BALANCED THREE-PHASE
AC CIRCUIT
Balanced Three-Phase Voltage Sources
Delta Connection
Star Connection
Balanced 3-phase Load
Delta Connection
Star Connection
Power in a Balanced Phase Circuit
�Introduction
Three Phase System
�Balanced Three Phase Voltages
Three-phase voltage sources
a) wye-connected source
b) delta-connected source
If the voltage source have the same amplitude and
frequency and are out of phase with each other by
120o, the voltage are said to be balanced.
Van = Vbn = Vcn
Van + Vbn + Vcn = 0
Balanced phase voltages are equal in magnitude and
out of phase with each other by 120o
�Balanced Three Phase Voltages
Vm
Va
Vb
Vc
t
V
abc sequence or positive sequence:
Van = Vp 00
Vbn = Vp 1200
Vcn = Vp 2400 = Vp + 1200
acb sequence or negative sequence:
Van = Vp 00
Vcn = Vp 1200
Vbn = Vp 2400 = Vp + 1200
Vp
is the effective or rms value
�Balanced Three Phase Loads
Two possible three-phase load configurations:
a) a Star or Y-connected load
For a balanced wye connected load:
Z1 = Z 2 = Z3 = Z Y
1
ZY = Z
3
b) a delta-connected load
For a balanced delta connected load:
Za = Z b = Zc = Z
Z = 3Z Y
�Example 1
Determine the phase sequence of the set of voltages
van = 2 200 cos(t + 10)
vbn = 2 200 cos(t 230), vcn = 2 200 cos(t 110)
Solution:
The voltages can be expressed in phasor form as
We notice that Van leads Vcn by 120 and Vcn in turn leads Vbn by
120.
Van = 20010V Vbn = 200 230V Vcn = 200 110V
Hence, we have an acb sequence.
Given that Vbn = 11030V
, find Van and Vcn, assuming a
positive (abc) sequence.
Answer:
Van = 110150V
Vcn = 110 90V
�Balanced Y-Y Connection
A balanced Y-Y system is a three phase system with a balanced Y connected
source and balanced Y connected load.
Zs =
Source impedance
Zl =
Line impedance
ZL =
Load impedance
ZY = Z s + Z l + Z L
ZY = ZL
�Balanced Wye-Wye Connection
Zs =
Source impedance
Zl =
Line impedance
ZL =
Load impedance
Z Y = Total impedance per phase
Z Y = Zs + Zl + Z L
ZY = ZL
�Balanced Y-Y Connection
Line to line voltages or line voltages
given that phase a voltage is reference
Vcn
can be shown to be:
Vab
Vab = 3Vp 300
Vbc = 3Vp 90
120
30o
Vca = 3Vp 2100
Vbn
VL = Vab = Vbc = Vca
Vp = Van = Vbn = Vcn
VL = 3V p
IL = I p
Van
�Balanced
Y-Y
Connection
Given the phase voltages, the line current can be calculated as:
Applying KVL to each phase:
Van
Ia =
ZY
Vbn Van 1200
Ib =
=
= I a 1200
ZY
ZY
Vcn Van 2400
Ic =
=
= I a 2400
ZY
ZY
I a + I b + I c = I n = 0
VnN = Z n I n = 0
Thus, the per-phase equivalent
circuit can be expressed as:
Ia =
Van
ZY
�Y-Y configuration Example:1
A balanced positive-sequence Y-connected 60 Hz three-phase source has
phase voltage Va=1000V. Each phase of the load consists of a 0.1-H
inductance in series with a 50-
resistance.
Find the line currents, the line voltages, the power and the reactive power
delivered to the load. Draw a phasor diagram showing line voltages, phase
voltages and the line currents. Assuming that the phase angle of Van is zero.
&
V
& = an = 15.97 370
0
I
aA
Z = R + jL = 50 + j 37.7 = 62.6237
Z
0
= 37
I&bB = 15.97 157 0 , I&cC = 15.97830
V&ab = V&an 3300 = 1732300 V&bc = 1732 900 ,V&ca = 17321500
�Example 2
1- Calculate the line
currents in the three wire
Y-Y system of figure
below.
2- A Y-connected balanced three-phase generator with an impedance of
0.4+j0.3 per phase is connected to a Y-connected balanced load with
an impedance of 24 + j19 per phase. The line joining the generator
and the load has an impedance of 0.6 + j0.7 per phase.
Assuming a positive sequence for the source voltages and that
V an = 120 30 0 V
Find: (a) the line voltages
(b) the line currents
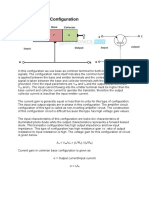
�Balanced Y-Delta Connection
A balanced Y- system consists of balanced Y connected source feeding a
balanced connected load.
Line voltages:
Vab = 3Vp 300 = VAB
Vbc = 3Vp 900 = VBC
Vca = 3Vp 2100 = VCA
Phase currents: I = V AB ; I = VBC ; I = VCA
AB
BC
CA
Z
Z
Z
Line currents:
I a = I AB I CA = 3I AB 30
I b = I BC I AB = 3I AB 150
I c = I CA I BC = 3I AB 90
�I CA = I AB
Balanced
Y-Delta
Connection
240
0
I a = I AB I CA = I AB (1 1 2400 )
I a = I AB 3 300
Magnitude line currents:
IL = Ia = Ib = Ic
IL = Ip 3
I p = I AB = I BC = I CA
A single phase equivalent circuit
ZY =
Ia =
Z
3
Van
V
= an
ZY
Z / 3
�Y-Delta configuration: Example 3
1- A balanced abc sequence Y-connected source with Van = 10010 0 V
is connected to a -connected balanced load (8+j4) per phase.
Calculate the phase and line currents.
2-One line voltage of a balanced Y-connected source is
V AB = 180 20 0 V
If the source is connected to a -connected load of 20 40 0 , find
the phase and line currents.
Assume the abc sequence.
�Balanced Delta-Delta
Connection
A balanced - system is one in which both balanced
source and balanced load are connected.
�Balanced Delta-Delta Connection
A balanced - system is the one in which both balanced source and balanced
load are connected.
Line voltages:
Vab = VAB
Vbc = VBC
Vca = VCA
Line currents:
I a = I AB I CA = 3I AB 30
Phase currents:
I b = I BC I AB = 3I AB 150
I c = I CA I BC = 3I AB 90
Magnitude line currents:
IL = Ip 3
Total impedance:
Z
ZY =
3
I AB =
V AB
Z
I BC =
V BC
Z
I CA =
V CA
Z
�Example4:
A delta-connected source
supplies a delta-connected
load through wires having
impedances of Zline=0.3+j0.4,
the load impedance are
Z=30+j6 , the balanced
source ab voltage is
Vab=1000<30
Find the line current, the line
volatge at the load, the current
in each phase of the load, the
power delivered to the load,
and dissipated in the line.
�1- A balanced connected load having an impedance of 20-j15
is connected to a connected, positive sequence generator having
Vab = 33000 V
Calculate the phase currents of the load and the line currents.
2- A positive-sequence, balanced -connected source supplies a
balanced -connected load. If the impedance per phase of the
load is 18+j12 and I a = 22.535 0 A , find IAB and VAB.
�Balanced Delta-Y Connection
Replace connected source to equivalent Y connected source.
Phase voltages:
A single phase equivalent circuit
Van =
Vp
V
I a = an =
ZY
30
ZY
Vbn =
Vcn =
Vp
3
Vp
3
Vp
3
300
1500
+ 900
�Y-Delta configuration: Example 5
1-A balanced Y connected load with a phase resistance of 40
and a reactance of 25 is supplies by a balanced, positive
sequence connected source with a line voltage of 210 V.
Calculate the phase currents. Use Vab as reference.
2-In a balanced -Y circuit, Vab = 24015 0 V
and ZY = (12 + j15) . Calculate the line currents.
�POWER IN A BALANCED SYSTEM
For Y connected load, the phase voltage:
v AN = 2V p cos t , v BN = 2V p cos(t 120 0 ), vCN = 2V p cos(t + 120 0 )
If Z = Z Phase current lag phase voltage by .
Y
The phase current:
ia =
2 I p cos( t )
ib =
2 I p cos( t 120 0 )
ic =
2 I p cos( t + 120 0 )
�POWER IN A BALANCED SYSTEM
Total instantaneous power:
p = p a + p b + p c = v AN i a + v BN i b + v CN i c
p = 3 V p I p cos
Average power per phase:
Pp = V p I p cos
Apparent power per phase:
S p = Vp I p
Reactive power per phase:
Q p = V p I p sin
Complex power per phase:
S p = Pp + jQ p = V p I *p
�POWER IN A BALANCED SYSTEM
Total average power:
P = 3 Pp = 3 V p I p cos =
3 V L I L cos
Total reactive power:
Q = 3 Q p = 3 V p I p sin =
3 V L I L sin
Total complex power:
2
3
V
S = 3S p = 3 V p I *p = 3 I 2p Z p = *p
Zp
S = P + jQ =
3VL I L
�Power: Example 6
1-A three-phase motor can be regarded as a balanced Y-load. A
three-phase motor draws 5.6 kW when the line voltage is 220 V
and the line current is 18.2 A. Determine the power factor of the
motor.
2- Calculate the line current required for a 30-kW three-phase
motor having a power factor of 0.85 lagging if it is connected to a
balanced source with a line voltage of 440 V.