Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English Novice 1st
Uploaded by
noviOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English Novice 1st
Uploaded by
noviCopyright:
Available Formats
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
KOMPETENSI DASAR 1.1.
MEMAHAMI UNGKAPAN-UNGKAPAN DASAR PADA INTERAKSI SOSIAL
UNTUK KEPENTINGAN KEHIDUPAN
GREETING
Formal Greeting
- Good morning
- Good afternoon
- Good evening
- Hello, how are you?
Reponses
- Hello
- Hello, good afternoon
- Good evening
- Im fine, thank you
LEAVE TAKINGS
Leave Takings
- Sorry, I have to go now.
- Ill talk to you later.
- Its been nice talking to you.
- Good bye.
- Bye-bye / Bye.
- See you tomorrow
Reponses
- Terrific. And you?
- Just fine, thanks.
- Great, thanks.
- Pretty well. What about
you
Responses
- Yes of course. See you.
- Sure. See you later.
- So long.
- Take care.
- Keep in touch.
- See you at school
INTRODUCING
Introducing oneself
- Hi, Im Baskara.
- Hello, my names Baskara.
- Good evening. My name is Baskara.
- May I introduce myself? Im Baskara.
- Let me introduce myself. My name is Baskara.
- How do you do? My name is Baskara.
Introducing others
- Do you know Baskara?
- Have you met Baskara?
- This is a friend of mine, Renata.
- Baska this is Rena, my friend.
- May I introduce our new member, Mr. Rafael
Romero?
- Please allow me to introduce our new District
Manager.
- Let me introduce you to Mr. Iskandar our
Marketing Manager. Mr. Iskandar, this is Mr.
Hermawan from Borneo Plantation Company.
THANKING
A. When someone gives you something
Thanking
- Thanks (a lot).
- Thank you very much (followed by):
- Its very nice/ beautiful.
- Its just what I want.
- But you really didnt have to /
You shouldnt have (if the gift is not expected)
B. When someone does a favor or helps you
- Thanks (a lot) for your help.
- Thanks (a lot) for helping me.
- I really appreciate your help.
- It was very kind of you to help me.
- Im very grateful to you for your visit.
- Im very grateful to you for inviting me
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Informal Greeting
- Hi, hows life?
- Whats news?
- Hows everything?
- Hows business?
- Good to see you.
Responses
- Hi, Im Renata. Glad to meet you.
- Hello. My names Renata. Pleased to meet you.
- Good evening. Im Renata. How do you do?
- How do you do? My name is Renata. Nice to
meet you.
Responses
- No, I dont think so.
- No, I havent.
- Hi, glad to meet you. Im Renata.
- Hello, Renata. Pleased to meet you.
- Im glad to know you.
- Its nice to meet you.
- How do you do?
- How do you do? Its very nice to meet you.
Responses
- You are welcome.
- No problem.
- Its OK/alright.
- Dont mention it.
- Im glad you like it
- You are welcome.
- No problem.
- Thats OK/ alright.
- Never mind.
- Its no trouble at all.
- Any time.
- Think nothing of it.
- Im glad I could help.
- Dont mention it.
- Forget it.
- It was my pleasure/ My pleasure.
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
APOLOGIZING
Apologizing
- Please, forgive me
- Im so sorry. I dont mean like that
- Did I hurt you?
- Sorry. Ive made you cry
- I want to apologize
- I promise. I will not do that anymore
Responses
- No problem. Just forget it.
- Its OK
- Come on! Dont take it too seriously
- Not at all
PRONOUNS
PERSONAL AND REFLEXIVE PRONOUN
Possessive
Subject
Object
Adjective
_____ Did it Show_____ _____ Book
Sing.
I
me
my
(=1)
you
you
your
he
him
his
she
her
her
it
it
its
Plural we
us
our
(>=2)
you
you
your
they
them
their
Possessive
Pronoun
It is _____
mine
yours
his
hers
ours
yours
theirs
Reflexive
Pronoun
Hurt _____
myself
yourself
himself
herself
itself
ourselves
yourselves
themselves
Saya
Kamu
Dia laki-laki
Dia perempuan
Benda/hewan
Kita
Kalian
Mereka
NOTE:
Subject pronoun adalah kata ganti orang yang berfungsi sebagai subject dalam pembicaraan
atau dalam kalimat. Letak dari subjek pronoun dalam kalimat positif adalah sebelum tobe, auxiliary
atau sebelum full verb (kata kerja penuh)
I am going to the school
Objek pronoun adalah kata ganti orang yang berfungsi sebagai objek dalam pembicaraan atau
dalam kalimat. Letak dari objek pronoun dalam kalimat positif adalah sesudah full verb (kata kerja
penuh) atau sesudah preposition (kata depan)
The policeman was looking for him
Possessive adjective adalah kata ganti yang menunjukkan kepunyaan atau milik, tidak bisa
berdiri sendiri atau selalu diikuti kata benda atau diletakkan sebelum kata benda.
Their coats are too small.
This is my book.
Possessive pronoun adalah kata ganti yang menunjukkan kepunyaan atau milik, dimana dapat
berdiri sendiri atau tidak diikuti kata benda karena benda yang dimaksud sudah dimengerti.
Their coats are too small. Theirs are too small
This is my book. This is mine
Reflexive pronoun adalah kata ganti yang menunjukkan perbuatan mengenai dirinya sendiri.
Reflexive pronoun mempunyai tiga kegunaan utama, yaitu:
1. Untuk menyatakan sesuatu mengenai diri sendiri, berfungsi sebagai objek dalam kalimat.
- Rona bought herself a new car
(herself = Rona)
, bandingkan
- Rona bought her a new car
(her = orang lain)
2. Untuk memberi tekanan atau penegasan arti terhadap subjek yang melakukan suatu tindakan.
Dalam posisi ini letaknya langsung dibelakang subjek.
- I myself believe that the proposal is good
3. Untuk memberikan penegasan terhadap pelaku suatu tindakan yang tidak memerlukan bantuan atau
hadirnya pihak lain (biasanya didahului oleh kata by.)
- She is afraid to go home by herself
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
SIMPLE PRESENT TENSE
Tense ini digunakan untuk menyatakan suatu kejadian/perbuatan yang menjadi kebiasaan atau
untuk menyatakan kebenaran/kenyataan umum. Time signal yang biasa dipakai dalam tense ini
diantaranya adalah:
- every / everyday (setiap/setiap hari) - normally (biasanya)
- always (selalu)
- occasionally (kadang-kadang)
- sometimes (kadang-kadang)
- frequently (sering)
- usually (biasanya)
- steadily (selalu, terus-menerus)
- generally (biasanya)
- nowadays (pada waktu sekarang)
- often (sering)
- every other day (dua hari sekali, berselang hari )
- seldom (jarang)
- now and then (kadang-kadang)
- ever (pernah)
- as a rule (biasanya, lazimnya)
- never (tidak pernah)
- once/once a week (sekali/sekali seminggu)
- regularly (secara tetap)
POLA PRESENT OF TO BE
(+) S + to be + O (adjective/adverb)
(-) S + to be + NOT + O (adjective/adverb)
(?) To be + S + O (adjective/adverb)
NOTE :
To be yang dipakai antara lain :
- am dipakai untuk subjek I
- are dipakai untuk subjek you, we, they
- is
dipakai untuk subjek he, she, it
Examples:
1. (+) I am an Indonesian President
(-) I am not an Indonesian President
(?) Am I an Indonesian President?
2. (+) They are room mate.
(-) They are not room mate
(?) Are they room mate?
POLA PRESENT OF VERB
=> Subjek : they, we, I, you
=> Subjek : she, he, it
(+) S + verb1 + (complement)
(+) S + verb1 + s/es + (complement)
(-) S + do not (dont) + verb1 + (complement) (-) S + does not (doesnt) + verb1 + (complement)
(?) Do + S + verb1 + (complement)
(?) Does + S + verb1 + (complement)
Examples:
1. (+) My parents always get up early.
(-) My parents do not always get up early
(?) Do my parents always get up early?
2. (+) She prepares the TOEIC test everyday.
(-) She doesnt prepare the TOEIC test everyday
(?) Does she prepare the TOEIC test everyday?
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
KOMPETENSI DASAR 2.2.
MENYEBUTKAN BENDA-BENDA, ORANG, CIRI-CIRI,
WAKTU, HARI, BULAN DAN TAHUN
ADJECTIVE
Adjective adalah kata yang menerangkan kata benda dan kata ganti, sedangkan descriptive
adjective adalah jenis kata sifat yang memberikan keterangan tentang ukuran, bentuk, rasa, keadaan,
dan sebagainya terhadap kata benda.
Descriptive adjective yang biasa digunakan antara lain:
Colors
Quality
Size
Shape
Material
Age
black
beautiful
big
circular
copper
new
blue
bad
fat
conical
cotton
old
brown
broken
heavy
cubic
glass
young
green
lovely
light
cylindrical
gold
grey
good
long
decagonal
iron
orange
short
heptagonal
leather
pink
skinny
hexagonal
paper
red
small
octagonal
plastic
white
tall
oval
rubber
yellow
thick
pentagonal
wood
purple
thin
pyramidal
rectangular
rhombus
square
triangular
PROFESSIONS
accountant
acrobat
administrator
archeologist
architect
artist
astronomer
athlete
author
baker
barber
banker
butcher
caddie
carpenter
cashier
chef
clerk
clown
composer
conductor
contractor
decorator
dentist
detective
doctor
editor
electrician
engineer
farmer
florist
geologist
grocer
hairdresser
hatter
journalist
judge
lawyer
librarian
ORIGIN AND NATIONALITY
Country
Afghanistan
Argentina
Australia
Austria
Brazil
Canada
China
Colombia
Denmark
Ecuador
Egypt
England
France
Germany
Greece
Holland
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
manager
mechanic
navigator
navy
novelist
nurse
optician
overseer/foreman
pastor
pharmacist
photographer
physician
pianist
People
Afghan
Argentinean
Australian
Austrian
Brazilian
Canadian
Chinese
Colombian
Dane
Ecuadorian
Egyptian
English
French
German
Greek
Dutch
pilot
plumber
porter
postman
principal
producer
reporter
sailor
salesman
scientist
sculptor
secretary
soldier
policeman
stenographer
steward
surgeon
tailor
teacher
tourist guide
trader/merchant
typist
waiter
watchmaker
Language
Pushtu, Persian
Spanish
English
German
Portuguese
French, English
Chinese
Spanish
Danish
Spanish
Arabic
English
French
German
Greek
Dutch
4
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
Hungary
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Israel
Italy
Japan
Korea
Lebanon
Malaysia
Mexico
Nigeria
Paraguay
Philippines
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Russia (USSR)
Saudi Arabia
Thailand
Singapore
Switzerland
United States of America (USA)
Hungarian
Indian
Indonesian
Iranian
Iraqi
Irish
Israeli
Italian
Japanese
Korean
Lebanese
Malaysian
Mexican
Nigerian
Paraguayan
Pilipino
Portuguese
Puerto Rican
Russian
Saudi Arabian
Thai
Singaporean
Swiss
American
Magyar
Hindustani
Bahasa Indonesia
Farsi, Persian
Arabic
English, Gaelic
Hebrew, Arabic
Italian
Japanese
Korean
Arabic
Malay
Spanish
English
Spanish
English, Spanish
Portuguese
Spanish, English
Russian
Arabic
Thai
Malay/English/Chinese/Tamil
French, German
English
QUESTION AND ANSWER
Questions
Color
Quality
Size
Shape
Material
Country, Nationality
& Language
Occupation
Answers
1 . What color is your shirt?
2. What color are your eyes?
1 . Whats the quality of your watch?
2. Whats the quality of this picture?
1 . How big is your house?
2. What size are your shoes?
1 . What shapes is the earth?
2. What shape are the tiles?
1 . What is a spanner made of?
2. What are your shoes made of?
1 . a. Where are you from?
b. Where do you come from?
2. a. What nationality are you?
b. What is your nationality?
3. a. Do you speak English?
b. Whats your friend native languages?
a. Whats your job?
b. Whats your profession?
c. Whats your occupation?
d. What are you?
e. What do you do?
Adjective in series:
Determiner Opinion
A
lovely/nice
An
expensive
Several
good
The
pretty
Size
big
small
big
small
Shape
circular
flat
square
Age
old
new
new
old
Color
brown
metallic
white
1. Its blue.
2. Theyre black.
1. Its good.
2. Its bad.
1. Its very big.
2. They are medium.
1. Its round.
2. Theyre square.
1. Its made of steel.
2. Theyre made of leather.
1. a. Im from Indonesia.
b. I come from Indonesia.
2. Im Indonesian.
3. a. Yes. I do
b. His native language is Greek
I am a teacher.
Origin
Javanese
Japanese
-
Material
wooden
stone
Noun
table
car
TVs
house
ADJECTIVES SHOWING PHYSICAL APPEARANCE and CHARACTERISTIC
A. PHYSICAL APPEARANCE
Height
Quite tall, rather short, tall, short
Build
Quite slim, thin, well-built, rather heavy, fat
Hair
Long brown, dark brown, blond, black, curly, straight, long, short, bald, wavy
Face
Oval, round, egg-shape, small eyes, large eyes, round eyes, narrow eyes, round face, thin
face, thick lips, flat nose, pointed nose, beard, moustache
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
Race
Age
Skin
Looks
European, Asian, Japanese, Indian, Chinese, black
Young, old, middle-aged, elderly.
Black, white, yellow, dark-brown, brown, oriental
handsome, ugly, beautiful, pretty, cute, fat, thin, skinny, slim, charming, attractive
B. CHARACTERISTIC
Good Characteristic
Polite and courteous towards others
Patient
Understanding
Get on well with other people
Listen to other peoples point of view
A good organizer
Hard working
Bad Characteristic
Arrogant
Bad-mannered
Short-tempered
Get into difficulties with other people
Try to force his/her opinion
A poor organizer
Lazy
TIME AND DATE (DAY, MONTH, YEAR)
Times
09.00 : Its nine oclock
02.10 : Its ten past two
05.15 : Its a quarter past five / Its fifteen past five / Its five fifteen
06.30 : Its a half past six / its thirty past six / its six thirty / its thirty to six
07.45 : Its a quarter to eight / its fifteen to eight / its seven forty five
12.55 : Its five to one
Date
Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday
Month January, February, March, April, May, June, July, September, October, November, December
Question and answer concerning time and date
Telling Time
What time is it (now)?
Can you tell me what time is it?
Its two oclock, isnt it?
Excuse me, can you tell me the correct time?
Will you be here at ten oclock tomorrow?
Well be on time, wont we?
Is your watch slow, Helen?
Can you tell me where my watch is?
Talking about Dates
What is today?
What day is today?
What day was yesterday?
What day is tomorrow?
What month is it?
Last month was January, wasnt it?
What month is next month?
What year is it?
What is the date?
What date is today?
Responses
Its two oclock
It must be about three thirty
I dont know my watch is fast and your watch is slow
No, I cant. I dont have a watch
Yes, I will
I hope so
Yes, I think it is
No, I cant. I dont know where your watch is.
Responses
It is Monday
Today is Saturday
Yesterday was Friday
Tomorrow is Sunday
It is February
Yes, It was
Next month is March
It is two thousand and seven
It is the 19th of February 2007
It is Feb. 19th 2007
Singular and Plural Noun
Noun adalah kata yang memberikan nama terhadap orang, tempat atau benda. Singular noun adalah
kata benda tunggal/jumlahnya hanya satu, sedangkan plural noun adalah kata benda jamak/jumlahnya
lebih dari satu. Untuk membentuk kata benda tunggal menjadi jamak dapat dilakukan dengan:
Kata benda jamak biasanya dibentuk dengan menambahkan akhiran s pada kata benda bentuk
tunggalnya.
- dog (anjing)
dogs
- house (rumah)
houses
Kata benda tunggal berakhiran huruf o, ss, sh, ch dan x mempunyai bentuk jamak
dengan menambahkan huruf es pada kata benda bentuk tunggalnya.
- tomato (tomat)
tomatoes
- kiss (ciuman)
kisses
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
- brush (sikat/kuas)
- watch (jam/arloji)
- box (kotak)
- pouch (kantong)
brushes
brushes
boxes
pouches
NOTE : beberapa kata benda yang berasal bukan dari bahasa inggris atau singkatan seperti piano
(piano), kimono (kimono), dynamo (dinamo), biro (sejenis bolpoin) dan photo (foto) mempunyai
bentuk jamak: pianos, kimonos, dynamos, biro dan photos.
Kata benda tunggal yang berakhiran huruf y didahului huruf mati mempunyai bentuk jamak
dengan menambahkan huruf ies pada kata benda bentuk tunggalnya, sedangkan huruf y
dihilangkan.
- baby (bayi)
babies
- lady (anak perempuan) ladies
Kata benda tunggal berakhiran huruf y didahului huruf hidup mempunyai bentuk jamak
dengan menambahkan huruf s pada kata benda bentuk tunggalnya, sedangkan huruf y tidak
dihilangkan.
- boy (anak laki-laki) boys
- day (hari)
days
Dua belas kata benda tunggal berakhiran huruf f atau fe mempunyai bentuk jamak dengan
menambahkan ves pada kata benda bentuk tunggalnya, sedangkan huruf f atau fe dihilangkan.
- wife (isteri)
wives
- life (kehidupan)
lives
- knife (pisau)
knives
- wolf (serigala)
wolves
- self (diri/sendiri)
selves
- calf (anak sapi, betis)
calves
- shelf (rak)
shelves
- leaf (daun)
leaves
- loaf (sepotong/sebongkah)
loaves
- thief (pencuri)
thieves
- sheaf (berkas, ikat)
sheaves
- half (separuh/setengah)
halves
NOTE : Kata benda seperti cliff (jurang), handkerchief (sapu tangan) dan safe (almari/ peti besi)
mempunyai bentuk jamak cliffs, handkerchiefs, safes.
Beberapa kata benda tunggal mempunyai bentuk jamak yang tidak teratur.
- man (laki-laki)
men
- woman (perempuan)
women
- louse (kutu)
lice
- goose (angsa)
geese
- foot (kaki)
feet
- tooth (gigi)
teeth
- fish (ikan)
fish
- sheep (domba)
sheep
- deer (rusa)
deer
- mouse (tikus)
mice
- child (anak)
children
- ox (lembu jantan)
oxen
Beberapa kata benda selalu berbentuk tunggal
- advice (saran/nasihat)
- baggage (bagasi/kopor/barang)
- information (informasi)
- luggage (bagasi/barang)
- knowledge (ilmu pengetahuan)
- furniture (mebel/perabot rumah)
- news (berita/kabar)
- rubbish (sampah)
Beberapa kata benda selalu berbentuk jamak
- pajamas (piyama)
- glasses (kacamata)
- trousers (celana panjang)
- spectacles (kacamata)
- police (polisi)
- pliers (tang)
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
- clothes (pakaian)
- breeches (celana)
- pants (celana)
- binoculars (teropong)
- shears (gunting besar)
- scissors (gunting)
- scales (timbangan)
- premises (dasar pikiran/alasan)
DIALOGUE
In pairs, practice the dialogue bellow!
Salesman : Good morning, Sir.
Mr. Made : Good morning
Salesman : Can I help you?
Mr. Made : Yes, I like to buy a table with four chairs
Salesman : What shape do you want, Sir? Round table or square table?
Mr. Made : I prefer square table, please?
Salesman : What about the dimension?
Mr. Made : Oh...... 2.5 meters long, 1.5 meters wide and 1.2 meters high.
Salesman : I am sorry, Sir. I dont have such dimension. What about 2.5 meters long, 1.5 meters
wide and 1.4 meter high.
Mr. Made : Its alright. How much does it cost?
Salesman : Well, let me count first. A hundred and ninety thousand for table, and ninety thousand
for one chair. The total is five hundred and fifty thousand.
Mr. Made : Oh..... its quite expensive.
Salesman : I dont think so, Sir. Its normal price.
Mr. Made : What about five hundred thousand?
Salesman : Emm..... It is alright
Mr. Made : Here it the money. Please deliver it this afternoon.
Salesman : Yes..... Sir.
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
KOMPETENSI DASAR 1.3.
MENDESKRIPSIKAN BENDA-BENDA, ORANG, CIRI-CIRI,
WAKTU, HARI, BULAN DAN TAHUN
CARDINAL AND ORDINAL NUMBER
DESCRIPTION OF EVENTS
ANTONYM/SYNOMYN
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
KOMPETENSI DASAR 1.4.
MENGHASILKAN TUTURAN SEDERHANA YANG CUKUP
UNTUK FUNGSI-FUNGSI DASAR
A. S-V AGREEMENT
Adalah suatu persesuaian antara subject, verb, complement dan modifier.
POLA:
Subject +Verb + Complement + Modifier
Contoh:
- Kartika and I drank coffee last night.
Dalam kalimat diatas Kartika and I berfungsi sebagai subjek, drank sebagai verb, coffee
sebagai complement dan last night sebagai modifier.
a. SUBJECT
Subject atau pelaku dalam kalimat aktif yaitu orang atau benda yang melakukan atau
bertanggung jawab atas tindakan yang dilakukan dalam kalimat tersebut.
Contoh:
- Milk contains calcium (single noun)
- The new English teacher is very attractive (noun phrase)
- It takes two month to finish the job. (impersonal verb)
- There was a boy at secretary ship study program (subject singular)
- There were many boys at Electrical Study Program (subject plural)
b. VERB
Dalam kalimat berita, verb terletak dibelakang subject, biasanya menunjukkan suatu tindakan
dalam suatu kalimat, berbentuk single verb atau verb phrase. Verb phrase adalah kata kerja yang terdiri
dari satu atau lebih auxiliary dan satu kata kerja inti. Letak modal auxiliary sebelum kata kerja inti.
Contoh:
- Lynda and Lina hate spinach (single verb)
- Power tends to corrupt (single verb)
- I am going to go home on time (verb phrase)
- The system of management at SMK should be computerized (verb phrase)
c. COMPLEMENT
Berfungsi sabagai pelengkap kata kerja pada kalimat aktif, berbentuk noun atau noun phrase
dan merupakan jawaban atas pertanyaan what? atau whom?. Complement tidak diawali dengan kata
depan.
Contoh:
- Nabil sold his car yesterday. (What did Nabil sell?)
- He saw Rema at the movies. (Whom did he see at the movies?)
d. MODIFIER
Berbentukprepositional phrase yang menggambarkan waktu, tempat atau cara/alat dari suatu
tindakan (on the table, in the afternoon, at the university). Prepositional phrase adalah kumpulan kata
yang dimulai dengan kata depan dan berakhir dengan kata benda. Jika dalam kalimat tersebut terdapat
lebih dari saatu modifier, maka modifier yang menggambarkan waktu biasanya diletakkan diakhir
kalimat. Disamping prepositional phrase, modifier juga dapat berbentuk adverb atau adverbial phrase
(last year, next week, yesterday, indoors, rapidly) dan merupakan jawaban atas pertanyaan when?,
where? atau How?
Contoh:
- Ilya sold her motorcycle at the dealer. (modifier of place where did Ilya sell her motorcycle?)
- We are going to have dinner at eight oclock. (modifier of time when are we going to have
dinner?)
- He finished his homework rapidly. (modifier of manner How did he finish his homework?).
CATATAN:
Modifier biasanya mengikuti complement, tetapi tidak selalu. Bagaimanapun juga, bila modifier
berbentuk prepositional phrase biasanya tidak terpisah dengan verb dan complement.
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
10
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
Contoh:
- Zaky
bought
verb
Zaky
bought
verb
at the bookstore
a TOEIC book
modifier of place
a TOEIC book
(salah)
complement
at the bookstore
complement
(benar)
modifier of place
B. APOLOGIZING AND EXPRESSING SYMPATHY
a. EXPRESSING APOLOGYZING
APOLOGY
Forgive me. Im terribly sorry about
Please accept my apology for
Please excuse (e.g., my cat)
I would like to apologize for
I apologize for
Im sorry. I didnt mean to
Im sorry that
Sorry
RESPONSE
Thats quite all right
I completely understand
You dont need to apologize.
Oh, thats all right. It can happen to anyone.
Its not your fault.
Dont worry about it
Its OK
No problem.
Forget it.
b. EXPRESSING SYMPATHY
- Im sorry to hear that.
- Thats ashamed.
- Thats a pity.
- Thats too bad
- How awful.
- How terrible
- What a pity.
- What a nuisance.
FOR EXAMPLE:
1. In a classroom
Edo
:
Mr. Kuncoro :
Edo
:
Mr. Kuncoro :
Edo
:
Mr. Kuncoro :
Edo
:
Good morning, sir.
Morning, Edo.
I would like to apologize for being late to class.
Why do you come late?
My motorbike had a flat tyre on the way to school.
Its OK this time. Please be on time in the future.
Yes, I will. Thank you, sir.
2. In a meeting.
Manager : Were sorry to have the meeting here. We know that its not comfortable here, but we
have no choice. The meeting room is being renovated.
Guest
: Thats all right, we completely understand .
Manager : Thank you.
3. In classroom
Lisa
: Sorry, I forgot to bring your magazine back.
Ani
: No problem, I have finished reading it and you may give it back to me next time.
Lisa
: Thanks.
4. At school.
Iwan
: I saw someone pick you up at school yesterday. Who was he?
Adi
: Oh, hes my uncle. He told me that my mother had just passed away. Then he asked
me to go home.
Iwan
: Im sorry to hear that, please accept my condolence.
Adi
: Thanks.
C. EXPRESSIONS USED FOR ASKING FOR & GIVING PERMISSION.
Asking for Permission
I wonder if I could
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
Giving Permission
By all means
Refusing Permission
Well, actually Id rather you didnt
11
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
Do you mind if I
Is it all right if I
May I
Could I .
Can I
Not at all
Go ahead
Certainly
Sure
Id rather you didnt
Im sorry, but .
Im afraid you cant.
Sorry, but
FOR EXAMPLE:
1. In a classroom, the students are doing mathematic task.
Student : Excuse me, Sir. I wonder if I could work in pairs to do this task.
Teacher : Sorry, but its an individual task. You must do yourself.
Student : All right, but may ask a question?
Teacher : What it is about?
Student : What formula should I use for number 3?
Teacher : Sorry, but you have to think it yourself.
2. In a waiting room.
Man
: Im getting nervous. Is it all right if I smoke?
Woman : Id rather you didnt. I feel dizzy when people smoke around me.
Man
: Well, Ill walk around for a moment then.
3. In a classroom.
Hasan : Do you have a pencil?
Erni
: Yes.
Hasan : May I borrow it, please?
Erni
: Of course, but dont forget to return it to me.
Hasan : Yes, Ill use it for a moment.
D. COMMAND, REQUEST, OFFERING THINGS OR SERVICES
a. COMMAND
(optional)
Please
Commands
Follow me.
Calm down.
Look ahead.
Be careful.
Dont drive too fast.
Dont go.
Dont be late.
b. REQUEST
Request
Can you
Could you
Will you
Would you
Would you mind
(V-ing)
c. OFFERING THINGS
Offering
1. Shall I .?
2. Would you like me to...?
3. Would you like ...?
Response
All right.
Yes, I will.
OK.
Certainly.
Sure.
Response
Id be glad to.
Certainly.
Sure.
Accepting an Offer
Oh yes, Id love to.
That sounds nice.
Thats very kind of you.
Oh, thank you. Yes, please.
Refusing an Offer
Im sorry I cant. I have to
Oh, Id love to, but I dont
think I cant.
Its all right.
I can
FOR EXAMPLES:
1. John and Martha are riding motorbike to school.
Martha : John, dont drive too fast.
John
: Im sorry but we must get to school on time. Otherwise well get a punishment.
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
12
Modul Bahasa Inggris Kelas X 2009/2010
Martha
John
Martha
John
:
:
:
:
Yes, I know, but its dangerous. The traffic is too heavy.
Dont worry! Just hold the side handles tightly and you will be safe.
OK, Watch out! Oh my god! You almost hit another motorbike.
Calm down. Youre making me nervous.
2. At the front door of an office.
Toni
: Would you mind helping me for a minute, please?
Abadi : Of course, what do you want me to do?
Toni
: Could you hold this package while I look for the key to the door?
Abadi : Id be glad to. Whats in this package? Its extremely heavy.
Toni
: Its just office stationeries for our activities.
Abadi : Well, hurry up and open the door. I told you this thing was very heavy.
Toni
: I cant find the key. You must have it.
Abadi : Youre right, but how can I get the key while Im holding this big package?
D. MODAL AUXILIARY (can, may, must, shall, will, should, might, could)
CAN
1. Ability
He can run fast
2. Permission
Can I open the window?
COULD
1. Past ability
I could lift that heavy box when I was
young
2. More polite way of asking permission
Could you help me?
MAY
1. Probability
Its cloudy. It may rain
2. Formal permission
May I go home now?
MIGHT
1. Past of may
He thought that I might be late
2. Possibility
He doesnt come. He might be sick
SHALL
1. Offering help
Shall I open the window? Its hot
Shall we move the chair there mom?
2. Future time we and I
I shall go with him tonight
We shall have some more activities this
afternoon
SHOULD
1. Giving Suggestion
You look tired, Tina. You should take a
rest.
We miss the buss again. We should
take a taxi.
2. Duty
You should obey the school rules
You ought to tell the truth
WILL
1. Future time
We will spent our holiday in Bali
The children will clean their room.
2. Asking help
Will you take me a glass of water,
please?
Will you type this letter?
MUST
1. Necessity
We must obey the law
2. Conclusion
Tom has several big houses. He must
be rich.
Ani always get top marks for all
lessons. She must be clever.
SMK PGRI Kota Tegal
13
You might also like
- Rukiga LessonsDocument61 pagesRukiga LessonsNatrium AmoNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect TenseDocument42 pagesPresent Perfect TenseJC_RC_777100% (4)
- Materi Ajar Bahasa Inggris Di PrintDocument24 pagesMateri Ajar Bahasa Inggris Di Printika sariNo ratings yet
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN IN ENGLISH 5 Present TenseDocument4 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN IN ENGLISH 5 Present TenseKrizzia Bano100% (1)
- MATERI Bahasa Inggris SMPDocument36 pagesMATERI Bahasa Inggris SMPAnisah Nur Izzah0% (1)
- Cara Mudah Menulis Kalimat Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument11 pagesCara Mudah Menulis Kalimat Dalam Bahasa Inggrisabdul wahidNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present ContinuousDocument23 pagesPresent Simple Present ContinuousAlicia DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanGladays PansitNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Past Simple: Night/week/month/year, Yesterday, EtcDocument19 pagesGrammar - Past Simple: Night/week/month/year, Yesterday, EtcMiruna CarmenNo ratings yet
- Week 12 - Simple Routine TasksDocument9 pagesWeek 12 - Simple Routine TasksFahri yahyaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument3 pagesSimple Present TenseSiti Nur AzizahNo ratings yet
- Kegiatan Belajar 1 Introduction (Perkenalan) Tujuan PembelajaranDocument9 pagesKegiatan Belajar 1 Introduction (Perkenalan) Tujuan PembelajaranNhino MaramisNo ratings yet
- English Review 1Document45 pagesEnglish Review 1Anonymous NBZpegWhtNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Present ContinuousDocument26 pagesPresent Simple Present ContinuousAlicia DominguezNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Present Tense: Lesson 3: Present Simple, Present Continuous, Present PerfectDocument39 pagesGrammar - Present Tense: Lesson 3: Present Simple, Present Continuous, Present PerfectthaoNo ratings yet
- Daily Activities (Kegiatan Sehari-Hari)Document6 pagesDaily Activities (Kegiatan Sehari-Hari)Ibu ErniNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris - Tenses Meeting 2Document13 pagesBahasa Inggris - Tenses Meeting 2miryan mapauNo ratings yet
- SPM Paper 2 Section A Consists ofDocument5 pagesSPM Paper 2 Section A Consists ofWan Ting Chanel Pang100% (2)
- Complete Present Tense Verbs ReviewDocument5 pagesComplete Present Tense Verbs Reviewapi-360191035No ratings yet
- TensesDocument28 pagesTensesmbakpithiNo ratings yet
- Simple Present TenseDocument16 pagesSimple Present Tenseari mulianiNo ratings yet
- 2 Final Exam Study GuideDocument7 pages2 Final Exam Study Guideapi-255384003No ratings yet
- Materi Soal English Lesson: Past - Present - Future PastDocument8 pagesMateri Soal English Lesson: Past - Present - Future PastghaniNo ratings yet
- 10th Meeting-Simple Present TenseDocument18 pages10th Meeting-Simple Present TenseRini YuniartiNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense: by Sri Rahayu JuniatiDocument9 pagesSimple Present Tense: by Sri Rahayu JuniatiWahyudi 04No ratings yet
- 6 TensesDocument51 pages6 TensesSyedWajahatAli100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Lesson 1b - Grammar - Page 18Document6 pagesUnit 1 - Lesson 1b - Grammar - Page 18bboido74No ratings yet
- Inglês LeonorDocument10 pagesInglês Leonormuchuaneosvaldo4No ratings yet
- Present Tense NotesDocument22 pagesPresent Tense Notesar.shuchi.07No ratings yet
- Modul 2 Jobs and RoutinesDocument17 pagesModul 2 Jobs and RoutinesElla SiooNo ratings yet
- SPT: Kenyataan Atau Kegiatan Yang Terjadi Sekarang Secara SimpleDocument3 pagesSPT: Kenyataan Atau Kegiatan Yang Terjadi Sekarang Secara SimpleDhalty ShotokaiNo ratings yet
- Inglês - AidaDocument10 pagesInglês - Aidamuchuaneosvaldo4No ratings yet
- Verb To BeDocument5 pagesVerb To BeAnita CarrizoNo ratings yet
- Grammar in Use - Intermediate (Cambridge)Document39 pagesGrammar in Use - Intermediate (Cambridge)alessandradlgNo ratings yet
- Zestawienie Czasow ItpDocument15 pagesZestawienie Czasow ItpKrolewskaNo ratings yet
- Bac Preparation 1st SessionDocument29 pagesBac Preparation 1st SessionSouad ĶasmiNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument62 pagesIlovepdf MergedMuhammad Sholeh HaddadNo ratings yet
- English Sentences 2Document29 pagesEnglish Sentences 2Ezzadin BabanNo ratings yet
- Clase A1 20-03-2022Document4 pagesClase A1 20-03-2022Joel LjNo ratings yet
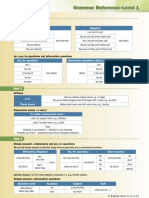
- Grammar Reference-Level 1 Grammar Reference-Level 1: Unit 1Document4 pagesGrammar Reference-Level 1 Grammar Reference-Level 1: Unit 1Anonymous ncxMy2bJkNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Past, Present and FutureDocument67 pagesGroup 1: Past, Present and FutureBinh Pham Thi ThanhNo ratings yet
- Detailedlessonplanforsimpletenseofverbs5 171007082636Document2 pagesDetailedlessonplanforsimpletenseofverbs5 171007082636Jasper JoyNo ratings yet
- Present Tense: Amisandare (Verb To Be)Document16 pagesPresent Tense: Amisandare (Verb To Be)Naing WinNo ratings yet
- 3.14 Vocabulary Daily ActivitiesDocument8 pages3.14 Vocabulary Daily Activitiesandri100% (1)
- Materi Jati DiriDocument5 pagesMateri Jati DiriMuji RahayuNo ratings yet
- Guia Gramatical InglesDocument33 pagesGuia Gramatical IngleskeithgaymerNo ratings yet
- Leccion 1: Nombra A Una Persona, Lugar, Cosa, o IdeaDocument49 pagesLeccion 1: Nombra A Una Persona, Lugar, Cosa, o IdeaArturo Hernandes100% (1)
- Complete These Sentences by Using Correct Verb. Choose Simple Present Tense, Simple Past Tense, or Present Perfect Tense!Document9 pagesComplete These Sentences by Using Correct Verb. Choose Simple Present Tense, Simple Past Tense, or Present Perfect Tense!Novel PDFNo ratings yet
- 2nd MeetingsDocument27 pages2nd MeetingsMuhammad AkbarNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Present Continuous TenseDocument15 pagesSimple Present and Present Continuous TenseThe LordNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Tense GuideDocument7 pagesSimple Present Tense GuideLía McQuaidNo ratings yet
- 3rd YearDocument70 pages3rd YearAndrea RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ملخص الأزمنة النهائيDocument35 pagesملخص الأزمنة النهائيOsama NajjarNo ratings yet
- Licence 1 English GrammarDocument28 pagesLicence 1 English GrammarAïda KouabenanNo ratings yet
- Materi 2 - Present Simple With Other Verbs: Positive SentenceDocument3 pagesMateri 2 - Present Simple With Other Verbs: Positive Sentencebusthamiyazid2741No ratings yet
- KISIDocument5 pagesKISIyuvensia dasoNo ratings yet
- English GrammerDocument10 pagesEnglish GrammerasadNo ratings yet
- Bahsa Inggris TensesDocument15 pagesBahsa Inggris TensesNaufal RafiNo ratings yet
- Grammar Units 1, 2 & 3Document4 pagesGrammar Units 1, 2 & 3ChoCo FreeSkaNo ratings yet
- C. Exercise 2 Analysis TenseDocument1 pageC. Exercise 2 Analysis TensenoviNo ratings yet
- Tenses DR QuizzDocument3 pagesTenses DR QuizznoviNo ratings yet
- Tenses Which One DR QuizzDocument4 pagesTenses Which One DR QuizznoviNo ratings yet
- B. 35 Soal Buat Tugas Xii (07.02.23)Document7 pagesB. 35 Soal Buat Tugas Xii (07.02.23)noviNo ratings yet
- Indentify Tenses DR QuizzDocument3 pagesIndentify Tenses DR QuizznoviNo ratings yet
- Can or Can't Esl Worksheet With Animals Vocabulary For KidsDocument2 pagesCan or Can't Esl Worksheet With Animals Vocabulary For Kidsnovi100% (1)
- Preview:: Relative Clauses-Exercises (B&W Version Included)Document1 pagePreview:: Relative Clauses-Exercises (B&W Version Included)noviNo ratings yet
- DerivativeDocument6 pagesDerivativenoviNo ratings yet
- Procedure Text Pengertian, Pembahasan Dan Contoh Soal Disertai JawabanDocument4 pagesProcedure Text Pengertian, Pembahasan Dan Contoh Soal Disertai JawabannoviNo ratings yet
- Preview:: Level: Intermediate Age: 10-100 Downloads: 216Document1 pagePreview:: Level: Intermediate Age: 10-100 Downloads: 216noviNo ratings yet
- Soal Semester GasalDocument51 pagesSoal Semester Gasalnovi0% (1)
- Comparatives 2 PDFDocument1 pageComparatives 2 PDFnoviNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal Soal Report Text Dan JawabanyaDocument18 pagesContoh Soal Soal Report Text Dan JawabanyanoviNo ratings yet
- Vocab Yang Sering MunculDocument12 pagesVocab Yang Sering MunculnoviNo ratings yet
- ConditionalDocument6 pagesConditionalnoviNo ratings yet
- Simulasi Ujian Nasional SMKDocument10 pagesSimulasi Ujian Nasional SMKnoviNo ratings yet
- Bedah SKL Versi MGMPDocument90 pagesBedah SKL Versi MGMPnoviNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahan Ajar SMT 1 18.19Document11 pagesSoal Bahan Ajar SMT 1 18.19noviNo ratings yet
- Cloze Test Latihan 16.17Document10 pagesCloze Test Latihan 16.17noviNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris 1bDocument64 pagesBahasa Inggris 1bnoviNo ratings yet
- Inter American University of Puerto Rico Guayama Campus: Title V Cooperative Project Prof. Marisol Piazza AguirreDocument45 pagesInter American University of Puerto Rico Guayama Campus: Title V Cooperative Project Prof. Marisol Piazza AguirrenoviNo ratings yet
- Final Examination of Jenggala CourseDocument24 pagesFinal Examination of Jenggala CoursenoviNo ratings yet
- Subjunctive Is Used in The Following CircumstancesDocument1 pageSubjunctive Is Used in The Following CircumstancesnoviNo ratings yet
- Jenis2 ParagrapDocument4 pagesJenis2 ParagrapnoviNo ratings yet
- Xi-Materi 1Document11 pagesXi-Materi 1novi100% (1)
- Bhartri Hari and The Theory of SphotaDocument4 pagesBhartri Hari and The Theory of SphotaAshish RajeNo ratings yet
- Superlatives + Pres - Perfect+Ever EasyDocument2 pagesSuperlatives + Pres - Perfect+Ever EasyLola MentoNo ratings yet
- First Conditional Advice: Worksheets, Activities & GamesDocument2 pagesFirst Conditional Advice: Worksheets, Activities & GamesNelson LeonNo ratings yet
- Adverbs 1Document5 pagesAdverbs 1JessicaMarínPestanaNo ratings yet
- Verb TenseDocument36 pagesVerb TenseChristian Kenn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Future Tenses Grammar Guide Willbe Going To and PR Grammar Drills Grammar Guides - 79613Document1 pageFuture Tenses Grammar Guide Willbe Going To and PR Grammar Drills Grammar Guides - 79613Gihan Al HawaryNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 AgreementDocument8 pagesUnit 4 AgreementYennieNo ratings yet
- Consolidation 1Document3 pagesConsolidation 1Toan TranNo ratings yet
- 3-L'articles+les AlimentsDocument2 pages3-L'articles+les AlimentsCapucine CrespoNo ratings yet
- ReferenceDocument10 pagesReferenceAlexis Martinez ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Fill in The Prefixes and Suffixes #2: Prefix - Root Word - Suffix Prefix - Root Word - SuffixDocument1 pageFill in The Prefixes and Suffixes #2: Prefix - Root Word - Suffix Prefix - Root Word - Suffixrainer andagNo ratings yet
- Refresher Course Module 2021-2022: EnglishDocument80 pagesRefresher Course Module 2021-2022: EnglishNancy TessNo ratings yet
- Phrasal VerbDocument6 pagesPhrasal VerbKaseh DhaahNo ratings yet
- Kellogg DiagramsDocument5 pagesKellogg DiagramsFran Lis Meerandar'sNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Mas Anggun Shintya - Keterampilan Mengelola KelasDocument5 pagesLesson Plan - Mas Anggun Shintya - Keterampilan Mengelola KelasAndre KarismaNo ratings yet
- Verb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankDocument5 pagesVerb Tenses Chart - GrammarBankLucas SeñaNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of Speech: Akhmad Khudri, M.KomDocument43 pagesThe Eight Parts of Speech: Akhmad Khudri, M.KomAkhmad Khudri M.Kom.No ratings yet
- Learning Plan in English 10Document5 pagesLearning Plan in English 10Brenda Lee LingayoNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Chapter QuizDocument7 pagesParts of Speech Chapter QuizDajhri Tuquero100% (1)
- Unit-2 (TOC) GGSIPU Previous Year QuestionsDocument4 pagesUnit-2 (TOC) GGSIPU Previous Year QuestionsShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- My Grammar FlipbookDocument10 pagesMy Grammar Flipbookapi-301139087No ratings yet
- Project 5 TémazáróDocument2 pagesProject 5 TémazáróCsabáné Ivony IldikóNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Present PerfectDocument7 pagesSimple Past Present PerfectcaptainofseaNo ratings yet
- Persuasive Techniques HandoutDocument2 pagesPersuasive Techniques HandoutTim Official họcNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT English Q4 W3 Day 2Document17 pagesGrade 5 PPT English Q4 W3 Day 2Rommel MarianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Reference SenseDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - Reference SenseNguyễn Ngọc Mỹ DuyênNo ratings yet
- ELTC JournalDocument3 pagesELTC Journalzzack96No ratings yet
- Portuguese Manual: Language and CultureDocument45 pagesPortuguese Manual: Language and CultureFilip VelickovicNo ratings yet
- Sectioncnoteexpand 130815211142 Phpapp01Document25 pagesSectioncnoteexpand 130815211142 Phpapp01Jake LimNo ratings yet
- Compound. A B A B: Write The Noun in B From Each Verb in ADocument2 pagesCompound. A B A B: Write The Noun in B From Each Verb in AHa TranNo ratings yet