Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2017 SAAO Forum 08-20-13 Lab 1 - Palpation and Landmarks: Be Able To Find ALL of The Following Landmarks
Uploaded by
UmaSid0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pagesOPP
Original Title
8-20-13 Saao Ms1 Forum
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentOPP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views3 pages2017 SAAO Forum 08-20-13 Lab 1 - Palpation and Landmarks: Be Able To Find ALL of The Following Landmarks
Uploaded by
UmaSidOPP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
2017 SAAO Forum 08-20-13
Lab 1 Palpation and Landmarks
LANDMARKS
Be able to find ALL of the following landmarks
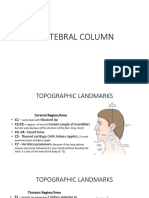
Skull and cervical spine
occipital bone & occipital protuberance (inion)
earlobes, mastoid process & superior nuchal line
transverse process C1 & spinous process C2
angle of mandible & vertex (top of head)
vertebral prominence (C7), lateral masses
Shoulder girdle and arm
spine of scapula (T3), acromion process, coracoid process
scapula acromioclavicular (AC) joint
borders of scapula, inferior angle scapula (T7)
head of humerus
Back and Pelvis
spinous processes & transverse processes
rib angle 12th rib (QL attachment)
sacral base, iliac crest
posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS), Anterior Superior iliac spine (ASIS)
Iliac crest (L4)
Ischial tuberosities
Pubic Symphysis
Lower Extremity
femur
o greater trochanter
knee
o popliteal crease
o patella
tibia
o anterior tibial tubercle
o medial malleolus
fibula
o fibular head
o lateral malleolus
ankle
foot
o calcaneous
o navicular
o cuboid
o metatarsals
o tarsal
Lab 2 Static Symmetry
I.
Document curves of the spine on the Osteopathic Musculoskeletal
Examination Form
a. This is to get you used to/learn how to formulate your diagnosis
b. Note: We have never had to fill out the exam form during a practical
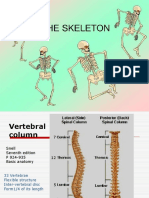
Normal (AP) curves of the spine
o Cervicals - lordosis
o Thoracics - kyphosis
o Lumbar lordosis
Postures
Kypholordosis
Swayback
Increased lordosis
Posterior pelvis
Increased kyphosis
rotation
Anterior pelvis
Head forward
rotation
Head forward
Military
Anterior pelvis
rotation
Head back
Flatback
Posterior pelvis
rotation
Head forward
Scoliosis (lateral curves) is named for the convexity of the curve
Left scoliosis/levoscoliosis
RLSR
o
o
o
Right scoliosis/dextroscoliosis
RRSL
Observe from Anterior, Posterior, Lateral
Stand behind when they bend over to observe rib angles
Have them swing their trunk side to side
Functional goes away when bent to a side
Structural stays when bent to both sides
II.
Plumb Line for Sagittal Posture
Start at the ear and adjust to hit as many landmarks as possible
Line should hit these landmarks:
o External auditory canal
o Head of the humerus
o L3
o Anterior 1/3 of sacrum
o Greater trochanter of femur
o Lateral condyle of the knee
o Lateral malleolus
Use these landmarks to determine type
of posture
III. Symmetry (yet again)
Compare sides of the body
o Posterior Evaluation
Earlobes
Shoulders
Angle of the scapulas
Iliac crests
Normal
Anterior
Posterior
Rotary
Greater trochanters
o Anterior Evaluation
Face
Trapezius
Body tilting or twisting
Sternum pectus excavatum (bows inward), pectus carinatum
(bows outward)
o Check feet arches and leg length
You might also like
- Vertebral Column: Osteology and ArthrologyDocument75 pagesVertebral Column: Osteology and ArthrologyGeorge WangNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology of Back and SpineDocument8 pagesKinesiology of Back and SpineVanessa Yvonne GurtizaNo ratings yet
- Back and Spinal CordDocument16 pagesBack and Spinal CordCarlos CaCoNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Breathing and Posture - Functions and InnervationDocument6 pagesMuscles of Breathing and Posture - Functions and Innervatione jeighNo ratings yet
- Origin Insertion Action InnervationDocument4 pagesOrigin Insertion Action Innervationstereomix987No ratings yet
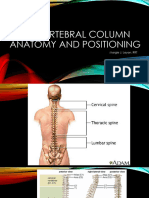
- The Vertebral Column Anatomy and PositioningDocument93 pagesThe Vertebral Column Anatomy and Positioningwintleah4No ratings yet
- Osteology of The Lower ExtremityDocument29 pagesOsteology of The Lower ExtremityIELTSNo ratings yet
- Bones & Joints of the Spine ExplainedDocument83 pagesBones & Joints of the Spine ExplainedJoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Master Muscle ListDocument7 pagesMaster Muscle ListSyed AbudaheerNo ratings yet
- Spine & ThoraxDocument90 pagesSpine & ThoraxSean JosephNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of SpineDocument77 pagesAnatomy of SpineJoy SahaNo ratings yet
- Shoulder: Dr. Paolo M. RamirezDocument40 pagesShoulder: Dr. Paolo M. RamirezPao RamirezNo ratings yet
- Vertebral ColumnDocument84 pagesVertebral ColumnGenesis GeronagaNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument388 pagesBooksMayank GoyalNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnDocument60 pagesStructure and Function of The Vertebral ColumnJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb by SheheryarDocument15 pagesUpper Limb by SheheryarsfrtrNo ratings yet
- Vertebral ColumnDocument9 pagesVertebral ColumnKaren LaureanoNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3572289752270573946Document92 pagesInbound 3572289752270573946Viola BlenteNo ratings yet
- BY: DR Rai M. Ammar Madni: (M.B .B .S, RMP)Document52 pagesBY: DR Rai M. Ammar Madni: (M.B .B .S, RMP)DCRUZNo ratings yet
- Biologi SelDocument105 pagesBiologi SelHekter Gunting KursiNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Vertebral Column: Your Subtitle Goes HereDocument54 pagesStructure and Function of The Vertebral Column: Your Subtitle Goes HereJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Muscle of Upper LimbsDocument5 pagesMuscle of Upper LimbsFong Yu-heng100% (1)
- Anatomy Midterm Study GuideDocument53 pagesAnatomy Midterm Study Guidelovelyc95No ratings yet
- Muscle Flash CardsDocument127 pagesMuscle Flash Cardsjoelh9100% (3)
- Lower Limb BONESDocument79 pagesLower Limb BONESDr.Kumar Satish Ravi100% (1)
- Human Anatomy 23Document80 pagesHuman Anatomy 23Eehan KapoorNo ratings yet
- Positioning Presentation-VertebraeDocument156 pagesPositioning Presentation-Vertebraeron reteracionNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document138 pagesWeek 4Anne nicole P. CasemNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note - Medical Course, 353241 Musculoskeletal SystemDocument107 pagesLecture Note - Medical Course, 353241 Musculoskeletal SystemKitchanan KosalathipNo ratings yet
- Anatomy #2 Vertebral Column-1Document49 pagesAnatomy #2 Vertebral Column-1ffNo ratings yet
- Vertebrae-and-Appendicular-ANAPHY-AND-PHYSIODocument10 pagesVertebrae-and-Appendicular-ANAPHY-AND-PHYSIOshannenmaehfajanilanNo ratings yet
- Anterior & Posterior Shoulder MusclesDocument3 pagesAnterior & Posterior Shoulder Musclesjjjj31No ratings yet
- Biomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnDocument44 pagesBiomechanics of The Vertebral ColumnVijay PradeepNo ratings yet
- Thoracic (Dorsal) SpineDocument77 pagesThoracic (Dorsal) Spineeashoor100% (2)
- 13 Anatomy Lower Limb BonesDocument50 pages13 Anatomy Lower Limb BonesAzizat MajolagbeNo ratings yet
- The Thorax: Axial & Appendicular Skeleton Mammary Glands Surface AnatomyDocument28 pagesThe Thorax: Axial & Appendicular Skeleton Mammary Glands Surface AnatomyDr-Arsalan ZahidNo ratings yet
- Chir12006 Week 7 Study Guide Answers 1 3Document8 pagesChir12006 Week 7 Study Guide Answers 1 3api-469904011No ratings yet
- The Anatomy of the ThoraxDocument237 pagesThe Anatomy of the ThoraxAbel Belete100% (1)
- 1 Lower Limb BONESDocument79 pages1 Lower Limb BONESZaid AbdulqadirNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Limb AnatomyDocument52 pagesUpper and Lower Limb AnatomycoolsuernameNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy GuideDocument9 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy Guidesimone dumbrell100% (1)
- Anatomylec 2Document43 pagesAnatomylec 2n gautamNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The BackDocument38 pagesMuscles of The BackPrashanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Regional Le: Hip and Thigh: Fuerte-Felicano-Pasha Tabajonda-VillahermosaDocument176 pagesRegional Le: Hip and Thigh: Fuerte-Felicano-Pasha Tabajonda-VillahermosaOlenFuerte100% (1)
- Hyoid BoneDocument14 pagesHyoid BoneAl-Shuaib Astami SonNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System Appendicular Bones and Joints GuideDocument46 pagesSkeletal System Appendicular Bones and Joints GuideJoshua CodillaNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Blade Bone: The ScapulaDocument7 pagesShoulder Blade Bone: The ScapulasujsamNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY MANUAL in GENERAL ANATOMY 1 PART 1Document29 pagesLABORATORY MANUAL in GENERAL ANATOMY 1 PART 1Ian Mar ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Back LectureffDocument28 pagesMuscles of Back LectureffNko NikoNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology of Back and SpineDocument6 pagesKinesiology of Back and Spinejoanna gurtizaNo ratings yet
- The Trunk and Spinal ColumnDocument41 pagesThe Trunk and Spinal Columnrex100% (1)
- Human Skeleton: Harichanra Gawas 3 Yr B.SC. M.I.TDocument76 pagesHuman Skeleton: Harichanra Gawas 3 Yr B.SC. M.I.TOmkar GaonkarNo ratings yet
- Axial SkeletonDocument69 pagesAxial SkeletonKharisulNo ratings yet
- Anatomy ReviewDocument283 pagesAnatomy ReviewmmbrewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 PelvicDocument21 pagesChapter 17 PelvicpoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument72 pagesAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormFrom EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- 8 Principles of Antimicrob Chemother 14 For StudentsDocument50 pages8 Principles of Antimicrob Chemother 14 For StudentsUmaSidNo ratings yet
- Pathoma Errata UpdatesDocument1 pagePathoma Errata UpdatesGrupi KatërtNo ratings yet
- 2017 SAAO Forum 2Document6 pages2017 SAAO Forum 2UmaSidNo ratings yet
- ACTH Hormone Sheet1Document3 pagesACTH Hormone Sheet1UmaSidNo ratings yet
- AkpsiDocument7 pagesAkpsiUmaSidNo ratings yet
- Statistics Hypothesis Tests: Normality, t-Tests, Proportions, ANOVA, CorrelationDocument1 pageStatistics Hypothesis Tests: Normality, t-Tests, Proportions, ANOVA, CorrelationUmaSidNo ratings yet
- ADH Hormone SheetDocument3 pagesADH Hormone SheetUmaSidNo ratings yet
- General Topic: General Purpose: To Provide New Information. Specific Purpose: Central IdeaDocument4 pagesGeneral Topic: General Purpose: To Provide New Information. Specific Purpose: Central IdeaUmaSidNo ratings yet
- Urolithiasis PDFDocument4 pagesUrolithiasis PDFaaaNo ratings yet
- Physical Paper +1ANNUALDocument5 pagesPhysical Paper +1ANNUALprabhnoorprimeNo ratings yet
- WHATs New in CPCRDocument4 pagesWHATs New in CPCRJessicaHernandezNo ratings yet
- Feasibility of Muntingia Calabura as WineDocument19 pagesFeasibility of Muntingia Calabura as WineKhen Raselle BaculioNo ratings yet
- How Do We Use Philosophy To Figure Out What Is True?Document5 pagesHow Do We Use Philosophy To Figure Out What Is True?Pik NikNo ratings yet
- Anti-Rabies Act of 2007 (Ra 9482) 2Document29 pagesAnti-Rabies Act of 2007 (Ra 9482) 2Ronz Rogan100% (1)
- Standards of Care in Child Care InstitutionsDocument36 pagesStandards of Care in Child Care InstitutionsVaishnavi JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Bacteria: Thiomargarita Namibiensis - 5 M in DiameterDocument6 pagesChapter 3: Bacteria: Thiomargarita Namibiensis - 5 M in DiameterShairaMNo ratings yet
- GEHC Brochure Senographe CareDocument7 pagesGEHC Brochure Senographe CareVremedSoluCionesNo ratings yet
- Phet Natural SelectionDocument6 pagesPhet Natural Selectionapi-315485944No ratings yet
- MCQ in MedicineDocument18 pagesMCQ in MedicineEslamAlmassri75% (4)
- 2011 Annual Accomplishment Report - MalabonDocument63 pages2011 Annual Accomplishment Report - MalabonBernadeth AganaNo ratings yet
- Cannabis Use and Disorder - Epidemiology, Comorbidity, Health Consequences, and Medico-Legal Status - UpToDateDocument34 pagesCannabis Use and Disorder - Epidemiology, Comorbidity, Health Consequences, and Medico-Legal Status - UpToDateAnonymous kvI7zBNNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Research G8Document24 pagesGroup 2 Research G8aurasaliseNo ratings yet
- 3rd Periodical Grade 10Document3 pages3rd Periodical Grade 10diomedescolar.13No ratings yet
- Clinical Procedures For Medical Assistants 9th Edition Bonewit Test BankDocument12 pagesClinical Procedures For Medical Assistants 9th Edition Bonewit Test Bankcarriejordanwboriaqmfn100% (16)
- AllergiesDocument11 pagesAllergiesAficionadoNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis (A Serious, Bacterial Skin Infection), Its Causes and Its Symptoms.Document2 pagesCellulitis (A Serious, Bacterial Skin Infection), Its Causes and Its Symptoms.Encompass HealthCare and Wound MedicineNo ratings yet
- Racial Bias in Pulse Oximetry Measurement: CorrespondenceDocument2 pagesRacial Bias in Pulse Oximetry Measurement: CorrespondenceYony Gutierrez100% (1)
- Neuroscience and The LawDocument46 pagesNeuroscience and The LawFrancisco Estrada100% (1)
- HRCA GK Quiz Syllabus Class 7-8Document19 pagesHRCA GK Quiz Syllabus Class 7-8Sualiha MalikNo ratings yet
- NEET Biology Through MCQDocument587 pagesNEET Biology Through MCQAnanth Dharanidharan100% (1)
- Cinnarizine A Contemporary ReviewDocument9 pagesCinnarizine A Contemporary ReviewprimaNo ratings yet
- Cement CSRDocument35 pagesCement CSRKasak Gupta100% (1)
- Project Report For 9000Document10 pagesProject Report For 9000GOLLAVILLI GANESH100% (1)
- Medicinal Properties of GarlicDocument7 pagesMedicinal Properties of GarlicFawzia Haznah Nurul Imani0% (1)
- First International congress on clinical Hypnosis & Related Sciences programDocument91 pagesFirst International congress on clinical Hypnosis & Related Sciences programGolnaz BaghdadiNo ratings yet
- Yes, aside from the educational SMS intervention, the groups were treated equally as they both received routine trainingDocument54 pagesYes, aside from the educational SMS intervention, the groups were treated equally as they both received routine trainingYogiNo ratings yet
- Pain Scales and Assessment UnhasDocument93 pagesPain Scales and Assessment Unhashaphahap0% (1)
- Dementia Presentation Feb 19Document28 pagesDementia Presentation Feb 19Rhu Pugo, La UnionNo ratings yet