Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Application Notes - Trigger Circuits: 1. Capacitive External Triggering
Uploaded by
Kapila Wijayaratne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesThis document summarizes different trigger circuit designs for flash tubes. It discusses three main types: 1) Capacitive external triggering which uses a trigger coil to generate a high voltage pulse that is applied to a separate trigger electrode. This allows for a compact design but has a relatively long delay time. 2) Direct series triggering connects the trigger coil directly to the anode or cathode, reducing the delay time but requiring larger components. 3) Triggering with doubled anode voltage which temporarily doubles the anode voltage during triggering to improve performance at high fill pressures.
Original Description:
(Application Notes)
Original Title
Trigger Circuits
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes different trigger circuit designs for flash tubes. It discusses three main types: 1) Capacitive external triggering which uses a trigger coil to generate a high voltage pulse that is applied to a separate trigger electrode. This allows for a compact design but has a relatively long delay time. 2) Direct series triggering connects the trigger coil directly to the anode or cathode, reducing the delay time but requiring larger components. 3) Triggering with doubled anode voltage which temporarily doubles the anode voltage during triggering to improve performance at high fill pressures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views3 pagesApplication Notes - Trigger Circuits: 1. Capacitive External Triggering
Uploaded by
Kapila WijayaratneThis document summarizes different trigger circuit designs for flash tubes. It discusses three main types: 1) Capacitive external triggering which uses a trigger coil to generate a high voltage pulse that is applied to a separate trigger electrode. This allows for a compact design but has a relatively long delay time. 2) Direct series triggering connects the trigger coil directly to the anode or cathode, reducing the delay time but requiring larger components. 3) Triggering with doubled anode voltage which temporarily doubles the anode voltage during triggering to improve performance at high fill pressures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Application Notes Trigger Circuits
The flashtube discharge is initiated by means of a high voltage pulse V
z
(trigger
voltage) which must be high than the static breakdown voltage of the tube.
V
z
ranges between 2kV and 20kV. The difference between V
z
and V
0
must be
sufficient to avoid spontaneous triggering.
It is recommended that:
V
z
is generated by a pulse transformer (trigger coil) at a transformation ratio of
1:20 to 1:100. A thyristor (or mechanical switch) discharges a trigger capacitor C
z
via the primary side of the trigger coil. On the secondary side a damped high
voltage oscillation is produced, the form of which greatly depends on the trigger
coil and the external circuitry.
1. Capacitive external triggering
This is the simplest form of triggering. In this case, the trigger electrode of the
tube has been insulated from anode and cathode. However, it extends over the
entire arc length.
Capacitive external triggering
Since the capacity of the trigger electrode is approximately 10pF against the
cathode and anode, the secondary side of the trigger coil can be highly resistive,
resulting in a compact construction of the coil.
The polarity of the first half wave of the trigger circuit can influence the trigger
ability.
Shown below is an example of trigger parameters with Heimann trigger coils.
As V
z
is proportional to V
0
, all intermediate values can be easily calculated.
Advantages of external trigger are:
Small size, low cost components
Low primary and secondary currents
Disadvantages of external triggering are:
Relatively high trigger delay time (approximately 10 5 s)
Produces electromagnetic interferences in case of long wires in circuit.
2. Direct Series Triggering
Direct series triggering
The secondary winding of the trigger coil is either on the anode or cathode side
of the tube and conducts, in any case, the entire discharge current.
The optional trigger electrode H can be connected with anode or cathode.
In comparison to the capacitive external triggering, the advantages of direct
series triggering are:
Short trigger delay time (<1 s) with minimum jitter.
Low emission of electromagnetic interferences.
Disadvantages of direct series triggering are:
Large size, high cost components.
3. Trigger with doubling of anode voltage (V
0
)
This simple circuit facilitates the triggerability of flashtubes with high Xenon-fill-
pressure considerably. When firing T, the discharge of C
z
produces in the trigger
coil the usual trigger events. Simultaneously also C
inv
is discharged bringing
down the cathode potential of the flashtube to V0 for a few microseconds. So
the effective anode voltage is V
0
.
4. Booster
The booster is an auxiliary anode voltage V
H
>V
0
which is applied to a capacitor
C
H
<<C
B
and blocked against V
0
by diode D. When triggered, the tube takes V
H
as anode voltage. This circuit is suitable in cases of high variations in the
operating voltage V
0
or when the tube-fill pressure is high (luminous efficiency).
You might also like
- Joule Thief - WikipediaDocument23 pagesJoule Thief - WikipediaBaro ZoltiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5b Diode - EEDocument90 pagesChapter 5b Diode - EEHarithZakariaNo ratings yet
- Supply 3Document34 pagesSupply 3david reyesNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Inductors in DC CircuitsDocument10 pagesCapacitors and Inductors in DC CircuitsLuka LasicNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Turn-On Methods and Firing CircuitsDocument33 pagesThyristor Turn-On Methods and Firing CircuitsOmkar GuravNo ratings yet
- Regulated Power Supply Circuits ExplainedDocument25 pagesRegulated Power Supply Circuits ExplainedJagadish Pal100% (1)
- Exam RevisionDocument61 pagesExam RevisionRachul heenimNo ratings yet
- AO Report (Theory)Document5 pagesAO Report (Theory)Farwa RaisNo ratings yet
- Universal IC 555 BuckDocument7 pagesUniversal IC 555 BuckSingam Sridhar100% (1)
- Aircraft Electronics, Microprocessor & ApplicationDocument78 pagesAircraft Electronics, Microprocessor & ApplicationJigar Soni100% (1)
- Project Proposal Triggering Circuit For ThyristorsDocument9 pagesProject Proposal Triggering Circuit For Thyristorsmohsin AwanNo ratings yet
- Generation of HveDocument29 pagesGeneration of HveManas Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- Selection of Power Diode:: Lecture - 5 Dated 11/1/2011 Power Electronics By: Ankur GargDocument7 pagesSelection of Power Diode:: Lecture - 5 Dated 11/1/2011 Power Electronics By: Ankur GargAnirudh SeksariaNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 - RedresorulDocument27 pagesLab 6 - RedresorulIonelNo ratings yet
- Measure Coil Resistance and Impedance of TransformerDocument8 pagesMeasure Coil Resistance and Impedance of TransformerFarizal JaafarNo ratings yet
- CS209Document6 pagesCS209RicardoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of ThyristorDocument75 pagesCharacteristics of Thyristoryogusmilu100% (1)
- Electronics Devices & Circuit Lab ManualDocument53 pagesElectronics Devices & Circuit Lab Manualbiswajit7sarkar100% (1)
- Chap-4 Diode CircuitsDocument17 pagesChap-4 Diode Circuitsvishal mishraNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Diode R & RDocument15 pagesLab 1 Diode R & RFAseeh MalikNo ratings yet
- Firing Circuits of Thyristor or SCRDocument10 pagesFiring Circuits of Thyristor or SCRdivakar r vlNo ratings yet
- Tesla CoilDocument6 pagesTesla CoilBilal IqbalNo ratings yet
- Ecd ReportDocument5 pagesEcd ReportFarwa RaisNo ratings yet
- Aim of The Experiment:: Sl. No. Name of Apparatus Specification QuantityDocument4 pagesAim of The Experiment:: Sl. No. Name of Apparatus Specification QuantityDevansh MankarNo ratings yet
- Capacitors in DC Circuits: U Is Formed Between The Electrodes. The Subsequent Graphic Image Shows An ExampleDocument15 pagesCapacitors in DC Circuits: U Is Formed Between The Electrodes. The Subsequent Graphic Image Shows An Examplebeta akuiNo ratings yet
- EEE572 Homework 1 Solutions Inductor Waveform Analysis DC-DC Converter CircuitsDocument6 pagesEEE572 Homework 1 Solutions Inductor Waveform Analysis DC-DC Converter Circuitsmitrax1pNo ratings yet
- Clipper and ClamperDocument11 pagesClipper and ClamperPoorni Jayaraman100% (1)
- Rinciples OF Lectric Ircuits: Capacitors, Inductors and TransformersDocument41 pagesRinciples OF Lectric Ircuits: Capacitors, Inductors and TransformersMahesh ThilakasiriNo ratings yet
- Cascadable Adiabatic Logic Circuits For Low-Power ApplicationsDocument37 pagesCascadable Adiabatic Logic Circuits For Low-Power ApplicationsJesh KakkadNo ratings yet
- Title: Study On Clamper Circuits.: Experiment No. 04Document4 pagesTitle: Study On Clamper Circuits.: Experiment No. 04shuvon3344No ratings yet
- Thyristor Diagnostics Simoreg and Sinamics DCMDocument2 pagesThyristor Diagnostics Simoreg and Sinamics DCMprashob7No ratings yet
- What Is A Buck Boost ConverterDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Buck Boost ConverterXavierNo ratings yet
- 4-Pin GM HEI Module NotesDocument6 pages4-Pin GM HEI Module Noteszampardi100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - CT&VT - Part 1Document63 pagesChapter 3 - CT&VT - Part 1zhafran100% (1)
- Representations of Power System ComponentsDocument46 pagesRepresentations of Power System Componentsবিবেক রত্নNo ratings yet
- Ke 20503Document34 pagesKe 20503Iqxca AzmYaniNo ratings yet
- EEP851 POWER ELECTRONICS LAB- SCR, IGBT & MOSFET CHARACTERISTICSDocument16 pagesEEP851 POWER ELECTRONICS LAB- SCR, IGBT & MOSFET CHARACTERISTICSGaurav Verma100% (2)
- The Blocking OscillatorDocument2 pagesThe Blocking OscillatorJoseGarciaRuizNo ratings yet
- Impulse Generator Practical Course WorkDocument8 pagesImpulse Generator Practical Course WorkKapila Kumara100% (1)
- Introductory ElectronicsDocument20 pagesIntroductory ElectronicsKiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- How a flyback diode prevents voltage spikes from inductive loadsDocument5 pagesHow a flyback diode prevents voltage spikes from inductive loadsEmad_AlexmarNo ratings yet
- Bef45203 HV Chapter 3 - HV GeneratorsDocument90 pagesBef45203 HV Chapter 3 - HV GeneratorsNUR AQILAH MOHD AZMANNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 (1903069)Document4 pagesLab 4 (1903069)Tahsin Zaman TalhaNo ratings yet
- Transistor CircuitsDocument9 pagesTransistor CircuitsYogesh YadavNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Limitation of Conventional Tubes:: Lead Inductance and Inter-Electrode Capacitance EffectDocument55 pagesHigh Frequency Limitation of Conventional Tubes:: Lead Inductance and Inter-Electrode Capacitance EffectRaveena GurralaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2 Transistors and Amplifiers: V Bipolar Junction transistor-CB, CE, CCDocument23 pagesUNIT-2 Transistors and Amplifiers: V Bipolar Junction transistor-CB, CE, CCMuthuvel MNo ratings yet
- ELEX1 Lecture 01 PDFDocument10 pagesELEX1 Lecture 01 PDFBarn Go100% (1)
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSURAJ GAUTAMNo ratings yet
- Generation of High Voltage and CurrentDocument14 pagesGeneration of High Voltage and CurrentpriyadarshniNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Power SuppliesDocument7 pagesCalculation of Power SuppliesAnonymous DjWqKpZ1No ratings yet
- Diode ApplicationsDocument33 pagesDiode Applicationspransdom10No ratings yet
- Analogue Lab ReportDocument5 pagesAnalogue Lab ReportZakaria MucheruNo ratings yet
- Power Supply 12V 3A With 2N3055Document1 pagePower Supply 12V 3A With 2N3055fergalvanNo ratings yet
- To Design A Clamper Circuit Design.: Components RequiredDocument10 pagesTo Design A Clamper Circuit Design.: Components RequiredSyed Ali Raza ShahNo ratings yet
- Eee421: Power Electronics: Power Semiconductor Devices: DiodeDocument12 pagesEee421: Power Electronics: Power Semiconductor Devices: DiodeRafat ShamsNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ExperimentsDocument45 pagesBasic Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab ExperimentsChirag Sachdeva100% (2)
- 2.01 First Transistor Model: Current Amplifier:, and V VDocument6 pages2.01 First Transistor Model: Current Amplifier:, and V VKirz SerranoNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Impulse Generator CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesHigh Voltage Impulse Generator CharacteristicsosddsNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Labview Core 1Document58 pagesLabview Core 1m240597No ratings yet
- Optimizing Hybridization of 1T and 2H Phases in MoS2 MonolayersDocument8 pagesOptimizing Hybridization of 1T and 2H Phases in MoS2 MonolayersKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 2017 Solar Eclipse Full MapDocument1 page2017 Solar Eclipse Full MapKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Yellowstone LandmarksDocument1 pageYellowstone LandmarksKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Superconductivity - B C S (Chapter 10)Document48 pagesSuperconductivity - B C S (Chapter 10)Kapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- WAVEGUIDE ParametersDocument1 pageWAVEGUIDE ParametersKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 04 General Solution Using Greens Fncs SphereDocument3 pages04 General Solution Using Greens Fncs SphereKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- KEPCO NTC Series Programmable Power Supply InstructionDocument16 pagesKEPCO NTC Series Programmable Power Supply InstructionKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Linear Response Theory ExplainedDocument59 pagesLinear Response Theory ExplainedKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- AC Stark Shift - IOP ScienceDocument20 pagesAC Stark Shift - IOP ScienceKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 02 BCs Method of Images Examples 3456Document8 pages02 BCs Method of Images Examples 3456Kapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- LABVIEW Core 1 Sample Course ManualDocument30 pagesLABVIEW Core 1 Sample Course ManualKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 02 Scalar Potential Surface ChargDocument8 pages02 Scalar Potential Surface ChargKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 03 BCs Method of Images Example 7Document9 pages03 BCs Method of Images Example 7Kapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 05 Energy Potential CapacitanceDocument6 pages05 Energy Potential CapacitanceKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 02 Math Review 1Document6 pages02 Math Review 1Kapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Statistical Mechanics NotesDocument2 pagesStatistical Mechanics NotesKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 01 BCs Method of Images Examples 12Document8 pages01 BCs Method of Images Examples 12Kapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Heisenberg PictureDocument3 pagesHeisenberg PictureKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Equilibrium: 20.1 A Review of Basic Reaction ConceptsDocument10 pagesChemical Reaction Equilibrium: 20.1 A Review of Basic Reaction ConceptsKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 03 Math Review 2Document7 pages03 Math Review 2Kapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Vector PotentialDocument21 pagesVector PotentialKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Perturbation TheoryDocument8 pagesPerturbation TheoryKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Jackson (Some) SolutionsDocument12 pagesJackson (Some) SolutionsKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
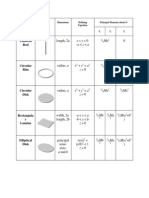
- Principal moments of inertia for common shapesDocument2 pagesPrincipal moments of inertia for common shapesKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- List of Mathematical SeriesDocument9 pagesList of Mathematical SeriesKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Delta FunctionDocument1 pageDelta FunctionKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Scope ManualDocument54 pagesScope ManualKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Relaxation NotesDocument14 pagesRelaxation NotesKapila WijayaratneNo ratings yet
- Bias Point Analysis by Hand and in SPICE DescriptionDocument6 pagesBias Point Analysis by Hand and in SPICE DescriptionMit MA0% (1)
- Plating Process Flow DiagramDocument4 pagesPlating Process Flow DiagramManu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Student Information Maintenance System ProjectDocument4 pagesStudent Information Maintenance System ProjectHarshpreet Singh0% (1)
- Production and Machinery: Wikov Manufacturing FacilityDocument2 pagesProduction and Machinery: Wikov Manufacturing FacilitytayefehNo ratings yet
- Dam Mitigation: Dam Mitigation: NYSDEC NYSDEC Permitting ProcessDocument8 pagesDam Mitigation: Dam Mitigation: NYSDEC NYSDEC Permitting ProcessHRNERRNo ratings yet
- Luxury 5-Bedroom Villa with Ocean Views in Sri LankaDocument3 pagesLuxury 5-Bedroom Villa with Ocean Views in Sri LankaMr. Firdaus NurulNo ratings yet
- 1 Rate of ReactionDocument21 pages1 Rate of ReactionEila AriffinNo ratings yet
- Installation Rules Paper 1 August 2019Document7 pagesInstallation Rules Paper 1 August 2019Abdirahman H JaamacNo ratings yet
- 615 Series Quick Start Guide 757435 ENa. Relay ABBDocument4 pages615 Series Quick Start Guide 757435 ENa. Relay ABBTung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Feltest Whitepaper - Correct Felt Permeability (ENG)Document6 pagesFeltest Whitepaper - Correct Felt Permeability (ENG)Engr. Waqar AliNo ratings yet
- Nagios XI Product OverviewDocument2 pagesNagios XI Product Overviewphduycanh0% (1)
- 2170908Document33 pages2170908bhavikNo ratings yet
- EPRI PMBD Gap Analysis TemplateDocument4 pagesEPRI PMBD Gap Analysis TemplatedanishaslNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Software Development StrategiesDocument41 pagesChapter 7 Software Development StrategiesBurime GrajqevciNo ratings yet
- CollectionsDocument6 pagesCollectionsiamsonalNo ratings yet
- Ebara Horizontal Multistage PumpDocument27 pagesEbara Horizontal Multistage PumpYohanes KrisNo ratings yet
- Inspection of Test Plan: Electrical EquipmentDocument7 pagesInspection of Test Plan: Electrical Equipmentzvlcar nainNo ratings yet
- Sony Ericsson Mix Walkman Wt13i White Paper PDFDocument13 pagesSony Ericsson Mix Walkman Wt13i White Paper PDFAshok ReddyNo ratings yet
- Specification May Change According To Project RequirementDocument1 pageSpecification May Change According To Project RequirementasdthuNo ratings yet
- 4N25 DatasheetDocument9 pages4N25 DatasheetStavros KalapothasNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor AND Microcontroller Practical Lab File: Name-Enrollment No. - Course/Branch - Btech/MaeDocument11 pagesMicroprocessor AND Microcontroller Practical Lab File: Name-Enrollment No. - Course/Branch - Btech/MaeShuktika SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Thika Water and Sewerage Company Limited Tender Notice PDFDocument1 pageThika Water and Sewerage Company Limited Tender Notice PDFUsman ArifNo ratings yet
- Vespa Range Brochure 2016Document24 pagesVespa Range Brochure 2016saskastepNo ratings yet
- SIMD-Accelerated Regular Expression MatchingDocument7 pagesSIMD-Accelerated Regular Expression Matching蘇意喬No ratings yet
- Service Manual: Super PlusDocument250 pagesService Manual: Super PlusАндрей Рычков100% (1)
- Oracle Apps Technical ConsultantDocument5 pagesOracle Apps Technical ConsultantRamesh Babu KadiyamNo ratings yet
- Synopsis (Fingerprint Reg)Document5 pagesSynopsis (Fingerprint Reg)Smiju SukumarNo ratings yet
- Yechout TableOfContentsDocument5 pagesYechout TableOfContentsessi90No ratings yet
- Orgone Motor SkepticismDocument2 pagesOrgone Motor SkepticismoyomiNo ratings yet