Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical Resistance IV
Uploaded by
rezhabloOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Resistance IV
Uploaded by
rezhabloCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical Resistance
Lesson Objective
*Knowledge of basic circuit symbols *Concept of resistance and knowledge of Ohm's Law *Ability to
recognise and use fixed and variable resistors - and special ones - LDRs and thermistors *Ability to
measure the resistance and verify Ohm's law *Knowledge of I-V graphs for resistors, filament bulbs and
diodes.
Lesson Plan
iGCSE Physics Lesson Plan
Module title: Section B: Electricity
Lesson title: Chapter 10 - Electrical Resistance
Time allocated: 1 week [1 single, 1 double, 1 prep]
Learning outcomes for ALL students ("MUST" and "SHOULD"):
*Knowledge of basic circuit symbols
*Concept of resistance and knowledge of Ohm's Law
*Ability to recognise and use fixed and variable resistors - and special ones - LDRs and thermistors
*Ability to measure the resistance and verify Ohm's law
*Knowledge of I-V graphs for resistors, filament bulbs and diodes.
Book References:
Edexcel iGCSE Physics - Brian Arnold
Experiments/Demos:
1. Experiment 1: Ohm's law of resistors: 150ohm resistors, variable voltage power pack, wires,
ammeters, voltmeters.
2. Experiment 2: I-V graph for filament light bulb: as experiment 1 but with a light bulb in the place of
the resistor.
3. Demo 1: LDR, thermistor: need one of each, a light source, a tub of hot water, a voltmeter.
Lesson notes: (brief, relevant description of lesson where Class Practicals (CP), Class Demos (CD),
Worksheets (WS) etc can be referred to by the initials and the numbers assigned in boxes above)
This may need reworking. It doesn't really work in this form as double and singles. Really need to time it so
that Ohm's Law with 2 experiments are just the one double.
Lesson 1: (double)
Starter:
1. Who am I? Circuit symbols and their function. Cut these out and match them up.
Main:
1. Stick the "non-resistor" (ahem) components in first (ammeter, voltmeter, light bulb, motor, led,
heater, cell, diode). Make sure that students use the text book to write as much detail on each
component - special interest in the diode.
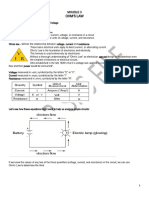
2. What is resistance? PPT on Ohm's Law (copy) and WS The relationship between V - I and R.
3. Need to practice V = IR. Do WS Electrical resistance Questions 1 - 6, go through each one on the
board, remembering LESS is MORE. Full working.
4. Stick in "resistor" components: resistor, variable resistor, thermistor, LDR. Use the text book to
write as much as possible about each. Demo thermistor and LDR.
Plenary:
1. PPT slide - explaining how to verify Ohm's Law. Do experiment with 150 resistors (single and then
2 in series or a 300 resistor). Probably only time to just take the results. To record use WS How
voltage, current and resistance are related.
Suggested homework tasks (differentiated where appropriate):
1. Complete the experimental write up. Need graph paper and need to consult the book to ensure
that they plot the correct variables on each axis. Leave determining R until next lesson.
2. PREP Current resistance and voltage
Lesson2: (single)
Starter:
1. Look at the graphs. Determine the gradient and from that the resistances of their experiments.
Really focus on taking large triangles for the gradient, full annotation and final units.
Main:
Take readings for the filament bulb. Stick in WS Current V voltage for a filament bulb and merely require students to
record a neat table and plot the graph. Again, refer them to the text book where they will see that the graph should
tail off at higher values of voltage. Students need to take the gradient for the linear part of their graph.
Lesson 3: (double)
Starter:
1. Remind students of the difference between Ohmic and Non-Ohmic. From: CNS I-V graphs
components and functionality.
Main:
1. Continue with this worksheet by cutting out the components and matching up with their
functionality.
Plenary:
Suggested homework tasks (differentiated where appropriate):
1. PREP Current Voltage Graphs
You might also like
- Electricity and Ohms Law Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesElectricity and Ohms Law Lesson PlanJuly BertNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- SLeM 6 BlancoBobis Current Voltage Resistance APPROVED FORMATDocument11 pagesSLeM 6 BlancoBobis Current Voltage Resistance APPROVED FORMATJuliana RoseNo ratings yet
- Abc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesFrom EverandAbc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesWürth ElektronikNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 4Document15 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 4richie cuizonNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 2 Skills: O/R/R and A/IDocument10 pagesExperiment: 2 Skills: O/R/R and A/IKayenNo ratings yet
- Guia WaniaDocument188 pagesGuia WaniaAnonymous R0s4q9X8No ratings yet
- Ae 212 Module 4Document9 pagesAe 212 Module 4kira arashiNo ratings yet
- Y11 Electricity WK 11Document45 pagesY11 Electricity WK 11Ololade OlaleyeNo ratings yet
- WK 11 Year 11 PhysicsDocument21 pagesWK 11 Year 11 PhysicsOlolade OlaleyeNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 4 FEEDocument10 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 4 FEErichie cuizonNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics EMDocument8 pages12 Physics EMAniketNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity WorksheeetDocument8 pagesCurrent Electricity WorksheeetVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Topic 11: Current and Resistance: Conceptual Physics Textbook, Lab Book and CPO Textbook and Lab BookDocument11 pagesTopic 11: Current and Resistance: Conceptual Physics Textbook, Lab Book and CPO Textbook and Lab BookDereck AntonyDengo DomboNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument117 pagesBasic ElectronicsPlatonic100% (2)
- 3rd Term PhysicsDocument14 pages3rd Term Physicssaidu musaNo ratings yet
- Total 64Document6 pagesTotal 64Vikram RaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics BookDocument57 pagesBasic Electronics BookNur Hafizah Kamilah SapawiNo ratings yet
- EE 251-05 Prelab 1 - Hailey TamaraDocument5 pagesEE 251-05 Prelab 1 - Hailey TamarahtfranceamaniaNo ratings yet
- Sage University Indore: Department of Computer Science and Information TechnologyDocument50 pagesSage University Indore: Department of Computer Science and Information TechnologyAbhishek PatelNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument15 pagesOhms LawM Kumar MarimuthuNo ratings yet
- 5-Ohm's LawDocument52 pages5-Ohm's Lawdp56yddhhnNo ratings yet
- ELE 110 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: SemiconductorsDocument19 pagesELE 110 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: SemiconductorspurseyNo ratings yet
- 4 Factors On Which The Resistance of A Conductor DependsDocument22 pages4 Factors On Which The Resistance of A Conductor DependsSunitha ShankarNo ratings yet
- Basic ElectricityDocument4 pagesBasic Electricityeduardo sepulvedaNo ratings yet
- Technology-Enhanced Science Unit: Target Population: 8 Grade Middle School Physical ScienceDocument38 pagesTechnology-Enhanced Science Unit: Target Population: 8 Grade Middle School Physical ScienceNguyễn Huy ĐạtNo ratings yet
- (CU) Electric CircuitsDocument2 pages(CU) Electric CircuitsFakeMe12No ratings yet
- Episode 107: Preparation For Electrical Resistance Topic: Advance WarningDocument2 pagesEpisode 107: Preparation For Electrical Resistance Topic: Advance WarninglaurahNo ratings yet
- Electricity and Ohm's Law Lesson Plan: Concept/principle To Be DemonstratedDocument20 pagesElectricity and Ohm's Law Lesson Plan: Concept/principle To Be DemonstratedVlad AndersonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - What Is Electricity-ADocument32 pagesLesson 1 - What Is Electricity-AMark WoodNo ratings yet
- Ohm'S Law: Energy and Power in Electric CircuitDocument19 pagesOhm'S Law: Energy and Power in Electric Circuitrazel besagasNo ratings yet
- Electric QuantitiesDocument34 pagesElectric Quantitiestear6025No ratings yet
- Lab 08 - Capacitors and InductorsDocument9 pagesLab 08 - Capacitors and InductorsAlinush AlinutsaNo ratings yet
- Presented by : PHYSICS THEORY (232/1&2)Document41 pagesPresented by : PHYSICS THEORY (232/1&2)Bonface KenaniNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document6 pagesLesson 1Leong Chee KuenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Electric Current, Battery and Bulb: Activity 1-1Document29 pagesWorksheet: Electric Current, Battery and Bulb: Activity 1-1Neil CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Law of Resistance (Parallel) PDFDocument12 pagesLaw of Resistance (Parallel) PDFAmogha kantakNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical Circuits: Polytechnic University of The Philippines - Binan CampusDocument106 pagesFundamentals of Electrical Circuits: Polytechnic University of The Philippines - Binan CampusEsmeralda Joyce RaymundoNo ratings yet
- 3RD Term S1 PhysicsDocument14 pages3RD Term S1 PhysicsMARYQUEEN AMARACHUKWUNo ratings yet
- Physics-Lab Fahim Aw PDFDocument13 pagesPhysics-Lab Fahim Aw PDFShaikh Allahma GalibNo ratings yet
- RoboticsDocument6 pagesRoboticsDavid MateusNo ratings yet
- Experiment I: Ohm's Law and Not Ohm's LawDocument14 pagesExperiment I: Ohm's Law and Not Ohm's LawPhillip PopeNo ratings yet
- 3RD TERM SS1 PHYSICS Scheme of WorkDocument15 pages3RD TERM SS1 PHYSICS Scheme of WorkloveandreverbNo ratings yet
- Ad Physics TomaroDocument12 pagesAd Physics TomaroRobert Kier Tanquerido TomaroNo ratings yet
- EE Lab ME - IntroDocument13 pagesEE Lab ME - IntroNandhu NandhuNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Aims and ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLesson Plan: Aims and ObjectivesNJABULO NGUBANENo ratings yet
- Electronics WorksheetDocument370 pagesElectronics WorksheetHENRY SINGCOLNo ratings yet
- Electricity 3 IV CharacteristicsDocument19 pagesElectricity 3 IV CharacteristicsJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- DS Differencie Circuits Electriques 1STI2D STLDocument12 pagesDS Differencie Circuits Electriques 1STI2D STLUrian51No ratings yet
- Electronics Module 3Document10 pagesElectronics Module 3Mary Ann Yongco CalalinNo ratings yet
- ETN1B PracDocument12 pagesETN1B Pracnkosingiphilephiri639No ratings yet
- Lab 3 Breadboard and Ohms LawDocument6 pagesLab 3 Breadboard and Ohms LawRasul Amirov100% (1)
- Voltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm's Law: Goals of ExperimentDocument3 pagesVoltage, Current, Resistance and Ohm's Law: Goals of ExperimentBatool MagedNo ratings yet
- G11 - Current ElectricityDocument65 pagesG11 - Current Electricityasmarandhana kmNo ratings yet
- Resistance, Ohm's Law, and The Temperature of A Light Bulb FilamentDocument8 pagesResistance, Ohm's Law, and The Temperature of A Light Bulb FilamentDanno NNo ratings yet
- Tugas Buku Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesTugas Buku Bahasa InggrisFandi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Earning Outcomes: AC 6 - Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument13 pagesEarning Outcomes: AC 6 - Basic Electrical EngineeringFerdinand Marcelo AbantoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Gen Phys 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Gen Phys 2Kazuya SenseiNo ratings yet
- RPP HeeDocument2 pagesRPP HeeJonni Maruli Tua SitorusNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer Systems Servicing (CSS NCII) ?Document11 pagesWhat Is Computer Systems Servicing (CSS NCII) ?rezhablo100% (1)
- CBLM PipeDocument44 pagesCBLM PipeAko Lang Poh100% (5)
- Visual Basic Lab ExercisesDocument74 pagesVisual Basic Lab ExercisesrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Marketing Plan DoneDocument16 pagesMarketing Plan DonerezhabloNo ratings yet
- Work Ready Powerpoint Part 1Document12 pagesWork Ready Powerpoint Part 1rezhabloNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Guide - Bread and Pastry Production NC IIDocument1 pageSelf Assessment Guide - Bread and Pastry Production NC IIrezhablo67% (3)
- Form 4.4: Training Needs: Training Needs (Learning Outcomes) Module Title/ Module of InstructionDocument1 pageForm 4.4: Training Needs: Training Needs (Learning Outcomes) Module Title/ Module of InstructionrezhabloNo ratings yet
- W2K8R2 02a Init Conf TasksDocument51 pagesW2K8R2 02a Init Conf TasksrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Cblm-SmawDocument43 pagesCblm-Smawrezhablo33% (3)
- Deepfreeze Deepfreeze Deepfreeze: Pc1 Drivec:/Persi0.Sys Pc1 Drivec:/Program Files (X86) /faronicsDocument1 pageDeepfreeze Deepfreeze Deepfreeze: Pc1 Drivec:/Persi0.Sys Pc1 Drivec:/Program Files (X86) /faronicsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Examination AnimationDocument6 pages2nd Quarter Examination Animationrezhablo100% (3)
- Chapter 21 - Oxyacetylene CuttingDocument37 pagesChapter 21 - Oxyacetylene CuttingrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Electric Fan Complete Troubleshooting GuideDocument6 pagesElectric Fan Complete Troubleshooting GuideFederico Estrada57% (7)
- 23 Best Laptop Safety TipsDocument6 pages23 Best Laptop Safety TipsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Action Research Sample FormatDocument2 pagesAction Research Sample Formatrezhablo94% (50)
- Assembly of Computer RubricDocument2 pagesAssembly of Computer Rubricrezhablo100% (3)
- How To Do A Clean Installation With Windows 7Document22 pagesHow To Do A Clean Installation With Windows 7rezhabloNo ratings yet
- Maintain FormsDocument12 pagesMaintain FormsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Competency Assessment Results Summary (Cars) : YES NODocument2 pagesCompetency Assessment Results Summary (Cars) : YES NOrezhabloNo ratings yet
- Waste Segregation PlanDocument4 pagesWaste Segregation Planrezhablo100% (1)
- How To Pass The NC2 Tesda ExamDocument3 pagesHow To Pass The NC2 Tesda Examrezhablo100% (2)
- Specific Instructions For The CandidateDocument2 pagesSpecific Instructions For The Candidaterezhablo100% (5)
- Whirlpool MD 101 WHDocument6 pagesWhirlpool MD 101 WHBert Debergh0% (1)
- Dgca Module 04 Part 01Document15 pagesDgca Module 04 Part 01PrakashJaiswalNo ratings yet
- Gate Turn-Off ThyristorsDocument14 pagesGate Turn-Off ThyristorsSubhash Murkute0% (1)
- Power Factor Correction Capacitors in Sheet Steel Cases 2016Document6 pagesPower Factor Correction Capacitors in Sheet Steel Cases 2016Taz UddinNo ratings yet
- Yuan 2016Document11 pagesYuan 2016Ahmed ShafeekNo ratings yet
- Pioneer sc-89 sc-87 rrv4550 Av Receiver PDFDocument89 pagesPioneer sc-89 sc-87 rrv4550 Av Receiver PDFAlexandru PădeanuNo ratings yet
- The Most Common Causes of UPS FailuresDocument2 pagesThe Most Common Causes of UPS FailuresAries dNo ratings yet
- CD4016Document8 pagesCD4016api-3708997100% (1)
- STV9302B: Vertical Deflection Booster For 2-A TV (50-60 HZ) Applications With 70-V Flyback GeneratorDocument15 pagesSTV9302B: Vertical Deflection Booster For 2-A TV (50-60 HZ) Applications With 70-V Flyback GeneratorJunior LopezNo ratings yet
- Variador TECO PDFDocument132 pagesVariador TECO PDFCarlos Garcia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of FPGA Based High Speed Data Acquisition Systems For Embedded ApplicationsDocument52 pagesDesign and Implementation of FPGA Based High Speed Data Acquisition Systems For Embedded ApplicationsachakracuNo ratings yet
- MDD20A DatasheetDocument6 pagesMDD20A DatasheetLeeNo ratings yet
- Embedded ControllerDocument284 pagesEmbedded ControllerKumar TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Logic Circuits and Switching Theory: By: John Neil F. RomasantaDocument59 pagesLogic Circuits and Switching Theory: By: John Neil F. RomasantaJules MartinezNo ratings yet
- BBU3900 Hardware Description (V100 - 03)Document81 pagesBBU3900 Hardware Description (V100 - 03)ikkemagic100% (2)
- Semiconductor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesSemiconductor - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaChâu Vĩnh LợiNo ratings yet
- Image Processing With VHDL PDFDocument131 pagesImage Processing With VHDL PDFNaeemNo ratings yet
- 7 220 V & 48 V DC Systems: 7.1 Guaranteed Technical Particulars Contractor's Data 220 V Battery ChargerDocument4 pages7 220 V & 48 V DC Systems: 7.1 Guaranteed Technical Particulars Contractor's Data 220 V Battery ChargerveerendraNo ratings yet
- CSS D1Document60 pagesCSS D1Art BrandNo ratings yet
- Isscc2022 000016CLDocument17 pagesIsscc2022 000016CLdashuai huaNo ratings yet
- 7915Document24 pages7915Balkrushna KankotiyaNo ratings yet
- MicroDAC UserGuide v1.0Document2 pagesMicroDAC UserGuide v1.0DouglasNo ratings yet
- Infovision Optoelectronics (Kunshan) Co.,LtdDocument20 pagesInfovision Optoelectronics (Kunshan) Co.,Ltdsergio ribeiroNo ratings yet
- Cisco Asa5506-K9-DatasheetDocument5 pagesCisco Asa5506-K9-DatasheetKishore Chowdary SNSNo ratings yet
- 0.3-3.0 GHZ High Dynamic Range Amplifier: Features Functional Block Diagram Cmm6004-ScDocument10 pages0.3-3.0 GHZ High Dynamic Range Amplifier: Features Functional Block Diagram Cmm6004-Scgonzalo2205No ratings yet
- TDA8510J Philips Elenota - PL PDFDocument16 pagesTDA8510J Philips Elenota - PL PDFMariuszChreptakNo ratings yet
- Horn Antenna Design PaperDocument12 pagesHorn Antenna Design PaperrvtanNo ratings yet
- Elecs 3Document5 pagesElecs 3Lanbert FranciscoNo ratings yet
- st70 2003 EnglishDocument483 pagesst70 2003 EnglishangeloNo ratings yet
- Ese EceDocument6 pagesEse EceGaurab DeyNo ratings yet