Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sample Paper - I: By: Directorate of Education, Delhi
Uploaded by
mahamOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sample Paper - I: By: Directorate of Education, Delhi
Uploaded by
mahamCopyright:
Available Formats
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
SAMPLE PAPER I
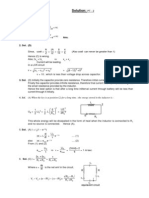
1.
Because magnetic monopole does not exist.
2.
A device that allows the passage of a number of frequencies (W c Wm)
along with carrier frequency W c
3.
Magnifying power is independent of aperture.
4.
(i) IR radiation (ii) Radiowaves
5.
Because emission is followed by antiparticles and .
6.
Plane Wavefront.
9.
A device consisting of a transmitter and a receiver. This is used to increase
communication Range as
1,2,3 and 4 etc are the repeaters arranged between source of information
and the use of information.
10.
Drift speed Vd a
eV
Relaxation time
V potential diff. across the conductor
Vd
(i)
Drift speed is halved.
(ii)
V V
E
Electric field is halved.
l 2 2
11.
[XII Physics]
188
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
OR + NOT NOR
Bcentre
8
Baxial
12.
r
x
0 .Ir 2
2 r 2 x
2 32
BN = BP BQ
BP = BQ
o I p
2 r 4
o IQ
2 3r 4
IQ = 3IP.
Ey = Eoy cos (wt kx)
2
15.
r0I
8 2r
x 3r .
13.
14.
3 108
Hz
2
(i)
Speed of em waves V
(ii)
Bo
3 108
2 108 m / s
1.5
E o 4 103
2 10 2T .
V
2 108
WAB = qo V = qo (VB VA)
VA
kq kQ
a
b
189
[XII Physics]
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
VB
kq kQ
b
b
1 1
WAB qo kq .
b a
B
A
q
16.
In S.I. system the unit of radioactivity is becquerel.
1 becquerel = 1 disintegration/second.
1 curie = 3.7 1010 bq.
T = mean life ln 2
mean life
1.44
2400
1.44
= 1667 years
17.
Definition of modulation N.C.E.R.T. Pg. 517 Vol-II.
18.
Linear fringe width
D
d
Angular fringe width,
D d
in some medium
d
1
decreases
d
(i)
(ii)
is undependent of D, no effect.
[XII Physics]
190
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
19.
(iii)
angular width increases
(iv)
1/M angular width decreases.
Statement of Gausss law
E E d A
= 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6
E d A1 0 0 0 0 0
E 0ai a 2 i
= E0a3
(ii)
20.
E = q/E0 q = E E0 = E0a3 E0
hc
E 2 E1
hc
1
1
13.6 z 2 2 2
n
n2
1
For shortest n1 = 1, n2 =
34
3 108
shortest 6.624 10
2.25 108 m
1 1
13.6 4
1
For longest n1 1,n 2
2
For longest
3 shortest
4
2.25 10 8 m
3
3 108m
t Re
191
[XII Physics]
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
21.
Principle, working
1, 2
OR
(i)
= MB Sin
max = MB sun 90 = MB
(ii)
W = U2 U1
U = MB Cos
MB (MB)
= 2 MB
22.
U = MB (stable equilib)
U = + MB (Unstable equilib)
(i) C = k Co = 5 x 4.8 = 24.0 f
(ii)
q 2 / 2Co
2
q / 2C
(iii) V
C
5
Co
V0 6
1.2volt .
k1 5
23.
NCERT (Part I) Solved Example
24.
Principle of potentiometer when a steady current is passed through a
potentiometer wire AB of length L, and V is the potential difference across
wire AB, then
Potentialgradient k
I=
V
L
E
4
810 3 A
R +RPQ 480 20
VPQ = I RPQ = 8 103 20 = 0.16 Volt.
VPQ 0.16
V / cm
Potential gradient k L
PQ 400
AJ=
4010 3
400
0.16
[XII Physics]
100 cm.
192
by : Directorate of Education, Delhi
25.
Define photoelectric effect
(i) Since Intensity is same, number of electrons emitted per second
remain same
(ii) K. Emax a ha
violet > blue
(E.Emax)violet > (K. Emax)blue
27.
Refer NCERT
OR
28.
Refer NCERT
P = Vrms Irms Cos
Cos =
P
IrmsVrms
Ploss = I2rms R. R resistance of transmission line.
Ploss a I2rms
Low power factor (cos) high
high power loss.
29.
Refer NCERT
193
[XII Physics]
You might also like
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocument11 pagesNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIYuhua SunNo ratings yet
- DAY 3 (Solutions)Document11 pagesDAY 3 (Solutions)bibekbhatta258No ratings yet
- 10 12 Physics CBSE Paper SolutionDocument20 pages10 12 Physics CBSE Paper SolutionnafehakhanNo ratings yet
- Cmda Mock Exam Phy 124Document4 pagesCmda Mock Exam Phy 124tajudeenabdullahaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Special Physics 12Document6 pagesCBSE Special Physics 12Arnab ChakrabartiNo ratings yet
- Mock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-III-PHY-PaperDocument7 pagesMock Test Paper-1920-CBSE-C-XII-Set-III-PHY-PaperHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocument10 pagesNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIYuhua SunNo ratings yet
- X X X XXX X X X X X X: SolutionsDocument2 pagesX X X XXX X X X X X X: SolutionsbediangNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Trial PHYSICS 2013 Sem 3Document6 pagesMark Scheme Trial PHYSICS 2013 Sem 3Zuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- ch32 PDFDocument14 pagesch32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Practice Test 1 Answer ExplanationsDocument15 pagesAP Physics 1 Practice Test 1 Answer ExplanationsMohamed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Britney Patterson - Six Week TestDocument10 pagesBritney Patterson - Six Week TestBritney PattersonNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionDocument15 pagesCBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionMichelle DennisNo ratings yet
- Pre Board Examination (2021-22) Class Xii: General InstructionsDocument3 pagesPre Board Examination (2021-22) Class Xii: General InstructionsRaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave ExerciseDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Wave ExerciseAnkit VatsaNo ratings yet
- q1 A Block of Mass M 500 KG Is Released Form Rest FromDocument2 pagesq1 A Block of Mass M 500 KG Is Released Form Rest Frommon chériNo ratings yet
- 12 Physics Model Test Papee 2023-24Document8 pages12 Physics Model Test Papee 2023-24satnams4812No ratings yet
- XII - Physics - Preboard 2 - Set B - MSDocument3 pagesXII - Physics - Preboard 2 - Set B - MSsidharthNo ratings yet
- Solution:: DT DQ e RC C V BDocument5 pagesSolution:: DT DQ e RC C V BAritra LahiriNo ratings yet
- Postask MigueldazaDocument19 pagesPostask MigueldazaMiGue DAzaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFDocument9 pagesCbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFIshika SinghNo ratings yet
- ModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Document1 pageModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Maulik KarasaliyaNo ratings yet
- 2013 CBSE XIIScience 4 1 SET1 SectioncDocument9 pages2013 CBSE XIIScience 4 1 SET1 SectioncShashank ShekharNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics II Term Test 2017 - 18Document3 pages12th Physics II Term Test 2017 - 18hodeegits9526No ratings yet
- Jurong Junior College: Physics 9646/2Document22 pagesJurong Junior College: Physics 9646/2Chen ZhihaoNo ratings yet
- AP 2012 Physics B Free Response QuestionsDocument12 pagesAP 2012 Physics B Free Response QuestionsAlan G.No ratings yet
- Final ExamPhysics1Document3 pagesFinal ExamPhysics1thảo nguyễn thanhNo ratings yet
- 2013 J2 H2 Physics CT2 P1Document17 pages2013 J2 H2 Physics CT2 P1Michael LeungNo ratings yet
- Annex 5 - Delivery Format - Post TaskDocument10 pagesAnnex 5 - Delivery Format - Post TaskDaniel BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Do Not Turn Over Until Told To Begin: University of London Msci/Bsc Examination 2011Document9 pagesDo Not Turn Over Until Told To Begin: University of London Msci/Bsc Examination 2011bbteenagerNo ratings yet
- Class Xii PT SUBJECTIVE 2021Document2 pagesClass Xii PT SUBJECTIVE 2021gojo satoruNo ratings yet
- ENEL2PAH1 - Physical Electronics 1Document5 pagesENEL2PAH1 - Physical Electronics 1qanaqNo ratings yet
- KIET PhysicsDocument82 pagesKIET Physicsap cpianNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 - Physics PB2Document9 pagesGrade 12 - Physics PB2Nazneen AliNo ratings yet
- Iit Jee Screening 2001Document9 pagesIit Jee Screening 2001Ashish535No ratings yet
- Gr12 WorksheetDocument3 pagesGr12 WorksheetDGGØDNo ratings yet
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Document4 pagesFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanNo ratings yet
- Em Waves JeeDocument14 pagesEm Waves JeeTobiramaNo ratings yet
- 2011 SBP Fizik SkemaDocument14 pages2011 SBP Fizik SkemaAimi LiyanaNo ratings yet
- PHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section IIIDocument12 pagesPHYS-2020: General Physics II Course Lecture Notes Section IIIAndropov AjebuaNo ratings yet
- PYC102: Foundation Physics: NotesDocument12 pagesPYC102: Foundation Physics: NotesPatrick SibandaNo ratings yet
- Exam3 T111Document15 pagesExam3 T111ammuNo ratings yet
- MWA Question Set 1Document2 pagesMWA Question Set 1Mahesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Ce316 3D Group 3 Laboratory Activity 2Document10 pagesCe316 3D Group 3 Laboratory Activity 2CHERRY SABASAJENo ratings yet
- Phy Set-2 QPDocument5 pagesPhy Set-2 QPSiddhartha HadimaniNo ratings yet
- Physics Questions Chapter 23Document5 pagesPhysics Questions Chapter 23hamadaxx2000100% (1)
- Quantum Mechanics TutorialDocument6 pagesQuantum Mechanics TutorialAnonymous ziJjOnGnNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering 2016 2016 2016 2016 2016: Networks TheoryDocument10 pagesElectrical Engineering 2016 2016 2016 2016 2016: Networks TheoryarunNo ratings yet
- 2010 h2 Prelims Revision ADocument55 pages2010 h2 Prelims Revision ABenjamin TeoNo ratings yet
- (Three Hours) : Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsDocument5 pages(Three Hours) : Sample Paper - 2011 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsValay DaveNo ratings yet
- 최신대학물리학2 19Document16 pages최신대학물리학2 19minsukkim2323No ratings yet
- Paper - 1Document23 pagesPaper - 1Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Step 5-Activities Guide and Evaluation Rubric: Andres Felipe Noreña Riaño Cod 1015423347Document9 pagesStep 5-Activities Guide and Evaluation Rubric: Andres Felipe Noreña Riaño Cod 1015423347chouji26No ratings yet
- AITS 2324 PT III JEEA Paper 2 SolDocument13 pagesAITS 2324 PT III JEEA Paper 2 Solnityapaliwal553No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1PallavNo ratings yet
- Ece1231 Mid Term SolnDocument10 pagesEce1231 Mid Term SolnOppa Sollehudin SapariNo ratings yet
- NEET 2023 Sample PaperDocument47 pagesNEET 2023 Sample PapermuthuNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IFrom EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields INo ratings yet
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsFrom EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- The Forbidden Equation I QC, by Miles MathisDocument5 pagesThe Forbidden Equation I QC, by Miles MathisBaba YagaNo ratings yet
- 6 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 1 PDFDocument2 pages6 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 1 PDFJoshi ThomasNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY - LeapfrogDocument3 pagesCASE STUDY - Leapfrogpakol4funNo ratings yet
- Math10 Quarter1 Module 5 Melc 8,9Document15 pagesMath10 Quarter1 Module 5 Melc 8,9Jhiemalyn RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Angoltanmenet5 OsztDocument23 pagesAngoltanmenet5 OsztSzimonetta BándoliNo ratings yet
- Installation Instructions Montageanleitung Notice de Montage Istruzioni Di Montaggio Instrucciones de Montaje Montageaanwijzing Mettler Toledo Quick Pit PFADocument16 pagesInstallation Instructions Montageanleitung Notice de Montage Istruzioni Di Montaggio Instrucciones de Montaje Montageaanwijzing Mettler Toledo Quick Pit PFAjean pablo huancas reañoNo ratings yet
- Main Duties and ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesMain Duties and ResponsibilitiessafiullahNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To CCARDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To CCARRanit Banerjee100% (1)
- GL Wand DatasheetDocument8 pagesGL Wand DatasheetAdams JibrinNo ratings yet
- FUYP+RZP CieloDocument19 pagesFUYP+RZP CieloCarlos ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Belinda Dwi Sukma Putri - ResumeDocument2 pagesBelinda Dwi Sukma Putri - ResumeDiah AyuNo ratings yet
- Choice of The Weight FunctionDocument1 pageChoice of The Weight FunctionCosmo FanaNo ratings yet
- Looser PDFDocument3 pagesLooser PDFrina yantiNo ratings yet
- ZBBR 123Document11 pagesZBBR 123Tony Peterz Kurewa0% (1)
- Factors Affecting Online Buying BehaviorDocument17 pagesFactors Affecting Online Buying BehaviorJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Section-14 Durability r1Document8 pagesSection-14 Durability r1EENo ratings yet
- Simulation of Formaldehyde Production ProcessDocument10 pagesSimulation of Formaldehyde Production ProcessDoctorObermanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Assistant in Prasar Bharti 2013 Final Result PDFDocument27 pagesEngineering Assistant in Prasar Bharti 2013 Final Result PDFKiran Jot SinghNo ratings yet
- ARC 393: Building For DisasterDocument13 pagesARC 393: Building For DisasterAbdullah Al Mamun PrantoNo ratings yet
- Contents - PID-based Practical Digital ControlDocument7 pagesContents - PID-based Practical Digital ControlGerman Silvino Alvarez GomezNo ratings yet
- 2012 RWCID Non-Resident Pool MembershipDocument1 page2012 RWCID Non-Resident Pool MembershipBrett Lord-CastilloNo ratings yet
- G H 1 2 3 - CompressedDocument94 pagesG H 1 2 3 - CompressednyilatlNo ratings yet
- Recover at Work Plan 5 ProposedDocument2 pagesRecover at Work Plan 5 ProposedSiosiana DenhamNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach To Building A Sporting NationDocument20 pagesA Practical Approach To Building A Sporting NationNUPUR GUPTANo ratings yet
- NSP/004/109 (OHI 9) Guidance On Anti-Climbing Devices, Safety Signs and Labels Required On Overhead Line SupportsDocument25 pagesNSP/004/109 (OHI 9) Guidance On Anti-Climbing Devices, Safety Signs and Labels Required On Overhead Line SupportsMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Music Players - Group 2 MusicDocument17 pagesEvolution of Music Players - Group 2 MusicLinda AgmataNo ratings yet
- PresentasiDocument6 pagesPresentasiAfanda Dwi R R100% (1)
- Valid Arguments For Tariffs or Export SubsidiDocument1 pageValid Arguments For Tariffs or Export SubsidiTrang Chử ThuNo ratings yet
- MT6755 Android ScatterDocument10 pagesMT6755 Android ScatterjenniferNo ratings yet
- Peyote Hearts ChristaBeadsDocument11 pagesPeyote Hearts ChristaBeadspaolallaqueNo ratings yet