Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tetanus
Tetanus
Uploaded by
Honey FranciscoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tetanus
Tetanus
Uploaded by
Honey FranciscoCopyright:
Available Formats
Tetanus
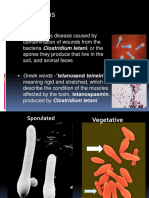
Definition: Tetanus is an infectious disease caused by Clostridium tetani,
which produces a potent exotoxin with prominent systemic neuromuscular
effects such as generalized spasmodic contractions of the skeletal
musculature.
Mode of transmission:
1. Rugged, Traumatic wounds and burns.
2. The Umbilical stump of the new born, especially if delivered at home
and thus have faulty cord dressings.
3. Babies delivered to mothers without tetanus to void immunization.
4. Unrecognized wound.
5. Dental extraction, circumcision and ear piercing.
Incubation Period:
Adults- 3 days to 3 weeks
New born- 3-30 days
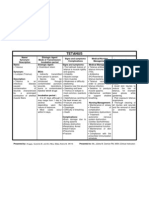
Pathophysiology
RF:
Lack of immunization
Presence of other infected
bacteria
Injured Tissue
Swelling around the injury
Clostridium
Enter through puncture
wounds
Local infection
Extensive
tissue
destruction
Release toxins that are
absorbed by blood streams
lymphatics/ peripheral motor
nerves
Spread into the
CNS
Hyper excitability
of the motor
neurons
Pathognomonic sign:
Lock jaw
Lock jaw
Fever & chills
Stiff neck
Increase BP
Sweating
Increase heart rate
Difficulty swallowing
Asphyxial
convulsion
Toxic
degeneration
Common Nursing Diagnosis:
Altered nutrition: Less than body requirements
Impaired physical mobility
Activity intolerance
Sensory perceptual alteration
High risk for infection/ complication
Hyper excitability
Knowledge deficit
Modalities Treatment:
1. Specific
a. Within 72 hours after a punctured wound, the patient should
receive ATS, TAT, or TIG, especially if the patient does not have
any previous immunization
b. Tetanus toxoid, sec IM, given on standard schedule
c. Pen GN or, to control infection
d. Muscle relaxant to decrease muscle rigidity and spasm
2. Non-specific
a. Oxygen inhalation
b. NGT feeding
c. Tracheostomy
d. Adequate fluid, electrolyte, and caloric intake
e. Good nursing care:
Maintain an adequate airway
Provide cardiac monitoring
Maintain an IV line for medication and emergency care if
necessary
Carry out efficient wound care
Avoid stimulation; warn visitors not to upset or overly
stimulate the patient
Prevent contractures and pressure care
Watch out for urinary retention
Closely monitor vital sign & muscle tone
Provide optimum comfort measures
Prevention and Control:
1. Active immunization with tetanus toxoid for adults and pregnant
women
2. DPLT for babies and children
You might also like
- Anatomy Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaDocument4 pagesAnatomy Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaHoney Francisco100% (2)
- Communicable Disease Nursing: Mrs. Dionesia Mondejar NavalesDocument64 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing: Mrs. Dionesia Mondejar NavalesChevelle Valenciano-Gaan0% (1)
- Inflammatory & Immunologic Diseases IIIDocument252 pagesInflammatory & Immunologic Diseases IIIiamaldrinoNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument23 pagesTetanusDhynie Soesila WahyudiNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument35 pagesTetanusWaNda GrNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument48 pagesTetanusJanuar RezkyNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument30 pagesRheumatic Heart DiseasejustinahorroNo ratings yet
- Tetanus 160530145856Document25 pagesTetanus 160530145856Gargi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph College Institute of Health Sciences Cavite City An Output of Activity in NCM 104 (Immunology) by BSN Iii Makadiyos Batch 2014Document5 pagesSt. Joseph College Institute of Health Sciences Cavite City An Output of Activity in NCM 104 (Immunology) by BSN Iii Makadiyos Batch 2014Florygene Kris DisagonNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument18 pagesTetanusRohan TejaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases PresentationDocument225 pagesCommunicable Diseases PresentationBenjamin GabrielNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument37 pagesTetanusMuwanga faizoNo ratings yet
- TETANUSDocument3 pagesTETANUSfxbukenyaNo ratings yet
- CD PresentationDocument225 pagesCD PresentationHersy Marie Azores GarayNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Guerrero, Djameica Danielle RDocument16 pagesTetanus: Guerrero, Djameica Danielle RDjameica GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Neonatal TetanusDocument44 pagesNeonatal TetanusJake MillerNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument3 pagesTetanusRoma Nova Pascual CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Management of TetanusDocument7 pagesManagement of TetanusamutiarNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Eu MBCHB 3 DR D M KillingoDocument44 pagesTetanus: Eu MBCHB 3 DR D M KillingoArjay VisitacionNo ratings yet
- Tetanus ADocument3 pagesTetanus ASadaqat KhanNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 - Case StudyDocument5 pagesActivity 2 - Case StudyGrace MendozaNo ratings yet
- Clostridium-Tetani Handout Group4Document6 pagesClostridium-Tetani Handout Group4Raiden EiNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument27 pagesTetanusMohammed FareedNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: HistoryDocument15 pagesTetanus: HistorydanielleNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Mrs.G.Manibharathi, MSC (N), Associate ProfessorDocument26 pagesTetanus: Mrs.G.Manibharathi, MSC (N), Associate ProfessormanibharathiNo ratings yet
- Disease of The Seventh DayDocument23 pagesDisease of The Seventh Dayapi-3743483No ratings yet
- !tetanus MDocument12 pages!tetanus MInam KhanNo ratings yet
- Common Communicable Infectious Disease:: TetanusDocument19 pagesCommon Communicable Infectious Disease:: TetanusJayvee Novenario CasaljayNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument47 pagesTetanusSyamsul Arifin100% (3)
- Tetanus: Ma. Theresa Dj. YumangDocument28 pagesTetanus: Ma. Theresa Dj. YumangJean SarocamNo ratings yet
- 19: 05 24 Sept 2011 Tetanus: SymtompsDocument5 pages19: 05 24 Sept 2011 Tetanus: SymtompsVania ParamithaNo ratings yet
- Diseases Affecting The Central Nervous SyetemDocument32 pagesDiseases Affecting The Central Nervous SyetemJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument22 pagesTetanusAlec AnonNo ratings yet
- Tetanus PDFDocument10 pagesTetanus PDFVina MuspitaNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument23 pagesTetanusNadya Noor Mulya Putri100% (1)
- TETANUSDocument15 pagesTETANUSLovely Michaela CaberioNo ratings yet
- Meningitis, Tetanus, LeprosyDocument39 pagesMeningitis, Tetanus, LeprosyKhemz Dalde LimNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: W Hat Is Tetanus?Document20 pagesTetanus: W Hat Is Tetanus?Stefanie BlueNo ratings yet
- Tetanus CDC For ClinicianDocument5 pagesTetanus CDC For ClinicianAspen HOAnakNo ratings yet
- 420 080 Guideline TetanusDocument9 pages420 080 Guideline TetanusFebrian TanNo ratings yet
- K6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICDocument23 pagesK6 - Tetanus PEDIATRICbanuperiahNo ratings yet
- 54 TetanusDocument25 pages54 Tetanusghofran001997No ratings yet
- What Is Tetanus?: Clostridium Tetani or The Tetanus Bacillus Is A Slender, Gram-Positive, Anaerobic Rod That MayDocument5 pagesWhat Is Tetanus?: Clostridium Tetani or The Tetanus Bacillus Is A Slender, Gram-Positive, Anaerobic Rod That MayraechcmNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument1 pageTetanusQueenie ArugayNo ratings yet
- Anisa A. Edris BSN January 25, 2012 Group A5: Central Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesAnisa A. Edris BSN January 25, 2012 Group A5: Central Nervous SystemEynie EdrisNo ratings yet
- Tetanus KuliahDocument26 pagesTetanus Kuliahdemi190794No ratings yet
- TetanusDocument4 pagesTetanusAjay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Surgery Lecture OnDocument23 pagesTetanus: Surgery Lecture OnJasonWalkerNo ratings yet
- Status InternusDocument12 pagesStatus InternusPriscaNo ratings yet
- Tetanus HCDocument5 pagesTetanus HCcring cringNo ratings yet
- 26 - TetanusDocument2 pages26 - TetanusLenard BangugNo ratings yet
- Kejang TetanusDocument26 pagesKejang Tetanusriska silviaNo ratings yet
- In The Name of ALLAH The Beneficent and MercifulDocument49 pagesIn The Name of ALLAH The Beneficent and Mercifulcute_honiya100% (1)
- TetanusDocument7 pagesTetanusArnella HutagalungNo ratings yet
- RehumaticDocument3 pagesRehumaticgopscharanNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On The Topic TetanusDocument16 pagesA Seminar On The Topic TetanusRajat PadhanNo ratings yet
- Askep Klien Dengan TetanusDocument43 pagesAskep Klien Dengan Tetanusicu keceNo ratings yet
- TetanusDocument7 pagesTetanusallah akbarNo ratings yet
- Ni Komang Saraswita Laksmi: Puskesmas Mendoyo I, Bali, IndonesiaDocument6 pagesNi Komang Saraswita Laksmi: Puskesmas Mendoyo I, Bali, IndonesiaRirhy SaragihNo ratings yet
- Tetanus: Rika Arista Dewi S1-3ADocument14 pagesTetanus: Rika Arista Dewi S1-3ArikaaristadNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy and NCP For CDDocument11 pagesDrugStudy and NCP For CDHoney FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Humanities - FinalsDocument5 pagesHumanities - FinalsHoney FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ketamine Found More Effective For Treating Highly-Agitated Patients During Transport To HospitalDocument2 pagesKetamine Found More Effective For Treating Highly-Agitated Patients During Transport To HospitalHoney FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue Integrity Related To Impaired Physical MobilityDocument5 pagesImpaired Tissue Integrity Related To Impaired Physical MobilityHoney FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Journal For Communicable DiseaseDocument1 pageJournal For Communicable DiseaseHoney FranciscoNo ratings yet