Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mechanics Tutorial on Bernoulli Equation
Uploaded by
MohammadDawodOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Mechanics Tutorial on Bernoulli Equation
Uploaded by
MohammadDawodCopyright:
Available Formats
CIVL2611 Introductory Fluid Mechanics
CIVL9611 Introductory Fluid Mechanics
Tutorial 6. Bernoulli Equation
(The problems marked with
will be explained at tutorials.)
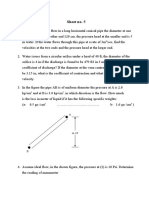
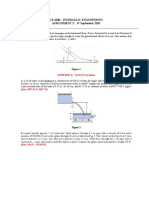
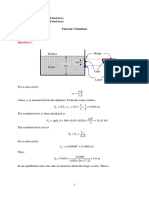
1.
A sluice gate is placed in a channel containing water so that the gap between the bottom
of the gate and the channel bottom is 0.1 m. The gate is 1-m wide, and the upstream
depth is 2 m, as shown below. As the flow exits from the gap, it contracts, so that the
depth of the flow is 61% of the gap height (i.e. the contraction coefficient is 0.61). What
is the flow rate Q? Assume that the water is incompressible and that viscous effects are
negligible. Note that for the flow through the channel the average flow velocity over the
cross-sectional area may be used.
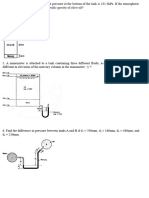
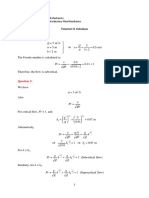
2.
Water flows from a large container on the right to the small container on the left as
shown below. Determine the flow rate through the submerged orifice. The contraction
coefficient is 0.63.
10 cm diameter
1.5 m
2m
0.75 m
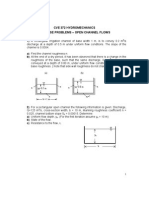
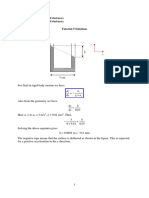
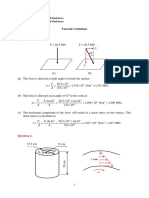
3.
Water is contained in a pressurised tank as shown below. The water is assumed to be
incompressible and viscous effects are negligible. The horizontal exit pipe contains a
valve and an elbow, so that the last part of the pipe is vertical.
(a) What is the gauge pressure at the valve when it is closed?
(b) When the valve is opened, what is the height h to which the resultant jet of water
will rise?
(c) Why is it that you do not need to know either the diameter or the lengths of the pipes
in this calculation?
4.
A fire hose of diameter 7.5 cm has a 3 cm nozzle. To meet requirements, the hose must
be able to deliver 15 liters/sec. Assume that there are no losses in either the hose or the
nozzle, and that the hose is horizontal. What gauge pressure is required upstream of the
nozzle?
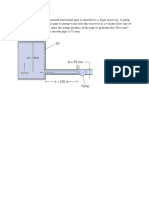
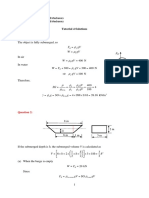
5.
A smooth plastic 10-m long garden hose with an inside diameter of 20 mm is used to
drain a wading pool as shown below. What is the flow rate from the pool?
You might also like
- Mixed TopicDocument105 pagesMixed TopicSigue Ramel Hinayas50% (2)
- Chap 16Document5 pagesChap 16shaito100% (2)
- Hydraulics 11 PDFDocument7 pagesHydraulics 11 PDFmunjalshah94100% (1)
- Exam 1 Study Guide Problems PDFDocument32 pagesExam 1 Study Guide Problems PDFS. GreenNo ratings yet
- 19 1 PDFDocument6 pages19 1 PDFآكوجويNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Geotech2Document101 pagesHydraulics Geotech2Sigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerDocument6 pagesTutorial Chapter 03 - Conservation of Energy - AnswerMukhzin Rashid100% (3)
- Phys 002 PHW2Document2 pagesPhys 002 PHW2roel elvambuenaNo ratings yet
- Tugas RPAAADocument1 pageTugas RPAAAadha panca wardanuNo ratings yet
- Taller 5mfDocument4 pagesTaller 5mfLuis MenaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Application of The Bernoulli EquationDocument5 pages3.5 Application of The Bernoulli EquationbabissoulNo ratings yet
- Problems ؤا 5Document4 pagesProblems ؤا 5Abdalla MemeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Assignment I-2012-2013Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics - Assignment I-2012-2013Robert WalusimbiNo ratings yet
- Seminar 1. Fluids DynamicsDocument2 pagesSeminar 1. Fluids DynamicsRicardo RochaNo ratings yet
- Compre Hydraulics PSDocument5 pagesCompre Hydraulics PSAlvin Lualhati0% (1)
- Energy Equation - Flow MeasurementDocument11 pagesEnergy Equation - Flow MeasurementAsa Ka50% (2)
- Agustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW1Document11 pagesAgustin - Mark Joshua - Ce142p-2 - E02 - CW1mark agustinNo ratings yet
- 20140523170533tutorial FluidsDocument1 page20140523170533tutorial FluidsSiti Norakma Syuhada ZainulabiddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Orifices Weirs and Tubes Practice ProblemsDocument14 pagesChapter Six Orifices Weirs and Tubes Practice ProblemsJerle ParondoNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment SolutionsPraveen SharmaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Chap3 - Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesWorksheet - Chap3 - Fluid Mechanicstibebubeza44No ratings yet
- Flow Rate Bernoulli's Equation Problem SetDocument1 pageFlow Rate Bernoulli's Equation Problem SetRj PangaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids QuestionsDocument2 pagesMechanical Properties of Fluids Questionsastitvabansal1No ratings yet
- EXERCISE Bernoullis PrincipleDocument1 pageEXERCISE Bernoullis PrincipleCrow NachorNo ratings yet
- Two Compartments A and B Are Connected by An Orifice Having A 150Document4 pagesTwo Compartments A and B Are Connected by An Orifice Having A 150matthew cometaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Problems SolvedDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics Problems SolvedClement Chima50% (2)
- Venturi Meter and Orifice Meter Flow Rate CalculationsDocument2 pagesVenturi Meter and Orifice Meter Flow Rate CalculationsVoora GowthamNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics Assignment on Pipe Flow and Reservoir ProblemsDocument2 pagesFluid Dynamics Assignment on Pipe Flow and Reservoir ProblemsAlexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics AssignmentsDocument3 pagesFluid Mechanics AssignmentsSahil DevNo ratings yet
- Sheet 5Document3 pagesSheet 5Hussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- CVE 372 Exercise Problems - Open Channel FlowDocument7 pagesCVE 372 Exercise Problems - Open Channel FlowDorry Magdy100% (1)
- Che 222 Tutorial 2Document15 pagesChe 222 Tutorial 2naverfallNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 TrueDocument29 pagesUnit 4 TrueJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Section 5Document5 pagesSection 5Aduchelab AdamsonuniversityNo ratings yet
- Assignement 3 FMDocument3 pagesAssignement 3 FMREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Sheet No - 5 - Fluid Dynamics.Document3 pagesSheet No - 5 - Fluid Dynamics.AHMED BAKRNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Assignment 3a Velocity, Pressure, and Flow Rate CalculationsDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics Assignment 3a Velocity, Pressure, and Flow Rate Calculationszhi yi leeNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii FLUID DYNAMICS: Surface and Body Forces, Concepts of Fluid System andDocument23 pagesUnit-Iii FLUID DYNAMICS: Surface and Body Forces, Concepts of Fluid System andyrajesh1050% (2)
- Tutorial On The Law of Conservation of MomentumDocument2 pagesTutorial On The Law of Conservation of MomentumhansleyNo ratings yet
- Fluid Static and Flow Measurement TOPICDocument6 pagesFluid Static and Flow Measurement TOPICGalihmery DamaiantiNo ratings yet
- FlowMaster Course - Assignments - 10QsDocument4 pagesFlowMaster Course - Assignments - 10QsSezgi MaralNo ratings yet
- Compri QuestionsDocument2 pagesCompri QuestionsCheryl ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- prac prob HGE 2Document8 pagesprac prob HGE 2jeannechoiashNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Mechanics-Problems 3Document5 pagesFluid-Mechanics-Problems 3Rhea EnriquezNo ratings yet
- (777577664) Numerical Problem 3Document5 pages(777577664) Numerical Problem 3Axel0% (1)
- Cive2400 2007Document4 pagesCive2400 2007Gert Duniceri0% (1)
- Soal Tugas BernoulliDocument7 pagesSoal Tugas BernoulliAnnisaNurulFadilahNo ratings yet
- Uniform Open Channel Flow Problem Sheet 2017 18Document2 pagesUniform Open Channel Flow Problem Sheet 2017 18Karan GuptaNo ratings yet
- FM Assignment 1Document2 pagesFM Assignment 1Sirish Chand PutlaNo ratings yet
- Pump Flow Rate Through Smooth Horizontal PipeDocument5 pagesPump Flow Rate Through Smooth Horizontal PipeNasser ShelilNo ratings yet
- PHY1015 Tutorial 9 - Fluid DynamicsDocument2 pagesPHY1015 Tutorial 9 - Fluid DynamicsBrian MachachaNo ratings yet
- CE 2040 Hydraulic Engineering Assignment ProblemsDocument4 pagesCE 2040 Hydraulic Engineering Assignment ProblemsAsh0% (1)
- PNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Document2 pagesPNG University of Technology CE322 Hydraulics II Assignment 1Nickson KomsNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document10 pagesSheet 1lawanNo ratings yet
- OrificeDocument36 pagesOrificeCamille Joy CucioNo ratings yet
- Compile AssignmentDocument13 pagesCompile AssignmentSilva deNo ratings yet
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsFrom EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsNo ratings yet
- Civl 2611 Tut 11 SolutionsDocument5 pagesCivl 2611 Tut 11 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- Tut9sol Civl2611 SolutionsDocument7 pagesTut9sol Civl2611 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 Tutorial 5Document1 pageCIVL2611 Tutorial 5MohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- Tut7sol Civl2611 SolutionsDocument5 pagesTut7sol Civl2611 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- Tut10sol Civl2611 SolutionsDocument7 pagesTut10sol Civl2611 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 Tutorial 4Document1 pageCIVL2611 Tutorial 4MohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 - Tutorial 5 SolutionsDocument4 pagesCIVL2611 - Tutorial 5 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 - Tutorial 4 SolutionsDocument5 pagesCIVL2611 - Tutorial 4 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 Tutorial 3Document2 pagesCIVL2611 Tutorial 3MohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 Tutorial 2Document2 pagesCIVL2611 Tutorial 2MohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 - Tutorial 3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesCIVL2611 - Tutorial 3 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 - Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesCIVL2611 - Tutorial 1 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 - Tutorial 2 SolutionsDocument4 pagesCIVL2611 - Tutorial 2 SolutionsMohammadDawodNo ratings yet
- CIVL2611 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesCIVL2611 Tutorial 1MohammadDawodNo ratings yet