Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fenomenos 2
Uploaded by
Paula Andrea Viviescas AyalaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fenomenos 2
Uploaded by
Paula Andrea Viviescas AyalaCopyright:
Available Formats
APPENDIX A
A-1 UNITS
meter (m) = 100 cm = 3.2808 ft
m2 = lo4 cm2 = 10.7637 ft2
m3 = lo6 cm3 = 35.3147 ft3 = 264.17 gallons
kg = 1000 g = 2.2046 lbm
newton (N) = lo5 dynes = 0.2248 lb force
joule (J ) = N m = lo7 ergs = 0.239 calories = 0.7376 ft lbf
= 9.4783 x Btu
watt = J /sec = 0.239 cal/sec = 0.7376 ft Ibf/sec
= 9.4783 x lop4 Btu/sec = 1.341 x lo-' horsepower
pascal = N/m2 = 10 dyne/cm2 = 1.4504 x 1 0-4 lbf/m2
= lop5 bar = 9.8687 x atm
pascal-second = 10 poise = 1000 CP = 0.672 l bdf t sec
watt/mK = 0.5778 Btu/ft hr"F = 2.39 x lop3 cal/cm"K
m2/sec = lo4 cm2/sec = 10.7637 ft2/sec
"R = 1.8("K)
(A'F) = I .~(A'F)
410
Transport Phenomena and Unit Operations: A Combined Approach
Richard G. Griskey
Copyright 0 2002 J ohn Wiley & Sons, Inc.
ISBN: 0-471-43819-7
BASIC DATA 41 1
"F = 1.8("C) + 32F
"K = "C + 273.16
"R = "F + 460
A-2 CONSTANTS
Gas constant*(R) = 8.314 J /a = 8.314 m3 Pda = 83.14 cm3 bar/a
= 82.06 cm3 atda = 1.987 cal/a = 1.987 Btuh
= 0.7302 ft3 at& = 10.73 ft2(psia)/b = 1545 ft I bfh
where a = g mole" K
b = lb moleo R
Acceleration of gravity = 9.8067 m/sec2 = 32.1740 ft/s2
Avogadro's number T? = 6.023 x molecules g-mole-'
Boltzmann's constant
Faraday's constant
Planck's constant h = 6.624 x erg sec
Stefan-Boltzmann constant CJ = 1.355 x cal sec-' cmP2" K-4
K = R/i? = 1.3805 x
F = 9.652 x lo4 abs-coulombs g-equivalent-'
erg molecule-'" K-'
= 0.1712 x lop8 Btu hr-' ftC2" R-4
Electronic charge e = 1.602 x abs-coulomb
Speed of light c = 2.99793 x 10" cm sec-l
A-3 BASIC DATA
Table A-3-1 Ratios, Forms and Dimensionless Groups (92)
Ratio
Dimensionless
Form Number
Inertia forces
Viscous forces
Inertia forces
Gravity forces
Inertia forces
Re y n o 1 d s
Froude (Fr)
Weber (We)
Surface tension forces
Y
(continued overleaf)
412 APPENDIX A
Table A-3-1 (continued)
Ratio
Dimensionless
Form Number
Surface tension forces
Gravity forces
Buoyancy forces Inertia forces
Viscous forces Viscous forces
Momentum diffusivity(kinematic viscosity)
Thermal diffusivity
Forced convection heat transfer
Conduction heat transfer
Heat produced by viscous heating
Conduction heat transfer
Free convection heat transfer
Conduction heat transfer
Convective heat transfer
Radiative heat transfer
Momentum diffusivity(kinematic viscosity)
Molecular diffusivity
Convective mass transfer
Molecular diffusion
Homogeneous chemical reaction
Bulk flow
Homogeneous chemical reaction
Bulk flow
Batch chemical reaction
Time
Heterogeneous chemical reaction
Bulk flow
AT L3p2
P
Bg,-
UV
k AT
Pg AT L3p2C,
lr
PC, V
PI P lr
a c T3
-
DAB PDAB
DV
~
DAB
r L
CV
-
V*
k,C2"-* L2T
r
sc
-
Eotvos (Eo)
Grashof (Gr)
Prandtl (Pr)
Peclet (Pe) also,
(Pe = RePr)
Brinkman (Br)
Gr Pr
Radiation group
Schmidt (Sc)
Mass transfer
Peclet (Pens) or
(PeAB = Re Sc)
(homogeneous)
Damkohler
Damkohler
(homogeneous
based on k, )
Unnamed
Damkohler
(heterogeneous)
In the above, L (a characteristic) length can be used for D (diameter).
Table A-3-2 Nomenclature for Table A-3-1 (92)
c = concentration mol eshi t
g = acceleration of gravity
k = thermal conductivity
T = temperature
V = average velocity
B = coefficient of thermal expansion
C, = specific heat AT = temperature difference
BASIC DATA 413
Table A-3-2 (continued)
k, = specific reaction rate
D = diameter
DAB = diffusivity
L = characteristic length
S = space velocity
y = surface tension
t = emissivity
(T = Stefan-Boltzmann constant
p = density
t = time
= viscosity
References 1-5 discuss the concepts of similitude and dimensionless groups.
Table A-3-3 Intermolecular Force Parameters and Critical Properties (1. 9- 14)
Lennard-Jones
Parameters (9, 10) Critical Constants (1 1 - 14)
PC kc
Molecular V, (g cm-' (caI s-'
Wt. a t l K T, P, (cm3 sec-') cm-'"K-' 1
Substance M (A) ( OK) ( OK) (atm) g-mole-') x104 x104
-
Light Elements:
HZ 2.016 2.915
He 4.003 2.576
Noble Gases:
Ne 20.183 2.789
Ar 39.944 3.418
Kr 83.80 3.498
Xe 131.3 4.055
Simple polyatomic substances:
Air 28.97 3.617
N2 28.02 3.681
0 2 32.00 3.433
co 28.01 3.590
COZ 44.01 3.996
NO 30.01 3.470
N20 44.02 3.879
so2 64.07 4.290
F2 38.00 3.653
c12 70.91 4.115
Br2 159.83 4.268
12 253.82 4.982
0 3 48.00 -
Hydrocarbons:
CH4 16.04 3.822
C2H2 26.04 4.221
C2H4 28.05 4.232
c2H6 30.07 4.418
C3H6
42.08 -
38.0
10.2
35.7
124
225
229
97.0
91.5
1 I 3
110
190
119
220
252
112
357
520
550
137
185
205
230
-
-
33.3 12.80
5.26 2.26
44.5 26.9
151 48.0
209.4 54.3
289.8 58.0
132 36.4
126.2 33.5
154.4 49.7
268 67
133 34.5
304.2 72.9
180 64
309.7 71.7
430.7 77.8
417 76.1
584 102
800 -
- -
190.7 45.8
309.5 61.6
282.4 50.0
305.4 48.2
365.0 45.5
65.0
57.8
41.7
75.2
92.2
118.8
86.6
90.1
74.4
89.4
93.1
94.0
57
96.3
122
124
144
-
-
99.3
113
124
148
181
34.7
25.4
156
264
396
490
193
180
250
190
343
258
332
41 1
420
-
-
-
-
159
237
215
210
233
-
-
79.2
71 .O
49.4
40.2
90.8
86.8
105.3
86.5
122
118.2
131
98.6
97.0
-
-
-
-
158.0
-
-
203.0
-
(continued overleaf)
You might also like
- Conversion TabletDocument2 pagesConversion TabletGreg CollinsNo ratings yet
- Chem II AP PacketDocument4 pagesChem II AP PacketAmanda Rose DalyNo ratings yet
- A - Conversion FactorsDocument14 pagesA - Conversion Factorssaeed65No ratings yet
- Full Calculations and DiscussionsDocument27 pagesFull Calculations and DiscussionsBudak TescoNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionDocument21 pagesUnit ConversioninsidereaderNo ratings yet
- Tester, Modell - Answers To Selected ProblemsDocument12 pagesTester, Modell - Answers To Selected ProblemsCoronel Mustang100% (1)
- Selected Key Equations Conversion Factors and Relationships: (Linearized Form)Document1 pageSelected Key Equations Conversion Factors and Relationships: (Linearized Form)iwannac0okieNo ratings yet
- Condensation and BoilingDocument14 pagesCondensation and BoilingCrislyn Akilit Bayawa100% (1)
- THD291Z 2009 10 e 1Document15 pagesTHD291Z 2009 10 e 1kasturiep15No ratings yet
- Conversion Factors and Values of The Gas Constant: Appendix ADocument27 pagesConversion Factors and Values of The Gas Constant: Appendix Aمرتضى كاظم غانمNo ratings yet
- Schroeder Answers Ch1 4Document3 pagesSchroeder Answers Ch1 4munkytecNo ratings yet
- Lardenoit's Fusion Calculations & Lawson CriterionDocument51 pagesLardenoit's Fusion Calculations & Lawson CriterionTim LardenoitNo ratings yet
- Basic Unit ConvertionDocument30 pagesBasic Unit ConvertionADIPESHNo ratings yet
- KFT 131 - Physical Chemistry I April 08Document17 pagesKFT 131 - Physical Chemistry I April 08simparminNo ratings yet
- Ideal Solutions Homework SolutionsDocument28 pagesIdeal Solutions Homework SolutionsFiqa Success89% (9)
- 2 Units Conversion FactorsDocument2 pages2 Units Conversion FactorsRalph Saint PierreNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors - Gas IndustryDocument2 pagesConversion Factors - Gas IndustryKailas Nimbalkar100% (3)
- UEMK1113 Formula SheetsDocument25 pagesUEMK1113 Formula SheetsTie Teck HoeNo ratings yet
- Diffusion of Liquids Through Stagnant Non Diffusing Air GRP ReportDocument23 pagesDiffusion of Liquids Through Stagnant Non Diffusing Air GRP ReportCharlyn Joy RamirezNo ratings yet
- Selected Numerical Answers To AS Physics Module Papers 1Document4 pagesSelected Numerical Answers To AS Physics Module Papers 1clownfish12341234123No ratings yet
- CHNG 3802 Heat Transfer Tutorial Answers Weeks 1-4Document9 pagesCHNG 3802 Heat Transfer Tutorial Answers Weeks 1-4IshanSaneNo ratings yet
- Selected Tables and Figures Miscellaneous: Data For SpecificDocument2 pagesSelected Tables and Figures Miscellaneous: Data For Specificlucky414No ratings yet
- Common Chemistry Conversions: English To Metric ConversionsDocument1 pageCommon Chemistry Conversions: English To Metric ConversionsAndy AspaasNo ratings yet
- Pages From Serway - Physics For Scientists, 8th EdDocument1 pagePages From Serway - Physics For Scientists, 8th EdSocheat TiengNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion TablesDocument6 pagesUnit Conversion Tablesines.santos.rodriguesNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 DoSDocument39 pagesAssignment 1 DoSAnwarul Shafiq AwalludinNo ratings yet
- Test Supplement 13Document16 pagesTest Supplement 13jimmys45No ratings yet
- Casa de Dos Pisos EtabsDocument19 pagesCasa de Dos Pisos EtabsYuber Tacuri CristobalNo ratings yet
- Basic Design of A Heat ExchangerDocument10 pagesBasic Design of A Heat ExchangerKvspavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Bracket Design For ReactorDocument32 pagesBracket Design For ReactorbrencejunNo ratings yet
- Quantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary UnitsDocument6 pagesQuantity Unit Symbol: Base and Supplementary Unitshb360No ratings yet
- Units and Conversion FactorsDocument30 pagesUnits and Conversion FactorsBun YaminNo ratings yet
- 6 Flow of FluidsDocument9 pages6 Flow of FluidsAnonymous z4Fe39jNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document12 pagesHomework 3Yıldırım KURTULUŞNo ratings yet
- Table I. Basic Units: Quantity Unit Symbol DefinitionDocument10 pagesTable I. Basic Units: Quantity Unit Symbol DefinitionAnonymous bRf25N8VcSNo ratings yet
- Roldan PS 3-4Document26 pagesRoldan PS 3-4Charles Warren GoNo ratings yet
- Must Know ConversionsDocument6 pagesMust Know Conversionslgar53801No ratings yet
- Name, Symbol, Dimensions Conversion Formula: Formulas For Unit ConversionsDocument3 pagesName, Symbol, Dimensions Conversion Formula: Formulas For Unit ConversionsQedew ErNo ratings yet
- HW#1Document7 pagesHW#1MahsaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document34 pagesChapter 7ShahrizatSmailKassimNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger - Effectiveness - NTU MethodDocument15 pagesHeat Exchanger - Effectiveness - NTU MethodhendiyrNo ratings yet
- Energy Systems DesignDocument3 pagesEnergy Systems DesigncheneyblakeNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetDocument16 pagesNew Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetAaron Horton100% (1)
- Acetic 2520acid 2520 - Design 2520of 2520equipments PDFDocument41 pagesAcetic 2520acid 2520 - Design 2520of 2520equipments PDFTanuj HandaNo ratings yet
- Tables 2Document89 pagesTables 2Kef CaminhõesNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics TableDocument82 pagesThermodynamics TableZenin EasaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering ConstantsDocument2 pagesChemical Engineering Constantssmartleo_waloNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Heterogeneous Catalysis at Nanoscale for Energy ApplicationsFrom EverandHeterogeneous Catalysis at Nanoscale for Energy ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Rock Engineering Rock Engineering Practice & Design Practice & DesignDocument46 pagesRock Engineering Rock Engineering Practice & Design Practice & DesignLuis MirandaNo ratings yet
- D2 Tool Steel - Heat Treatment Process PDFDocument3 pagesD2 Tool Steel - Heat Treatment Process PDFGayathriRajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities Reviewer ComprehensiveDocument3 pagesBuilding Utilities Reviewer ComprehensiveReynald HarrisNo ratings yet
- CFM56-3 Familiarization Training Manual MTU Maintenance Zhuhai Co. LTDDocument59 pagesCFM56-3 Familiarization Training Manual MTU Maintenance Zhuhai Co. LTDrenjithaero100% (4)
- Lecture - 09 - Dimensional Analysis and SimilitudeDocument11 pagesLecture - 09 - Dimensional Analysis and SimilitudeHizana D.SNo ratings yet
- Innovation by Experience: Lo Hacemos SencilloDocument36 pagesInnovation by Experience: Lo Hacemos SencilloDejan DosljakNo ratings yet
- Fuji Electric VFZ501A 7W DatasheetDocument2 pagesFuji Electric VFZ501A 7W Datasheetghmp123No ratings yet
- Design Standards and SpecificationsDocument47 pagesDesign Standards and Specificationsabhi0912No ratings yet
- Asl Ga55+90-02 9095 0504 76 PDFDocument72 pagesAsl Ga55+90-02 9095 0504 76 PDFMushfiqur RahmanNo ratings yet
- PHD Thesis - Anthony Lo - 9 Dec 2014Document264 pagesPHD Thesis - Anthony Lo - 9 Dec 2014Hiei ArshavinNo ratings yet
- Eccentric ConnecctionsDocument41 pagesEccentric ConnecctionsShyam Suryawanshi100% (1)
- Seams & Joint Design For Emc EnclosuresDocument7 pagesSeams & Joint Design For Emc Enclosureszackhack01No ratings yet
- Format WPQDocument2 pagesFormat WPQAkash Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Tractor: Workshop ManualDocument292 pagesTractor: Workshop Manualyosy prastiyoNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Analysis of Ballistic Impact UsingDocument8 pagesSimulation and Analysis of Ballistic Impact UsingSaeid VarmazyariNo ratings yet
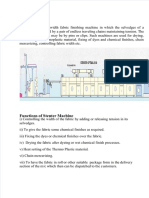
- Dokumen - Tips Stenter-DryerDocument18 pagesDokumen - Tips Stenter-DryerchuyNo ratings yet
- Question Set 1 PDFDocument6 pagesQuestion Set 1 PDFSeljen AceNo ratings yet
- CE 249 MidtemDocument6 pagesCE 249 MidtemJepoy EliseoNo ratings yet
- ROHR2fesu FeaturelistDocument20 pagesROHR2fesu FeaturelistJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- ASME PTC 22 (Gas Turbine Test Code)Document46 pagesASME PTC 22 (Gas Turbine Test Code)Nanang Hanani Wijaya100% (5)
- Tablas Medidas Tubos de Acero API5L - ASTM A53 - A106Document6 pagesTablas Medidas Tubos de Acero API5L - ASTM A53 - A106Reinaldo AndaraNo ratings yet
- Scheda Autoclave VT - Med ResDocument2 pagesScheda Autoclave VT - Med Resengomar nadyNo ratings yet
- Boiling and CondensationDocument13 pagesBoiling and CondensationPrithvi de VilliersNo ratings yet
- 1B) Manicooler & Outlet BoxDocument2 pages1B) Manicooler & Outlet BoxSonthi MooljindaNo ratings yet
- 6.missile DescriptionDocument31 pages6.missile DescriptionJorge Antonio Chávez MirandaNo ratings yet
- Slab Analysis of Ring Rolling AssumingConstantShearFrictionDocument7 pagesSlab Analysis of Ring Rolling AssumingConstantShearFrictionMatteo Dalla Vecchia100% (1)
- Oil and Gas ProcessingDocument3 pagesOil and Gas ProcessingRaghav AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Flat Wakaf Mek Zainab P1Document1 pageFlat Wakaf Mek Zainab P1Nur NaziraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Unit 3 Notes RGPVDocument14 pagesEngineering Chemistry Unit 3 Notes RGPVMufaddal HamidNo ratings yet
- Statically Indeterminate BeamsDocument7 pagesStatically Indeterminate BeamsMary Jane PelaezNo ratings yet