Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PB N × T NM: Discussion
Uploaded by
riadhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PB N × T NM: Discussion
Uploaded by
riadhCopyright:
Available Formats
8
BrakePower,Pb
Pb =
2
NT
= 2 3.142 29.46 0.00392
Nm
=
7.249
W
Turbine Efficiency, Et
Et =
100%=
100%=
8.218 %
Discussion
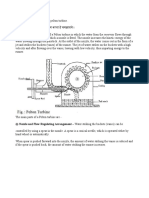
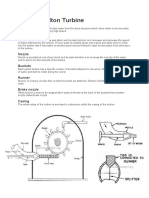
The working principle of Pelton wheel turbine is water flows along the tangent to the path of the
runner. Nozzles direct forceful streams of water against a series of spoon-shaped bucketsmounted
around the edge of a wheel. As water flows into the bucket, the direction of the water velocity changes
to follow the contour of the bucket. When the water-jet contacts the bucket, thewater exerts pressure
on the bucket and the water is decelerated as it does a "u-turn" and flowsout the other side of the
bucket at low velocity. In the process, the water's momentum istransferred to the turbine. This
"impulse" does work on the turbine. For maximum power and efficiency, the turbine system is
designed such that the water-jet velocity is twice the velocity of the bucket. A very small percentage of
the water's original kinetic energy will still remain in the water; however, this allows the bucket to
be emptied at the same rate it is filled, thus allowing the water flow to continue un interrupted.From
the results obtained, we can see how Pelton Wheel reacts to different kind of input.Different flow rates
give different value of work input. The slower the flow rates, the larger thework being put into the
wheel. The efficiency of the slower flow rates is also better than faster one. The speed of the wheel
also dropped when much weight being dropped until it stoppedsuddenly when the weight is too much
for it to go against.
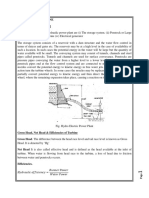
Water turbines
Pelton turbine, a type of impulse water turbine.
Francis turbine, a type of widely used water turbine.
Kaplan turbine, a variation of the Francis Turbine.
Turgo turbine, a modified form of the Pelton wheel.
Cross-flow turbine, also known as Banki-Michell turbine, or Ossberger turbine.
2
Procedures
1.
First of all, perform the general start-up procedures.2.
Fully open the throttle valve and allow the water to circulate until all air bubbles
havedispersed.3.
Open and adjust the spear valve for a particular nozzle opening.4.
Tighten up the tensioning screw on the pulley wheel until the turbine is almost stalled (rotor
just turning).5.
Decide on suitable increments in force to give adequate sample points and note the valueof the
pulley brake.6.
Slacken off the tensioning screw so no force is being applied to the turbine.7.
Tighten the screw to give the first increment in force for the brake. When readings aresteady
enough, record all the readings again.8.
Repeats step 7 above for a gradually increasing set of fb values. The final sample pointwill
correspond to the turbine stalling.9.
The data may now be used for analysis and to plot the pelton turbine characteristicscurve.10.
Now decrease the volume flow rate to a new setting by changing the throttle valve position
and at the same time also change the spear valve position to maintain the pressure at 1.0
kgf/cm
You might also like
- Pelton TDocument12 pagesPelton TAnime WonderNo ratings yet
- Exp # 07Document11 pagesExp # 07Eng TariqNo ratings yet
- Governing of Pelton WheelDocument3 pagesGoverning of Pelton WheelErica100% (1)
- Full Report Pelton TurbineDocument10 pagesFull Report Pelton TurbineMuhammad AimiNo ratings yet
- PMFM Viva QuestionsDocument17 pagesPMFM Viva QuestionsVineet KumarNo ratings yet
- En208 Innovative ProjectDocument11 pagesEn208 Innovative Project2K2O-A17-11 Vishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machine Lab: by Suman Kumar Dash REG - NO: LE-20Document15 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machine Lab: by Suman Kumar Dash REG - NO: LE-20Suman kumar DashNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION Turbomachinery1Document4 pagesINTRODUCTION Turbomachinery1DICKSON SIMUTAMINo ratings yet
- PP Lab 10 FinalDocument10 pagesPP Lab 10 FinalAnime WonderNo ratings yet
- Pelton Wheel Turbine (Brief Notes)Document27 pagesPelton Wheel Turbine (Brief Notes)Harshanagasai ManyamNo ratings yet
- CE 208 Innovative Project PresentationDocument16 pagesCE 208 Innovative Project Presentationkartiksharma7117No ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine Group 1-2Document18 pagesPelton Turbine Group 1-2Suryansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Pelton WheelDocument5 pagesPelton WheelMuhammedShafiNo ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine - Basic Working PrincipleDocument5 pagesPelton Turbine - Basic Working Principlerpal0960No ratings yet
- Pelton TurbineDocument22 pagesPelton TurbineadxtyasharmaNo ratings yet
- Lab No 4Document13 pagesLab No 4Rahim BalouchNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines: General Layout of Hydro-Electric Power PlantDocument6 pagesHydraulic Turbines: General Layout of Hydro-Electric Power PlantnarendraidealNo ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine Test Rig: BackgroundDocument4 pagesPelton Turbine Test Rig: Backgroundanil chejara100% (1)
- Pelton TurbineDocument6 pagesPelton Turbineendoparasite50% (2)
- Project Report: of "Power Generations" TopicDocument7 pagesProject Report: of "Power Generations" TopicDurga prasadNo ratings yet
- Group Member Name Id Card NoDocument12 pagesGroup Member Name Id Card NolataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Pelton TurbineDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Pelton TurbineSachin MohalNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Water TurbineDocument20 pagesProject Report On Water TurbineNAVEEN ROY67% (3)
- Turbines and PumpsDocument24 pagesTurbines and PumpsANUDEEP SNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbines: Theory of OperationDocument34 pagesHydraulic Turbines: Theory of OperationAnilkumar GopiNo ratings yet
- Turbines StudentDocument68 pagesTurbines StudentMariaEzzaSyUyNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Pelton TurbineDocument12 pagesUnit IV Pelton TurbinePavanNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5eyobNo ratings yet
- Pelton TurbineDocument18 pagesPelton Turbinefedila jemalNo ratings yet
- The Pelton Wheel ExperimentDocument18 pagesThe Pelton Wheel ExperimentRestu PutraNo ratings yet
- Lab No - Doc2Document3 pagesLab No - Doc2Faiza IqbalNo ratings yet
- Abhay Report HydraulicDocument29 pagesAbhay Report HydraulicSandesh KedarNo ratings yet
- Pelton Turbin: Abbas Bilal Sami Hussein Name: Subject: Third Power Plant Class /branch: D.Laith Ayad SupervisorDocument9 pagesPelton Turbin: Abbas Bilal Sami Hussein Name: Subject: Third Power Plant Class /branch: D.Laith Ayad Supervisorabbas bilalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document21 pagesChapter 4ゞ『HaiDerツ98〆No ratings yet
- Experiment-1: Aim-To Conduct The Performance Test and To Find Out The Efficiency of PeltonDocument15 pagesExperiment-1: Aim-To Conduct The Performance Test and To Find Out The Efficiency of PeltonLEAGUE OF WARLORDSNo ratings yet
- Lab No - Doc3Document4 pagesLab No - Doc3Faiza IqbalNo ratings yet
- Ans. Fig.: Shows The Layout of A Pelton Turbine in Which The Water From The Reservoir Flows ThroughDocument7 pagesAns. Fig.: Shows The Layout of A Pelton Turbine in Which The Water From The Reservoir Flows ThroughSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorNo ratings yet
- REPORT OF Pelton Turbine WheelDocument79 pagesREPORT OF Pelton Turbine WheelTalluri NaniNo ratings yet
- TurbineDocument19 pagesTurbineTawsiful AlamNo ratings yet
- Pelton WheelDocument14 pagesPelton WheelAqsajabeenNo ratings yet
- Hydro Presentation1Document40 pagesHydro Presentation1Young BrotherNo ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine ReportDocument10 pagesPelton Turbine ReportShea Cheng Kuang100% (2)
- Chapter II The Centrifugal Fire PumpDocument21 pagesChapter II The Centrifugal Fire PumpmjsebasNo ratings yet
- Pelton Turbine Question AnswerDocument8 pagesPelton Turbine Question AnswerKamrul HasanNo ratings yet
- Types of Turbines: Turbine ClassificationsDocument6 pagesTypes of Turbines: Turbine ClassificationsalbertNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Fluid Machine ME-315-FDocument0 pagesLaboratory Manual: Fluid Machine ME-315-FBalvinder100% (2)
- Pelton WheelDocument24 pagesPelton WheelSuranga GayanNo ratings yet
- Governing of Pelton TurbineDocument5 pagesGoverning of Pelton Turbinensbaruaole100% (4)
- Pelton WheelDocument12 pagesPelton WheelFASNANo ratings yet
- Pelton Wheel FunctionDocument6 pagesPelton Wheel Functionरवि जमवालNo ratings yet
- Pelton TurbineDocument3 pagesPelton TurbineJerin CyriacNo ratings yet
- Module 5.1 Small HydroDocument30 pagesModule 5.1 Small HydroADR20ME024 BINNU THOMASNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Fluid Machine ME-315-FDocument29 pagesLaboratory Manual: Fluid Machine ME-315-FAshish DaundkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document55 pagesUnit 4Ashish KhariNo ratings yet
- 3.7 Reciprocating Inertia (Joggle) PumpsDocument27 pages3.7 Reciprocating Inertia (Joggle) PumpsNourTarekHassenNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4: TitleDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 4: TitleKamran AliNo ratings yet
- Power Off Reset Reason BackupDocument5 pagesPower Off Reset Reason Backupmohamed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Physics XIDocument13 pagesPhysics XIArokiaraj RajNo ratings yet
- 截屏 2021-08-05 17.02.20Document98 pages截屏 2021-08-05 17.02.204WEM GTNo ratings yet
- Buenos Aires, Argentina Sabe/Aep Rnpzrwy31: JeppesenDocument1 pageBuenos Aires, Argentina Sabe/Aep Rnpzrwy31: Jeppesenfrancisco buschiazzoNo ratings yet
- Camcor Coriolis Meter User ManualDocument140 pagesCamcor Coriolis Meter User ManualGerardo OrtigozaNo ratings yet
- Free Computer Fundamentals and Programming in C by Reema TharejaDocument5 pagesFree Computer Fundamentals and Programming in C by Reema TharejaGopi S0% (1)
- Caie As Computer Science 9618 Theory v3Document20 pagesCaie As Computer Science 9618 Theory v3James HoangNo ratings yet
- MCAT Uhs Past Paper (2008-2016)Document180 pagesMCAT Uhs Past Paper (2008-2016)Abdullah SheikhNo ratings yet
- Active Mathematics PDFDocument22 pagesActive Mathematics PDFgoingforward77No ratings yet
- Cost Center Budget Availability Control - S - 4 HANA 1909Document24 pagesCost Center Budget Availability Control - S - 4 HANA 1909sekhar dattaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Pre LabDocument3 pagesLab 3 Pre LabMina VoNo ratings yet
- La 3391p Rev0.3novo DesbloqueadoDocument48 pagesLa 3391p Rev0.3novo DesbloqueadoRogeriotabiraNo ratings yet
- Spice-Simulation Using LTspice Part 1Document76 pagesSpice-Simulation Using LTspice Part 1suzsoltNo ratings yet
- R172 NTG4.5 EngineeringMenuDocument5 pagesR172 NTG4.5 EngineeringMenualeksandar_tudzarovNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper 10G Ethernet 10-08Document16 pagesWhitepaper 10G Ethernet 10-08Bogdan IhnatiucNo ratings yet
- 7 - Introduction To Intelligent ControlDocument21 pages7 - Introduction To Intelligent ControlIsmael Espinoza100% (1)
- 5 Key Factors To The Correct Cable Selection and ApplicationDocument7 pages5 Key Factors To The Correct Cable Selection and ApplicationSugeng SumarnoNo ratings yet
- Netxknx Opc 3 - 5 - 4 EngDocument93 pagesNetxknx Opc 3 - 5 - 4 Engtai_sao_khong_1307No ratings yet
- Vector AlgebraDocument7 pagesVector AlgebraDeeeNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Elements II PDFDocument6 pagesDesign of Machine Elements II PDFRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- All Intervals From G For Guitar (Ear Training Exercise)Document1 pageAll Intervals From G For Guitar (Ear Training Exercise)dalcha100% (1)
- Computer Networks: Introduction (Chapter 1)Document92 pagesComputer Networks: Introduction (Chapter 1)Speed PianoNo ratings yet
- Astm Parte 5Document5 pagesAstm Parte 5Jimmy David Espinoza MejiaNo ratings yet
- E-Studio 205L, 255, 305, 355, 455 MFP Service HandbookDocument732 pagesE-Studio 205L, 255, 305, 355, 455 MFP Service HandbookAnonymous gn8qxx66% (35)
- Enhancement of IDoc TypeDocument12 pagesEnhancement of IDoc TypeRakesh RaiNo ratings yet
- Structure Lab Manual FullDocument318 pagesStructure Lab Manual FullRodrigo Requelme BorjaNo ratings yet
- ReadmeRC8007 PDFDocument2 pagesReadmeRC8007 PDFمنير أحمدNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods in Rock Mechanics - 2002 - International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining SciencesDocument19 pagesNumerical Methods in Rock Mechanics - 2002 - International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining SciencesAnderson Lincol Condori PaytanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Testing: Four Wheel Drive (4WD) Systems - Electronic ShiftDocument38 pagesDiagnosis and Testing: Four Wheel Drive (4WD) Systems - Electronic ShiftLojan Coronel José Humberto100% (1)
- Forces Revision Questions 1. Resistive Force.: Island School 1Document13 pagesForces Revision Questions 1. Resistive Force.: Island School 1Deepal PrasankaNo ratings yet