Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2 2 Humans Moving Substances Around Body
Uploaded by
griggans100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
144 views3 pagesName, locate and state the functions of parts of the breathing system and the parts of the lungs. Explain fatigue in terms of lactic acid build up; why lactic acid needs to be removed, and oxygen debt. Explain the advantage of the double circulatory system in mammals and adaptations of arteries, veins and capillaries.
Original Description:
Original Title
2 2 Humans moving substances around body
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentName, locate and state the functions of parts of the breathing system and the parts of the lungs. Explain fatigue in terms of lactic acid build up; why lactic acid needs to be removed, and oxygen debt. Explain the advantage of the double circulatory system in mammals and adaptations of arteries, veins and capillaries.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
144 views3 pages2 2 Humans Moving Substances Around Body
Uploaded by
griggansName, locate and state the functions of parts of the breathing system and the parts of the lungs. Explain fatigue in terms of lactic acid build up; why lactic acid needs to be removed, and oxygen debt. Explain the advantage of the double circulatory system in mammals and adaptations of arteries, veins and capillaries.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
2.
2 Humans (Moving substances around Key Points Key terms
the body)
Plasma
Circulation
Veins
Arteries
Capillaries
Alveoli
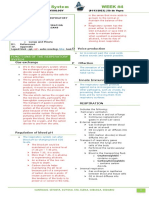
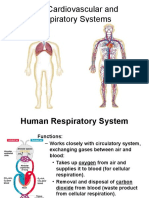
Syllabus Summary (H) = higher only Respiration
• Aerobic (with oxygen) respiration: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water +
You should be able to energy
Name, locate and state the functions of parts of the
breathing system and the parts of the lungs
• During rapid exercise oxygen cannot be delivered to the muscle fast enough for
aerobic respiration to take place. So instead anaerobic (without oxygen)
State the difference between inhaled and exhaled Lungs
air respiration occurs: glucose → lactic acid + energy
Diaphragm
State the work equation for aerobic respiration • Lactic acid from anaerobic respiration needs to be broken down. Lactic acid is Ribs
State the symbol equation for aerobic respiration (H) broken down by oxygen and the oxygen required is known as the oxygen debt. Bronchus
explain that during exercise the body may Lactic acid + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water Aerobic
respire anaerobically; • Energy released by respiration is used to build up larger molecules from smaller Anaerobic
state the word equation for anaerobic ones, to make muscles move and to keep warm. Respiration
respiration: • The alveoli in the lungs have a large surface area and are moist and thin to allow
Blood
state that anaerobic respiration releases much gases to be exchanged easily
Platelets
less energy than aerobic. • When we exercise breathing and pulse rate increase so that oxygen and glucose
get to the muscles quicker
explain fatigue in terms of lactic acid build up;
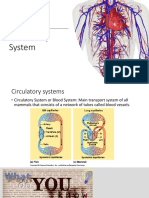
why lactic acid needs to be removed, and The Circulatory System and Heart
oxygen debt (H) • heart (the muscular pump that keeps
explain that during exercise, breathing and the blood moving)
pulse rates increase to deliver oxygen and
glucose to muscles more quickly; • arteries (which carry blood away from
the heart under high pressure) have
explain that high levels of CO2 in the blood are
thick walls
toxic and must be removed from the body by
the respiratory system; • veins (which return blood to the heart
describe how the parts of the respiratory under low pressure) have thin walls and
system work together to bring about gaseous valves
exchange • capillaries (tiny blood vessels that are
describe the changes in position of the ribs and close to the body’s cells) have very thin
diaphragm that cause inhalation and walls
exhalation;
explain that when increased CO2 levels in the
blood are detected the brain then brings about
an increase in breathing rate (H)
explain how the alveoli are adapted for efficient
gaseous exchange (H)
explain the way in which inhalation and
exhalation are brought about by pressure The Blood
changes (H) • The blood consists of plasma, platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells
• White blood cells – fight disease
describe how the parts of the circulatory
• Red blood cells – carry oxygen
system work
• Platelets – clot blood
name and locate parts of the heart and
• Plasma – carries carbon dioxide from organs to lungs, products of digestion from
describe their functions
intestine to other organs and urea from liver to kidneys
explain the advantage of the double circulatory
system in mammals and adaptations of
arteries, veins and capillaries (H)
State what blood contains and the function of
plasma
Explain the role of haemoglobin (H)
You might also like
- Focus On Combined Science Form 2Document184 pagesFocus On Combined Science Form 2wellington89% (9)
- Pt3 Revision ScienceDocument62 pagesPt3 Revision ScienceDeepa Darshini100% (2)
- Diving PhysiologyDocument334 pagesDiving PhysiologyemilidiverNo ratings yet
- 6O + C H O - 6H O + 6co + 38 ATP Oxygen + Glucose - Water + Carbon Dioxide + EnergyDocument2 pages6O + C H O - 6H O + 6co + 38 ATP Oxygen + Glucose - Water + Carbon Dioxide + EnergyRacha Abdel Fattah MetwallyNo ratings yet
- Respiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsDocument8 pagesRespiration: - Respiration Is The Release of Energy From Food Substances in All Living CellsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument30 pagesBiologyVictor OkosunNo ratings yet
- T4 SC 17 Aerobic Respiration and Paralympic Athletes PowerPoint - Ver - 3Document12 pagesT4 SC 17 Aerobic Respiration and Paralympic Athletes PowerPoint - Ver - 3William AnthonyNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingDocument26 pages1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingAla' ShehadehNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingDocument26 pages1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingAla' ShehadehNo ratings yet
- 9BR - RESPIRATION Week 24Document8 pages9BR - RESPIRATION Week 24Said SakerNo ratings yet
- Paper 1: The Structure and Functions of The Cardio-Respiratory System (Part 1)Document1 pagePaper 1: The Structure and Functions of The Cardio-Respiratory System (Part 1)isaaceden24No ratings yet
- Define Diffusion.: Give An Example in The BodyDocument14 pagesDefine Diffusion.: Give An Example in The BodyViolet RiddleNo ratings yet
- Respiratorio-Openstax Biology2e ch39Document43 pagesRespiratorio-Openstax Biology2e ch39ANo ratings yet
- Cardiorespiratory QuestionsDocument12 pagesCardiorespiratory QuestionsKim Oliveri ReedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document17 pagesChapter 1wallacec1017No ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument29 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchangemiriam odonkorNo ratings yet
- 2023 Science Progression Test Study GuideDocument29 pages2023 Science Progression Test Study Guideahaja ahajoNo ratings yet
- Biology ScienceDocument9 pagesBiology SciencetalaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System and RespirationDocument7 pagesThe Respiratory System and RespirationAntonateNo ratings yet
- Revision For Assessment II (Y8)Document33 pagesRevision For Assessment II (Y8)Nan Hay Zun Naung LattNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory System PDFDocument43 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory System PDFGames Account Secure itNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 1 NotesLim Zhi EnNo ratings yet
- Colorful Playful Creative Portfolio PresentationDocument10 pagesColorful Playful Creative Portfolio Presentationfaridahfadzil73No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument60 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsBeng QuinnNo ratings yet
- Respiration and The Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesRespiration and The Respiratory Systemfrancis iduruNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Week4 Respiratory-SystemDocument13 pagesAnaphy Week4 Respiratory-SystemMarc QuireNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory Systemapi-521773978No ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY-SYSTEM AnaPhy TransDocument19 pagesRESPIRATORY-SYSTEM AnaPhy TransEna CharmagneNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Gas ExchangeDocument30 pagesRespiratory System: Gas ExchangeDawn Regile MorilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bio NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- WWW Studyrankers Com 2017 07 Notes of CH 6 Life Process Part II Class 10th HTMLDocument15 pagesWWW Studyrankers Com 2017 07 Notes of CH 6 Life Process Part II Class 10th HTMLbaapmatsikha5No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument14 pagesRespiratory SystemTedi FetoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular-System-Workbook 2023-10-09 20 - 48 - 39Document13 pagesCardiovascular-System-Workbook 2023-10-09 20 - 48 - 39rubylexihNo ratings yet
- Respiration 2Document23 pagesRespiration 2api-233649346No ratings yet
- Science 9: 1St QuarterDocument42 pagesScience 9: 1St QuarterCharmel Joy TeopeNo ratings yet
- Nurs 13 Week 2Document20 pagesNurs 13 Week 2cheskalyka.asiloNo ratings yet
- Respiration BiologyDocument32 pagesRespiration BiologyMuhammad KhanNo ratings yet
- Learning Tasks 1-5 Week 1Document13 pagesLearning Tasks 1-5 Week 1Thartson Oliveros Magdadaro100% (1)
- Animal Organ SystemDocument139 pagesAnimal Organ SystemMilyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- Respiration: The Exchange of GasesDocument20 pagesRespiration: The Exchange of GasesElyza Marie OcampoNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in The LungsDocument30 pagesGas Exchange in The LungsYasasviNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesRespiratory SystemListiyani IsmailNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKarel Mae SanoriaNo ratings yet
- CB8a Efficient Transport and Exchange CB8b The Circulatory System CB8c The HeartDocument3 pagesCB8a Efficient Transport and Exchange CB8b The Circulatory System CB8c The HeartSiaNo ratings yet
- Human Body and Organ SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Body and Organ SystemAaryan KakadNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systemnarichu92No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsDocument60 pagesChapter 1 - Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Working With The Other Organ SystemsPatricia Sofia DizonNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument6 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory / Respiratory Systems Group Discussion (Ch. 42)Document2 pagesCirculatory / Respiratory Systems Group Discussion (Ch. 42)api-524061079No ratings yet
- Concept of Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesConcept of Respiratory SystemNur Oktavia RhosaniNo ratings yet
- 11 Circulatory SystemsDocument6 pages11 Circulatory SystemstosittilNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument36 pagesHearttalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesChapter 11. Gas Exchangerep.0mar13No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and RespiratoryDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and RespiratoryAya PalomeraNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans Grade 9Document49 pagesGas Exchange in Humans Grade 9harliv2.5chandhokNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemAlexi Nicole CastaloneNo ratings yet
- 8Cb Gas Exchange (Part 1)Document19 pages8Cb Gas Exchange (Part 1)maryamNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument2 pagesCirculatory Systemapi-522789883No ratings yet
- Respiratory System Physiology PDFDocument121 pagesRespiratory System Physiology PDFVizhiNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Unit 2E Homeostasis and Excretion - Self-Assessment SheetDocument6 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Unit 2E Homeostasis and Excretion - Self-Assessment SheetAli ALEBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Biology FieldworkqsDocument9 pagesBiology FieldworkqsgriggansNo ratings yet
- Physics p1 Core PracticalsDocument19 pagesPhysics p1 Core PracticalsgriggansNo ratings yet
- Exam-QuestionsQUADRATS AND TRANSECTSDocument8 pagesExam-QuestionsQUADRATS AND TRANSECTSgriggansNo ratings yet
- Heart Gcse Qs OnlyDocument6 pagesHeart Gcse Qs OnlygriggansNo ratings yet
- Chemistry c1 Core PracticalsDocument18 pagesChemistry c1 Core PracticalsgriggansNo ratings yet
- BTEC Science UNIT 5 NervesDocument4 pagesBTEC Science UNIT 5 NervesgriggansNo ratings yet
- Biology b1 Core Practical QuestionsDocument17 pagesBiology b1 Core Practical Questionsgriggans0% (1)
- Chromatography StarterDocument1 pageChromatography StartergriggansNo ratings yet
- GSK AssignmentDocument4 pagesGSK Assignmentgriggans100% (4)
- The Haber ProcessDocument1 pageThe Haber ProcessgriggansNo ratings yet
- Hormones: Part of Homeostasis and ControlDocument7 pagesHormones: Part of Homeostasis and ControlgriggansNo ratings yet
- BTEC First Diploma in Applied Science Student Tracking SheetsDocument6 pagesBTEC First Diploma in Applied Science Student Tracking Sheetsgriggans100% (6)
- Questions On Chrom Ato Graph yDocument5 pagesQuestions On Chrom Ato Graph ygriggans100% (1)
- Microscopes Assignment Brief and Task ListDocument2 pagesMicroscopes Assignment Brief and Task Listgriggans100% (1)
- Tomatosphere AssignmentDocument2 pagesTomatosphere AssignmentgriggansNo ratings yet
- Task and Mark Sheet 1)Document6 pagesTask and Mark Sheet 1)griggans100% (1)
- Btec Front Sheet ParticlesDocument2 pagesBtec Front Sheet ParticlesgriggansNo ratings yet
- Btec Front Sheet UnitsDocument1 pageBtec Front Sheet Unitsgriggans100% (2)
- Btec Front Sheet RocketsDocument2 pagesBtec Front Sheet Rocketsgriggans100% (1)
- Cats Milk Assignment Brief Sept 2006Document2 pagesCats Milk Assignment Brief Sept 2006griggansNo ratings yet
- 2 3 Useful Chemical Building BlocksDocument1 page2 3 Useful Chemical Building Blocksgriggans100% (1)
- Assignment Title Chemical and Physical EvidenceDocument6 pagesAssignment Title Chemical and Physical EvidencegriggansNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Living Organisms GeneticsDocument1 page2 1 Living Organisms GeneticsgriggansNo ratings yet
- Sats Revision QuizDocument126 pagesSats Revision QuizgriggansNo ratings yet
- Bankier Et Al 2024 Fleischner Society Glossary of Terms For Thoracic ImagingDocument55 pagesBankier Et Al 2024 Fleischner Society Glossary of Terms For Thoracic ImagingAna CamachoNo ratings yet
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeDocument283 pagesModul Perfect Score SBP Biology SPM 2013 Question and SchemeCikgu Faizal87% (15)
- Capitol University College of Nursing: in Partial Fulfillment in Related Learning Experince (RLE8)Document16 pagesCapitol University College of Nursing: in Partial Fulfillment in Related Learning Experince (RLE8)Jongjong Efondo RamosoNo ratings yet
- RPT Science DLP T3Document30 pagesRPT Science DLP T3RAFIQNo ratings yet
- B 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq AnswersDocument22 pagesB 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq Answersapi-516879364No ratings yet
- First Aid and Water SurvivalDocument119 pagesFirst Aid and Water SurvivalNi Cho LayyNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Pretest and Post TestDocument5 pagesGrade 9 Pretest and Post TestKebu YenNo ratings yet
- Ud: Warm Up: 1. ConceptDocument4 pagesUd: Warm Up: 1. ConceptrakelarausNo ratings yet
- LS2 DLL (Respiratory System)Document5 pagesLS2 DLL (Respiratory System)vanessa mabagaNo ratings yet
- Ammonium HydroxideDocument8 pagesAmmonium HydroxideAli Abbas SheraziNo ratings yet
- Basic SCBA: Self Contained Breathing ApparatusDocument33 pagesBasic SCBA: Self Contained Breathing ApparatusBalasuperamaniam Raman100% (1)
- HHW Biology X PDFDocument9 pagesHHW Biology X PDFNikhil bhatiNo ratings yet
- Past PE Papers Viva TopicsDocument29 pagesPast PE Papers Viva TopicsLouis MasonNo ratings yet
- Thoracentesis IntroductionDocument8 pagesThoracentesis Introductionjyoti singhNo ratings yet
- Science Practical Year 4 01Document94 pagesScience Practical Year 4 01JAGATHIS A/L RAVI CHANDRAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Bersihan MukosilierDocument58 pagesBersihan MukosilierbennyrolandnababanNo ratings yet
- Science 9 ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience 9 ReviewerArgie MabagNo ratings yet
- Msds HNO3Document6 pagesMsds HNO3Ariesa Nurruhiyatna Al-adzaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Speech Mechanism Study GuideDocument33 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Speech Mechanism Study GuidePhilip LuoNo ratings yet
- Pneupac BrochureDocument9 pagesPneupac BrochureahmedNo ratings yet
- Yoruba Respiratory System BiologyDocument2 pagesYoruba Respiratory System Biologyajibade ademolaNo ratings yet
- Copy Editing PDFDocument75 pagesCopy Editing PDFAdam Frick100% (1)
- Tacar High Resolution Computed Tomography of The LungsDocument79 pagesTacar High Resolution Computed Tomography of The Lungssindy suarezNo ratings yet
- ReaderstheaterabouthumanbodysystemsDocument7 pagesReaderstheaterabouthumanbodysystemsJessa Lou Liba CapapasNo ratings yet
- TEST Cardiovascular and Respiratory AssessmentDocument2 pagesTEST Cardiovascular and Respiratory AssessmentGabriel VelascoNo ratings yet
- DLL Biology FinalDocument11 pagesDLL Biology FinalRUTH PIANGNo ratings yet
- Bates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxDocument15 pagesBates Chapter 8 Lung and ThoraxAdrian CaballesNo ratings yet
- Animal Form and Function-I ZOL-2643: Program BS ZoologyDocument6 pagesAnimal Form and Function-I ZOL-2643: Program BS ZoologyMunazza ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and DigestiveDocument6 pagesRespiratory and DigestiveGoldaire Maris MalabananNo ratings yet