Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design & Testing of A RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Amplifier
Uploaded by
Aaron GonsalvesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design & Testing of A RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Amplifier
Uploaded by
Aaron GonsalvesCopyright:
Available Formats
By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E.
(IISc),
Associate Professor, MCE, HASSAN
1
DESIGN & TESTING OF A RC COUPLED SINGLE STAGE BJT AMPLIFIER
Aim: Wiring of a RC coupled single stage BJT amplifier and determination of the gain-
frequency response, input and output impedances.
Apparatus required: Transistor BC107, power supply, capacitors 0.22F, 47F,
resistors, connecting board, signal generator, digital multimeter and CRO.
Theory:
This is the most popular type of coupling because it is cheap and provides excellent audio
fidelity over a wide range of frequency. It is usually employed for voltage amplification.
Fig.3.1 shows the single stage of an RC coupled amplifier. The coupling does not affect
the Q point of the next stage since the C
2
blocks the dc voltage of the first stage from
reaching the base of the second stage or output. The function of C
1
is to couple the signal
source v
i
to the base of the transistor. At the same time it prevents the dc current of V
cc
from reaching the signal source v
i
and also prevents any dc component present in v
i
from
reaching of base.
The bypass capacitor C
e
is used to prevent the loss of gain due to negative feedback
across the resistor R
e.
Resistors R
1
, R
2
, and R
e
are used to bias the transistor so that the operating point lie on
the middle of the dc load line.
The resistor R
c
acts as ac load for the amplifier.
The RC network is broadband in nature. Therefore, it gives a wideband frequency
response and hence used to cover AF range of amplifier.
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUM
By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (IISc),
Associate Professor, MCE, HASSAN
2
Procedure to obtain frequency response:
1) Before wiring the circuit, check all the components using multimeter.
Connect the circuit as shown in the figure. Set Vcc for the designed value, and check
the DC biasing conditions such as V
BE,
V
CE.
V
BE
0.6V (for Silicon transistor)
,
V
CE
V
CC
/2.
2) If the DC biasing conditions satisfy then set the signal generator (input-voltage)
amplitude (peak-to-peak sine wave) so that the output remains sinusoidal. Note
the maximum signal handling capacity (MSHC) of the amplifier. It is the input
signal to the amplifier at which output remains just sinusoidal. This means that if
the input increased beyond this value, output no longer remains sinusoidal.
3) Keep the input signal less than MSHC (do not change the input further) and vary
the frequency of the input from lower range to higher range. Observe both input
and output simultaneously on the CRO. Note the input value (peak to peak) and
outputs across R
L
corresponding to the variation in frequencies of the input signal
at different intervals. The output voltage remains constant at mid frequency range.
4) Plot the graph with frequency along X-axis and gain dB along Y-axis.
5) From graph determine bandwidth.
Procedure to find input impedance:
1) Connect the circuit as shown in Fig 3.2.
2) Connect a resistance R
S
in series with the input signal and amplifier as shown in
the figure 3.2.
3) Set the signal generator (input voltage) amplitude (peak to peak sine wave) less
than MSHC at a mid frequency band.
4) Measure and note down the input voltage V
i
before R
S
and voltage V
i
after R
S.
5) Calculate the input impedance.
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUM
By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (IISc),
Associate Professor, MCE, HASSAN
3
Procedure to find output impedance:
1) Connect the circuit as shown in Fig 3.3.
2) Connect a resistance R
L
across the output terminals of the amplifier as shown in
the figure 3.3.
3) Set the signal generator (input voltage) amplitude (peak to peak sine wave) less
than MSHC at a mid frequency band.
4) Measure and note down the output voltage V
o
across output terminals when R
L
is open circuited and output voltage V
o
when R
L
connected across the output
terminals
.
5) Calculate the output impedance.
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUM
By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (IISc),
Associate Professor, MCE, HASSAN
4
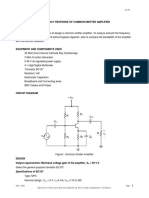
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Figure 3.1
DESIGN
Let Vcc=20V Ic=10mA ;VcE=Vcc/2=10V ;Pd=VcEQICEQ=10*10*1e-3=100mw
VEVcc/10=20/10=2V ;IEIc ;RE=VE/IE=2/10*1e-3=200
select standard value RE=220
VE=2*10*1e-3=2.2V
Rc=(Vcc-VcE-VE)/Ic =(20-10-2)/10*1e-3=780
select standard value Rc=820
R2RE/10 =GFE=125(min)
2750
select R2=2.7K
VB=0.7+2.2=2.9V
2.9=(2.7*1e3*20)/(R1+2.7*1e3)
= 15920
select standard value of 18K
Lower cut off frequency f1=100Hz
C20.22F
C1=C2=0.22F
CF=1/(2f1Xc2) Xc2=hie/(1+hfe) hie=1.5K, hfe=60
=24.6
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUM
By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (IISc),
Associate Professor, MCE, HASSAN
5
CF=64.69F
Select standard value of 47F or 100F
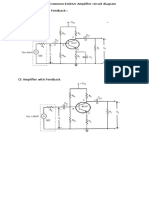
Circuit Diagram to Measure Input Impedance:
Fig.3.2
Circuit Diagram to Measure Output Impedance:
Fig.3.3
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUM
By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (IISc),
Associate Professor, MCE, HASSAN
6
Tabulation:
Maximum Signal Handling Capacity =___________mV
Input Voltage V
i
= _________mV
Sl.
No.
Frequency
f in Hz
Output voltage
V
0
in mV
Gain in dB= 20log(V
0
/V
i
)
Calculations:
Input Impedance Z
i
= V
i
`*R
S
/(V
i
-V
i
`)
Output Impedance Z
O
= (V
o
-V
o
`)R
L
/V
o
`
Current gain A
I
= -A
V
(Z
i
/R
L
)
Voltage gain A
v
= V
o
/V
i
www.bookspar.com | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUMS
www.bookspar.com | Website for Students | VTU NOTES | QUESTION PAPERS | NEWS | RESULTS | FORUM
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument49 pagesAnalog Electronics Lab ManualReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Design and Testing of Darlington Emitter Follower: By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (Iisc), Associate Professor, Mce, HassanDocument6 pagesDesign and Testing of Darlington Emitter Follower: By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (Iisc), Associate Professor, Mce, HassankanchankonwarNo ratings yet
- AEC LabManualDocument30 pagesAEC LabManualPrateek PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Objectives:: Electronics I Laboratory - EXPERIMENT 10 Common Emitter AmplifierDocument6 pagesObjectives:: Electronics I Laboratory - EXPERIMENT 10 Common Emitter AmplifierRabindraMaharanaNo ratings yet
- Design A RC Coupled CE Transistor AmplifierDocument7 pagesDesign A RC Coupled CE Transistor AmplifierSudeep Nayak100% (1)
- By: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (Iisc), Associate Professor, Mce, HassanDocument6 pagesBy: Mr.L.Kumaraswamy M.E. (Iisc), Associate Professor, Mce, Hassansarala20021990No ratings yet
- Expt 6Document3 pagesExpt 6sabitavabiNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications QtyDocument0 pagesCommon Emitter Amplifier: S.No Name of The Component/ Equipment Specifications Qtyagama1188No ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Lab ManualDocument68 pagesAnalog Electronics Lab ManualZealWolfNo ratings yet
- Lab10 2011Document5 pagesLab10 2011Venkat RamananNo ratings yet
- EC Lab ManualDocument27 pagesEC Lab ManualMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- EC1 Lab Exp3 PDFDocument2 pagesEC1 Lab Exp3 PDFRitu RoyNo ratings yet
- Ec Manual NewDocument59 pagesEc Manual NewWasz MujthabaNo ratings yet
- Sharmi ECE a-D-Circuits Lab ManualDocument74 pagesSharmi ECE a-D-Circuits Lab ManualSharmila83No ratings yet
- Cascode AmplifierDocument6 pagesCascode AmplifierRajesh NatarajanNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument8 pagesTransistorwei.cheng.auNo ratings yet
- Adc Lab Manual PDFDocument74 pagesAdc Lab Manual PDFJega Deesan75% (4)
- Cascode AmplifierDocument4 pagesCascode AmplifierappuamreddyNo ratings yet
- aeclAB 1Document41 pagesaeclAB 1ayjagadishNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectsDocument36 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectsTushar Kush100% (4)
- Analysis and Design of MOSFET Based Amplifier in Different ConfigurationsDocument10 pagesAnalysis and Design of MOSFET Based Amplifier in Different Configurationsmani_vlsiNo ratings yet
- ADC Lab ManualDocument46 pagesADC Lab ManualDinesh Kumar A RNo ratings yet
- ECII & Sim LabDocument49 pagesECII & Sim LabSivan LoveNo ratings yet
- Analog Communications Lab ManualDocument61 pagesAnalog Communications Lab ManualSriLakshmi RaheemNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierSajawal AliNo ratings yet
- ST - Joseph College of Engineering: SriperumbudurDocument45 pagesST - Joseph College of Engineering: SriperumbudurSuryaNo ratings yet
- Long Report Lab 7Document15 pagesLong Report Lab 7Saragadam Naga Shivanath RauNo ratings yet
- 9 CE AmplifierDocument5 pages9 CE AmplifierAnsh PratapNo ratings yet
- Ec FinalDocument46 pagesEc FinalManjunath YadavNo ratings yet
- EDC II Lab ManualDocument46 pagesEDC II Lab Manualshreeyak841No ratings yet
- Eca Lab ManualDocument78 pagesEca Lab ManualNageswariah.MNo ratings yet
- AEC Lab ManualDocument70 pagesAEC Lab ManualRohan BoseNo ratings yet
- RC CoupledDocument3 pagesRC CoupledRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Common Collector Circuit - DC OperationDocument7 pagesCommon Collector Circuit - DC OperationDebbie ComissionNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Question Bank 3 PDFDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics Question Bank 3 PDFPRAVEEN YADAWNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of A Single Stage RC Coupled AmplifierDocument26 pagesFrequency Response of A Single Stage RC Coupled AmplifierkanchankonwarNo ratings yet
- Expt No. 2 (B) Common Base AmplifierDocument11 pagesExpt No. 2 (B) Common Base Amplifierrani kumarNo ratings yet
- 19eee114 Lab4Document3 pages19eee114 Lab4Surya MurugesanNo ratings yet
- RC Coupled Transistor AmplifierDocument7 pagesRC Coupled Transistor AmplifierIshratNo ratings yet
- Applied Electronics Lab 1Document9 pagesApplied Electronics Lab 1Rickel RoweNo ratings yet
- EC 351 AC Analog Communication Lab ManualDocument117 pagesEC 351 AC Analog Communication Lab Manualhodibaaba1No ratings yet
- Ae Hardware PDFDocument55 pagesAe Hardware PDFIshani JhaNo ratings yet
- American International University-Bangladesh: Electronic DevicesDocument5 pagesAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Electronic DevicesAnamNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector Amplifier5611 M.Mubeen M.yaseenNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector AmplifierDocument5 pagesExperiment No. 02: RC Coupled Single Stage BJT Common Collector Amplifier5611 M.Mubeen M.yaseenNo ratings yet
- Ex #8 Emitter FolleowerDocument5 pagesEx #8 Emitter FolleowermanishNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1: Wiring of RC Coupled Single Stage AmplifierDocument7 pagesExperiment No 1: Wiring of RC Coupled Single Stage AmplifierShweta GadgayNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation-562-IV-CORE-32511408 - OC-OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS AND APPLICATIONS-13 Jun 2021Document1 pageInstrumentation-562-IV-CORE-32511408 - OC-OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS AND APPLICATIONS-13 Jun 2021Ricky RawNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument56 pagesLab ManualNarendra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ee 352 Ec Ii LabDocument61 pagesEe 352 Ec Ii LabSatya SandeepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document34 pagesChapter 8Abhinav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Multistage Amplifier Configurations: ObjectiveDocument19 pagesDesign and Analysis of Multistage Amplifier Configurations: ObjectivePreet PatelNo ratings yet
- EmtDocument115 pagesEmtRaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 - Center Tapped Full Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesExperiment 3 - Center Tapped Full Wave RectifierRandred GarciaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Multistage Amplifier Configurations: ObjectiveDocument12 pagesDesign and Analysis of Multistage Amplifier Configurations: ObjectivePreet PatelNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Https - Threejs - Org - Examples - Webgl - Fire - HTMLDocument9 pagesHttps - Threejs - Org - Examples - Webgl - Fire - HTMLMara NdirNo ratings yet
- AN-PFC-TDA 4863-3 Calculation-Tool For PFC-Preconverter Using TDA 4863Document9 pagesAN-PFC-TDA 4863-3 Calculation-Tool For PFC-Preconverter Using TDA 4863NaciConSolNo ratings yet
- Travelsinvarious03clar BWDocument522 pagesTravelsinvarious03clar BWSima Sorin MihailNo ratings yet
- Toda People in IndiaDocument9 pagesToda People in IndiaAmoona KopiKoNo ratings yet
- Graviola1 Triamazon, AntiCancer, InglesDocument2 pagesGraviola1 Triamazon, AntiCancer, InglesManuel SierraNo ratings yet
- Concrete Saw Core Drilling Swms 10067-8Document12 pagesConcrete Saw Core Drilling Swms 10067-8JamesNo ratings yet
- Exact Solution Tank DrainageDocument8 pagesExact Solution Tank DrainageFelipe CastNo ratings yet
- Shi Et Al-2019-Intensive Care MedicineDocument11 pagesShi Et Al-2019-Intensive Care MedicineJavier BlancNo ratings yet
- The Online Math Open Fall Contest December 4-15, 2020Document8 pagesThe Online Math Open Fall Contest December 4-15, 2020Raghav GoelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Arts of East AsiaDocument21 pagesLesson 2 Arts of East Asiarenaldo ocampoNo ratings yet
- Analisis Keterampilan Berpikir Kritis Mahasiswa Pada Materi KinematikaDocument11 pagesAnalisis Keterampilan Berpikir Kritis Mahasiswa Pada Materi KinematikaTrisnaNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument18 pagesEnglishSarah SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Sample Design Calculations For Block Found. For Vib. Equip.Document17 pagesSample Design Calculations For Block Found. For Vib. Equip.Adam Michael GreenNo ratings yet
- Baldor Motor TestDocument14 pagesBaldor Motor TestChecho BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S0956713515002546 Main PDFIfwat ThaqifNo ratings yet
- P eDocument22 pagesP eKiks AshNo ratings yet
- 510 1453 1 PB Tiang ReklameDocument6 pages510 1453 1 PB Tiang ReklameGunaedy UtomoNo ratings yet
- Attacks On Cryptosystems PDFDocument18 pagesAttacks On Cryptosystems PDFUjjayanta BhaumikNo ratings yet
- WPP Jak Campus - Defect All Level - 18042023Document15 pagesWPP Jak Campus - Defect All Level - 18042023bbm FebriNo ratings yet
- Iare Ece Aec012 DSP QB 0Document20 pagesIare Ece Aec012 DSP QB 0projects allNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Worksheet - SHHSDocument3 pagesCatalyst Worksheet - SHHSNerd 101No ratings yet
- Phase-Locked Loop Independent Second-Order Generalized Integrator For Single-Phase Grid SynchronizationDocument9 pagesPhase-Locked Loop Independent Second-Order Generalized Integrator For Single-Phase Grid SynchronizationGracella AudreyNo ratings yet
- JMO Solutions 2008Document4 pagesJMO Solutions 2008ichkhuyNo ratings yet
- PT3 Guided WritingDocument8 pagesPT3 Guided WritingDayang Haffizah Abg AbdillahNo ratings yet
- Opti Turn Tu 2004 V ManualDocument80 pagesOpti Turn Tu 2004 V ManualCharu NavneetNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Deflection of Beams - Conjugate Beam MethodMbali MagagulaNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal PHDDocument19 pagesResearch Proposal PHDSuleiman Mukhtar100% (2)
- Brenda Patton Guided Reflection QuestionsDocument3 pagesBrenda Patton Guided Reflection QuestionsCameron JanzenNo ratings yet
- Math Diagnostic ExamDocument4 pagesMath Diagnostic ExamMananquil JeromeNo ratings yet
- Nav Bharat Nirman: Indispensable Ideas For Green, Clean and Healthy IndiaDocument4 pagesNav Bharat Nirman: Indispensable Ideas For Green, Clean and Healthy IndiaRishabh KatiyarNo ratings yet