Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AbdusSatter WF Slides PDF
Uploaded by
Waleed El-azabOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AbdusSatter WF Slides PDF
Uploaded by
Waleed El-azabCopyright:
Available Formats
Water Flood Workshop
October 23rd 2013
Long Beach, California
Water Flooding and
Waterflood Design
by
Dr. Abdus Satter
Water Flooding
Water Flood Process
Reasons for Water flooding
History of Water flooding
Water Flood Patterns
Water Flood Recovery Efficiency
Oil Displacement by Water flooding
Variables Affecting Recovery Efficiencies
Water Flood Process
Water flooding consists of injecting water into a set
of wells while producing from the surrounding
wells. It maintains reservoir pressure and
displaces oil from the injectors to the producers
Reasons for Water Flooding
Primary Production Method Leaves Behind 1/3 to 1/2
or More of the Original Oil In Place
After Primary Production, Waterflooding Enhances
Substantially Production and Reserves
It Is the Most Widely Used Recovery Method After
Primary
Generally Available Water
Efficient Agent for Displacing Light/Medium Gravity
Oil
Low Capital Investment, Operating Costs, and
favorable Economics
Easy to Inject and spreads easily
History of Water flooding
Accidental Water Injection in Pithole City Area in
1865
In Earliest Days started at a Single well and then
to Circle Drive, Line Drive, Peripheral Floods
First 5-Spot Flood Initiated in 1924 in Bradford
Field
Grew to Oklahoma in 1931and then to Texas in
1936
Widespread application started in early 1950
Water Flood Patterns
Five Spot Regular 4 Injectors and 1Producer
Five Spot Inverted 1 Injector and 4 Producers
Seven Spot Regular 6 Injectors and 1Producer
Seven Spot Inverted 1 Injector and 6 Producers
Nine Spot Regular 8 Injectors and 1Producer
Nine Spot Inverted 1 Injector and 8 Producer
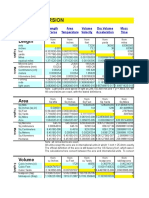
Waterflooding Recovery Efficiency
Overall Recovery Efficiency
ER = ED x EV
Where:
ER
Overall recovery efficiency, %
ED
Displacement efficiency within the
volume swept by water, %
EV
Reservoir Volume swept by water, %
EA x EI
EA
Areal sweep efficiency, %
EI
Vertical or invasion sweep efficiency,
%
Oil Displacement by Waterflooding
Variables Affecting Efficiencies
Displacement Efficiency by Rock and Fluid
Properties, and Throughput (Pore Volume
Injected)
Areal and Pattern Sweep Efficiencies by Flooding
Pattern Types, Mobility Ratio, Reservoir
Heterogeneity, and Throughput
Typical Successful Waterflood Performance
Water Flood Design
Design Considerations
Example Water Flood Development
Plan
Design Considerations
Reservoir Characterization Geoscience and
Engineering Data
Potential Flooding Plans Peripheral, Pattern, Well
Spacing
Estimate Injection, Production Rates
Facilities Design Fluid Volumes and Rates for
Sizing Equipment, Water Source and Disposal
Capital Expenditures and Operating Costs
Economic Evaluation, Risk, and Uncertainties
Water Flood Development Plan
Discovery
Exploration
Delineation
Reservoir
Management
Abandonment
Tertiary
Development
Primary
Waterflood Mature Field
Production
Professionals Involved
Exploration - Geologists, Geophysicists
Discovery - Drilling and Reservoir Engineers
Petrophysicists
Delineation - Sam as above
Development - Reservoir, Drilling, Operation, and
Facilities Engineers
Production Production Engineers
WF Project Development Approach
Build Integrated Geoscience and
Engineering Model Using Available Data
Simulate Full-Field Primary
Performance
Forecast Performance under Peripheral
and Pattern Waterflood Drive
Top Structure Map
Waterflood Prospect Reservoir
-4
W-9
-4
29
-4270
-4
28
30
W-8
-4 28
-42 50
W-3
-4 24
-42 30
-427
W-2
-4 28
-4220
-428
0
W-1
-4 24
-423 0
W-4
W-5
-4
28
-42 50
-4
-427
W-8
28
-4
W-7
-4 29
29
0
-4
28
Top Structure Map
-4 30
Development Cases
Case 2
Case 1
Case 5
Case 4
Cum. Oil Produced (MSTB)
12000
Case 3
Case
Case
Case
Case
Case
1
2
3
4
5
Peripheral
Peripheral
Pattern
Pattern
Pattern
5
9
1
4
12
4
8
4
9
13
Cumulative Oil Recovery vs.
Time
10000
Secondary
8000
6000
Primary
4000
2000
0
0.00
Depletion
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
25.00
30.00
TIME (Years)
Depletion
Case-1
Case-2
Case-3
Case-4
Case-5
Oil Recovery vs. Water Injected
Oil Recovery (fraction)
0.5
0.4
Case-2
Case-4
0.3
Case-5
Case-1
Case-3
0.2
0.1
0
0
0.25
0.5
0.75
PV Water Injected (fraction)
Case-1
Case-2
Case-3
Case-4
Case-5
Economic Criteria
Payout Time Time needed to recover investment
Discounted Cash Flow Rate of Return Maximum
discount rate needed to be charged for the
investment capital to produce a break-even venture
Profit- to- investment Ratio Total undiscounted
cash flow without capital investment divided by the
total investment
Present Worth Net Profit Present value of the entire
cash flow discounted at a specified discount rate
Economic Evaluation Results
Case-1
Case-2
Case-3
Case-4
Case-5
1.853
4.882
0.973
3.484
8.799
1.965
5.138
1.378
3.176
5.105
15
15
15
15
15
2.58
1.78
2.44
2.74
2.28
Discounted Cash
Flow Return on
Investment, %
69.64
131.15
80.12
87.83
104.84
Profit-toInvestment Ratio
16.88
16.44
23.32
13.91
8.74
Development
Costs, $/STBO
0.94
0.95
0.71
1.10
1.72
Capital
Investment, $MM
Reserves,
MMSTBO
Project Life
Payout Time, Years
You might also like
- Scan 0006Document1 pageScan 0006Waleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Rapid On-Site Analysis of Fats, Oil and Grease (FOG)Document2 pagesRapid On-Site Analysis of Fats, Oil and Grease (FOG)Waleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- BRO Fluorescence SpectrosDocument24 pagesBRO Fluorescence SpectrosWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Expression of UncertaintyDocument60 pagesExpression of UncertaintyWaleed El-azab67% (3)
- International Biodeterioration & BiodegradationDocument8 pagesInternational Biodeterioration & BiodegradationWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Brief Review of Important Concepts For Quantitative AnalysisDocument20 pagesBrief Review of Important Concepts For Quantitative AnalysisWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- 44 74453BRO LS 55andLS 45FluorescenceSpectrophotometerDocument8 pages44 74453BRO LS 55andLS 45FluorescenceSpectrophotometerumesh123patilNo ratings yet
- New Iec 60296 Ed 4 From A Transformer Oil Manufactures Perspective 2013-09-01Document5 pagesNew Iec 60296 Ed 4 From A Transformer Oil Manufactures Perspective 2013-09-01Sreeram PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Dsa 1183Document44 pagesDsa 1183Waleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- PRD FlexibilityDocument5 pagesPRD FlexibilityWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Quality Control / Quality Assurance in Analytical LaboratoriesDocument110 pagesQuality Control / Quality Assurance in Analytical LaboratoriesWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Errors in Chemical AnalysisDocument19 pagesErrors in Chemical AnalysisWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Gas Reinjection: Reducing Flaring and Improving RecoveryDocument29 pagesGas Reinjection: Reducing Flaring and Improving RecoveryWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Calibrations, Standardizations, and Blank Corrections for Accurate AnalysisDocument43 pagesCalibrations, Standardizations, and Blank Corrections for Accurate AnalysisWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- 8015 BDocument28 pages8015 BAbdul Raheem U LNo ratings yet
- Validation of ISO 6974 For The Measurement of The Composition of Hydrogen-Enriched Natural GasDocument8 pagesValidation of ISO 6974 For The Measurement of The Composition of Hydrogen-Enriched Natural GasWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Gpa 2261-00 2000 PDFDocument22 pagesGpa 2261-00 2000 PDFWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Gas FlaringDocument14 pagesGas FlaringWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Oil Analysis OverviewDocument36 pagesOil Analysis OverviewWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- D Chesher - Troubleshooting Failed Quality Control PDFDocument34 pagesD Chesher - Troubleshooting Failed Quality Control PDFWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- 04chapter2 PDFDocument17 pages04chapter2 PDFWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- For Further Tran: - Eeac and Devewment CommaiDocument14 pagesFor Further Tran: - Eeac and Devewment CommaiWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- C Elementar Vario MACRO Cube PDFDocument16 pagesC Elementar Vario MACRO Cube PDFWaleed El-azab100% (1)
- Sample Receiving ProceduresDocument1 pageSample Receiving ProceduresWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Manual of Petroleum Measurement StandardsDocument23 pagesManual of Petroleum Measurement StandardsWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Water Sampling PDFDocument7 pagesWater Sampling PDFWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Degradation of AcetalDocument1 pageDegradation of AcetalWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion: LengthDocument35 pagesUnit Conversion: LengthAnonymous 8aj9gk7GCLNo ratings yet
- Study ProducedWaterRecyclingReuse DraftReportDocument79 pagesStudy ProducedWaterRecyclingReuse DraftReportWaleed El-azabNo ratings yet
- <html> <head> <title>DansGuardian - Access Denied</title> </head> <body bgcolor=#FFFFFF> <center> <table border=0 cellspacing=0 cellpadding=2 height=540 width=700> <tr> <td colspan=2 bgcolor=#FEA700 height=100 align=center> <font face=arial,helvetica size=6> <b>Access has been Denied!</b> </td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan=2 bgcolor=#FFFACD height=30 align=right> <font face=arial,helvetica size=3 color=black> <b>- </b> </td> </tr> <tr> <td align=center valign=bottom width=150 bgcolor=#B0C4DE> <font face=arial,helvetica size=1 color=black> Allahabad University </td> <td width=550 bgcolor=#FFFFFF align=center valign=center> <font face=arial,helvetica color=black> <font size=4> Access to the page: <br><br> <a href="http://www.scribd.com/titlecleaner?title=water+analysis.pdf" target="_blank">http://www.scribd.com/titlecleaner?title=water+analysis.pdf</a> <br><br> <font size=3> ... has been denied for the following reason: <br><br> <foDocument22 pages<html> <head> <title>DansGuardian - Access Denied</title> </head> <body bgcolor=#FFFFFF> <center> <table border=0 cellspacing=0 cellpadding=2 height=540 width=700> <tr> <td colspan=2 bgcolor=#FEA700 height=100 align=center> <font face=arial,helvetica size=6> <b>Access has been Denied!</b> </td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan=2 bgcolor=#FFFACD height=30 align=right> <font face=arial,helvetica size=3 color=black> <b>- </b> </td> </tr> <tr> <td align=center valign=bottom width=150 bgcolor=#B0C4DE> <font face=arial,helvetica size=1 color=black> Allahabad University </td> <td width=550 bgcolor=#FFFFFF align=center valign=center> <font face=arial,helvetica color=black> <font size=4> Access to the page: <br><br> <a href="http://www.scribd.com/titlecleaner?title=water+analysis.pdf" target="_blank">http://www.scribd.com/titlecleaner?title=water+analysis.pdf</a> <br><br> <font size=3> ... has been denied for the following reason: <br><br> <foyounusgulNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Complex Fluid For Olga 5Document10 pagesComplex Fluid For Olga 5angry_granNo ratings yet
- Kinetics: Effects of Concentration & Temperature on Reaction RatesDocument4 pagesKinetics: Effects of Concentration & Temperature on Reaction Ratescrybaby0% (1)
- The Changes of Leaves in AutumnDocument9 pagesThe Changes of Leaves in AutumnKei's EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Accident Radio Logic GOIANIADocument157 pagesAccident Radio Logic GOIANIACatalin CuraliucNo ratings yet
- Current Monitoring Series CMR - Current Control: Ordering InformationDocument5 pagesCurrent Monitoring Series CMR - Current Control: Ordering InformationPrasadPurohitNo ratings yet
- Can Your Roof Handle The Weight of Solar Panels?Document2 pagesCan Your Roof Handle The Weight of Solar Panels?Princess Joan UlitNo ratings yet
- SuperOhm 3754 (3748-11) - Technical Data Sheet - ECC - Rev 2 - 2016-09Document2 pagesSuperOhm 3754 (3748-11) - Technical Data Sheet - ECC - Rev 2 - 2016-09igor brocaNo ratings yet
- PU158TIDocument2 pagesPU158TITrevor BurnettNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Areas: European & IEC Classification Definition of Zone or Division North American ClassificationDocument3 pagesHazardous Areas: European & IEC Classification Definition of Zone or Division North American Classificationmuddisetty umamaheswarNo ratings yet
- LM1117Document20 pagesLM1117Shahril RizalNo ratings yet
- 7.MMCR JuliDocument5,281 pages7.MMCR JuliAngga StwnNo ratings yet
- OCR Advanced GCE Physics A - 2826/01 - Unifying Concepts in Physics - January 2007Document12 pagesOCR Advanced GCE Physics A - 2826/01 - Unifying Concepts in Physics - January 2007Soham PatwardhanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument16 pagesElectrochemistry NotesRandomNo ratings yet
- Dual Cab Locomotive HandbookDocument80 pagesDual Cab Locomotive HandbookRah Mli80% (5)
- Engine Construction and OperationDocument31 pagesEngine Construction and OperationRohit NewarNo ratings yet
- Sensor Lect4Document23 pagesSensor Lect4morton1472No ratings yet
- BOSL Controllers Standard-1Document82 pagesBOSL Controllers Standard-1Anonymous bnhNfqZXaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS Level: Environmental Management 8291/12Document12 pagesCambridge International AS Level: Environmental Management 8291/12zohaibNo ratings yet
- Dealer price list AKDocument1 pageDealer price list AKKunal TanwarNo ratings yet
- Kings Motorbikes 80cc Bicycle Engine Kit Installation ManualDocument11 pagesKings Motorbikes 80cc Bicycle Engine Kit Installation ManualnwobastardsNo ratings yet
- Lessons Learned-Nuclear Gauge002Document66 pagesLessons Learned-Nuclear Gauge002Michael Murillo BaraquioNo ratings yet
- MBQ60T65PES Target Datasheet: 650V Field Stop IGBTDocument1 pageMBQ60T65PES Target Datasheet: 650V Field Stop IGBTamrNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations & ReactionsDocument78 pagesChemical Equations & ReactionsDelsie FalculanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 30 - Enamine and Iminium OrganocatalysisDocument22 pagesLecture 30 - Enamine and Iminium OrganocatalysisDênisPiresdeLimaNo ratings yet
- Mike Busch on Engines What Every Aircraft Owner Needs to Know About the Design Operation Condition Monitoring Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Piston Aircraft Engines 1nbsped 1718608950 9781718608955 CompressDocument509 pagesMike Busch on Engines What Every Aircraft Owner Needs to Know About the Design Operation Condition Monitoring Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Piston Aircraft Engines 1nbsped 1718608950 9781718608955 CompressHugo HernandNo ratings yet
- Climate Change The Facts (Annotated)Document3 pagesClimate Change The Facts (Annotated)api-276929919No ratings yet
- Concept of Microgrid AND Evolution of Smart Grid: Dileep GDocument45 pagesConcept of Microgrid AND Evolution of Smart Grid: Dileep GDileep GNo ratings yet
- Reduce Your Energy Bill - Increase Your Confidence: Air-Cooled Liquid Chillers and Heat Pumps 40-160 KWDocument6 pagesReduce Your Energy Bill - Increase Your Confidence: Air-Cooled Liquid Chillers and Heat Pumps 40-160 KWGonADFNo ratings yet
- The Sun As The AxisDocument20 pagesThe Sun As The AxisNeb Nyansapo Noopooh100% (2)
- ABB String Inverters: PVS-50/60-TLDocument4 pagesABB String Inverters: PVS-50/60-TLBianca OlaruNo ratings yet