grains Consists of Three Major Parts, IncludingDocument6 pagesLet's Explore!: Grains Consists of Three Major Parts, IncludingJohn Alloysius ZamaylaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Variety Grains and FloursDocument24 pagesCH 6 Variety Grains and FloursYarina MoralesNo ratings yet
- Baking With Wholewheat Flour 101Document1 pageBaking With Wholewheat Flour 101Mohamed RayNo ratings yet
- Preparations of Cereals and Starch DishesDocument78 pagesPreparations of Cereals and Starch Dishesbenjie ausanNo ratings yet
- Waste Generation From Rice, WheatDocument26 pagesWaste Generation From Rice, WheatJhanvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- ,,,cereal Technology - Group-5Document42 pages,,,cereal Technology - Group-5Mehwish Butt100% (1)
- Cereals: - : IntroductionDocument8 pagesCereals: - : IntroductionAmit Kr GodaraNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Cookery 10 Quarter 1 Week 5-6: Mrs. Jennelyn M. Iñigo TLE TeacherDocument41 pagesWelcome To Cookery 10 Quarter 1 Week 5-6: Mrs. Jennelyn M. Iñigo TLE TeacherGlow WhxtxNo ratings yet
- Wheat FlourDocument18 pagesWheat Flourbarii barNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 3 in TleDocument18 pagesModule 2 Lesson 3 in TleZadd DadullaNo ratings yet
- 3.03 Grains Guided NotesDocument2 pages3.03 Grains Guided NotesBernardo ThenNo ratings yet
- Cereal Grains NotesDocument6 pagesCereal Grains Notesjellyn.lai.owoNo ratings yet
- Iohm Bakery 6aDocument15 pagesIohm Bakery 6aSanika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cereal Grains NotesDocument6 pagesCereal Grains Notesjellyn.lai.owoNo ratings yet
- Rice Corn and Other CerealsDocument9 pagesRice Corn and Other CerealskassycarandangNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Baking IngredientsDocument23 pagesLec 2 Baking IngredientsAsadNo ratings yet
- Processing of Cereal GrainsDocument43 pagesProcessing of Cereal GrainsSagar ShahNo ratings yet
- EL-10 Cereals-2Document12 pagesEL-10 Cereals-2HELENA SUSANTI PANGNo ratings yet
- Theory Sem I FlourDocument29 pagesTheory Sem I Floursiddhant rautNo ratings yet
- Wheat To FlourDocument6 pagesWheat To Flourkumari shaliniNo ratings yet
- Lecture TwoDocument41 pagesLecture Twoሸዋረጋ ሀብታሙ ሀይሌNo ratings yet
- CEREALSDocument18 pagesCEREALSSheryl BorromeoNo ratings yet
- AttachmentDocument27 pagesAttachmentJuliet MalasNo ratings yet
- Cereal and Cereal Products 2Document21 pagesCereal and Cereal Products 2maskr2005_840560613No ratings yet
- Intro To CerealsDocument19 pagesIntro To CerealsJairus KentNo ratings yet
- Starch D4eDocument11 pagesStarch D4ePRATIK AGAJNo ratings yet
- Baking Bread - The Beginner's Guide.: Tricks Flour Introduction To Sourdough Proof Box Recipe BinDocument15 pagesBaking Bread - The Beginner's Guide.: Tricks Flour Introduction To Sourdough Proof Box Recipe Binva2luv100% (1)
- Cereal and Cereal Products 1Document35 pagesCereal and Cereal Products 1maskr2005_840560613No ratings yet
- CEREALS PPT 72Document72 pagesCEREALS PPT 72Raifa FathimaNo ratings yet
- Type of GrainDocument5 pagesType of GrainChris Michelle JapinNo ratings yet
- Types of BreadsDocument3 pagesTypes of BreadsMisis Ni RanNo ratings yet
- HNF 101 Module 4 - 2ndsem22-23Document36 pagesHNF 101 Module 4 - 2ndsem22-23Irene DecolongonNo ratings yet
- Flours Theory 1Document22 pagesFlours Theory 1dexter.lychenNo ratings yet
- CerealsDocument9 pagesCerealsapi-307436208No ratings yet
- Ingredients & FunctionsDocument57 pagesIngredients & FunctionsRahman RamlanNo ratings yet
- Types of Flour: Non-Wheat FloursDocument4 pagesTypes of Flour: Non-Wheat FloursRegine De VeneciaNo ratings yet
- CH 5 Wheat FlourDocument43 pagesCH 5 Wheat FlourYarina MoralesNo ratings yet
- 10,000 B.C It All Started in EGYPTDocument6 pages10,000 B.C It All Started in EGYPTRyan SorianoNo ratings yet
- What Occurs During Mixing?Document2 pagesWhat Occurs During Mixing?Ryan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Kitchen Ranks Description of Hierarchy in The Pastry Kitchen Highly Qualified WorkmanDocument4 pagesKitchen Ranks Description of Hierarchy in The Pastry Kitchen Highly Qualified WorkmanRyan SorianoNo ratings yet
- 10,000 B.C It All Started in EGYPTDocument6 pages10,000 B.C It All Started in EGYPTRyan SorianoNo ratings yet