Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Paper 1: The Structure and Functions of The Cardio-Respiratory System (Part 1)
Uploaded by
isaaceden24Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Paper 1: The Structure and Functions of The Cardio-Respiratory System (Part 1)
Uploaded by
isaaceden24Copyright:
Available Formats
Paper 1: The structure and functions of the cardio-respiratory system (part 1)
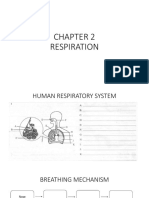
The pathway of air into the lungs: Gaseous exchange
Features that assist in gas exchange
• Alveoli have very tiny air sacs with moist thin walls (only one cell thick)
• Alveoli have a very large surface area
• Alveoli are surrounded by capillaries
• It provides a large blood supply
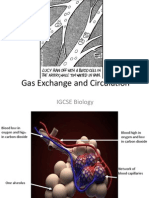
Gaseous exchange
• Gases move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. If there is more
oxygen in the alveoli than the capillaries oxygen will move into the capillaries
• Oxygen is diffused into the blood. It binds with the haemoglobin in the blood to form
oxyhaemoglobin
• Oxyhaemoglobin is transported to the working muscles where it is used for aerobic activity
• During aerobic activity carbon dioxide is produced this is removed from the muscles by
haemoglobin
• Gaseous exchange occurs at the alveoli – capillaries and capillaries – muscle tissue
Blood vessels:
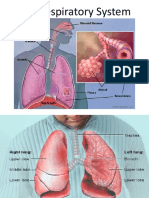
Nose and mouth: Air enters the body through the nose and mouth
Trachea: Air from the nose and mouth enters the wind pipe called the
trachea. The trachea is surrounded by rings of cartilage to keep its
shape and prevent it collapsing
Bronchi: Air travels from the trachea and to each lung via a bronchus.
Bronchi is the term for both the left and right bronchus. The passage of Artery Vein Capillary
air gets smaller and smaller • Thick muscular walls • Thin walls • Very thin walls (one cell thick)
Bronchioles: The smaller airways that branch off the bronchi are called • Thick elastic walls • Large lumen (internal diameter) • Small lumen (internal
bronchioles. Bronchioles branch out throughout the lungs and carry the • Small lumen (internal diameter) • Carry blood at low pressure diameter)
air from the bronchi to the alveoli • Carry blood at high pressure • Contain valves • Link smaller arteries with
Alveoli: The bronchioles carry the air to the alveoli which are tiny air • Cary blood away from the heart • Mainly carry deoxygenated small veins
sacs They are attached to the bronchioles. The exchange of oxygen and • Usually carry oxygenated blood blood (except the pulmonary • Allow gaseous exchange
carbon dioxide occurs at the alveoli (except the pulmonary artery) vein) • Carry blood at low pressure
Redistribution of blood:
Vasoconstriction means that the blood Vasodilation means that the blood
When we exercise blood is redistributed. The working vessels constrict to make them smaller. vessels dilate to make them bigger.
muscles need more oxygen than other inactive areas Chemical changes signal the nervous Chemical changes signal the nervous
of the body such as the stomach. Blood is diverted system to constrict blood vessels to system to dilate blood vessels that
away from inactive areas to the working muscles. inactive areas. supply active areas.
You might also like
- Pt3 Revision ScienceDocument62 pagesPt3 Revision ScienceDeepa Darshini100% (2)
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemKarel Mae SanoriaNo ratings yet
- Revision For Assessment II (Y8)Document33 pagesRevision For Assessment II (Y8)Nan Hay Zun Naung LattNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemAlexi Nicole CastaloneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and RespiratoryDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and RespiratoryAya PalomeraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument51 pagesCardiovascular and Respiratory Systemnarichu92No ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in The LungsDocument30 pagesGas Exchange in The LungsYasasviNo ratings yet
- 6) Gaseous ExchangeDocument32 pages6) Gaseous ExchangeDizzy DeeNo ratings yet
- All Lessons NotesDocument34 pagesAll Lessons NotesKiem Ashley DeluvioNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Gas ExchangeDocument9 pages1.2 Gas ExchangesiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document17 pagesChapter 1wallacec1017No ratings yet
- Science 9: 1St QuarterDocument42 pagesScience 9: 1St QuarterCharmel Joy TeopeNo ratings yet
- 1BDocument10 pages1BNazish UsamaNo ratings yet
- Ventilation and Gas ExchangeDocument14 pagesVentilation and Gas ExchangeBianca Astrid AndoneNo ratings yet
- Animal Organ SystemDocument139 pagesAnimal Organ SystemMilyn Mae PalganNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular-System-Workbook 2023-10-09 20 - 48 - 39Document13 pagesCardiovascular-System-Workbook 2023-10-09 20 - 48 - 39rubylexihNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument4 pagesBlood VesselsSanti JuliantiNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and Circulation: IGCSE BiologyDocument12 pagesGas Exchange and Circulation: IGCSE BiologyVeshalini NaiduNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesThe Respiratory Systemhanatabbal19No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System and RespirationDocument7 pagesThe Respiratory System and RespirationAntonateNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Science For Grade 9 StudentsDocument29 pagesReviewer Science For Grade 9 StudentsevanescentNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 - Respiration and Gas Exchange-2Document28 pagesUnit 10 - Respiration and Gas Exchange-2thraaaladyNo ratings yet
- L10 - Respiratory System ShortenedDocument38 pagesL10 - Respiratory System ShortenedgfsgfdsgfdNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument29 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchangemiriam odonkorNo ratings yet
- G7 - Respiration - NotesDocument6 pagesG7 - Respiration - NotesSahithi PNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Heart, Lungs, Pancreas, Liver, Kidneys and SkinDocument71 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Heart, Lungs, Pancreas, Liver, Kidneys and SkinSilvia-Mihaela TatomirNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesAnatomy of Respiratory SystemAbdelwadod Mahmood HassanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingDocument26 pages1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingAla' ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Life's Transport, Exchange and Defense SystemsDocument7 pagesLife's Transport, Exchange and Defense SystemshjNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument7 pagesScience ReviewerWayne AngeloNo ratings yet
- Ch09 - Notes - e 2Document7 pagesCh09 - Notes - e 21A22 LI SIU MAN 李兆旻100% (1)
- 2 2 Humans Moving Substances Around BodyDocument3 pages2 2 Humans Moving Substances Around Bodygriggans100% (1)
- Chapter 2-2.2 Gases Exchange-NtmDocument14 pagesChapter 2-2.2 Gases Exchange-NtmNITIASSWARENo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Second HalfDocument35 pagesRespiratory System: The Second HalfnicopiiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - RespirationDocument3 pagesChapter 1 - Respirationqin donNo ratings yet
- Science Notes WITH CHEMDocument11 pagesScience Notes WITH CHEMAlfredNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesIntroduction To The Respiratory Systemapi-656424610No ratings yet
- Breathing Study SheetDocument8 pagesBreathing Study Sheetshimaa youssifNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory System PDFDocument43 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory System PDFGames Account Secure itNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SC Pt6tDocument5 pagesChapter 8 SC Pt6tDavid ChangNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingDocument26 pages1.1 The Human Respiratory System - 1.2 Gas Exchange - 1.3 BreathingAla' ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System REVISEDDocument12 pagesRespiratory System REVISEDKim GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideDocument22 pagesRespiratory System: The Organs That Help To Get Oxygen From The Air Into Your Blood, and To Get Rid of Carbon DioxideTravel UnlimitedNo ratings yet
- Full Notes - Transport in AnimalsDocument39 pagesFull Notes - Transport in Animalsmiriam odonkorNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument30 pagesCirculatory SystemScheherazade CNo ratings yet
- (Notes) Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Document12 pages(Notes) Science Form 3 - Chapter 2 (Respiration)Aizzat BahiahNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemMotiourNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 New Syllabus NotesDocument69 pagesUnit 1 New Syllabus Notesmalak sherif100% (1)
- Grade 7 CH 4.06 What Makes Blood FlowDocument18 pagesGrade 7 CH 4.06 What Makes Blood FlowMunmun AfnanNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesMammalian Respiratory SystemRaven CortezaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System BloodDocument85 pagesCardiovascular System BloodEbrahem ShaheinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document36 pagesChapter 9HC GamerNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Prepared By: Jameel KobeissiDocument14 pagesRespiration: Prepared By: Jameel KobeissiJameel KobeissiNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument8 pagesRespirationAwn Tarek AmmariNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument35 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemScheherazade CNo ratings yet
- Heart & LungsDocument3 pagesHeart & Lungsyzoo13068No ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate (Document2 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate (Anime Player ccNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesRespiratory Systemamulyajadhav119No ratings yet
- The Excretory System: By: Mike Bow, Anup Shah, Christal AlonzoDocument35 pagesThe Excretory System: By: Mike Bow, Anup Shah, Christal AlonzoikaNo ratings yet
- Issues Exam 3Document20 pagesIssues Exam 3isaaceden24No ratings yet
- 02 KogoalsettingDocument1 page02 Kogoalsettingisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Christianity 2019Document12 pagesChristianity 2019isaaceden24No ratings yet
- The Timeline of Artificial IntelligenceDocument1 pageThe Timeline of Artificial Intelligenceisaaceden24No ratings yet
- RE Year 11 Exam Checklist 2023Document6 pagesRE Year 11 Exam Checklist 2023isaaceden24No ratings yet
- TicketDocument2 pagesTicketisaaceden24No ratings yet
- P4 Knowledge OrganiserDocument1 pageP4 Knowledge Organiserisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Structured Blank Mind Maps BiologyDocument25 pagesStructured Blank Mind Maps Biologyisaaceden24No ratings yet
- 10 GCSE PE 2. Fitness Strength 1Document4 pages10 GCSE PE 2. Fitness Strength 1isaaceden24No ratings yet
- P3 11 TransformersDocument65 pagesP3 11 Transformersisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Relationships 1Document1 pageRelationships 1isaaceden24No ratings yet
- Banquo, Macduff and The WitchesDocument13 pagesBanquo, Macduff and The WitchesxenaNo ratings yet
- Past Paper Questions Eduqas For Public WebsiteDocument12 pagesPast Paper Questions Eduqas For Public Websiteisaaceden24No ratings yet
- PE Revision SupportDocument2 pagesPE Revision Supportisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Issues Exam 6Document20 pagesIssues Exam 6isaaceden24No ratings yet
- Inheritance Exam Questions HIGHERDocument25 pagesInheritance Exam Questions HIGHERisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Chromatography - IGCSEDocument4 pagesChromatography - IGCSEisaaceden24No ratings yet
- B2 OrganisationDocument9 pagesB2 Organisationisaaceden24No ratings yet
- B6 - InheritanceDocument7 pagesB6 - Inheritanceisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Mock Exam Power People 2024Document5 pagesMock Exam Power People 2024isaaceden24No ratings yet
- Islam Paper 3Document12 pagesIslam Paper 3isaaceden24No ratings yet
- Issues Exam 3Document20 pagesIssues Exam 3isaaceden24No ratings yet
- Islam Paper 3Document12 pagesIslam Paper 3isaaceden24No ratings yet
- B7 EcologyDocument9 pagesB7 Ecologyisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Issues Exam 1Document20 pagesIssues Exam 1isaaceden24No ratings yet
- B1 Cell BiologyDocument11 pagesB1 Cell Biologyisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Issues Exam 6Document20 pagesIssues Exam 6isaaceden24No ratings yet
- CR Muhammad Arif Ardiansyah Tugas BingDocument4 pagesCR Muhammad Arif Ardiansyah Tugas BingMUHAMMAD ARIF ARDIANSYAHNo ratings yet
- Erba Lisawash - Service ManualDocument9 pagesErba Lisawash - Service ManualEricj Rodríguez100% (1)
- Group Nursing and ActivitiesDocument2 pagesGroup Nursing and ActivitieschyNo ratings yet
- WN.74. Akira Annaisha - Case Notes - Acute Meningoencephalitis - Writing - Nursing - OETDocument3 pagesWN.74. Akira Annaisha - Case Notes - Acute Meningoencephalitis - Writing - Nursing - OETmk1971953No ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument16 pagesAnimal NutritionShop AliceNo ratings yet
- Perspectives On ConflictDocument19 pagesPerspectives On Conflictẞhåñ TïêNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination - Pre-Med - 401Document73 pagesNeurological Examination - Pre-Med - 401Surat Tanprawate100% (4)
- Jurnal Munir Et AlDocument4 pagesJurnal Munir Et AlsepriNo ratings yet
- Impact of Literacy Projects On Rural Poor in Northern UgandaDocument67 pagesImpact of Literacy Projects On Rural Poor in Northern Ugandakeisha babyNo ratings yet
- Research ApaDocument17 pagesResearch ApaJohn Lorenz InterinoNo ratings yet
- 4P S of Marketing CarabaoDocument3 pages4P S of Marketing CarabaoAlejandra Martinez ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Value Education PDFDocument19 pagesUnit I Introduction To Value Education PDFMubasshir Shaikh100% (3)
- A History of Daniel KeyesDocument12 pagesA History of Daniel KeyesAllyssa Camille QuijanoNo ratings yet
- RLE 40 ChecklistDocument3 pagesRLE 40 ChecklistJenny Turado ArbitrarioNo ratings yet
- Tests Mechanical Devices and Registration SamplingDocument3 pagesTests Mechanical Devices and Registration SamplingJocel D. MendozaNo ratings yet
- Dat AssDocument19 pagesDat AssMa k Kk75% (12)
- Aquaculture Checklist Edition 9Document109 pagesAquaculture Checklist Edition 9elflaquito80No ratings yet
- 701 W. 51st Street Austin, Texas 78751 Phone-512-438-4800Document2 pages701 W. 51st Street Austin, Texas 78751 Phone-512-438-4800api-550348575No ratings yet
- 1.2.2.5 Lab - What Was TakenDocument2 pages1.2.2.5 Lab - What Was TakenPhillip NguyenNo ratings yet
- 166-176 The Role of Financial Behavior in Mediation The Influence of Financial Literacy and Financial Self Efficacy On Financial Will BeingDocument11 pages166-176 The Role of Financial Behavior in Mediation The Influence of Financial Literacy and Financial Self Efficacy On Financial Will BeingJuvy ParaguyaNo ratings yet
- DAFTARRUJUKANDocument4 pagesDAFTARRUJUKANIndahNo ratings yet
- Fitness Tips: Presented By: Bill ByronDocument30 pagesFitness Tips: Presented By: Bill ByronSamson ChelliahNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Aging 2.0 San Diego Nov 05,19Document26 pagesPresentation - Aging 2.0 San Diego Nov 05,19Bijou LullaNo ratings yet
- QR Scientifique Technique EN 011119Document29 pagesQR Scientifique Technique EN 011119Vio CondreiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyJamie LeeNo ratings yet
- TFN03-Nursing Theories and ModelsDocument26 pagesTFN03-Nursing Theories and ModelsLyn YmiNo ratings yet
- Peads Quiz MCQSDocument10 pagesPeads Quiz MCQSM.A. Ch.No ratings yet
- Model Pembelajaran Problem Based Learning (PBL) : Efeknya Terhadap Pemahaman Konsep Dan Berpikir KritisDocument10 pagesModel Pembelajaran Problem Based Learning (PBL) : Efeknya Terhadap Pemahaman Konsep Dan Berpikir KritisSiska AlvionitaNo ratings yet
- Sample Questionnaire For Thesis Likert ScaleDocument4 pagesSample Questionnaire For Thesis Likert Scalednrssvyt100% (1)
- Test OgenDocument65 pagesTest OgenMichael PogodaNo ratings yet